- Ubuntu Documentation
- Introduction to File systems
- Journaling
- Table
- Файловые системы в Linux
- 7 Ways to Determine the File System Type in Linux (Ext2, Ext3 or Ext4)
- 1. Using df Command
- 2. Using fsck Command
- 3. Using lsblk Command
- 4. Using mount Command
- 5. Using blkid Command
- 6. Using file Command
- 7. Using fstab File
- If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
- What is Linux File System? Easy Guide
- What is Linux File System?
- What are the Linux File System Types?
- What file system does my system use?
- What is Top Level in Linux?
- What Are the Linux File System Directories?
- /bin – essential utilities
- /boot – Boot for a Boot
- /dev – Devices or Files
- /etc – Configuration files
- /home – Home Folder Containment
- /lib – Libraries for Programs
- /media – Mounted Media
- /mnt – Temporary Mounts
- /opt – Optional Packages
- /proc – Kernel and Process Pseudo Files
- /root – Root User Directory
- /sbin – System Administration Programs
- /tmp – Temporary Files
- /usr – User Shared Read-Only Data
- /var – Variable Data
Ubuntu Documentation
Introduction to File systems
File systems are one of the things any newcomer to linux must become acquainted with. In the world of Microsoft you never really have to worry about it, the default being NTFS. Linux however, being built on a world of open source and differing opinions, is not limited in this way and so the user should have an understanding of what a file system is, and how it affects the computer.
At the core of a computer, it’s all 1s and 0s, but the organization of that data is not quite as simple. A bit is a 1 or a 0, a byte is composed of 8 bits, a kibibyte is 1024 (i.e. 2^10) bytes, a mebibyte is 1024 kibibytes and so on and so forth. All these bits and bytes are permanently stored on a Hard Drive. A hard drive stores all your data, any time you save a file, you’re writing thousands of 1s and 0s to a metallic disc, changing the magnetic properties that can later be read as 1 or 0. There is so much data on a hard drive that there has to be some way to organize it, like a library of books and the old card drawers that indexed all of them, without that index, we’d be lost. Libraries, for the most part, use the Dewey Decimal System to organize their books, but there exist other systems to do so, none of which have attained the same fame as Mr. Dewey’s invention. File systems are the same way. The ones most users are aware of are the ones Windows uses, the vFat or the NTFS systems, these are the Windows default file systems.
There are several different attributes which are necessary in defining file systems, these include their max file size, max partition size, whether they journal or not.
Journaling
A journaling file system is more reliable when it comes to data storage. Journaling file systems do not necessarily prevent corruption, but they do prevent inconsistency and are much faster at file system checks than non-journaled file systems. If a power failure happens while you are saving a file, the save will not complete and you end up with corrupted data and an inconsistent file system. Instead of actually writing directly to the part of the disk where the file is stored, a journaling file system first writes it to another part of the hard drive and notes the necessary changes to a log, then in the background it goes through each entry to the journal and begins to complete the task, and when the task is complete, it checks it off on the list. Thus the file system is always in a consistent state (the file got saved, the journal reports it as not completely saved, or the journal is inconsistent (but can be rebuilt from the file system)). Some journaling file systems can prevent corruption as well by writing data twice.
Table
Now below is a very brief comparison of the most common file systems in use with the Linux world.
Источник
Файловые системы в Linux
XFS — начало разработки 1993 год, фирма Silicon Graphics, в мае 2000 года предстала в GNU GPL, для пользователей большинства Linux систем стала доступна в 2001-2002 гг. Отличительная черта системы — прекрасная поддержка больших файлов и файловых томов, 8 эксбибайт — 1 байт (8*2 60 -1 байт) для 64-х битных систем. Ко всему прочему обладает другими немаловажными особенностями — непрерывные области дискового пространства, задержка выделения пространства и онлайн дефрагментация. Является одной из старейших журналируемых файловых систем для *nix, и содержит в себе наиболее отлаженный, в этом контексте, исходный код.
ReiserFS (Reiser3) — одна из первых журналируемых файловых систем под Linux, разработана Namesys. Имеет некоторые врождённые головные боли, но в целом неплохая система, ведущая отсчёт дней своих с 2001 года. Оговорюсь, что смысл журналируемых систем заключается в дисковых транзакциях, которые последовательно пишутся в специальную зону диска (журнал, он же лог), перед тем как данные попадают в конечные точки файловой системы. Максимальный объём тома для этой системы равен 16 тебибайт (16*2 40 байт).
JFS (Journaled File System) — файловая система, детище IBM, явившееся миру в далёком 1990 году для ОС AIX (Advanced Interactive eXecutive). В виде первого стабильного релиза, для пользователей Linux, система стала доступна в 2001 году. Из плюсов системы — неплохая масштабируемость. Из минусов — не особо активная поддержка на протяжении всего жизненного цикла. Максимальный рамер тома 32 пэбибайта (32*2 50 байт).
ext (extended filesystem) — появилась в апреле 1992 года, это была первая файловая система, изготовленная специально под нужды Linux ОС. Разработана Remy Card с целью преодолеть ограничения файловой системы Minix.
ext2 (second extended file system) — была разработана Remy Card в 1993 году. Не журналируемая файловая система, это был основной её недостаток, который исправит ext3.
ext3 (third extended filesystem) — по сути расширение исконной для Linux ext2, способное к журналированию. Разработана Стивеном Твиди (Stephen Tweedie) в 1999 году, включена в основное ядро Linux в ноябре 2001 года. На фоне других своих сослуживцев обладает более скромным размером пространства, до 4 тебибайт (4*2 40 байт) для 32-х разрядных систем. На данный момент является наиболее стабильной и поддерживаемой файловой системой в среде Linux.
Reiser4 — первая попытка создать файловую систему нового поколения для Linux. Впервые представленная в 2004 году, система включает в себя такие передовые технологии как транзакции, задержка выделения пространства, а так же встроенная возможность кодирования и сжатия данных. Ханс Рейзер (Hans Reiser), главный разработчик системы, рекламировал использовать своё детище непосредственно как БД с улучшенными метаданными. После того, как Ханс Рейзер был осуждён за убийство в 2008 году, дальнейшая судьба системы стала сомнительной.
ext4 — попытка создать 64-х битную ext3 способную поддерживать больший размер файловой системы (1 эксбибайт). Позже добавились возможности — непрерывные области дискового пространства, задержка выделения пространства, онлайн дефрагментация и прочие. Обеспечивается прямая совместимость с системой ext3 и ограниченная обратная совместимость при недоступной способности к непрерывным областям дискового пространства.
UPD: Btrfs (B-tree FS или Butter FS) — проект изначально начатый компанией Oracle, впоследствии поддержанный большинством Linux систем. Многие считаеют систему эдаким ответом на ZFS. Ключевыми особенностями данной файловой системы являются технологии: copy-on-write, позволяющая сделать снимки областей диска (снапшоты), которые могут пригодится для последующего восстановления; контроль за целостностью данных и метаданных (с повышенной гарантией целостности); сжатие данных; оптимизированный режим для накопителей SSD (задаётся при монтировании) и прочие. Немаловажным фактором является возможность перехода с ext3 на Btrfs. С августа 2008 года данная система выпускается под GNU GPL.
Tux2 — известная, но так и не анонсированная публично файловая система. Создатель Дэниэл Филипс (Daniel Phillips), система базируется на алгоритме «Фазового Дерева», который как и журналирование защищает файловую систему от сбоев. Организована как надстройка на ext2.
Tux3 — наступая на пятки Btrfs, представлена новая файловая система. Система создана на основе FUSE (Filesystem in Userspace), специального модуля для создания файловых систем на *nix платформах. Данный проект ставит перед собой цель избавиться от привычного журналирования, взамен предлагая версионное восстановление (состояние в определённый промежуток времени). Преимуществом используемой в данном случае версионной системы, является способ описания изменений, где для каждого файла создаётся изменённая копия, а не переписывается текущая версия. Такой подход позволяет более гибко управлять версиями.
UPD: Xiafs — задумка и разработка данной файловой системы принадлежат Frank Xia, основана на файловой системе MINIX. В настоящее время считается устаревшей и практически не используется. Наряду с ext2 разрабатывалась, как замена системе ext. В декабре 1993 года система была добавлена в стандартное ядро Linux. И хотя система обладала большей стабильностью и занимала меньше дискового пространства под контрольные структуры — она оказалась слабее ext2, ведущую роль сыграли ограничения максимальных размеров файла и раздела, а так же способность к дальнейшему расширению.
UPD: ZFS (Zettabyte File System) — изначально созданная в Sun Microsystems файловая система, для небезызвестной операционной системы Solaris в 2005 году. Отличительные особенности — отсутствие фрагментации данных как таковой, возможности по управлению снапшотами (snapshots), пулами хранения (storage pools), варьируемый размер блоков, 64-х разрядный механизм контрольных сумм, а так же способность адресовать 128 бит информации! В Linux системах может использоваться посредствам FUSE.
Источник
7 Ways to Determine the File System Type in Linux (Ext2, Ext3 or Ext4)
A file system is the way in which files are named, stored, retrieved as well as updated on a storage disk or partition; the way files are organized on the disk.
A file system is divided in two segments called: User Data and Metadata (file name, time it was created, modified time, it’s size and location in the directory hierarchy etc).
In this guide, we will explain seven ways to identify your Linux file system type such as Ext2, Ext3, Ext4, BtrFS, GlusterFS plus many more.
1. Using df Command
df command reports file system disk space usage, to include the file system type on a particular disk partition, use the -T flag as below:

For a comprehensive guide for df command usage go through our articles:
2. Using fsck Command
fsck is used to check and optionally repair Linux file systems, it can also print the file system type on specified disk partitions.
The flag -N disables checking of file system for errors, it just shows what would be done (but all we need is the file system type):

3. Using lsblk Command
lsblk displays block devices, when used with the -f option, it prints file system type on partitions as well:

4. Using mount Command
mount command is used to mount a file system in Linux, it can also be used to mount an ISO image, mount remote Linux filesystem and so much more.
When run without any arguments, it prints info about disk partitions including the file system type as below:

5. Using blkid Command
blkid command is used to find or print block device properties, simply specify the disk partition as an argument like so:

6. Using file Command
file command identifies file type, the -s flag enables reading of block or character files and -L enables following of symlinks:

7. Using fstab File
The /etc/fstab is a static file system info (such as mount point, file system type, mount options etc) file:

That’s it! In this guide, we explained seven ways to identify your Linux file system type. Do you know of any method not mentioned here? Share it with us in the comments.
If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
TecMint is the fastest growing and most trusted community site for any kind of Linux Articles, Guides and Books on the web. Millions of people visit TecMint! to search or browse the thousands of published articles available FREELY to all.
If you like what you are reading, please consider buying us a coffee ( or 2 ) as a token of appreciation.
We are thankful for your never ending support.
Источник
What is Linux File System? Easy Guide
You may already know a little bit about Linux, but you may not know exactly how your data is being handled under the hood. Because if you’re like a lot of other Linux users, you just take for granted these sorts of things.
But your Linux file system isn’t so carefree, so, today that’s exactly what we will be talking about – the Linux File System.
Table of Contents
What is Linux File System?
Linux file system is the collection of data and/or files stored in a computer’s hard disk or storage, your computer relies on this file system to ascertain the location and positioning of files in your storage, were it not there, the files would act as if they are invisible, obviously causing many problems.
There are actually many different file systems that exist for Linux, if you’re wondering which one you should use, we will provide a comprehensive list of the file systems that are supported by Linux.
What are the Linux File System Types?
Upon installation, Linux offers various file systems like the ones below that you can select from:
- Ext
- Ext2
- Ext3
- Ext4
- JFS
- XFS
- btrfs
- swap
We’ll delve into each one of these Linux File Systems and give a brief description.
Ext: “ext” is an acronym that stands for “extended file system” and was created in 1992 and is the very first file system designed specifically for Linux.
Its functionality was designed partly based on the UNIX file system. The purpose of its creation originally was to innovate beyond the file system used before it (the MINIX file system) and overcome its limitations.
As this file system is about 30 years old at the time this article was written, many Linux distros no longer support it, so it is not really used anymore.
Ext2: also referred to as “second extended system”. Created in 1993, ext2 was designed to be the successor of the original extension system for Linux.
It innovated in areas such as storage capacity, and general performance. This file system notably allows for up to 2 TB of data. Like ext, this file system is very old, so it really should just be avoided.
Ext3: ext3, or third extended system, created in 2001, surpasses ext2 in that it is a journaling file system. A journaling file system is a system that records in a separate log changes and updates to files and data before such actions have been completed.
This means that if for some reason, the computer or hard disk(s) crash or experience some kind of power failure, this separate log containing the changes made before the crash can be used to access that stored data, thus repairing and restoring the files upon reboot.
Nowadays, there are so many better options to choose from that there’s hardly any reason to use this extended file system anymore either.
Ext4: ext4, standing for “fourth extended system”, was created in 2006. Because this file system overcomes numerous limitations that the third extended system had, it is both widely used, and the default file system that most Linux distros use.
While it may not be the most cutting edge, it is absolutely reliable and stable – which is really valuable in Linux.
Thus, if you aren’t particularly keen on racking your brain between the different pros and cons of all the many file systems you can choose from, we definitely recommend you just go with this one.
JFS: The file system JFS was created by IBM in 1990 and the name JFS is an acronym standing for Journaling File System, as we’ve already covered this concept with the number 3 file system in this article, you should already be quite familiar with what exactly this means.
It’s easy to recover data after a power failure and quite reliable. What’s more is it uses less CPU power than the other file systems.
XFS: xfs, an acronym that stands for “Extent File System”, was created by Silicon Graphics and originally made for their OS “IRIX”, but was later given to Linux.
Created in 1990, XFS is a 64-bit high performance journaling file system. It’s particularly noteworthy for how incredibly well it works with very large files. Though contrarily, not especially the
best with smaller files.
Btrfs: btrfs, which is yet another acronym standing for B Tree File System, created by Oracle in 2009. It is regarded as a rival file system to ext4, though it’s consensus that overall ext4 is the better file system, as it transfers data faster and offers more stability but although this is the case, that does not mean btrfs isn’t worth looking into.
There are a couple things that are unique and advantageous about btrfs. And in general it has excellent performance.
If you couldn’t tell already from the comparisons made in our list, ext4 is and is regarded as the best Linux File System.
What file system does my system use?
If you’re wondering which file system your distro has by default or simply just which one you have currently, you can define that for yourself using some pretty nifty commands in your terminal.
There are multiple ways that you can do this, but we’ll show you the easiest one down below:
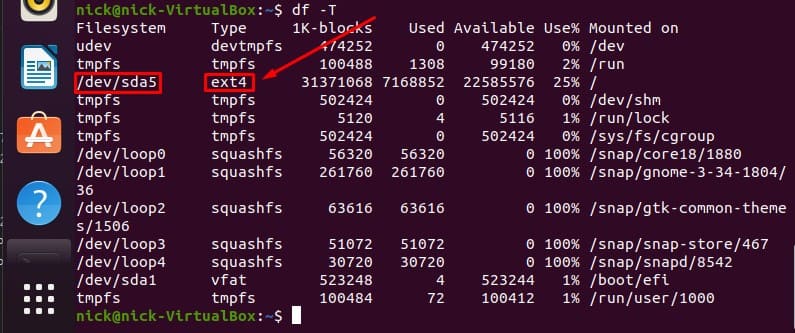
Short for “disk free”, df is a command used to display the free disk space in Linux and other similar operating systems. It is also used to understand and ascertain the file systems that are mounted.
Now, you may have noticed that I mentioned that this command can be used to define the file system mounted, but when you run the “df” command yourself, there is no mention of any types of file systems. (shown below)
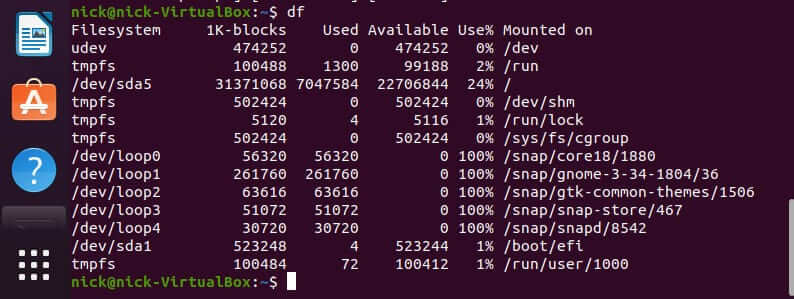
Well, that is where this interesting little option comes in: open your terminal and execute this command:
This is a variation of the df command. It will display the file system type along with other currently irrelevant information. (shown below)
As you can see, in the second column under “Type” the file system type is defined. You should now be able to ascertain which file system you currently have mounted on your Linux distro.
What is Top Level in Linux?
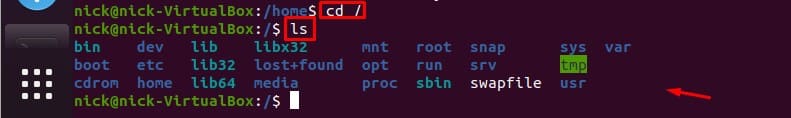
/ is the top level directory of a Linux system. The name “top level” means the “root”, thus it is the root directory of the system. Though it is separate from “/root directory”, so you shouldn’t confuse the two.
All other directories stem from this top level directory like a pyramid. This concept is not unique to Linux, as the same thing can be observed in other Operating Systems such as a very interesting one you may have heard of called Windows. Windows has partitions such as C: and D:.
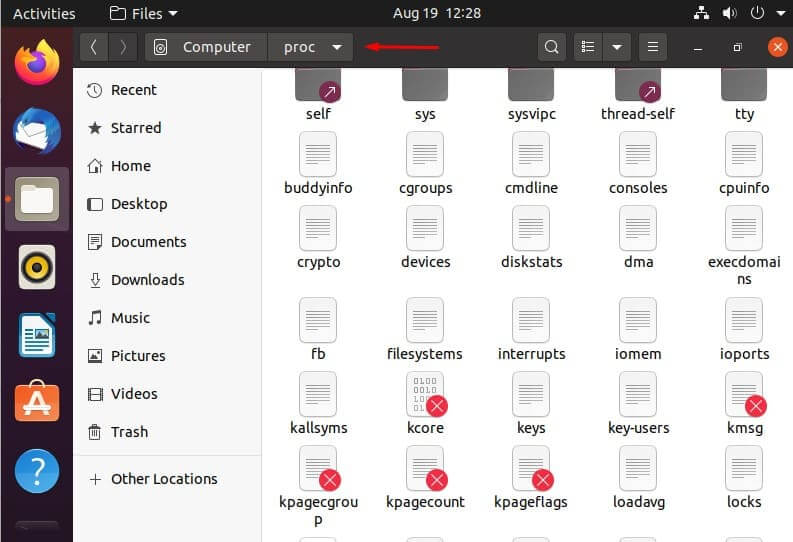
In Linux, these directories in the so-called “pyramid” exist in a hierarchy with a specific structure. This can be observed in your terminal by using the command:
, and then displaying the directories and files while in the top level directory. (shown below)
Most distros have the same structure, and the differences between some of them being only minuscule. Now that you know what the top level directory is, let’s take a comprehensive dive into what the rest of these directories are and what you can do with them.
What Are the Linux File System Directories?
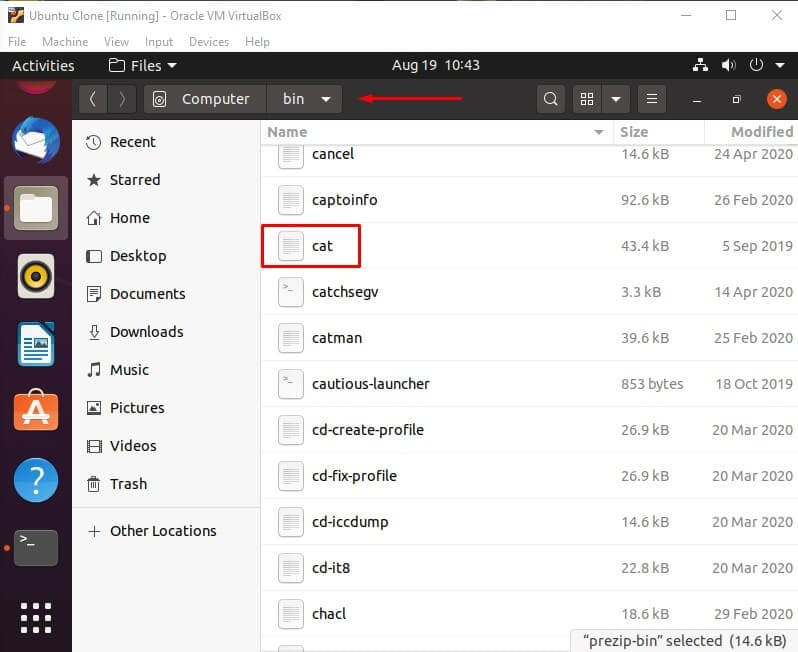
/bin – essential utilities
The directory contains the core system programs and important utilities. For example, commonly used and well known commands such as “cat” are located in “/bin”.
The reason for this is that if these utilities are not stored in this directory, there is no certainty that the system will have access to them if there isn’t a file system mounted.
There is the directory /sbin that is very similar to /bin, as it contains core system administration binaries (programs).
/boot – Boot for a Boot
Contains files that are required in order for the system to be booted. For example, BIOS, which stands for Basic Input/Output System.
The BIOS is responsible for executing the Master Boot Record (MBR) boot loader.
It checks the integrity of the hard disk(s) of the system before launching the MBR. /boot also contains Linux kernels and many other files in addition to BIOS.
Though, these files’ configuration files are not stored in /boot, rather they are stored in /etc, along with the many other various config files.
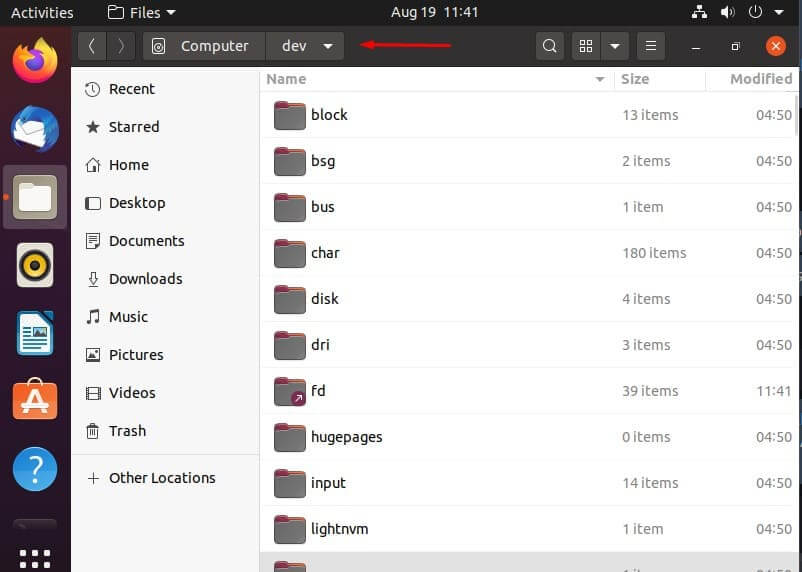
/dev – Devices or Files
Linux displays connected devices as files and the /dev directory contains these files. Though, the thing is, as you can see by the title, these are not “actual” files, they just appear as files. /dev is also where physical drives can be mounted.
/etc – Configuration files
As we discussed before, the configuration files of BIOS and other similar files can be found in /etc. You can edit these configuration files in a text editor as you see fit.
Basically, every single kind of configuration file is located in /etc, including but not limited to system configuration files.
/home – Home Folder Containment
There’s a home folder for every user on your system and each one is contained together in the /home directory. These folders are created using the name of your user name.
For example, your user name is joe, so your home folder would be located in /home/joe.
These home folders contain your user data files and configuration files that are specific to the user, which is also the one of the only types of configuration files that are stored elsewhere besides /etc as we explained above.
If one wants to modify other files on a system, they must become the root user, as each user only has write permissions for their own home folder.
/lib – Libraries for Programs
Each program or binary uses specific libraries to function and the /lib directory is where these libraries can be located.
/media – Mounted Media
Contains subdirectories where your physical media devices are mounted. For example, a CD, if inserted into your system, you can access its contents through its directory that is created in the /media directory upon insertion.
/mnt – Temporary Mounts
This directory is used for mounting temporary file systems. If you are using a file system for a very specific purpose and for a relatively brief period of time, you would probably mount it in /mnt. Though you can mount it anywhere on the system if you so chose.
/opt – Optional Packages
The /opt directory contains a set of subdirectories where optional software packages are located and managed by the package manager.
/proc – Kernel and Process Pseudo Files
The /proc directory is another interesting case of a directory that contains these “fake” files, very similarly to the /dev directory that we discussed earlier in this list. These files are special files that are actually, and interestingly, system and process information.
/root – Root User Directory
As we’ve discussed before, every user has his own home directory. This is the home directory of the root user. The root user’s home directory is located at /root.
Which is noteworthy because it is, unlike the rest of the users’ home directories, not located in /home. Like we’ve said above, in an earlier section of this article, /root is different from the root directory “/”, and this fact should be committed to memory if possible.
/sbin – System Administration Programs
The /sbin directory is similar to the /bin directory in that it contains essential programs. But it differs with the addition that it is intended to be used by the root user.
/tmp – Temporary Files
The /tmp directory is used to store temporary files that are deleted when the system is restarted. Utilities such as tmpwatch can be used to delete these temporary files in the /tmp directory.
/usr – User Shared Read-Only Data
The /usr directory is used to contain applications and files that are used and shared by and between users.
/var – Variable Data
The /var directory is used like the /usr directory, only instead of being read-only, it is writable. This directory contains system logs and other various variable data.
And with that, we conclude this topic. You should now have a pretty solid idea about what a Linux File System is and how to use it. Hope you learned something and thanks for reading!
Источник