- Записки угрюмого поднимателя пингвинов.
- пятница, 20 ноября 2015 г.
- Как определить FC ID(WWN) диска(LUN) на Linux сервере
- База знаний wiki
- Содержание
- fc подключение к схд сервера под linux
- Задача:
- Решение:
- Обновление драйвера QLE2562
- Получение параметров HBA
- Многопутевой ввод-вывод (Multipath I/O)
- Установка OceanStor UltraPath
- Настройка UltraPath
- Пересканировать SCSI
- How to find WWN and WWPN of HBA card in Linux
- What is SAN?
- Purpose of wwn number
- Checking HBA card information
- Method-1: Checking wwn number manually
- Method-2: Checking wwn number using systool command
- How to install systool in Linux
- Conclusion
- How To Find WWN in Linux Check HBA Connectivity Status
- How To Find WWN in Linux Check HBA Connectivity Status
- Method 2 – Find WWN in Linux
- Related Articles
- How to find HBA cards/ports and WWN in Linux Redhat/Centos
- Method 1
- Method 2 : Using systool
Записки угрюмого поднимателя пингвинов.
*nix заметки на память
пятница, 20 ноября 2015 г.
Как определить FC ID(WWN) диска(LUN) на Linux сервере
Бывает трудно найти к какому SAN относится диск и как он подключен, если к серверу подключено более двух SAN одного типа. Получаем FC адрес на HBA.
# systool -c fc_host -v
Class = «fc_host»
Class Device = «host1»
Class Device path = «/sys/class/fc_host/host1»
fabric_name = «0x1000000533a43ae2»
issue_lip =
node_name = «0x5001438016793705»
port_id = «0x800100»
port_name = «0x5001438016793704»
port_state = «Online»
port_type = «NPort (fabric via point-to-point)»
speed = «8 Gbit»
supported_classes = «Class 3»
supported_speeds = «1 Gbit, 2 Gbit, 4 Gbit, 8 Gbit»
symbolic_name = «QMH2562 FW:v5.06.03 DVR:v8.03.07.15.05.09-k»
system_hostname = «»
tgtid_bind_type = «wwpn (World Wide Port Name)»
uevent =
Device = «host1»
Device path = «/sys/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:07.0/0000:06:00.0/host1»
edc =
fw_dump =
nvram = «ISP «
optrom_ctl =
optrom =
reset =
uevent =
vpd = «-8»
Class Device = «host2»
Class Device path = «/sys/class/fc_host/host2»
Определяем FC и WWN.
# systool -c fc_transport -v
Class = «fc_transport»
Class Device = «0:0»
Class Device path = «/sys/class/fc_transport/target1:0:0»
node_name = «0x500000e0d4465600»
port_id = «0x431900»
port_name = «0x500000e0d4465680»
uevent =
Device = «target1:0:0»
Device path = «/sys/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:07.0/0000:06:00.0/host1/rport-1:0-0/target1:0:0»
uevent =
Class Device = «0:0»
Class Device path = «/sys/class/fc_transport/target2:0:0»
node_name = «0x500000e0d4465600»
port_id = «0x441900»
port_name = «0x500000e0d4465681»
uevent =
Device = «target2:0:0»
Device path = «/sys/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:07.0/0000:06:00.1/host2/rport-2:0-0/target2:0:0»
uevent =
Class Device = «0:10»
Class Device path = «/sys/class/fc_transport/target1:0:10»
node_name = «0x500110a0005ad776»
port_id = «0x433400»
port_name = «0x500110a0005ad777»
uevent =
Device = «target1:0:10»
Device path = «/sys/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:07.0/0000:06:00.0/host1/rport-1:0-10/target1:0:10»
uevent =
Class Device = «0:10»
Class Device path = «/sys/class/fc_transport/target2:0:10»
node_name = «0x500110a0005ad86f»
port_id = «0x3e4200»
port_name = «0x500110a0005ad870»
uevent =
Device = «target2:0:10»
Device path = «/sys/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:07.0/0000:06:00.1/host2/rport-2:0-10/target2:0:10»
uevent =
WWN(port_name) и WWNN(node_name) получены. Определяем соответствие между SCSI HBTL адресами и дисками. В RHEL/CentOS/Fedora нужен пакет sg3_utils.
# sg_map -x
Device /dev/nst18 is busy
/dev/sg0 1 0 0 0 0 /dev/sda
/dev/sg1 1 0 0 1 0 /dev/sdb
/dev/sg2 1 0 0 2 0 /dev/sdc
/dev/sg3 1 0 0 3 0 /dev/sdd
/dev/sg4 1 0 1 0 0 /dev/sde
/dev/sg5 1 0 1 1 0 /dev/sdf
/dev/sg6 1 0 1 2 0 /dev/sdg
/dev/sg7 1 0 1 3 0 /dev/sdh
/dev/sg8 1 0 2 0 8
/dev/sg9 1 0 3 0 1 /dev/nst0
/dev/sg10 1 0 4 0 1 /dev/nst1
/dev/sg11 1 0 5 0 1 /dev/nst2
/dev/sg12 1 0 6 0 1 /dev/nst3
/dev/sg13 1 0 7 0 1 /dev/nst4
/dev/sg14 1 0 8 0 1 /dev/nst5
/dev/sg15 1 0 9 0 1 /dev/nst6
/dev/sg16 1 0 10 0 1 /dev/nst7
/dev/sg17 1 0 11 0 1 /dev/nst8
/dev/sg18 1 0 12 0 1 /dev/nst9
/dev/sg19 1 0 13 0 1 /dev/nst10
/dev/sg20 1 0 14 0 1 /dev/nst11
/dev/sg21 2 0 0 0 0 /dev/sdi
/dev/sg22 2 0 0 1 0 /dev/sdj
/dev/sg23 2 0 0 2 0 /dev/sdk
/dev/sg24 2 0 0 3 0 /dev/sdl
/dev/sg25 2 0 1 0 0 /dev/sdm
/dev/sg26 2 0 1 1 0 /dev/sdn
/dev/sg27 2 0 1 2 0 /dev/sdo
Источник
База знаний wiki
Продукты
Статьи
Содержание
fc подключение к схд сервера под linux
Применимость: Linux, выделенный сервер
Слова для поиска: storage, Huawei OceanStor
Задача:
Как подключиться к LUN выделенному на системе хранения
Решение:
Обновите систему и перезагрузите сервер с новым ядром
Обновление драйвера QLE2562
Ядро уже содержит драйвер для QLE2562, но вы можете использовать самый свежий драйвер с сайта производителя. Скачайте архив с драйвером
Установка компиляторов и прочих пакетов:
Распаковать архив с драйвером и выполнить установку:
Проверить версию установленного драйвера:
Получение параметров HBA
Найти HBA карты на вашем сервере:
Есть другие способы чтобы получить информацию о HBA, но удобнее использовать systool (пакет sysfsutils).
Найти WWN портов:
Сообщите эти значения администратору для настройки параметров доступа к вашему LUN
Определить статус портов:
Если статус Online и настроен доступ на СХД, то можно перезагрузить модуль адаптера и попытаться увидеть ваш LUN
В этом примере мне выделен один LUN на 200GB, но я вижу 8 штук. Причина в том, что этот LUN виден по 8-ми путям. 2 порта на моем сервере и группа из 4-х портов на СХД образуют 8 возможных путей прохождения данных.
Это необходимо для распределения нагрузки и отказоустойчивости.
— Какое же из устройств использовать? — Если вы просто будете использовать в таком варианте одно из устройств, то это означает использование только одного пути.
Для использования всех нужно использовать либо службу Multipath или Huawei OceanStor UltraPath
Многопутевой ввод-вывод (Multipath I/O)
Использовать много-путевой доступ необходимо даже в том случае если на вашем сервере используется 1 порт.
Иначе, например, в случае обновления прошивки на одном из контроллеров СХД произойдет временное отключение вашего сервера от СХД и данные на вашем LUN могу быть повреждены.
Многопутевой ввод-вывод (Multipath I/O) — технология подключения узлов сети хранения данных с использованием нескольких маршрутов. В случае отказа одного из контроллеров, операционная система будет использовать другой для доступа к устройству. Это повышает отказоустойчивость системы и позволяет распределять нагрузку.
Multipath устройства объединяются в одно устройство с помощью специализированного программного обеспечения в новое устройство. Multipath обеспечивает выбор пути и переключение на новый маршрут при отказе текущего. Это происходит невидимо для программ и процессов использующих это устройство. Кроме того Multipath способен распределять передачу данных по разным путям посредством различных алгоритмов, например:
Преимущества Huawei UltraPath
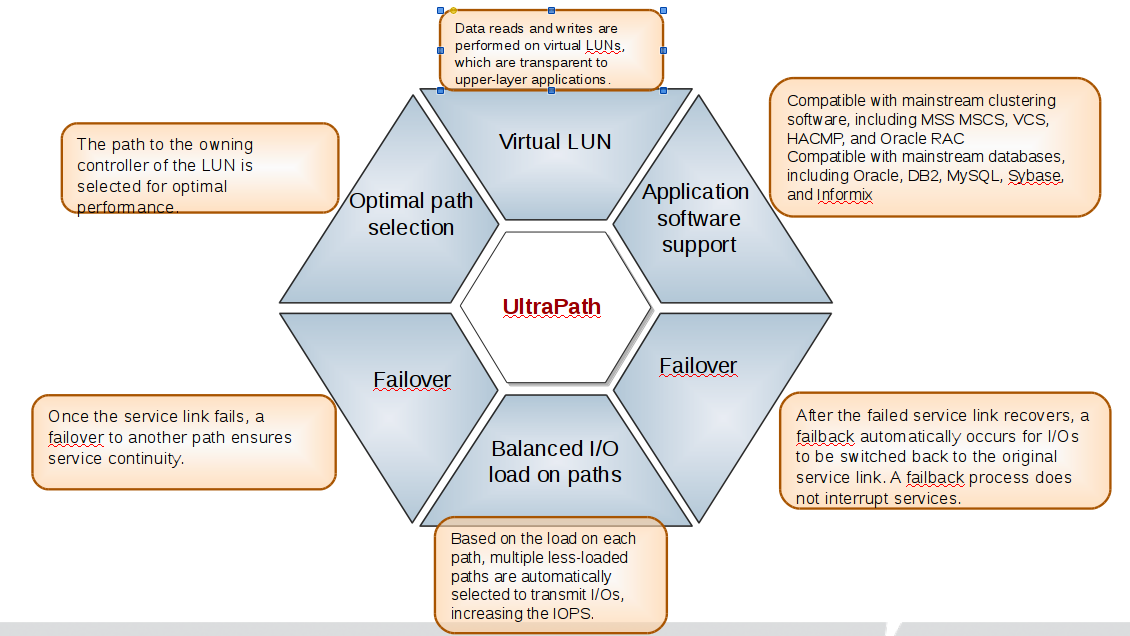
Установка OceanStor UltraPath
Запросить у службы поддержки ссылку на пакет OceanStor UltraPath соответствующий версии вашей ОС.
В ходе установки вам будет предложено выбрать опции:
Если система у вас установлена на локальном HDD, то ваш выбор должен быть — 1: Boot from local Если ваша система установливалась на диск доступный по Fibre Channel или iSCSI, то ваш выбор должен быть — 2: Boot from SAN
Следующий шаг — согласиться или отказаться от перезагрузки системы.
Если для подключения к системе хранения используются HBA адаптеры HCA, QLogic или Emulex, мы рекомендуем установить значение N.
Установите следующие параметры драйвера HBA адаптера:
Например для QLogic (qla2xxx) в файле /etc/modprobe.d/nxupmodules.conf следует добавить строки, если их там нет:
Для программного адаптера Linux-iscsi (Red Hat AS4) в файле /etc/iscsi.conf должны быть параметры:
Для программного адаптера open-iscsi (RHEL-7, Centos) в файле /etc/iscsi/iscsid.conf должны быть параметры:
Убедитесь, что UltraPath работает
lsscsi | grep updisk [8:0:0:1] disk up updisk 4303 /dev/sdc
В данном случае виртуальный диск созданный UltraPath имеет имя /dev/sdc
В дальнейшем вы можете использовать его для всех нужд
Создать файловую систему XFS:
Настройка UltraPath
Для управления параметрами используется утилита upadmin
Конфигурация по умолчанию после установки:
Здесь стоит изменить параметр Working Mode чтобы данные одновременно передавались по всем путям
Контроль I/O по путям для LUN с идентификатором 0:
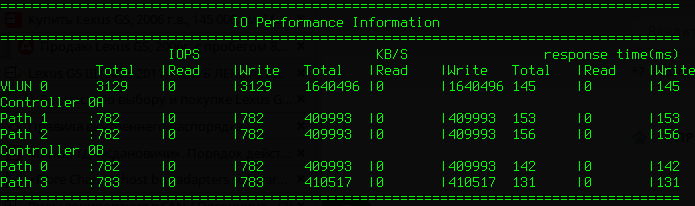
Пересканировать SCSI
Если у вас изменился список scsi устройств (добавили LUN), то система не увидит их сама В дистрибутивах основанных на Red Hat есть скрипт:
После отрабатывания скрипта проверьте вывод команды:
Источник
How to find WWN and WWPN of HBA card in Linux
There are several ways to detect the WWN of a Fibre Channel (FC) HBA and their details in Linux/Unix operating systems.
In this article, we will explain you the two best ways to find wwn number in Linux.
What is SAN?
A Storage Area Network (SAN) is a dedicated, independent, high-speed network that provides block-level network access to storage.
A SAN typically consists of cabling, host bus adapters, and SAN switches connected to storage arrays and servers.
SCSI (Small Computer System Interface) is a protocol used to communicate between servers and storage devices.
Purpose of wwn number
To add storage to the host, server has to be mapped with storage device by zoning the WWN of both host and storage in Fabric switch.
Once the zone is created, the storage team can assign LUNs to a specific Linux host, and new LUN can be discovered by scanning the storage LUN ID at the host end.
Popular FC host bus adapters are QLogic, Emulex, Brocade, Cisco, etc.
Some of the important abbreviations are listed below:
- WWN – World Wide Name
- WWNN – World Wide Node Name
- WWPN – World Wide Port Name
- WWID – World Wide Identifier
- OUI – Organizationally Unique Identifier
Checking HBA card information
You can easily identify how many HBA cards are installed in your Linux system by running ‘lspci’ command as shown below:
Method-1: Checking wwn number manually
HBA card wwn number can be manually identified by filtering the associated files under the “/sys” file system.
The files under sysfs provide information about devices, kernel modules, filesystems, and other kernel components, which are typically mounted automatically by the system at /sys.
To check the available HBA ports, use the below file:
The ‘fc_transport’ determines the correct host, channel, and target information from currently presented LUN:
You can verify a list of ‘wwn’ number of the fc host (HBA card) using the following file:
Use the following file to check a specific fc host wwn number:
To find the status of HBA ports, use the below file (online/offline):
Method-2: Checking wwn number using systool command
The systool is a tool that uses APIs provided by libsysfs to gather information. It allows you to view system device information by bus, class, and topology.
When you run systool without parameters, it will present all available bus types, device classes, and root devices.
How to install systool in Linux
systool can be easily installed from the distribution official repository.
For RHEL/CentOS 6/7 systems, use the yum command to install systool:
For RHEL/CentOS 8 and Fedora systems, use the dnf command to install systool:
Once the sysfsutils package is installed on the Linux system, run the following command to find the WWN number of fc host:
Run the following command to check the state of HBA ports:
If you want to check wwn number of a specific fc host , run the following command:
Conclusion
In this guide, we have shown you 2 simple methods to find WWN, WWPN of HBA card and the status of HBA ports in Linux.
If you have any questions or feedback, feel free to comment below.
Источник
How To Find WWN in Linux Check HBA Connectivity Status
by ARK · May 7, 2018
Find WWN in Linux is easy using existing commands and installing few systools will help us in getting the FC HBA adapter WWN in Linux. There are several ways to find out FC HBA WWN in Linux/Unix operating systems.
How To Find WWN in Linux Check HBA Connectivity Status
We can use lspci command to find the FC HBA adapter details first. lspci is a utility for displaying information about PCI buses in the system and devices connected to them.
Method 1
above command will give us an whether Host Bus Adapter is installed in our Linux machine or not. If HBA is installed then we can see it’s details as shown above.
check how many hosts (Ports/Cards) are there in your Linux machine using below command
Using below command find if FC HBA is Online or Offline Or Link Status. If link status is down also we can get WWN in Linux. Below while loop script will list all of your HBA card details.
Find all the card information using below command
Method 2 – Find WWN in Linux
Another way of finding WWN in Linux is using systool utility this is an extra package you have to install in your Linux server using below command
After successful installation run below command to get all the details about FC HBA
All above details are not required for us just grep the required details using grep command
Highlighted in orange color is the WWN of FC HBA card host3
That’s it about finding the WWN in Linux using command line utilities
Related Articles
Thanks for your wonderful Support and Encouragement
Источник
How to find HBA cards/ports and WWN in Linux Redhat/Centos
Maybe you are new in a professional environment where you have to become familiar with new terms like HBA cards and storage via Fiber or others
A host bus adapter (HBA) is a circuit board and/or integrated circuit adapter that provides input/output (I/O) processing and physical connectivity between a host system, or server, and a storage and/or network device
How to find HBA cards/ports and WWN in Linux Redhat/Centos ?
Method 1
To find the HBA cards installed on your system use :
To check the available HBA ports :
To find the state of HBA ports (online/offline) :
To find the WWN numbers of the above ports :
Method 2 : Using systool
Another useful command to find the information about HBAs is systool. If not already installed please do it with the following command.
To check the available HBA ports :
To find the WWNs for the HBA ports :
To check the state of the HBA ports (online/offline) :
Источник








