- NVIDIA 470.63.01 + Xwayland on Fedora 34 and Gnome 40.2
- Table of Contents
- 8. Enable Xwayland with NVIDIA 470.63.01 proprietary drivers on Fedora 34 GNOME 40.2 desktop
- 8.1 Change root user
- 8.2 Edit /etc/default/grub
- 8.3 Update grub2 conf
- 8.4 Update /usr/lib/udev/rules.d/61-gdm.rules
- 8.5 Generate initramfs
- 8.6 Enable kms-modifiers through gsettings (as normal user)
- 8.7 Reboot
- Fedora 34/33/32 NVIDIA Drivers Install Guide
- Table of Contents
- 1. Before NVIDIA drivers installation
- 1.1 Check is your NVIDIA card supported
- 1.2 NVIDIA Optimus Technology
- 1.3 Disable UEFI Secure Boot or Check Howto Sign NVIDIA Kernel Module
- 2. Install NVIDIA proprietary drivers on Fedora 33/32/31/30/29 and disable the nouveau driver
- 2.1 Download NVIDIA Installer Package
- Tested versions with 5.13+ / 5.12+ / 5.11+ / 5.10+ / 5.9+ kernels:
- 2.2 Make NVIDIA installer executable
- 2.3 Change root user
- 2.4 Make sure that you system is up-to-date and you are running latest kernel
- 2.5 Install needed dependencies
- 2.6 Disable nouveau
- 2.6.1 Create or edit /etc/modprobe.d/blacklist.conf
- 2.6.2 Edit /etc/default/grub
- 2.6.3 Update grub2 conf
- 2.6.4 Remove xorg-x11-drv-nouveau
- 2.6.5 Generate initramfs
- 2.7 Reboot to runlevel 3
- 2.8 Install NVIDIA proprietary drivers for GeForce 6/7 & GeForce 8/9/200/300 & GeForce 400/500/600/700/800/900/10/20 series cards
- 2.8.1 Log in as root user
- 2.8.2 Run NVIDIA Binary
- 2.8.3 NVIDIA Installer Register the Kernel Source Modules with DKMS
- 2.8.4 NVIDIA Installer 32-bit Compatibility Libraries
- 2.8.5 NVIDIA Installer Installing Drivers and Building kernel module
- 2.8.6 NVIDIA Installer Automatic Xorg Config and Backup
- 2.8.7 NVIDIA Drivers Installation Complete
- 2.9 All Is Done and Then Reboot Back to Runlevel 5
- 2.10 VDPAU/VAAPI support
- 3. Some Screenshots Using Different Cards and Drivers
- 3.1 NVIDIA 465.31 drivers on Fedora 34 Gnome 40 with Kernel 5.12.8
- 3.2 VIDIA 460.80 drivers on Fedora 34 Gnome 40 with Kernel 5.12.8
- 3.3 NVIDIA 450.119.03 drivers on Fedora 34 Gnome 40 with Kernel 5.12.8
- 3.4 NVIDIA 435.21 drivers on Fedora 34 Gnome 40 with Kernel 5.12.8
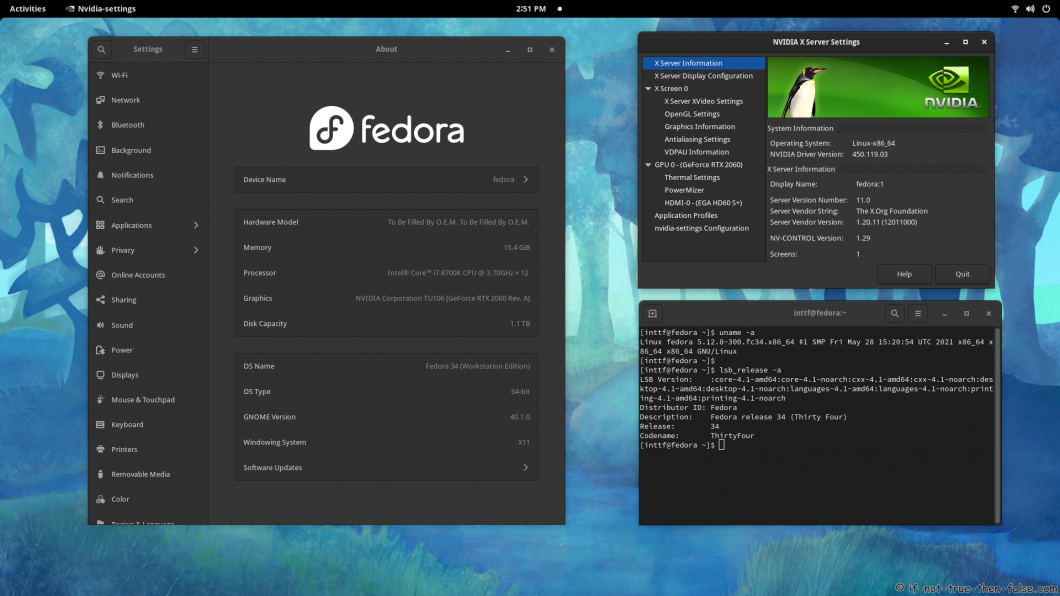
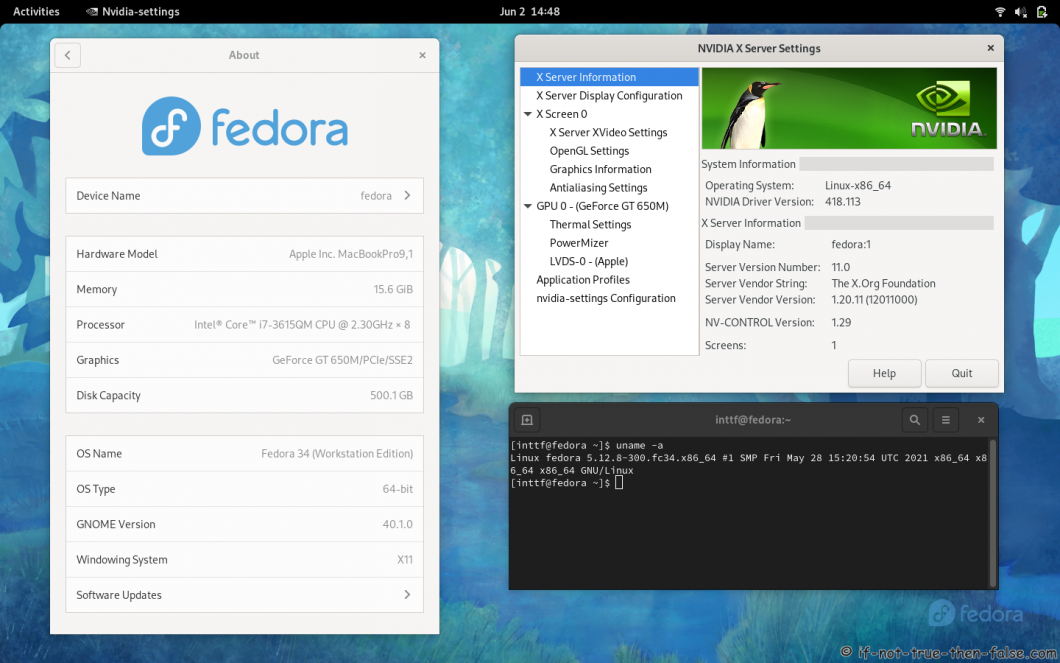
- 3.5 NVIDIA 418.113 drivers on Fedora 34 Gnome 40 with Kernel 5.12.8
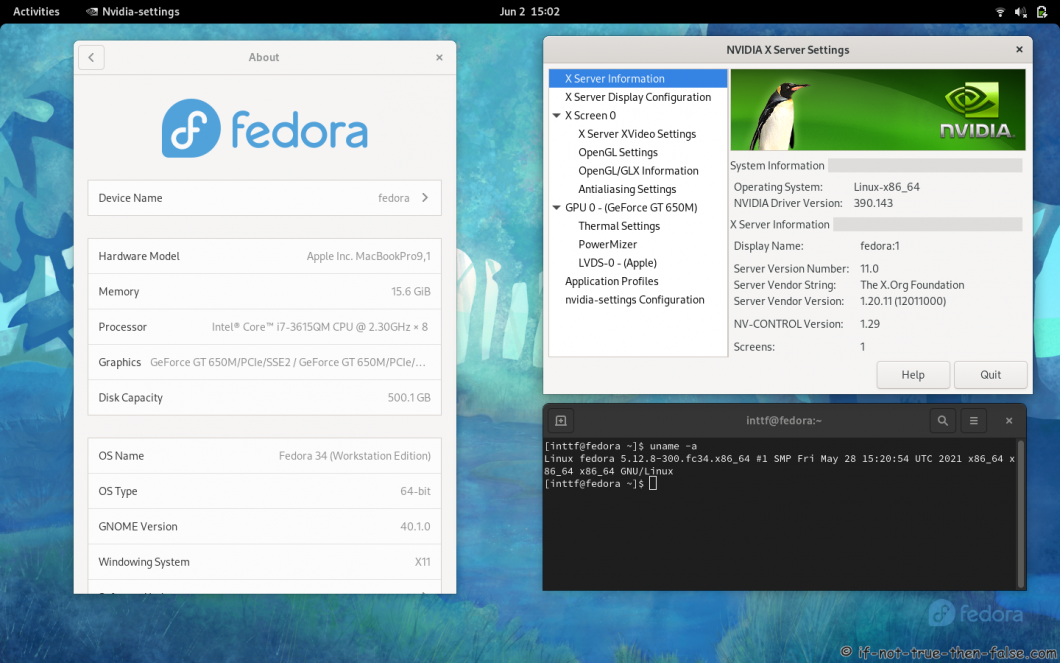
- 3.6 NVIDIA 390.143 drivers on Fedora 34 Gnome 40 with Kernel 5.12.8
- 3.6 NVIDIA 340.108 drivers on Fedora 34 Gnome 40 with Kernel 5.12.8
- How to Set Nvidia as Primary GPU on Optimus-based Laptops
- Introduction
- Why would you want to do that?
- Why would you not want to do that?
NVIDIA 470.63.01 + Xwayland on Fedora 34 and Gnome 40.2
Table of Contents
This is guide, howto enable NVIDIA accelerated 3D rendering and Xwayland on on Fedora 34 with NVIDIA 470.63.01 proprietary drivers on GNOME 40.2. Tested with latest NVIDIA drivers, I assume here that you have installed NVIDIA drivers using this guide. This might work normally with any other installation methods too, but it’s not tested.
Note: Do this using fully updated system and latest kernel, also NVIDIA 470.63.01 drivers installed. Check also NVIDIA’s own guide for this OpenGL and Vulkan on Xwayland.
Check video version of guide:
Before you start you will at least following packages installed:
- Xwayland >= 21.1.1.901
- libxcb >= 1.13
- egl-wayland >= 1.1.7
Check your packages using following command:
If some missing, then install all using following command:
8. Enable Xwayland with NVIDIA 470.63.01 proprietary drivers on Fedora 34 GNOME 40.2 desktop
8.1 Change root user
8.2 Edit /etc/default/grub
Append ‘nvidia-drm.modeset=1’ to end of ‘GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX=”…”‘.
8.3 Update grub2 conf
Fedora 34
Fedora 33/32/31/30
8.4 Update /usr/lib/udev/rules.d/61-gdm.rules
Comment line which starts with DRIVER==”nvidia”:
8.5 Generate initramfs
8.6 Enable kms-modifiers through gsettings (as normal user)
8.7 Reboot
When you system boot you should be able to select GNOME Wayland session, login using it and open terminal and type:
Источник
Fedora 34/33/32 NVIDIA Drivers Install Guide
This is guide, howto install NVIDIA proprietary drivers (manually using .run files) on Fedora 34/33/32/31/30 and disable Nouveau driver. This guide works with GeForce 8/9/200/300/400/500/600/700/800/900/10/20/30 series cards.
- GeForce RTX 30 series cards works with 470.xx, 465.xx and 460.xx NVIDIA drivers, (RTX 3090, RTX 3080 and RTX 3070)
- GeForce RTX 20 series cards works with 470.xx, 465.xx, 460.xx and 450.xx NVIDIA drivers (RTX 2080 Ti, RTX 2080, RTX 2070 Ti, RTX 2070, RTX 2060)
- GeForce GT/GTX 600/700/800/900/10 series cards works with 470.xx, 465.xx, 460.xx, 450.xx and 390.xx NVIDIA drivers (GTX 1080 Ti, GTX 1080, GTX 1070, GTX 1060, GTX 1660 …)
- GeForce GT/GTX 400/500 series cards works with 390.xx NVIDIA drivers
- GeForce GT 8/9/200/300 series cards works with 340.xx NVIDIA drivers
Check video version of guide, Fedora 34 (improved version) and Fedora 33, both works with Fedora 34 and Fedora 33:
I got following question in Youtube:
It’s good question and I decided to add my answer here as well:
Actually nothing, but with manual installation you can control NVIDIA drivers versions as you wish.
You can easily install / change / test / run:
- NVIDIA New Feature Branch (NFB) drivers
- NVIDIA Long Lived Branch (LLB) drivers
- NVIDIA Short Lived Branch (SLB) drivers
- NVIDIA LEGACY drivers
- NVIDIA BETA drivers
- Install NVIDIA drivers with custom patches
- Just stay in some particular NVIDIA version
This is totally different guide than my earlier guides, like Fedora 20 NVIDIA driver install. This guide uses NVIDIA drivers directly from NVIDIA site and dkms to help on kernel updates. I decided go back to old school (and bit ugly) method and install NVIDIA drivers “manually”. I have tested this guide with 340.xx (patched), 390.xx (patched), 418.xx (patched), 435.xx (patched), 450.xx, 460.xx, 465.xx, 470.xx drivers/cards.
With DKMS, you can just update your kernel and your NVIDIA drivers are compiled automatically. If you want to upgrade NVIDIA drivers, then you have to download new installer package from NVIDIA site.
Table of Contents
Let me know, if you have some problems?
Or if you succeed, you could post output of following commands:
Backup first important files before you start installation. And this is of course at your own risk, because graphic cards, components and monitors are different and some combinations might cause totally unexpected results.
1. Before NVIDIA drivers installation
1.1 Check is your NVIDIA card supported
If you see multiple VGA controllers, then check next step and sometimes you might see example Intel VGA controller which have nothing to do with Optimus, normally you can go to BIOS and simply disable it.
1.2 NVIDIA Optimus Technology
If your lspci |grep -E “VGA|3D” output looks like following:
Or you know that your computer have NVIDIA Optimus Technology, and it is impossible to turn Intel Graphics / NVIDIA Optimus off in the BIOS then this guide might not work for you and it’s not tested. You should read this NVIDIA Optimus page first and maybe check Bumblebee Project or NVIDIA XRun Project.
1.3 Disable UEFI Secure Boot or Check Howto Sign NVIDIA Kernel Module
If you have UEFI Secure Boot enabled, then you have to disable Secure Boot or sign your NVIDIA kernel module.
2. Install NVIDIA proprietary drivers on Fedora 33/32/31/30/29 and disable the nouveau driver
2.1 Download NVIDIA Installer Package
Go to http://www.nvidia.com/Download/Find.aspx?lang=en-us and find latest version of installer package. When you use browser this is normally downloaded /home/ /Downloads/NVIDIA-Linux-xxxx.run location.
Tested versions with 5.13+ / 5.12+ / 5.11+ / 5.10+ / 5.9+ kernels:
| Fedora 34 | Fedora 33 | Fedora 32 | Fedora 31/30 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 470.74 (September 20, 2021) | 470.74 (September 20, 2021) | 470.74 (September 20, 2021) | 470.74 (September 20, 2021) |
| 465.31 (May 18, 2021) | 465.31 (May 18, 2021) | 465.31 (May 18, 2021) | 465.31 (May 18, 2021) |
| 460.91.03 (July 20, 2021) | 460.91.03 (July 20, 2021) | 460.91.03 (July 20, 2021) | 460.91.03 (July 20, 2021) |
| 450.119.03 (April 19, 2021) | 450.119.03 (April 19, 2021) | 450.119.03 (April 19, 2021) | 450.119.03 (April 19, 2021) |
| 435.21 (August 29, 2019) | 435.21 (August 29, 2019) | 435.21 (August 29, 2019) | 435.21 (August 29, 2019) |
| 418.113 (November 5, 2019) | 418.113 (November 5, 2019) | 418.113 (November 5, 2019) | 418.113 (November 5, 2019) |
| 390.144 (July 20, 2021) | 390.144 (July 20, 2021) | 390.144 (July 20, 2021) | 390.144 (July 20, 2021) |
| 340.108 (December 23, 2019) | 340.108 (December 23, 2019) | 340.108 (December 23, 2019) | 340.108 (December 23, 2019) |
Note 418.113 and 435.21 users: These are not official NVIDIA LEGACY drivers, but there is example GeForce GTX 1650 Mobile card which is not supported by older or newer drivers. (Download inttf NVIDIA patcher and patch NVIDIA-Linux-x86_64-418.113 and NVIDIA-Linux-x86_64-435.21 for Kernel 5.13+ / 5.12+ / 5.11+ / 5.10+)
Note Older Fedora users: If you have any problems with GDM (black screen). You can easily switch Display Manager example to LXDM, LightDM, SDDM or KDM.
2.2 Make NVIDIA installer executable
2.3 Change root user
2.4 Make sure that you system is up-to-date and you are running latest kernel
After update reboot your system and boot using latest kernel:
2.5 Install needed dependencies
2.6 Disable nouveau
2.6.1 Create or edit /etc/modprobe.d/blacklist.conf
Append ‘blacklist nouveau’
2.6.2 Edit /etc/default/grub
Append ‘rd.driver.blacklist=nouveau’ to end of ‘GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX=”…”‘.
2.6.3 Update grub2 conf
Fedora 34
Fedora 33/32/31/30
2.6.4 Remove xorg-x11-drv-nouveau
2.6.5 Generate initramfs
2.7 Reboot to runlevel 3
Note: You don’t have Desktop/GUI on runlevel 3. Make sure that you have some access to end of guide. (Open it on mobile browser, Print it, use lynx/links/w3m, save it to text file).
OR alternatively you can change the runlevel on GRUB2 adding one additional parameter. Quick guide howto change runlevel on GRUB2. If you use this method, then don’t set multi-user.target and don’t set graphical.target on step 2.9 (just reboot).
2.8 Install NVIDIA proprietary drivers for GeForce 6/7 & GeForce 8/9/200/300 & GeForce 400/500/600/700/800/900/10/20 series cards
2.8.1 Log in as root user
Or alternatively change root user (you shouldn’t have nouveau and xorg loaded)
2.8.2 Run NVIDIA Binary
Following command executes driver install routine. Use full file name command if you have multiple binaries on same directory.
2.8.3 NVIDIA Installer Register the Kernel Source Modules with DKMS
2.8.4 NVIDIA Installer 32-bit Compatibility Libraries
2.8.5 NVIDIA Installer Installing Drivers and Building kernel module
Note: If you get libglvnd error, then abort installation and try this. Also “Install and overwrite existing files” works, but fixing this error is more clean way to install NVIDIA Drivers.
2.8.6 NVIDIA Installer Automatic Xorg Config and Backup
2.8.7 NVIDIA Drivers Installation Complete
2.9 All Is Done and Then Reboot Back to Runlevel 5
2.10 VDPAU/VAAPI support
To enable video acceleration support for your player (Note: you need Geforce 8 or later).
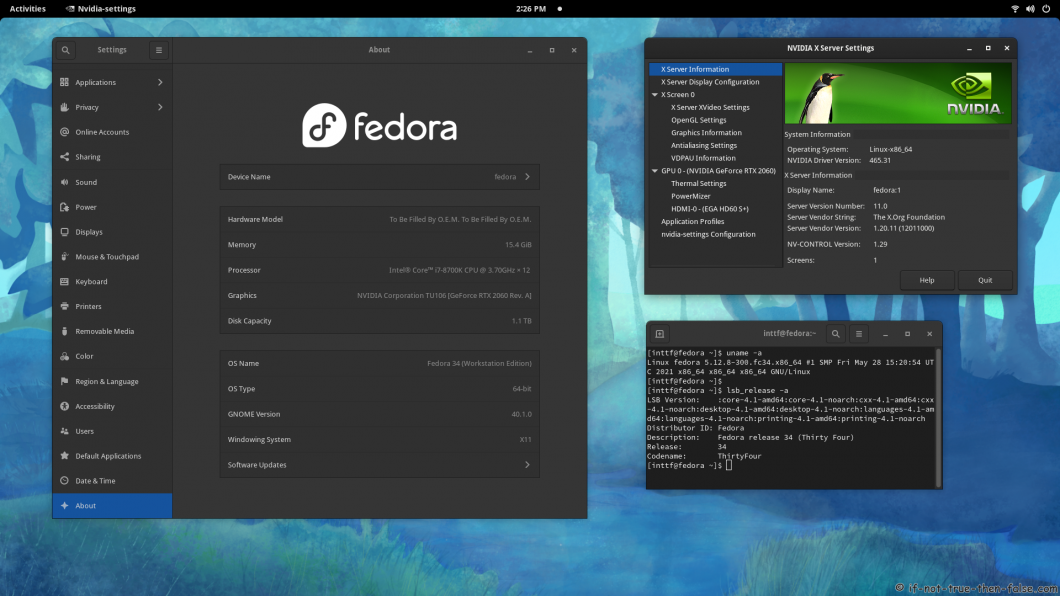
3. Some Screenshots Using Different Cards and Drivers
3.1 NVIDIA 465.31 drivers on Fedora 34 Gnome 40 with Kernel 5.12.8
3.2 VIDIA 460.80 drivers on Fedora 34 Gnome 40 with Kernel 5.12.8
3.3 NVIDIA 450.119.03 drivers on Fedora 34 Gnome 40 with Kernel 5.12.8
3.4 NVIDIA 435.21 drivers on Fedora 34 Gnome 40 with Kernel 5.12.8
3.5 NVIDIA 418.113 drivers on Fedora 34 Gnome 40 with Kernel 5.12.8
3.6 NVIDIA 390.143 drivers on Fedora 34 Gnome 40 with Kernel 5.12.8
3.6 NVIDIA 340.108 drivers on Fedora 34 Gnome 40 with Kernel 5.12.8
Let me know, if you have problems?
Or if you succeed, you could post output of following commands:
Источник
How to Set Nvidia as Primary GPU on Optimus-based Laptops
This page discusses third-party software sources not officially affiliated with or endorsed by the Fedora Project. Use them at your own discretion. Fedora recommends the use of free and open source software and avoidance of software encumbered by patents.
Introduction
The objective is to enable NVIDIA GPU of an Optimus-based laptop all the time and use it for every single activity. Please do not use this guide if you want to render your desktop using the integrated GPU and specifically select applications to be rendered using the NVIDIA GPU.
The steps listed here have been verified to be working on Fedora 32 Workstation. Please update your installation to include your experiences and any other tweaks that may be needed if you are using any other desktop environments.
Some guides on the internet advise a different approach to installing nVidia drivers on Fedora, such as directly using the binaries provided by nVidia. The Fedora Project cannot ensure these will always work on every Fedora release, and we therefore recommend following the steps in this document instead.
As Prime works less satisfactorily with Wayland server, following the steps provided in this guide would default the server to Xorg.
This guide requires the secure boot to be turned off to load up the unsigned NVIDIA kernel modules.
In order to make all the rendering default to the NVIDIA GPU, you need the follow the steps very carefully.
First, you need to see if you really want to achieve this.
Why would you want to do that?
The use of NVIDIA GPU all the time would allow for smoother transitions and richer animation effects. Premium desktop environments like GNOME would benefit a lot from this.
Enabling the NVIDIA GPU all the time would lead to lower CPU load and memory consumption which otherwise would have been high due to added in-memory video buffer.
Why would you not want to do that?
With the NVIDIA GPU used all the time, there would be a slight increase in battery consumption which should not be a concern if your device is used while being plugged in.
Increased generation of heat from the all-the-time enabled NVIDIA GPU can be worrisome. You would not want to play AAA-titles on Proton while placing your laptop on your lap.
Источник