- Поиск больших файлов и директорий в Linux
- Поиск больших файлов командой find
- Простой поиск
- Вывод подробной информации
- Поиск больших файлов и директорий командой du
- How to Find Out Top Directories and Files (Disk Space) in Linux
- How to Find Biggest Files and Directories in Linux
- Find Largest Directories in Linux
- Find Out Top File Sizes Only
- If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
- Поиск больших файлов Linux
- Поиск больших файлов Linux
- 1. GDMap
- 2. Утилита ncdu
- 3. Утилита du
- 4. Утилита find
- Выводы
- How To Find Largest Top 10 Files and Directories On Linux / UNIX / BSD
- How to find out top 10 files and directories on Linux or Unix
- Steps to find Largest Directories in Linux
- How to find out top Directories and files in Linux
- Find the largest file in a directory and its subdirectories using the find command
- Hunt down disk space hogs with ducks
Поиск больших файлов и директорий в Linux
Дисковое пространство не вечно. Рано или поздно приходит момент, когда его катастрофически не хватает. Эффективный способ это исправить — найти файлы и директории, которые занимают больше всего места.
Рассмотрим, как это сделать в Linux с использованием команд find и du .
Поиск больших файлов командой find
Простой поиск
Команда find имеет опцию -size , которая позволяет указать размер файлов для поиска.
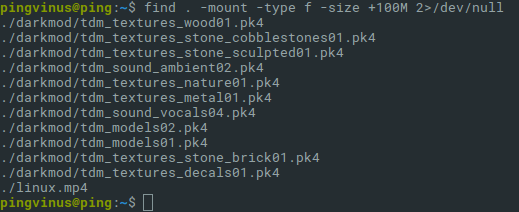
Найдем файлы, которые занимают больше 1Gb:
- Символ точка . после самой команды find, означает, что поиск нужно вести в текущей директории. Вместо точки вы можете указать, например, корневой раздел / или путь до любой другой директории.
- -mount означает, что в процессе поиска не нужно переходить на другие файловые системы.
- -type f означает, что мы ищем файлы.
- -size +1G означает, что нужно найти файлы, размер которых превышает 1Gb. Размер можно указать в различных форматах:
- b — блоки размером 512 байт. Числом указывается количество блоков.
- c — в байтах. Например: -size +128с
- w — в двухбайтовых словах
- k — в килобайтах
- M — в мегабайтах
- G — в гигабайтах
- 2>/dev/null используется, чтобы не показывать ошибки (например, если нет доступа к файлу).
В результате выполнения команды будет выведен список файлов без какой-либо дополнительной информации.
Вывод подробной информации
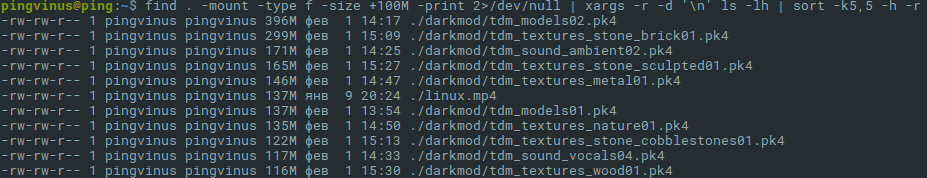
Добавим в вывод информацию о каждом файле и отсортируем список по размеру. Выполняем команду
Данная команда состоит из трех частей:
- Команда find ищет файлы, которые имеют размер больше 512 мегабайт.
- Результирующий список файлов передается команде xargs , которая, в свою очередь, запускает команду ls -lh над этим списком файлов. В результате получается таблица с файлами и информацией о файлах.
Опция -r , команды xarg, используется для того, чтобы не запускать команду ls, если команда find вернула пустой результат (не нашла файлов). Вместо -r можно использовать длинную запись — опцию —no-run-if-empty
Опция -d ’\n’ используется, чтобы разделять список файлов только по символу новой строки (по \n ). А у нас так и есть — каждый файл на новой строке. Иначе неправильно будут обработаны файлы, в названии которых содержится пробел, так как по умолчанию команда xarg в качестве разделителя использует одновременно пробел, табуляцию или символ новой строки.
Примечание: Для BSD-систем вместо -d ’\n’ нужно использовать опцию −0 , а у команды find вместо -print использовать -print0 . Пример: find . -mount -type f -size +512M -print0 2>/dev/null | xargs -0 ls -lh | sort -k5,5 -h -r
Ключ -h означает, что результат нужно вывести в удобно-читаемом виде (human-readable).
Ключ -r означает, что сортировку нужно выполнять по убыванию (reverse).
Поиск больших файлов и директорий командой du
Команда du используется для вывода размеров файлов и директорий в Linux. Ее можно использовать для поиска больших файлов и директорий. Для этого выполняется команда du и результат сортируется по размеру. Таким образом можно увидеть, кто занимает больше всего места на диске.
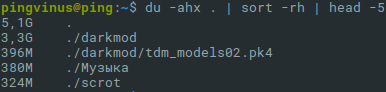
Найдем пять самых больших файлов и директорий:
- Символ . указывает путь и означает текущую директорию. Для поиска в другой директории укажите вместо точки ее путь.
- Опции -ahx означают:
a — искать и файлы и директории;
h — выводить информацию в удобно-читаемом формате;
x — не выполнять поиск на других файловых системах. - sort -rh выполняет сортировку результата.
- head −5 выводит только пять первых результатов.
Источник
How to Find Out Top Directories and Files (Disk Space) in Linux
As a Linux administrator, you must periodically check which files and folders are consuming more disk space. It is very necessary to find unnecessary junk and free up them from your hard disk.
This brief tutorial describes how to find the largest files and folders in the Linux file system using du (disk usage) and find command. If you want to learn more about these two commands, then head over to the following articles.
How to Find Biggest Files and Directories in Linux
Run the following command to find out top biggest directories under /home partition.

The above command displays the biggest 5 directories of my /home partition.
Find Largest Directories in Linux
If you want to display the biggest directories in the current working directory, run:

Let us break down the command and see what says each parameter.
- du command: Estimate file space usage.
- a : Displays all files and folders.
- sort command : Sort lines of text files.
- -n : Compare according to string numerical value.
- -r : Reverse the result of comparisons.
- head : Output the first part of files.
- -n : Print the first ‘n’ lines. (In our case, We displayed the first 5 lines).
Some of you would like to display the above result in human-readable format. i.e you might want to display the largest files in KB, MB, or GB.

The above command will show the top directories, which are eating up more disk space. If you feel that some directories are not important, you can simply delete a few sub-directories or delete the entire folder to free up some space.
To display the largest folders/files including the sub-directories, run:

Find out the meaning of each option using in above command:
- du command: Estimate file space usage.
- -h : Print sizes in human-readable format (e.g., 10MB).
- -S : Do not include the size of subdirectories.
- -s : Display only a total for each argument.
- sort command : sort lines of text files.
- -r : Reverse the result of comparisons.
- -h : Compare human readable numbers (e.g., 2K, 1G).
- head : Output the first part of files.
Find Out Top File Sizes Only
If you want to display the biggest file sizes only, then run the following command:

To find the largest files in a particular location, just include the path beside the find command:

The above command will display the largest file from /home/tecmint/Downloads directory.
That’s all for now. Finding the biggest files and folders is no big deal. Even a novice administrator can easily find them. If you find this tutorial useful, please share it on your social networks and support TecMint.
If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
TecMint is the fastest growing and most trusted community site for any kind of Linux Articles, Guides and Books on the web. Millions of people visit TecMint! to search or browse the thousands of published articles available FREELY to all.
If you like what you are reading, please consider buying us a coffee ( or 2 ) as a token of appreciation.
We are thankful for your never ending support.
Источник
Поиск больших файлов Linux
Если на вашем жёстком диске закончилось свободное пространство, самый простой способ его освободить — найти и удалить самые большие и при этом ненужные файлы. Такая задача может возникнуть как на сервере, так и на домашнем компьютере, поэтому существуют удобные решения для обоих ситуаций. Способов поиска больших файлов существует очень много.
Как вы уже поняли, в этой небольшой инструкции мы рассмотрим, как найти большие файлы Linux с помощью графического интерфейса или консольных утилит. Будем двигаться от самого простого к более сложному.
Поиск больших файлов Linux
1. GDMap
Несмотря на то, что графических утилит есть около десятка, все они мне не очень нравятся. Например в Gnome можно использовать GDMap, а в KDE — fileslight. Обе утилиты сканируют файловую систему и выводят все файлы в виде диаграммы. Размер блока зависит от размера файла. Чем больше файл или папка, тем больше блок. Для установки GDMap в Ubuntu выполните:
sudo apt install gdmap
Затем запустите утилиту из главного меню. По умолчанию она отображает домашнюю папку. Здесь можно оценить, какие файлы самые увесистые.
2. Утилита ncdu
Это псевдографическая утилита, которая работает в терминале Linux. Она отображает список файлов и директорий по объёму и, что самое интересное, тут же позволяет удалять ненужные файлы. Для установки утилиты выполните:
sudo apt install ncdu
Затем запустите утилиту, передав ей в качестве параметра папку, которую надо просканировать. Можно проверить ту же домашнюю папку:
У утилиты очень простое управление. Для перемещения по списку используйте кнопки со стрелками вверх и вниз, для открытия папки — клавишу Enter, а для удаления файла — кнопку d. Также можно использовать для перемещения кнопки в Vim стиле — h, j, k, l.
3. Утилита du
Если у вас нет возможности устанавливать новые утилиты, может помочь установленная по умолчанию во всех дистрибутивах утилита du. С помощью следующей команды вы можете вывести 20 самых больших файлов и папок в нужной папке, для примера снова возьмём домашнюю папку:
sudo du -a /home/ | sort -n -r | head -n 20
Мы не можем использовать опцию -h для вывода размера в читабельном формате, потому что тогда не будет работать сортировка.
4. Утилита find
С помощью команды find вы тоже можете искать большие файлы Linux. Для этого используйте опцию -size. Например, давайте найдём файлы, которые больше 500 мегабайтов в той же домашней папке:
sudo find /home -xdev -type f -size +500M
Можно пойти ещё дальше — вывести размер этих файлов и отсортировать их по размеру:
find / -xdev -type f -size +100M -exec du -sh <> ‘;’ | sort -rh
Самые большие файлы Linux будут сверху, а более мелкие — ниже.
Выводы
В этой небольшой статье мы разобрались, как выполняется поиск больших файлов Linux. После того, как вы их нашли, остаётся выбрать ненужные и удалить, если подобное происходит на сервере, то, обычно, это логи различных сервисов или кэш. Обратите внимание, что после удаления файлов место в файловой системе может и не освободится. Для полного освобождения места следует перезагрузить компьютер. Это довольно частая проблема на серверах и VPS.
Источник
How To Find Largest Top 10 Files and Directories On Linux / UNIX / BSD
How to find out top 10 files and directories on Linux or Unix
There is no simple command available to find out the largest files/directories on a Linux/UNIX/BSD filesystem. However, combination of following three commands (using pipes) you can easily find out list of largest files:
| Tutorial details | |
|---|---|
| Difficulty level | Easy |
| Root privileges | Yes |
| Requirements | Linux and Unix-like OS |
| Est. reading time | 3 minutes |
Steps to find Largest Directories in Linux
- du command : Estimate file space usage.
- sort command : Sort lines of text files or given input data.
- head command : Output the first part of files i.e. to display first 10 largest file.
- find command : Search file.
How to find out top Directories and files in Linux
Type the following command at the shell prompt to find out top 10 largest file/directories:
# du -a /var | sort -n -r | head -n 10
Sample outputs:
If you want more human readable output try (works with GNU/Linux du version/user only):
$ cd /path/to/some/where
$ du -hsx * | sort -rh | head -10
$ du -hsx — * | sort -rh | head -10
Where,
- du command -h option : display sizes in human readable format (e.g., 1K, 234M, 2G).
- du command -s option : show only a total for each argument (summary).
- du command -x option : skip directories on different file systems.
- sort command -r option : reverse the result of comparisons.
- sort command -h option : compare human readable numbers. This is GNU sort specific option only.
- head command -10 OR -n 10 option : show the first 10 lines.
The above command will only work of GNU/sort is installed. Other Unix like operating system should use the following version (see comments below):
Find the largest file in a directory and its subdirectories using the find command
Type the following GNU/find command:
You can skip directories and only display files, type:
Hunt down disk space hogs with ducks
Let us find out top directories and files using disk space in Linux or Unix with help of the following bash shell alias:
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
Run it as follows to get top 10 files/dirs eating your disk space:
$ ducks
Sample outputs:
Fig.01 Finding the largest files/directories on a Linux or Unix-like system
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
| Category | List of Unix and Linux commands |
|---|---|
| Documentation | help • mandb • man • pinfo |
| Disk space analyzers | df • duf • ncdu • pydf |
| File Management | cat • cp • less • mkdir • more • tree |
| Firewall | Alpine Awall • CentOS 8 • OpenSUSE • RHEL 8 • Ubuntu 16.04 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Linux Desktop Apps | Skype • Spotify • VLC 3 |
| Modern utilities | bat • exa |
| Network Utilities | NetHogs • dig • host • ip • nmap |
| OpenVPN | CentOS 7 • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Debian 8/9 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Package Manager | apk • apt |
| Processes Management | bg • chroot • cron • disown • fg • glances • gtop • jobs • killall • kill • pidof • pstree • pwdx • time • vtop |
| Searching | ag • grep • whereis • which |
| Shell builtins | compgen • echo • printf |
| Text processing | cut • rev |
| User Information | groups • id • lastcomm • last • lid/libuser-lid • logname • members • users • whoami • who • w |
| WireGuard VPN | Alpine • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Firewall • Ubuntu 20.04 |
Comments on this entry are closed.
Great, but what if I only want the largest files and not the directories?
To find out largest file only use command ls as follows in current directory:
ls -lSh . | head -5
Output:
-rw-r–r– 1 vivek vivek 267M 2004-08-04 15:37 WindowsXP-KB835935-SP2-ENU.exe
-rw-r–r– 1 vivek vivek 96M 2005-12-30 14:03 VMware-workstation-5.5.1-19175.tar.gz
ls -lSh /bin | head -5
You can also use find command but not du:
find /var -type f -ls | sort -k 7 -r -n | head -10
Hope this helps
And yes to find the smallest files use command:
ls -lSr /var
Or use find command with -size flag.
find / -type f -size +20000k -exec ls -lh <> ; | awk ‘< print $8 “: ” $5 >’
Read man page of find for more info.
“find / -type f -size +20000k -exec ls -lh <> ; | awk ‘< print $8 “: ” $5 >’”
needs to have the exec altered
find / -type f -size +20000k -exec ls -lh <> \; | awk ‘< print $8 “: ” $5 >’
Also, I find this output easier to read
find . -type f -size +20000k -exec ls -lh <> \; | awk ‘
How do I can list all the files in several directories and at the end write the totat of all the files and directories.I’m using the du command as fallow:
du -sh /public/base/sites/F*/*20070115*
this command give me the size of all the files but not the global total.
can somebody help me. please write me. john_fernandez@verizon.com.do
“If you want more human readable output try:
# du -ha /var | sort -n -r | head -n 10”
Im pretty sure that this will put 999kb above 1gb so I don’t think that this works.
This does not work.
# du -ha /var | sort -n -r | head -n 10″
as Joe says this ignores files over 1gb
You could try this, gives a human readable output in MB
find . -type f | xargs ls -s | sort -rn | awk ‘
Human readable version:
for X in $(du -s * | sort -nr | cut -f 2); do du -hs $X ; done
If you set du to human readable I think it will not sort the way you really want.
For the above problems. I would like to find a way to list only the last level directories’ sizes.
(I want to filter somehow this:
/home
/home/user
/home/user/mail
I just want to see the lasts of the tree!)
this is what i use.
for i in G M K; do du -ah | grep 5$i | sort -nr -k 1; done | head -n 11
Worked like charm
find . -type f -print0| xargs -0 ls -s | sort -rn | awk ‘
! -print0 for filenames with spaces …
(and xargs -0 combined)
No wonder windows rule
Yeah you just go ahead and wait the 3 hours this search would take on Windows.
How about the 3 hours it takes to read through a bunch of unexplained programming nonsense. I swear half of the time all Linux guys do is insult other users….Example, the first listing is great as it begins to explain what the flags do, but I have no idea were to put some of them, pipes are not explained…ect
This is why Winblows users should not try and use Linux, they are very unintelligent and lack the ability to look up simple things.
Fast forwarda few years, Linux won, bro 🙂
“Late last week, hell had apparently frozen over with the news that Microsoft had developed a Linux distribution of its own. The work was done as part of the company’s Azure cloud platform, which uses Linux-based network switches as part of its software-defined networking infrastructure.” — SOURCE HERE.
Winfan, I read this page wondering how to do these things in Windows — can you post instructions? Thanks!
This may vary depending on the version of Windows you’re using, but the basic procedure is: open the find/search window, go to the advanced options, and there will be an option there to enter in a size parameter. Simple.
In XP, press F3 or go Start->Search. Choose “All files and folders”, then “More advanced options”, then “What size is it?”, then specify a size.
I believe beez was being sarcastic towards Winfan as was his right after Winfans brainless comment. Most Linux distro GUI’s come with search function just like Windows GUI.
Now just try to do the search on command line on Windows (server)…
@winfan… how do you do this in windows? you don’t 😛
c:\>dir /S /O-S | more
The simple dir /S command from c:\ will give you all files and directories from c:\ all the way through the drive and will sort from largest to smallest running through each directory. You can filter using /A if you’d like to restrict by hidden, system, archive files, read only files etc. and passing the output to another windows command if you need to further restrict or search in the files for something like “show me all the files on my hard drive over 6MB that contain the word ‘log’ from largest to smallest.”
/O will Specify the sort order for the files with the S after it sorting by file size (smallest first) putting the – in front of the S reverses the order.
| more – you’re a unix dude, you should know what this means…
But if someone is doing some cleanup through their harddrive, this is the simple command I’d start with.
Just a note about the cockyness or us Unix admins (as I happen to be one now)
Not everyone that uses windows started using it with a mouse kid. Also not everyone who prefers windows is not cross-platform… We were running 64 bit clustered NT boxes on RISC processors at Digital Equipment Corporation with failover and failback in 1996 brother. Don’t believe me? Find a really old copy of Windows NT ver 3.51 open it and you’ll see two folders NT and Alpha.
The Department of Veterans Affairs had no problems with ever needing to reboot a “lousy unreliable windows box” because the Intel platform itself was the problem, not windows. We ran Alpha on 64 bit RISC processors and it was just as reliable as any Unix box or Mainframe we had. I had a Jensen Alpha running an exchange server for 5 years, and we only rebooted it every 6 months for giggles…
Windows machines are made to be used by the masses which means more dumbasses can kinda run one. A good Admin is a good Admin, no matter what platform. Be nice and be helpful or don’t post.
Notafan wrote:
@winfan… how do you do this in windows? you don’t 😛
Well, actually, there *is* cygwin (unix commands for Windows systems)
http://www.cygwin.com/
I find the following works rather well…
It lists all files or directories bigger than 50MB (just change size>50 to alter that) in the current directory (change the “.” to a directory path to specify another one) in a friendly, human-readable way and happily plays with spaces (I used it on an NTFS mount in fact).
I get a syntax error when coptying and pasting this command
Источник