- How to Run or Repeat a Linux Command Every X Seconds Forever
- 1. Use watch Command
- Monitor Memory Usage
- Monitor Logged-In Users, Uptime and Load Average
- Monitor Progress of Copy Command
- 2. Use sleep Command
- for loop Example
- while loop Example
- Conclusion
- If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
- How To Run A Linux Command Every X Seconds Forever
- Run A Linux Command Every X Seconds Forever With Watch Command
- Run A Linux Command Every X Seconds Forever With While loop
- Conclusion
- How to run a command in Linux every x seconds
- Changing the execution time interval
- Conclusion
- Subscribe to My Blog
- Repeat a Linux Command Every X Seconds Forever- using watch
How to Run or Repeat a Linux Command Every X Seconds Forever
A system administrator often needs to run a command repeatedly in a certain periods of time. Often such tasks can be easily completed with simple cron commands. In most of the cases this should work, but the shortest period which you can run cron command is every 1 minute. Believe it or not, in many cases this is too slow.

In this tutorial, you will learn a simple scripting techniques to monitor or keep a eye on a particular command in continuously running state similar to top command (continuously monitor the process and memory utilization) for every 3 seconds by default.
We will not stop to discuss the reasons, why you would need to run commands this often. I believe everyone has different reasons for that in their daily jobs or even at home PCs and laptops.
1. Use watch Command
Watch is a Linux command that allows you to execute a command or program periodically and also shows you output on the screen. This means that you will be able to see the program output in time. By default watch re-runs the command/program every 2 seconds. The interval can be easily changed to meet your requirements.
Monitor Memory Usage
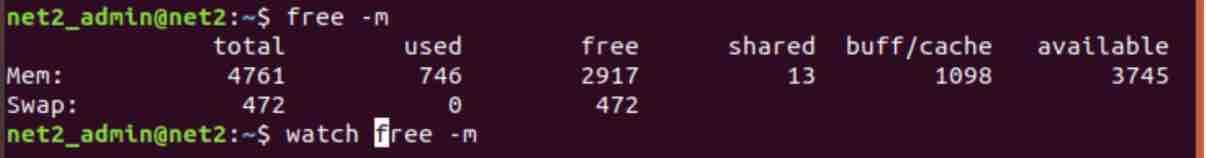
“Watch” is extremely easy to use, to test it, you can fire up a Linux terminal right away and type the following command:
The above command will check your system free memory and update the results of the free command every two seconds.

As seen per the above output, you have a header, displaying information about (from left to right) update interval, command that is being executed and current time. If you wish to hide this header, you can use the -t option.
The next logical question is – how to change the execution interval. For that purpose, you can use the -n option, that specifies the interval with which the command will be executed. This interval is specified in seconds. So let’s say you want to run your script.sh file every 10 seconds, you can do it like this:
Note that if you run the command like shown above, you will need to cd to the directory (learn Learn 15 cd Command Examples) where the script is located or otherwise specify the full path to that script.
Other useful options of watch command are:
- -b – creates a beep sound if the exit of the command is non-zero.
- -c – Interprets ANSI color sequences.
- -d – highlights the changes in the command output.
Monitor Logged-In Users, Uptime and Load Average
Let’s say you want to monitor logged-in users, server uptime and load average output in continuously phase every few seconds, then use following command as shown:

To exit the command, press CTRL+C .
Here, the ‘uptime’ command will run and display the updated results every 2 seconds by default.
Monitor Progress of Copy Command
In Linux, while copying files from one location to other using cp command, the progress of data is not shown, to see the progress of data being copied, you can use the watch command along with du -s command to check the disk usage in real time.

If you think that the above process is too complicated to achieve, then I suggest you to go for Advance copy command, which shows progress of data while copying.
2. Use sleep Command
Sleep is often used to debug shell scripts, but it has many other useful purposes as well. For example, when combined with for or while loops, you can get pretty awesome results.
If you are new to bash scripting, you can check our guide about bash loops here.
In case this is the first time you hear about the «sleep» command, it is used to delay something for a specified amount of time. In scripts, you can use it to tell your script to run command 1, wait for 10 seconds and then run command 2.
With the above loops, you can tell bash to run a command, sleep for N amount of seconds and then run the command again.
Below you can see examples of both loops:
for loop Example
The above one liner, will run the echo command and display the current date, total of 10 times, with 5 seconds sleep between executions.
Here is a sample output:
You can change the echo and date commands with your own commands or script and change the sleep interval per your needs.
while loop Example
Here is sample output:
The above command will run until it is either killed or interrupted by the user. It can come in handy if you need to run a command running in the background and you don’t want to count on cron.
Important: When using the above methods, it is highly recommend that you set interval long enough to give enough time of your command to finish running, before the next execution.
Conclusion
The samples in this tutorial are useful, but are not meant to completely replace the cron utility. It is up to you to find which one works better for you, but if we have to separate the usage of both techniques, I would say this:
- Use cron when you need to run commands periodically even after system reboots.
- Use the methods explained in this tutorial for programs/scripts that are meant to run within the current user session.
As always if you have any questions or comments, do not hesitate to submit them in the comment section below.
If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
TecMint is the fastest growing and most trusted community site for any kind of Linux Articles, Guides and Books on the web. Millions of people visit TecMint! to search or browse the thousands of published articles available FREELY to all.
If you like what you are reading, please consider buying us a coffee ( or 2 ) as a token of appreciation.
We are thankful for your never ending support.
Источник
How To Run A Linux Command Every X Seconds Forever
Have you ever been in a situation where you had to run a specific Linux command every few seconds repeatedly? Well, if you don’t know already, this tutorial will teach you how. Of course you can do this using a shell script or cron jobs. You can also repeat a Linux command at a particular interval without having to manually run it every time. Here is where Watch command comes in handy. This command can be used to execute the given command repeatedly, and monitor the output. To put this in simple words, we can use Watch command to run a Linux command every X seconds forever and it will keep displaying the output in the console until we stop it manually by pressing CTRL+C or kill the process or forcibly reboot the system. By default, the given command will run every 2 seconds, or you can define the time interval of your choice.
Run A Linux Command Every X Seconds Forever With Watch Command
The syntax of watch command is:
Below I have given a few examples to teach you where you can use watch command to run a specific Linux command repeatedly.
Example 1:
Let us say you want to run the uptime command every 2 seconds to monitor the uptime of your system. To do so, simply run:
Sample output:
- Every 2.0s: uptime — The uptime command will run every 2 seconds and display the result.
- sk — The currently logged in user
- Wed Feb 9 20:14:46 2018 — The current date and time when we executed the command.
This will keep running until you manually end it. To exit the command, press CTRL+C .
You can also save the output of the uptime command in a file. To do so, run:
This can be useful when you wanted to send the uptime of your system to a technical support for getting help.
Example 2:
As I mentioned before, watch command executes a program every 2 seconds by default. We can change it to a particular interval, for example 5 seconds, using -n parameter.
Let us display the file system disk space usage for every 5 seconds.
Sample output:
To check whether this command really works, create or delete any file/folder. You will notice that the free space has changed in the output after creating or deleting the files/folders.
Example 3:
To watch contents of a directory change, run:
Here, The -d or —differences flag will highlight the differences between successive updates.
Sample output:
Also, you can display the contents of a directory change which is owned by a particular user (Eg. sk).
This can be useful in multi-user system.
Example 4:
To display the memory details, run:
Example 5:
To display the output of du command every 10 seconds, you can use:
Sample output:
This monitor the disk usage every 10 seconds until you exit it manually.
For more details, I recommend you to refer man pages.
Run A Linux Command Every X Seconds Forever With While loop
You can also do this with the help of While loop.
To repeat a command every 2 seconds forever, run:
Conclusion
You know now how to run a command every X seconds using Watch command. Generally, Watch command is used for monitoring disk usage and memory usage. Please do not confuse this command with other monitoring tools. This command is intend to execute a command every particular second forever, until you manually stop it.
Источник
How to run a command in Linux every x seconds
Oftentimes you need to run a command every X seconds on Linux. Granted you can use cron but unfortunately, it does not handle time granularities of less than a minute.
The watch command on Linux allows you to run a program periodically. By default, the watch command has a repeat period of 2 seconds but this can be changed as per the requirement.
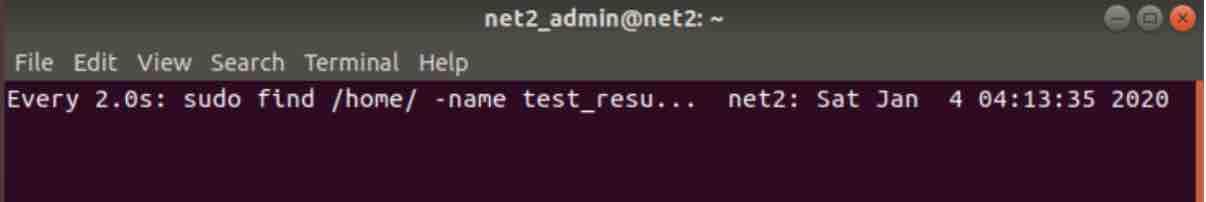
Say you would like to perform a periodic search of a file you expect to receive from a remote machine.The find command will look like :
find /home/ -name “test_results.txt”
Now in order to carry out this task every two seconds, you could use the watch command as follows :
watch find /home/ -name “test_results.txt”
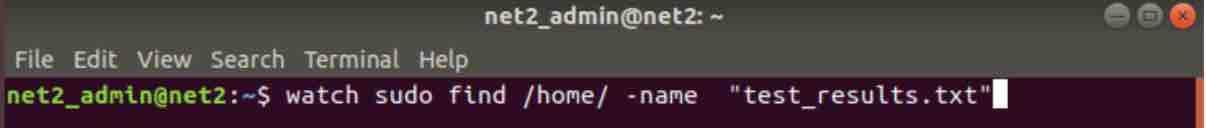
linux watch command
Once you hit Enter you would see:
The snapshot above shows a header with information about the update interval along with the command being executed. To hide the header, use the -t option.
Changing the execution time interval
In case you want to change the default period of 2 seconds to another value, you can use the -n option with the watch command. This will indicate the period in seconds.
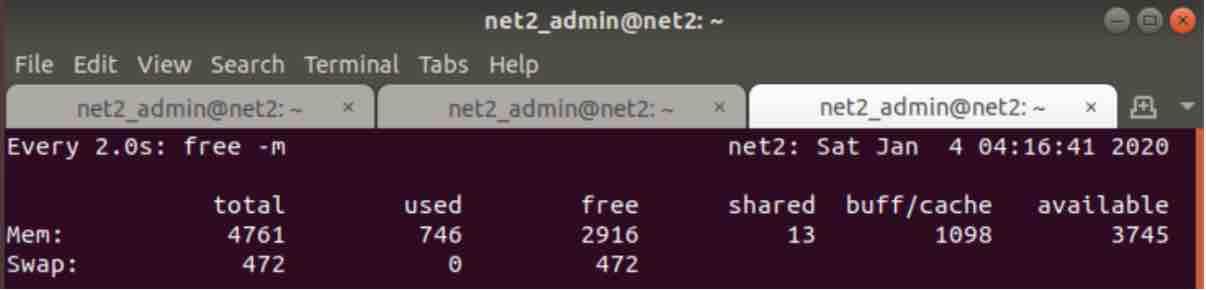
For instance, you would like to run an ‘free -m’ command every 5 seconds, you simply need to proceed as follows :
watch -n 5 free -m
if you have a script that needs to be executed every 10 seconds, you simply run the command :
watch -n 10 your_script.sh
The execution of the script above requires you to do a cd to the directory in which the script is located or you can simply mention the full path to your script.
Conclusion
You have seen how to use the watch command to perform repeated tasks. You can as well use a while or a for loop along with the sleep command. If you have other methods let us know.
If you like the content, we would appreciate your support by buying us a coffee. Thank you so much for your visit and support.
Источник
Subscribe to My Blog
Repeat a Linux Command Every X Seconds Forever- using watch
Use watch Command
Watch is a Linux command that allows you to execute a command or program periodically and also shows you output on the screen. This means that you will be able to see the program output in time. By default watch re-runs the command/program every 2 seconds. The interval can be easily changed to meet your requirements.
Monitor Memory Usage
“Watch” is extremely easy to use, to test it, you can fire up a Linux terminal right away and type the following command:
The above command will check your system free memory and update the results of the free command every two seconds.
Monitor Memory Usage in Linux
As seen per the above output, you have a header, displaying information about (from left to right) update interval, command that is being executed and current time. If you wish to hide this header, you can use the -t option.
The next logical question is – how to change the execution interval. For that purpose, you can use the -n option, that specifies the interval with which the command will be executed. This interval is specified in seconds. So let’s say you want to run your script.sh file every 10 seconds, you can do it like this:
Note that if you run the command like shown above, you will need to cd to the directory (learn Learn 15 cd Command Examples) where the script is located or otherwise specify the full path to that script.
Other useful options of watch command are:
Monitor Logged-In Users, Uptime and Load Average
Let’s say you want to monitor logged-in users, server uptime and load average output in continuously phase every few seconds, then use following command as shown:
Here, the ‘uptime’ command will run and display the updated results every 2 seconds by default.
Monitor Progress of Copy Command
In Linux, while copying files from one location to other using cp command, the progress of data is not shown, to see the progress of data being copied, you can use the watch command along with du -s command to check the disk usage in real time.
Monitor Progress of Copy Command
If you think that the above process is too complicated to achieve, then I suggest you to go for Advance copy command, which shows progress of data while copying.
Use sleep Command
Sleep is often used to debug shell scripts, but it has many other useful purposes as well. For example, when combined with for or while loops, you can get pretty awesome results.
If you are new to bash scripting, you can check our guide about bash loops here.
In case this is the first time you hear about the “sleep” command, it is used to delay something for a specified amount of time. In scripts, you can use it to tell your script to run command 1, wait for 10 seconds and then run command 2.
With the above loops, you can tell bash to run a command, sleep for N amount of seconds and then run the command again.
Below you can see examples of both loops:
for loop Example
The above one liner, will run the echo command and display the current date, total of 10 times, with 5 seconds sleep between executions.
Here is a sample output:
You can change the echo and date commands with your own commands or script and change the sleep interval per your needs.
while loop Example
Here is sample output:
The above command will run until it is either killed or interrupted by the user. It can come in handy if you need to run a command running in the background and you don’t want to count on cron.
Источник