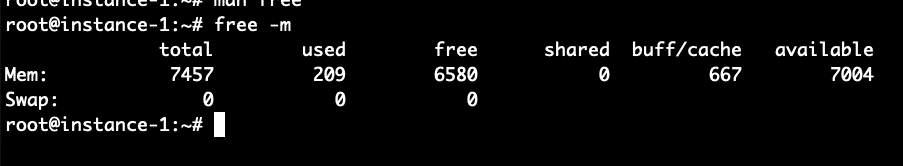- How to Clear Memory Cache in Linux
- How to Clear Memory Cache on Linux
- Scheduleng the Clear Memory Cache with Crontab
- How to find Cached Memory in Linux
- How to clear the buffer/pagecache (disk cache) under Linux
- What is Memory Cache
- What is the purpose of /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches
- How to clear the Memory Cache using /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches
- How to clear the Memory Cache using sysctl
- How to Clear RAM Memory Cache, Buffer and Swap Space on Linux
- How to Clear Cache in Linux?
- Free Buffer and Cache in Linux
- Clear RAM Cache on Linux Production Server?
- How to Clear Swap Space in Linux?
- If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
- How to Clear Cache on Linux
- How Linux File System Cache Works
- Using Free command to view Cache Usage
- Proc Sys VM Drop Caches Command
- Experimental Verification that Drop Caches Works
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Linux Wolfman
How to Clear Memory Cache in Linux
Sometimes the system goes out of memory due to huge RAM is used by cached objects. In that cases, either you need to increase physical memory in the system or add more swap space. You can also instruct kernel to clear RAM memory cache on system by adding a number in /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches file.
It is safe but not recommended to clear the memory cache on a Linux system. Clearing the Memory cache in Linux systems slows down the system performance as reading files from memory is much faster than persistent disk. Since it discards cached objects from memory, it may cost a significant amount of I/O and CPU to recreate the dropped objects. This tutorial will help you to clear the memory cache on Linux/Unix system via the command line.
How to Clear Memory Cache on Linux
There are three options available to clear the memory cache in Linux. Choose one of the below options to flush the Linux system cache memory as per your requirements.
- Clear PageCache, dentries and inodes in cache memory. In short it will clear all the memory cache:
- Clear dentries and inodes only in cache memory
- Clear page cache only in cache memory
Here the first command sync is used to synchronize all the in-memory cache files to the persistent storage. The next command is separated with a “;”. Once the first command is completed, the next command will be triggered to clear cache memory.
Scheduleng the Clear Memory Cache with Crontab
You can also schedule a corn job to clear the cache on a regular basis. Schedule the following in system crontab to automatically flush cache memory at a regular interval.
Open a terminal and execute ‘crontab -e’ command to edit crontab:
Append below entry to the file:
The above cron will execute on every hour and flushes the memory cache on your system.
On the production servers, it is not recommended to schedule a clear cache command. It can lead to data corruption or data loss. So beware before running the above command in a production environment.
How to find Cached Memory in Linux
Use free command to find out cache memory uses by Linux system. The output of the free command is like below
Here the last column is showing cached memory (12953 MB) on Linux system. The -m option is used to show output MB’s.
Источник
How to clear the buffer/pagecache (disk cache) under Linux
Are you facing a performance issue and you suspect it might be related to cache usage? High cache usage should not normally cause performance issues, but it might be the root cause in some rare cases.
What is Memory Cache
In order to speed operations and reduce disk I/O, the kernel usually does as much caching as it has memory By design, pages containing cached data can be repurposed on-demand for other uses (e.g., apps) Repurposing memory for use in this way is no slower than claiming pristine untouched pages.
What is the purpose of /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches
Writing to /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches allows one to request the kernel immediately drop as much clean cached data as possible. This will usually result in some memory becoming more obviously available; however, under normal circumstances, this should not be necessary.
How to clear the Memory Cache using /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches
Writing the appropriate value to the file /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches causes the kernel to drop clean caches, dentries and inodes from memory, causing that memory to become free.
1. In order to clear PageCache only run:
2. In order to clear dentries (Also called as Directory Cache) and inodes run:
3. In order to clear PageCache, dentries and inodes run:
Running sync writes out dirty pages to disks. Normally dirty pages are the memory in use, so they are not available for freeing. So, running sync can help the ensuing drop operations to free more memory.
Page cache is memory held after reading files. Linux kernel prefers to keep unused page cache assuming files being read once will most likely to be read again in the near future, hence avoiding the performance impact on disk IO.
dentry and inode_cache are memory held after reading directory/file attributes, such as open() and stat(). dentry is common across all file systems, but inode_cache is on a per-file-system basis. Linux kernel prefers to keep this information assuming it will be needed again in the near future, hence avoiding disk IO.
How to clear the Memory Cache using sysctl
You can also Trigger cache-dropping by using sysctl -w vm.drop_caches=[number] command.
1. To free pagecache, dentries and inodes, use the below command.
2. To free dentries and inodes only, use the below command.
3. To free the pagecache only, use the below command.
Источник
How to Clear RAM Memory Cache, Buffer and Swap Space on Linux
Like any other operating system, GNU/Linux has implemented memory management efficiently and even more than that. But if any process is eating away your memory and you want to clear it, Linux provides a way to flush or clear ram cache.
How to Clear Cache in Linux?
Every Linux System has three options to clear cache without interrupting any processes or services.
1. Clear PageCache only.
2. Clear dentries and inodes.
3. Clear pagecache, dentries, and inodes.
Explanation of the above command.
sync will flush the file system buffer. Command Separated by “;” run sequentially. The shell waits for each command to terminate before executing the next command in the sequence. As mentioned in the kernel documentation, writing to drop_cache will clean cache without killing any application/service, command echo is doing the job of writing to file.
If you have to clear the disk cache, the first command is safest in enterprise and production as “. echo 1 > ….” will clear the PageCache only. It is not recommended to use the third option above “. echo 3 >” in production until you know what you are doing, as it will clear pagecache, dentries, and inodes.
Is it a good idea to free Buffer and Cache in Linux that might be used by Linux Kernel?
Free Buffer and Cache in Linux
When you are applying various settings and want to check, if it is actually implemented specially on the I/O-extensive benchmark, then you may need to clear the buffer cache. You can drop cache as explained above without rebooting the System i.e., no downtime required.
Linux is designed in such a way that it looks into the disk cache before looking onto the disk. If it finds the resource in the cache, then the request doesn’t reach the disk. If we clean the cache, the disk cache will be less useful as the OS will look for the resource on the disk.
Moreover, it will also slow the system for a few seconds while the cache is cleaned and every resource required by OS is loaded again in the disk cache.
Now we will be creating a shell script to auto clear RAM cache daily at 2 am via a cron scheduler task. Create a shell script clearcache.sh and add the following lines.
Set execute permission on the clearcache.sh file.
Now you may call the script whenever you are required to clear the ram cache.
Now set a cron to clear RAM cache every day at 2 am. Open crontab for editing.
Append the below line, save and exit to run it at 2 am daily.
For more details on how to cron a job, you may like to check our article on 11 Cron Scheduling Jobs.
Is it a good idea to auto clear the RAM cache on the production server?
Clear RAM Cache on Linux Production Server?
No! it is not. Think of a situation when you have scheduled the script to clear ram cache every day at 2 am. Every day at 2 am the script is executed and it flushes your RAM cache. One day for whatsoever reason may be more than expected users are online on your website and seeking resources from your server.
At the same time, the scheduled script runs and clears everything in the cache. Now all the users are fetching data from the disk. It will result in a server crash and corrupt the database. So clear ram-cache only when required, and known your footsteps, else you are a Cargo Cult System Administrator.
How to Clear Swap Space in Linux?
If you want to clear Swap space, you may like to run the below command.
Also, you may add the above command to a cron script above, after understanding all the associated risks.
Now we will be combining both above commands into one single command to make a proper script to clear RAM Cache and Swap Space.
After testing both the above commands, we will run the command “free -h” before and after running the script and will check the cache.
That’s all for now, if you liked the article, don’t forget to provide us with your valuable feedback in the comments to let us know, what you think is a good idea to clear ram cache and buffer in production and Enterprise?
If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
TecMint is the fastest growing and most trusted community site for any kind of Linux Articles, Guides and Books on the web. Millions of people visit TecMint! to search or browse the thousands of published articles available FREELY to all.
If you like what you are reading, please consider buying us a coffee ( or 2 ) as a token of appreciation.
We are thankful for your never ending support.
Источник
How to Clear Cache on Linux
How Linux File System Cache Works
The kernel reserves a certain amount of system memory for caching the file system disk accesses in order to make overall performance faster. The cache in linux is called the Page Cache. The size of the page cache is configurable with generous defaults enabled to cache large amounts of disk blocks. The max size of the cache and the policies of when to evict data from the cache are adjustable with kernel parameters. The linux cache approach is called a write-back cache. This means if data is written to disk it is written to memory into the cache and marked as dirty in the cache until it is synchronized to disk. The kernel maintains internal data structures to optimize which data to evict from cache when more space is needed in the cache.
During Linux read system calls, the kernel will check if the data requested is stored in blocks of data in the cache, that would be a successful cache hit and the data will be returned from the cache without doing any IO to the disk system. For a cache miss the data will be fetched from IO system and the cache updated based on the caching policies as this same data is likely to be requested again.
When certain thresholds of memory usage are reached background tasks will start writing dirty data to disk to ensure it is clearing the memory cache. These can have an impact on performance of memory and CPU intensive applications and require tuning by administrators and or developers.
Using Free command to view Cache Usage
We can use the free command from the command line in order to analyze the system memory and the amount of memory allocated to caching. See command below:
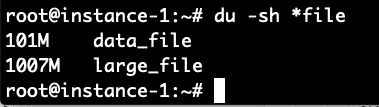
What we see from the free command above is that there is 7.5 GB of RAM on this system. Of this only 209 MB is used and 6.5 MB is free. 667 MB is used in the buffer cache. Now let’s try to increase that number by running a command to generate a file of 1 Gigabyte and reading the file. The command below will generate approximately 100MB of random data and then append 10 copies of the file together into one large_file.
Now we will make sure to read this 1 Gig file and then check the free command again:
We can see the buffer cache usage has gone up from 667 to 1735 Megabytes a roughly 1 Gigabyte increase in the usage of the buffer cache.
Proc Sys VM Drop Caches Command
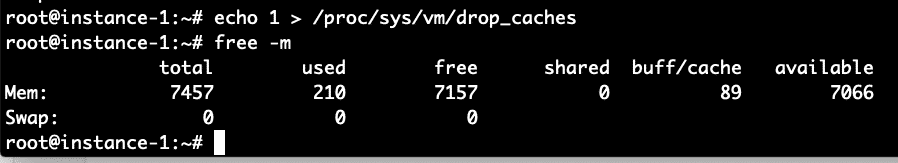
The linux kernel provides an interface to drop the cache let’s try out these commands and see the impact on the free setting.
We can see above that the majority of the buffer cache allocation was freed with this command.
Experimental Verification that Drop Caches Works
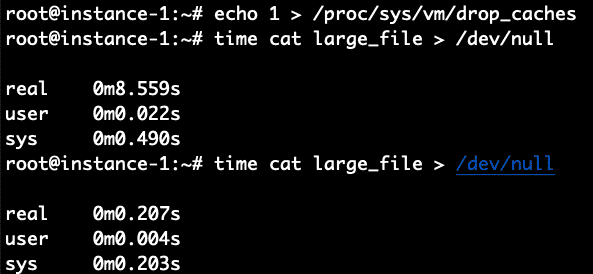
Can we do a performance validation of using the cache to read the file? Let’s read the file and write it back to /dev/null in order to test how long it takes to read the file from disk. We will time it with the time command. We do this command immediately after clearing the cache with the commands above.
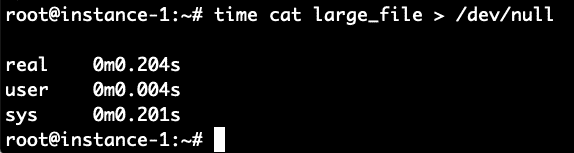
It took 8.4 seconds to read the file. Let’s read it again now that the file should be in the filesystem cache and see how long it takes now.
Boom! It took only .2 seconds compared to 8.4 seconds to read it when the file was not cached. To verify let’s repeat this again by first clearing the cache and then reading the file 2 times.
It worked perfectly as expected. 8.5 seconds for the non-cached read and .2 seconds for the cached read.
Conclusion
The page cache is automatically enabled on Linux systems and will transparently make IO faster by storing recently used data in the cache. If you want to manually clear the cache that can be done easily by sending an echo command to the /proc filesystem indicating to the kernel to drop the cache and free the memory used for the cache. The instructions for running the command were shown above in this article and the experimental validation of the cache behavior before and after flushing were also shown.
About the author
Linux Wolfman
Linux Wolfman is interested in Operating Systems, File Systems, Databases and Analytics and always watching for new technologies and trends. Reach me by tweeting to @linuxhint and ask for the Wolfman.
Источник