- Команда Echo в Linux с примерами
- эхо-команда
- echo Примеры
- Выводы
- Linux echo command
- Description
- Syntax
- Options
- Options
- Options
- Escape sequences
- Examples
- Related commands
- 15 Practical Examples of ‘echo’ command in Linux
- If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
- 16 Echo Command Examples in Linux
- 1) Display a simple message on the terminal
- 2) Print out the value of a variable with echo command
- 3) Print a line of text comprising of double quotes
- 4) Display a line of text consisting of a single quote
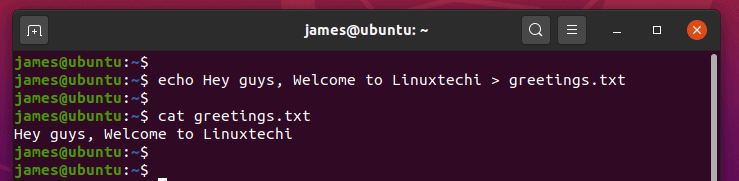
- 5) Redirect echo command output to a file
- 6) Use echo command to match identical files
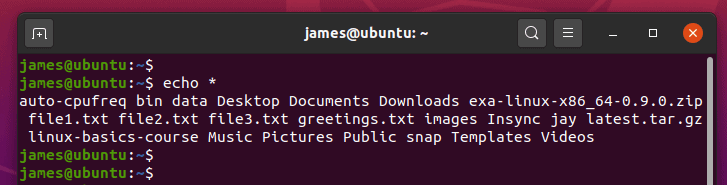
- 7) List all files and folders in the current directory
- 8) Create new lines using the echo command
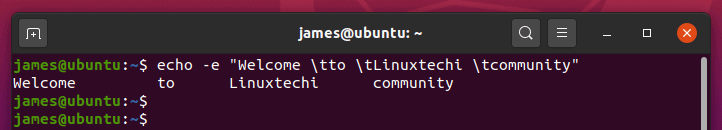
- 9) Create tab spaces between words in a sentence
- 10) Combine new line and tab spacing options in echo command
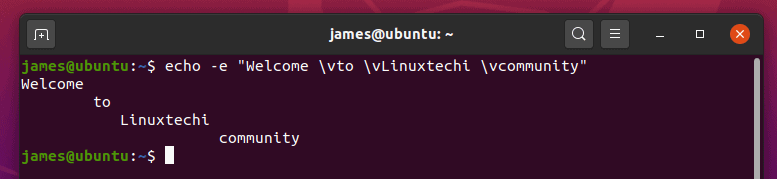
- 11) Create vertical tab spaces in echo command output
- 12) Combine new line and vertical tab spaces in echo command
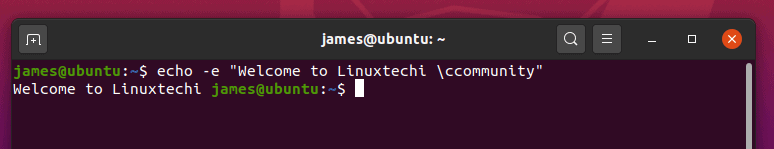
- 13) Use the carriage return option
- 14) Truncate echo command output of text
- 15) Remove all spaces from the text string with echo command
- 16) Echo command usage in bash shell script
Команда Echo в Linux с примерами
Команда echo — одна из самых основных и часто используемых команд в Linux. Аргументы, переданные в echo выводятся на стандартный вывод.
echo обычно используется в сценариях оболочки для отображения сообщения или вывода результатов других команд.
эхо-команда
echo — это оболочка, встроенная в Bash и большинство других популярных оболочек, таких как Zsh и Ksh. Его поведение немного отличается от оболочки к оболочке.
Существует также отдельная утилита /usr/bin/echo , но обычно встроенная версия оболочки имеет приоритет. Мы рассмотрим встроенную в Bash версию echo .
Синтаксис команды echo следующий:
- Когда используется опция -n , завершающий символ новой строки подавляется.
- Если задана опция -e будут интерпретироваться следующие символы, экранированные обратной косой чертой:
- \ — отображает обратную косую черту.
- a — Предупреждение (BEL)
- b — отображает символ возврата.
- c — подавить любой дальнейший вывод
- e — отображает escape-символ.
- f — отображает символ перевода страницы.
- n — отображает новую строку.
- r — отображает возврат каретки.
- t — отображает горизонтальную вкладку.
- v — отображает вертикальную вкладку.
- Параметр -E отключает интерпретацию escape-символов. Это значение по умолчанию.
При использовании команды echo следует учитывать несколько моментов.
- Оболочка заменит все переменные, сопоставление подстановочных знаков и специальные символы перед передачей аргументов команде echo .
- Хотя это и не обязательно, рекомендуется заключать аргументы, передаваемые в echo в двойные или одинарные кавычки.
- При использовании одинарных кавычек » буквальное значение каждого символа, заключенного в кавычки, будет сохранено. Переменные и команды расширяться не будут.
echo Примеры
В следующих примерах показано, как использовать команду echo:
Вывести строку текста на стандартный вывод.
Отобразите строку текста, содержащую двойные кавычки.
Чтобы напечатать двойную кавычку, заключите ее в одинарные кавычки или экранируйте символ обратной косой черты.
Отобразите строку текста, содержащую одинарную кавычку.
Чтобы напечатать одинарную кавычку, заключите ее в двойные кавычки или используйте кавычки ANSI-C .
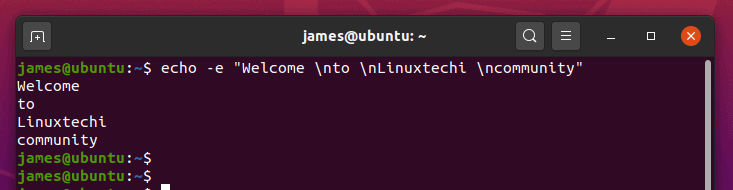
Вывести сообщение, содержащее специальные символы.
Используйте параметр -e чтобы включить интерпретацию escape-символов.
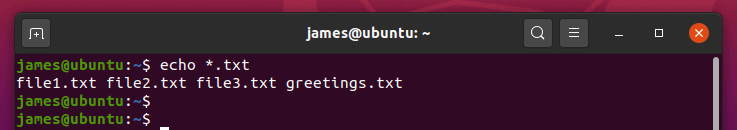
Символы соответствия шаблону.
Команда echo может использоваться с символами сопоставления с образцом, такими как подстановочные знаки. Например, приведенная ниже команда вернет имена всех файлов .php в текущем каталоге.
Перенаправить в файл
Вместо отображения вывода на экране вы можете перенаправить его в файл с помощью операторов > , >> .
Если файл file.txt не существует, команда создаст его. При использовании > файл будет перезаписан, а символ >> добавит вывод в файл .
Используйте команду cat для просмотра содержимого файла:
Отображение переменных
echo также может отображать переменные. В следующем примере мы напечатаем имя текущего вошедшего в систему пользователя:
$USER — это переменная оболочки, в которой хранится ваше имя пользователя.
Отображение вывода команды
Используйте выражение $(command) чтобы включить вывод команды в аргумент echo . Следующая команда отобразит текущую дату :
Отображение в цвете
Используйте escape-последовательности ANSI, чтобы изменить цвета переднего плана и фона или установить свойства текста, такие как подчеркивание и полужирный шрифт.

Выводы
К настоящему времени вы должны хорошо понимать, как работает команда echo .
Если у вас есть какие-либо вопросы или отзывы, не стесняйтесь оставлять комментарии.
Источник
Linux echo command
On Unix-like operating systems, the echo command prints text to standard output, e.g., the terminal.
This page covers the GNU/Linux version of echo.
Description
echo is a fundamental command found in most operating systems. It is frequently used in scripts, batch files, and as part of individual commands; anywhere you may need to output text.
Most command shells, including bash, ksh and csh implement echo as a built-in command. The behavior of built-in echo commands is similar, but the options may be different; those commands are not documented here.
This page covers the stand-alone program, /bin/echo. Its options are slightly different than the built-in echo command that is included in your shell. If you are using the bash shell, you can determine which echo is the default, using the type command:
To specify that you want to run the stand-alone program instead of the shell built-in, use its complete path in the command, i.e., run it like this:
This page describes the GNU/Linux stand-alone version of echo.
Syntax
Options
Options
These options may be specified before the string, and affect the behavior of echo.
| -n | Do not output a trailing newline. |
| -e | Enable interpretation of backslash escape sequences (see below for a list of these). |
| -E | Disable interpretation of backslash escape sequences. This is the default. |
Options
If a long option is specified, you may not specify a string to be echoed. These options are for getting information about the program only.
| —help | Display a help message and exit. |
| —version | Output version information and exit. |
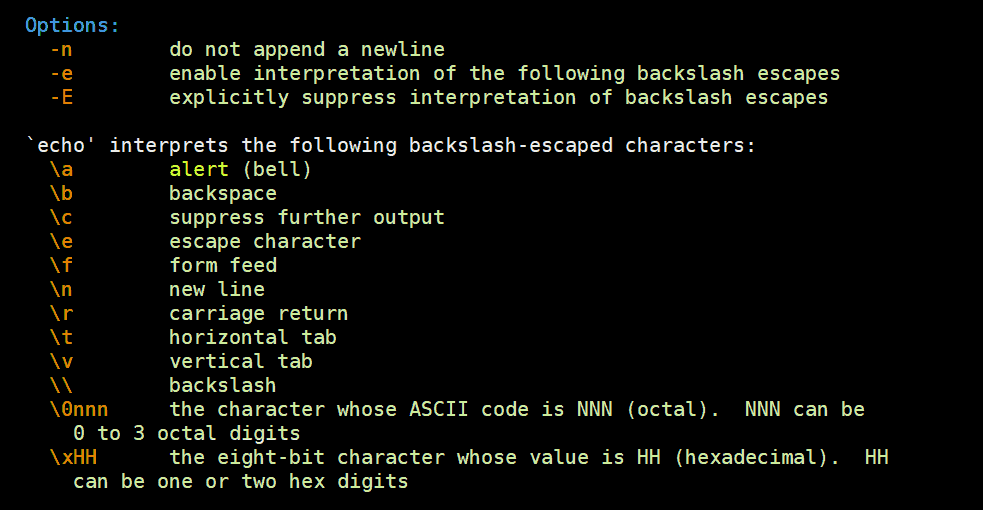
Escape sequences
If you specify the -e option, the following escape sequences are recognized in your string:
| Sequence | Interpreted as |
|---|---|
| \\ | A literal backslash character («\«). |
| \a | An alert (The BELL character). |
| \b | Backspace . |
| \c | Produce no further output after this. |
| \e | The escape character; equivalent to pressing Esc . |
| \f | A form feed. |
| \n | A newline. |
| \r | A carriage return. |
| \t | A horizontal tab. |
| \v | A vertical tab. |
| \0NNN | Byte with octal value NNN (which can be 1 to 3 digits). |
| \xHH | Byte with hexadecimal value HH (which can be either 1 or 2 digits) |
Each shell generally has its own implementation of echo, which may be slightly different than the version described here. Refer to your shell’s documentation for details about the options it supports.
Examples
In the above command, the two words (Hello, and world!) are passed to echo as separate arguments, and echo prints them in sequence, separated by a space:
The next command produces the same output:
However, unlike the first example, the above command provides the single-quoted string ‘Hello, world!‘ as a single argument.
Single-quoting a string will reliably protect it from interpretation by the shell, passing special characters and escape sequences literally to echo.
For instance, in the bash shell, variable names are preceded by a dollar sign ($). In the next command, the variable name inside the quotes is treated literally; outside the quotes, it is converted to its value.
Escape sequences are not interpreted, by default:
However, if you provide the -e option, they are interpreted:
If you need to insert newlines in your echo output, specify the -e option and include the \n escape sequence wherever you want a new line:
Related commands
cat — Output the contents of a file.
printf — Write formatted output.
tac — Output the contents of files in reverse order.
tee — Route a file’s contents to multiple outputs.
touch — Update the timestamp of a file or directory.
tr — Translate one set of characters to another.
Источник
15 Practical Examples of ‘echo’ command in Linux
The echo command is one of the most commonly and widely used built-in commands for Linux bash and C shells, that typically used in a scripting language and batch files to display a line of text/string on standard output or a file.

The syntax for the echo command is:
1. Input a line of text and display it on standard output
Outputs the following text:
2. Declare a variable and echo its value. For example, Declare a variable of x and assign its value=10.
Note: The ‘-e‘ option in Linux acts as an interpretation of escaped characters that are backslashed.
3. Using option ‘\b‘ – backspace with backslash interpretor ‘-e‘ which removes all the spaces in between.
4. Using option ‘\n‘ – New line with backspace interpretor ‘-e‘ treats new line from where it is used.
5. Using option ‘\t‘ – horizontal tab with backspace interpretor ‘-e‘ to have horizontal tab spaces.
6. How about using option new Line ‘\n‘ and horizontal tab ‘\t‘ simultaneously.
7. Using option ‘\v‘ – vertical tab with backspace interpretor ‘-e‘ to have vertical tab spaces.
8. How about using option new Line ‘\n‘ and vertical tab ‘\v‘ simultaneously.
Note: We can double the vertical tab, horizontal tab, and new line spacing using the option two times or as many times as required.
9. Using option ‘\r‘ – carriage return with backspace interpretor ‘-e‘ to have specified carriage return in output.
10. Using option ‘\c‘ – suppress trailing new line with backspace interpretor ‘-e‘ to continue without emitting new line.
11. Omit echoing trailing new line using the option ‘-n‘.
12. Using option ‘\a‘ – alert return with backspace interpretor ‘-e‘ to have the sound alert.
Note: Make sure to check the Volume key, before firing.
13. Print all the files/folders using echo command (ls command alternative).
14. Print files of a specific kind. For example, let’s assume you want to print all ‘.jpeg‘ files, use the following command.
15. The echo can be used with a redirect operator to output to a file and not standard output.
echo Options
| Options | Description |
| -n | do not print the trailing newline. |
| -e | enable interpretation of backslash escapes. |
| \b | backspace |
| \\ | backslash |
| \n | new line |
| \r | carriage return |
| \t | horizontal tab |
| \v | vertical tab |
That’s all for now and don’t forget to provide us with your valuable feedback in the comments below.
If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
TecMint is the fastest growing and most trusted community site for any kind of Linux Articles, Guides and Books on the web. Millions of people visit TecMint! to search or browse the thousands of published articles available FREELY to all.
If you like what you are reading, please consider buying us a coffee ( or 2 ) as a token of appreciation.
We are thankful for your never ending support.
Источник
16 Echo Command Examples in Linux
Echo command in Linux is one of the widely used command in day-to-day operations task. The echo command is a built-in command-line tool that prints the text or string to the standard output or redirect output to a file. The command is usually used in a bash shell or other shells to print the output from a command. Echo command is also used frequently in bash shell scripts.
Syntax of echo command
$ echo [option] [string]
In this guide, we will explain Linux echo command with 16 practical examples.
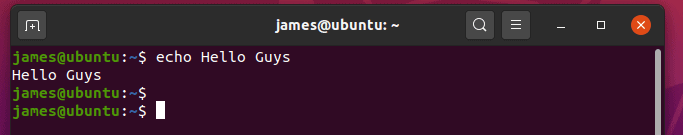
1) Display a simple message on the terminal
To print a simple text message on the terminal with echo command , run the command:
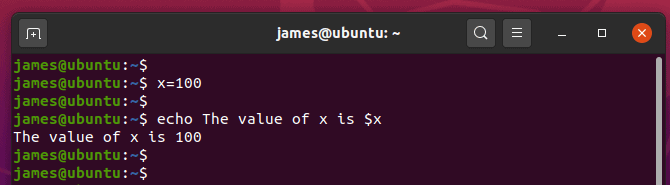
2) Print out the value of a variable with echo command
Let’s assume that you have initialized a variable x and assigned it a value of 100 as shown
You can echo its value by prefixing the variable name with a dollar sign as shown
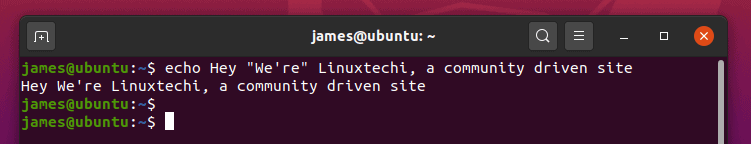
3) Print a line of text comprising of double quotes
To print a line of text with double quotes with echo command, simply enclose the phrase in double-quotes between single quotes.
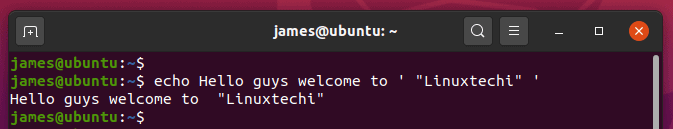
4) Display a line of text consisting of a single quote
If you wish to print a line with a word containing a single quote, enclose the word inside double quotation marks as shown:
5) Redirect echo command output to a file
To redirect echo command output to a file instead of printing it on the screen use the greater than( > ) and double greater than ( >> ) operators.
When you use the greater than( > ) operator, the file will be overwritten. If the file does not exist, it will be created.
The double greater than operator ( >> ) appends text to a file. For example, to add an entry to the /etc/hosts files use the syntax shown
6) Use echo command to match identical files
You can use echo command with a wildcard character to return identical files i.e files that bear the same file extension. For example, to print out all text files with the .txt extension , run the command.
7) List all files and folders in the current directory
The echo command can act as the ls command and list all the files and folders in your current directory using the wildcard as shown:
8) Create new lines using the echo command
Using the backslash interpreter -e , you can manipulate how the line appears on the output. For example, to print a new line, use the ‘ \n ‘ escape character option as shown below:
9) Create tab spaces between words in a sentence
Apart from creating a new line, you can increase the spacing between words in a sentence using the ‘\t ‘ or TAB option as shown.
10) Combine new line and tab spacing options in echo command
You can combine the ‘\n’ and ‘\t’ options at the same time as shown:
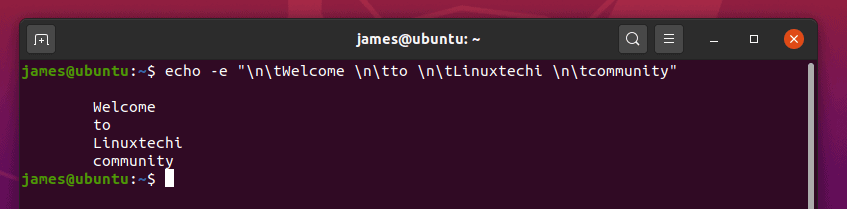
11) Create vertical tab spaces in echo command output
The \v option enables you to create vertical tab spaces as shown:
12) Combine new line and vertical tab spaces in echo command
Additionally, you can experiment and combine the ‘\n’ and ‘\v ‘ options as shown.
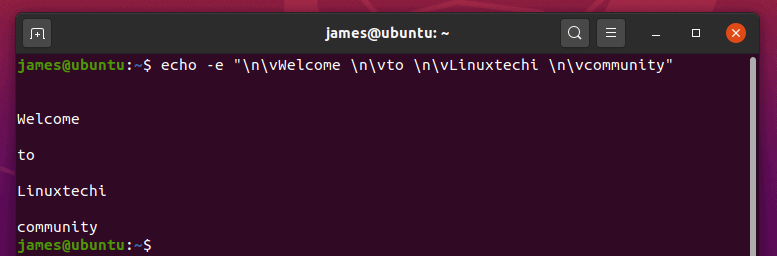
13) Use the carriage return option
The \r option omits the preceding text. For example, the output of the command below omits the first 2 words.
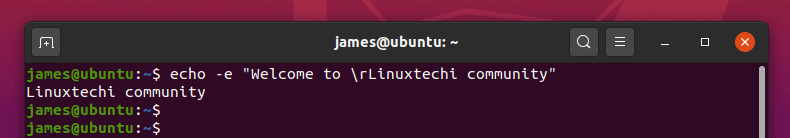
14) Truncate echo command output of text
To suppress any further output and proceed without going to the next line use the ‘\c’ option as shown:
15) Remove all spaces from the text string with echo command
Use ‘ \b’ option along with -e option in echo command to remove all the spaces from the text string, example is shown below:
16) Echo command usage in bash shell script
As we have already stated that echo command is frequently used in bash shell scripts. Example of echo command usage in shell script are listed below:
Output of above script when it is executed:
And that’s it. Thank you for taking your time in this guide. Hopefully, you are now better informed.
Also Read : 14 Grep Command Examples in Linux
Источник