- How to increase the ulimit and file descriptors limit in linux.
- How to increase the ulimit and file descriptors limit in linux.
- Linux file descriptor limit
- To Increase the File Descriptor Limit (Linux)
- Linux Increase The Maximum Number Of Open Files / File Descriptors (FD)
- Command To List Number Of Open File Descriptors
- System-wide File Descriptors (FD) Limits
- The Number Of Maximum Files Was Reached, How Do I Fix This Problem?
- User Level FD Limits
- A note about RHEL/CentOS/Fedora/Scientific Linux users
- How to set ulimit and file descriptors limit on Linux Servers
- To see what is the present open file limit in any Linux System
- ulimit command :
- How to fix the problem when limit on number of Maximum Files was reached ?
- Set User level resource limit via limit.conf file
- Linux file descriptor limit
- To Increase the File Descriptor Limit (Linux)
How to increase the ulimit and file descriptors limit in linux.
What is the swappiness value in Linux and how to modify it?
Track file changes using auditd
How to increase the ulimit and file descriptors limit in linux.
If you get the error “too many open files” , please check below steps :
The file-max is the maximum File Descriptors (FD). It is a kernel setting enforced at the system level. The ulimit is enforced at the user level. It should be configured to be less than file-max.
The default settings are very low , for high performance servers it should be increased. The default settings assume that the several user share the same system and limit is sufficient.
To change the file descriptor setting, edit the kernel parameter file /etc/sysctl.conf. Add line fs.file-max=[new value] to it.
for eg. # vi /etc/sysctl.conf and enter fs.file-max = 400000
To apply the changes :
#sysctl -p
To change the ulimit setting, edit the file /etc/security/limits.conf and set the hard and soft limits in it :
for eg. # vi /etc/security/limits.conf
* soft nofile 40000
* hard nofile 40000
After changed reboot the server.
# reboot
Now,test system settings using the below commands:
To check the current open file descriptor limit:
# more /proc/sys/fs/file-max
OR sysctl -a | grep fs.file-max
To find out how many file descriptors are currently being used:
To find out how many files are currently open:
Источник
Linux file descriptor limit
To ensure good server performance, the total number of client connections, database files, and log files must not exceed the maximum file descriptor limit on the operating system (ulimit -n). By default, the directory server allows an unlimited number of connections but is restricted by the file descriptor limit on the operating system. Linux systems limit the number of file descriptors that any one process may open to 1024 per process. (This condition is not a problem on Solaris machines, x86, x64, or SPARC).
After the directory server has exceeded the file descriptor limit of 1024 per process, any new process and worker threads will be blocked. For example, if the directory server attempts to open a Oracle ® Berkeley JE database file when the operating system has exceeded the file descriptor limit, the directory server will no longer be able to open a connection that can lead to a corrupted database exception. Likewise, if you have a directory server that exceeds the file descriptor limit set by the operating system, the directory server can become unresponsive as the LDAP connection handler consumes all of the CPU’s processing in attempting to open a new connection.
To fix this condition, set the maximum file descriptor limit per process on Linux machines.
To Increase the File Descriptor Limit (Linux)
- Display the current hard limit of your machine.
The hard limit is the maximum server limit that can be set without tuning the kernel parameters in proc file system.
The system file limit is set in /proc/sys/fs/file-max .
Источник
Linux Increase The Maximum Number Of Open Files / File Descriptors (FD)
H ow do I increase the maximum number of open files under CentOS Linux? How do I open more file descriptors under Linux?
The ulimit command provides control over the resources available to the shell and/or to processes started by it, on systems that allow such control. The maximum number of open file descriptors displayed with following command (login as the root user).
Command To List Number Of Open File Descriptors
Use the following command command to display maximum number of open file descriptors:
cat /proc/sys/fs/file-max
Output:
75000 files normal user can have open in single login session. To see the hard and soft values, issue the command as follows:
# ulimit -Hn
# ulimit -Sn
To see the hard and soft values for httpd or oracle user, issue the command as follows:
# su — username
In this example, su to oracle user, enter:
# su — oracle
$ ulimit -Hn
$ ulimit -Sn
System-wide File Descriptors (FD) Limits
The number of concurrently open file descriptors throughout the system can be changed via /etc/sysctl.conf file under Linux operating systems.
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
The Number Of Maximum Files Was Reached, How Do I Fix This Problem?
Many application such as Oracle database or Apache web server needs this range quite higher. So you can increase the maximum number of open files by setting a new value in kernel variable /proc/sys/fs/file-max as follows (login as the root):
# sysctl -w fs.file-max=100000
Above command forces the limit to 100000 files. You need to edit /etc/sysctl.conf file and put following line so that after reboot the setting will remain as it is:
# vi /etc/sysctl.conf
Append a config directive as follows:
fs.file-max = 100000
Save and close the file. Users need to log out and log back in again to changes take effect or just type the following command:
# sysctl -p
Verify your settings with command:
# cat /proc/sys/fs/file-max
OR
# sysctl fs.file-max
User Level FD Limits
The above procedure sets system-wide file descriptors (FD) limits. However, you can limit httpd (or any other users) user to specific limits by editing /etc/security/limits.conf file, enter:
# vi /etc/security/limits.conf
Set httpd user soft and hard limits as follows:
httpd soft nofile 4096
httpd hard nofile 10240
Save and close the file. To see limits, enter:
# su — httpd
$ ulimit -Hn
$ ulimit -Sn
A note about RHEL/CentOS/Fedora/Scientific Linux users
Edit /etc/pam.d/login file and add/modify the following line (make sure you get pam_limts.so):
Save and close the file.
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
Источник
How to set ulimit and file descriptors limit on Linux Servers
Introduction: Challenges like number of open files in any of the production environment has become common now a day. Since many applications which are Java based and Apache based, are getting installed and configured, which may lead to too many open files, file descriptors etc. If this exceeds the default limit that is set, then one may face access control problems and file opening challenges. Many production environments come to standstill kind of situations because of this.
Luckily, we have “ulimit” command in any of the Linux based server, by which one can see/set/get number of files open status/configuration details. This command is equipped with many options and with this combination one can set number of open files. Following are step-by-step commands with examples explained in detail.
To see what is the present open file limit in any Linux System
To get open file limit on any Linux server, execute the following command,
The above number shows that user can open ‘146013’ file per user login session.
This clearly indicates that individual Linux operating systems have different number of open files. This is based on dependencies and applications which are running in respective systems.
ulimit command :
As the name suggests, ulimit (user limit) is used to display and set resources limit for logged in user.When we run ulimit command with -a option then it will print all resources’ limit for the logged in user. Now let’s run “ulimit -a” on Ubuntu / Debian and CentOS systems,
Ubuntu / Debian System,
CentOS System
As we can be seen here different OS have different limits set. All these limits can be configured/changed using “ulimit” command.
To display the individual resource limit then pass the individual parameter in ulimit command, some of parameters are listed below:
- ulimit -n –> It will display number of open files limit
- ulimit -c –> It display the size of core file
- umilit -u –> It will display the maximum user process limit for the logged in user.
- ulimit -f –> It will display the maximum file size that the user can have.
- umilit -m –> It will display the maximum memory size for logged in user.
- ulimit -v –> It will display the maximum memory size limit
Use below commands check hard and soft limits for number of open file for the logged in user
How to fix the problem when limit on number of Maximum Files was reached ?
Let’s assume our Linux server has reached the limit of maximum number of open files and want to extend that limit system wide, for example we want to set 100000 as limit of number of open files.
Use sysctl command to pass fs.file-max parameter to kernel on the fly, execute beneath command as root user,
Above changes will be active until the next reboot, so to make these changes persistent across the reboot, edit the file /etc/sysctl.conf and add same parameter,
save and exit file,
Run the beneath command to make above changes into effect immediately without logout and reboot.
Now verify whether new changes are in effect or not.
Use below command to find out how many file descriptors are currently being utilized:
Note:- Command “sysctl -p” is used to commit the changes without reboot and logout.
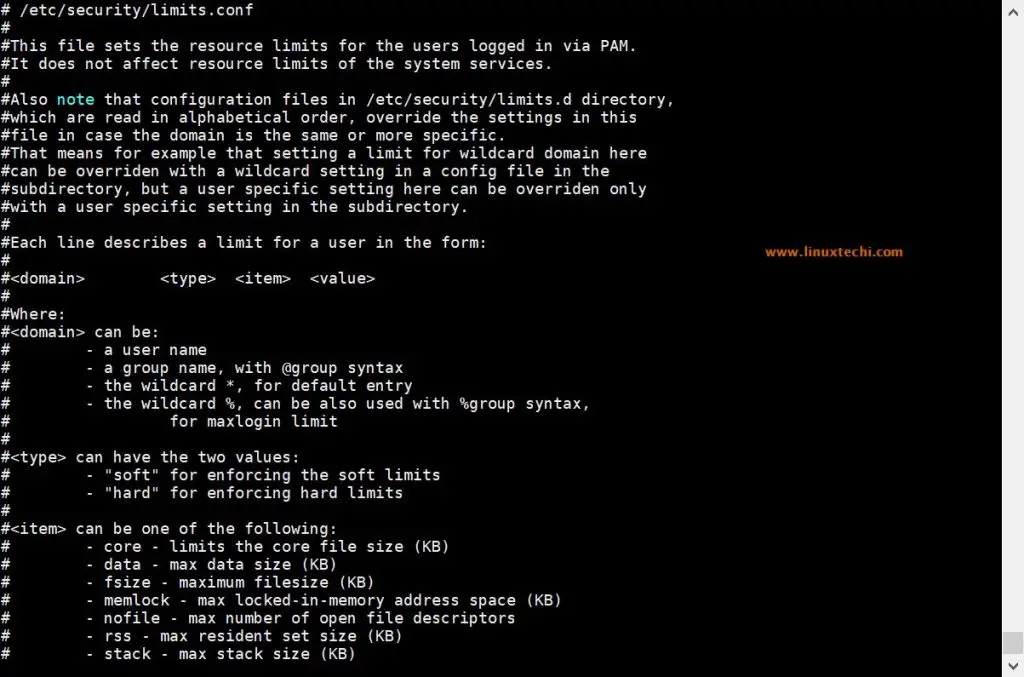
Set User level resource limit via limit.conf file
“/etc/sysctl.conf” file is used to set resource limit system wide but if you want to set resource limit for specific user like Oracle, MariaDB and Apache then this can be achieved via “/etc/security/limits.conf” file.
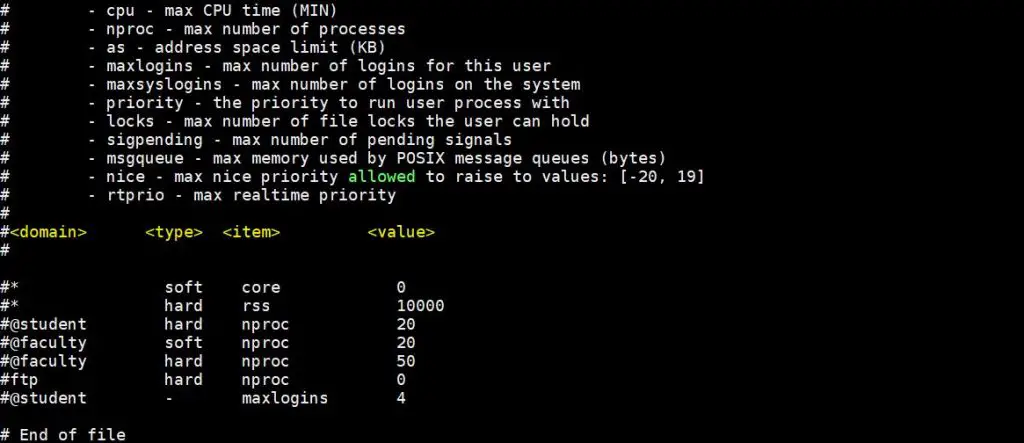
Sample Limit.conf is shown below,
Let’s assume we want to set hard and soft limit on number of open files for linuxtechi user and for oracle user set hard and soft limit on number of open process, edit the file “/etc/security/limits.conf” and add the following lines
Save & exit the file.
Note: In case you want to put resource limit on a group instead of users, then it can also be possible via limit.conf file, in place of user name , type @ and rest of the items will be same, example is shown below,
Verify whether new changes are in effect or not,
Note: Other majorly used command is “ lsof ” which is used for finding out “how many files are opened currently”. This command is very helpful for admins.
Conclusion:
As mentioned in the introduction section “ulimit” command is very powerful and helps one to configure and make sure application installations are smoother without any bottlenecks. This command helps in fixing many of the number of file limitations in Linux based servers.
Источник
Linux file descriptor limit
To ensure good server performance, the total number of client connections, database files, and log files must not exceed the maximum file descriptor limit on the operating system (ulimit -n). By default, the directory server allows an unlimited number of connections but is restricted by the file descriptor limit on the operating system. Linux systems limit the number of file descriptors that any one process may open to 1024 per process. (This condition is not a problem on Solaris machines, x86, x64, or SPARC).
After the directory server has exceeded the file descriptor limit of 1024 per process, any new process and worker threads will be blocked. For example, if the directory server attempts to open a Oracle ® Berkeley JE database file when the operating system has exceeded the file descriptor limit, the directory server will no longer be able to open a connection that can lead to a corrupted database exception. Likewise, if you have a directory server that exceeds the file descriptor limit set by the operating system, the directory server can become unresponsive as the LDAP connection handler consumes all of the CPU’s processing in attempting to open a new connection.
To fix this condition, set the maximum file descriptor limit per process on Linux machines.
To Increase the File Descriptor Limit (Linux)
- Display the current hard limit of your machine.
The hard limit is the maximum server limit that can be set without tuning the kernel parameters in proc file system.
The system file limit is set in /proc/sys/fs/file-max .
Источник