- Собираем Flutter приложение для десктопа
- Flutter for Desktop: Create and Run a Desktop Application
- Prerequisites
- Manual Configuration
- Running Existing Apps on Desktop
- Linux install
- System requirements
- Get the Flutter SDK
- Install Flutter using snapd
- Install Flutter manually
- Run flutter doctor
- Update your path
- Update path directly
- Android setup
- Install Android Studio
- Set up your Android device
- Set up the Android emulator
- Agree to Android Licenses
- Linux setup
- Additional Linux requirements
- Enable desktop support
- Web setup
- Next step
Собираем Flutter приложение для десктопа
Сегодня я покажу вам, как же запустить ваше существующие Flutter приложение на десктопе (MacOS, Linux или Windows).
Во-первых, вам прийдется переключить канал Flutter c release на master. Для этого вам потребуется выполнить следующие команды в командной строке:
Затем вам нужно задать переменной окружения ENABLE_FLUTTER_DESKTOP значение true.
Для это выполните в командой строке следующее:
Mac OS и Linux
Windows PowerShell
Windows CMD
После этого вы должны видеть ваш десктоп в списке доступных устройств для запуска Flutter. Чтобы проверить это, выполните команду flutter devices
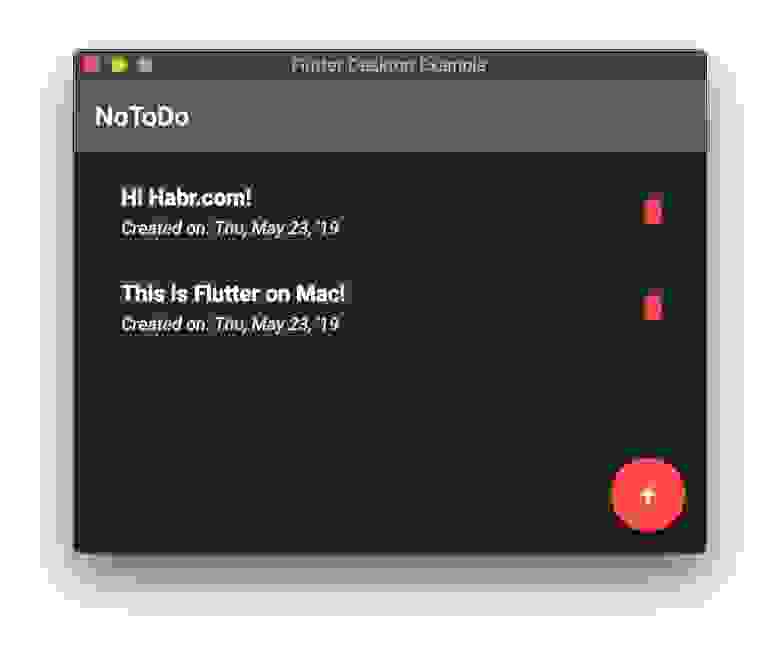
Как вы можете видеть на скриншоте, у меня в списке доступных устройств появилась Mac OS.
Нас интересует содержание директории example, а именно папки macos, linux и windows. Это раннеры для соответствующих платформ — нативные приложения, внутри которых работает Flutter. Точно такие же, какие вы можете увидеть в директории вашего проекта, когда создаете проект с помошью команды flutter create.
Просто скопируйте раннер для интересующей вас платформы в директорию проекта. Этот шаг необходим, так как flutter create пока не поддерживает автоматическое создание раннеров для десктопа.
Уже почти готово. Сейчас нужно немного отредактировать ваш main.dart
Добавьте следующие импорты:
Измените main() следующим образом:
Последний шаг. Выполните следующие команды:
Готово! Теперь просто запустите flutter run и ваше приложение соберется на десктоп!
Важное замечание:
Стоит иметь ввиду, что многие сторонние плагины, которые вы использовали в ваших Flutter приложениях не будут работать на десктопе, так как они зависят от нативных API. В будущем ситуация, конечно, изменится, но пока лучше не использовать этот способ для чего то серьезного.
Источник
Flutter for Desktop: Create and Run a Desktop Application
Google I/O 2019 was about innovation, and for Flutter it was about going beyond mobile apps. The technical preview for Flutter Web was released, and a live demonstration showed how Flutter apps can run on Desktop environments, like Chrome OS, Linux, Mac OS, or Windows. In this article we will go through the process of running a new or an existing Flutter application on a Desktop environment.
In my attempts, I have found that there are multiple ways to do it, so for the sake of simplicity, let’s go with the easiest one.
Prerequisites
For Flutter to run on Desktop, we must be on the master channel, with the latest release. To ensure the same, fire up a terminal and run the following commands.
we should see an output like the one shown below (as of 17th May, 2019)
Now with that out of our way, we can see that our even though I am on Ubuntu, the Linux system is not being displayed as a connected device, capable of running Flutter. This is because by default Flutter does not not have desktop support enabled. We can do so by setting the environment variable ENABLE_FLUTTER_DESKTOP=true.
To do this, in a terminal key in the appropriate command:
On macOS or Linux:
Please note that this sets the environment variable for the current terminal session, hence we will be doing all the future steps in this terminal itself.
Now, let’s run the following command to ensure that our system shows up.
And in the output, I now see that Linux is connected and available.
Manual Configuration
Flutter for Desktop is still an experimental feature, which means that there is no tooling support for Flutter, also the flutter create command does not currently support creating a new desktop application. So the only option is to manually configure the system specific files. Thankfully for us, the Flutter team at Google already did that for us.
Go ahead and run this in the terminal:
The example directory is a Flutter application which has all the necessary build scripts, which will be required to run Flutter on MacOS, Windows, and Linux. If we open the example folder in VS Code we will be able to see something like this:
All that is left to do, is run the following command from inside the example folder.
Just one last step before we go ahead and run our app. The desktop system specific build tools are not download by default, and even though Flutter will download the same when we first run our app, I want to ensure that we have it beforehand. To download the same, run:
Make sure to replace linux with windows or macos, depending on your system.
Congratulations! We are now ready to run our Flutter app as a Desktop application.
Let’s just run the app first, and we will go over the code boilerplate code after that. In the terminal window, execute:
The terminal output should be something like this:
And the ever so beautiful desktop application, will look something like this:
Let’s go through the boilerplate code now:
Most of this code is the usual Flutter stuff, but there are some lines that are different.
This code provides a way to override the default target platform. This can be used based on the requirements of the application. To know more about the same, click here.
Running Existing Apps on Desktop
Now that we have the necessary config files and scripts. We can run any of our existing apps on desktop.
To do that there are two ways:
- We can copy the system specific folder (linux, macos, or windows) from the example directory to our existing project directory. ( not recommended)
- We can replace the lib folder inside the example directory with our existing code, and replace the pubspec.yaml file, with our existing one. ( recommended)
I would recommend going with the second method, because a lot of times, I have seen that the 1st one doesn’t work. I have an app called Cryptex, and when I ran it on desktop, here’s what I had.
Источник
Linux install
System requirements
To install and run Flutter, your development environment must meet these minimum requirements:
- Operating Systems: Linux (64-bit)
- Disk Space: 600 MB (does not include disk space for IDE/tools).
- Tools: Flutter depends on these command-line tools being available in your environment.
- bash
- curl
- file
- git 2.x
- mkdir
- rm
- unzip
- which
- xz-utils
- zip
- Shared libraries: Flutter test command depends on this library being available in your environment.
- libGLU.so.1 — provided by mesa packages such as libglu1-mesa on Ubuntu/Debian and mesa-libGLU on Fedora.
Get the Flutter SDK
On Linux, you have two ways you can install Flutter.
Install Flutter using snapd
The easiest way to install Flutter on Linux is by using snapd. For more information, see Installing snapd.
Once you have snapd, you can install Flutter using the Snap Store, or at the command line:
Note: Once the snap is installed, you can use the following command to display your Flutter SDK path:
Install Flutter manually
If you don’t have snapd , or can’t use it, you can install Flutter using the following steps.
Download the following installation bundle to get the latest stable release of the Flutter SDK:
For other release channels, and older builds, see the SDK releases page.
Extract the file in the desired location, for example:
If you don’t want to install a fixed version of the installation bundle, you can skip steps 1 and 2. Instead, get the source code from the Flutter repo on GitHub with the following command:
You can also change branches or tags as needed. For example, to get just the stable version:
Add the flutter tool to your path:
This command sets your PATH variable for the current terminal window only. To permanently add Flutter to your path, see Update your path.
Optionally, pre-download development binaries:
The flutter tool downloads platform-specific development binaries as needed. For scenarios where pre-downloading these artifacts is preferable (for example, in hermetic build environments, or with intermittent network availability), iOS and Android binaries can be downloaded ahead of time by running:
For additional download options, see flutter help precache .
You are now ready to run Flutter commands!
Note: To update an existing version of Flutter, see Upgrading Flutter.
Run flutter doctor
Run the following command to see if there are any dependencies you need to install to complete the setup (for verbose output, add the -v flag):
This command checks your environment and displays a report to the terminal window. The Dart SDK is bundled with Flutter; it is not necessary to install Dart separately. Check the output carefully for other software you might need to install or further tasks to perform (shown in bold text).
The following sections describe how to perform these tasks and finish the setup process.
Once you have installed any missing dependencies, run the flutter doctor command again to verify that you’ve set everything up correctly.
Warning: The Flutter tool may occasionally download resources from Google servers. By downloading or using the Flutter SDK you agree to the Google Terms of Service.
For example, when installed from GitHub (as opposed to from a prepackaged archive), the Flutter tool will download the Dart SDK from Google servers immediately when first run, as it is used to execute the flutter tool itself. This will also occur when Flutter is upgraded (e.g. by running the flutter upgrade command).
The flutter tool uses Google Analytics to report feature usage statistics and send crash reports. This data is used to help improve Flutter tools over time.
Flutter tool analytics are not sent on the very first run. To disable reporting, run flutter config —no-analytics . To display the current setting, use flutter config . If you opt out of analytics, an opt-out event is sent, and then no further information is sent by the Flutter tool.
Dart tools may also send usage metrics and crash reports to Google. To control the submission of these metrics, use the following options on the dart tool:
- —enable-analytics : Enables anonymous analytics.
- —disable-analytics : Disables anonymous analytics.
The Google Privacy Policy describes how data is handled by these services.
Update your path
You can update your PATH variable for the current session at the command line, as shown in Get the Flutter SDK. You’ll probably want to update this variable permanently, so you can run flutter commands in any terminal session.
The steps for modifying this variable permanently for all terminal sessions are machine-specific. Typically you add a line to a file that is executed whenever you open a new window. For example:
- Determine the path of your clone of the Flutter SDK. You need this in Step 3.
- Open (or create) the rc file for your shell. For example, Linux uses the Bash shell by default, so edit $HOME/.bashrc . If you are using a different shell, the file path and filename will be different on your machine.
Add the following line and change [PATH_OF_FLUTTER_GIT_DIRECTORY] to be the path of your clone of the Flutter git repo:
Verify that the flutter/bin directory is now in your PATH by running:
Verify that the flutter command is available by running:
Note: As of Flutter’s 1.19.0 dev release, the Flutter SDK contains the dart command alongside the flutter command so that you can more easily run Dart command-line programs. Downloading the Flutter SDK also downloads the compatible version of Dart, but if you’ve downloaded the Dart SDK separately, make sure that the Flutter version of dart is first in your path, as the two versions might not be compatible. The following command tells you whether the flutter and dart commands originate from the same bin directory and are therefore compatible.
As shown above, the two commands don’t come from the same bin directory. Update your path to use commands from /path-to-flutter-sdk/bin before commands from /usr/local/bin (in this case). After updating your shell for the change to take effect, running the which command again should show that the flutter and dart commands now come from the same directory.
To learn more about the dart command, run dart -h from the command line, or see the dart tool page.
Update path directly
In some cases, your distribution may not permanently acquire the path when using the above directions. When this occurs, you can change the environment variables file directly. These instructions require administrator privileges:
Determine the path of your clone of the Flutter SDK.
Locate the etc directory at the root of the system, and open the profile file with root privileges.
Update the PATH string with the location of your Flutter SDK directory.
Once you start a new session, verify that the flutter command is available by running:
For more details on setting the path in Bash, see this StackExchange question. For information on setting the path in Z shell, see this StackOverflow question.
Android setup
Note: Flutter relies on a full installation of Android Studio to supply its Android platform dependencies. However, you can write your Flutter apps in a number of editors; a later step discusses that.
Install Android Studio
- Download and install Android Studio.
- Start Android Studio, and go through the ‘Android Studio Setup Wizard’. This installs the latest Android SDK, Android SDK Command-line Tools, and Android SDK Build-Tools, which are required by Flutter when developing for Android.
- Run flutter doctor to confirm that Flutter has located your installation of Android Studio. If Flutter cannot locate it, run flutter config —android-studio-dir to set the directory that Android Studio is installed to.
Set up your Android device
To prepare to run and test your Flutter app on an Android device, you need an Android device running Android 4.1 (API level 16) or higher.
- Enable Developer options and USB debugging on your device. Detailed instructions are available in the Android documentation.
- Windows-only: Install the Google USB Driver.
- Using a USB cable, plug your phone into your computer. If prompted on your device, authorize your computer to access your device.
- In the terminal, run the flutter devices command to verify that Flutter recognizes your connected Android device. By default, Flutter uses the version of the Android SDK where your adb tool is based. If you want Flutter to use a different installation of the Android SDK, you must set the ANDROID_SDK_ROOT environment variable to that installation directory.
Set up the Android emulator
To prepare to run and test your Flutter app on the Android emulator, follow these steps:
- Enable VM acceleration on your machine.
- Launch Android Studio, click the AVD Manager icon, and select Create Virtual Device…
- In older versions of Android Studio, you should instead launch Android Studio > Tools > Android > AVD Manager and select Create Virtual Device…. (The Android submenu is only present when inside an Android project.)
- If you do not have a project open, you can choose Configure > AVD Manager and select Create Virtual Device…
- Choose a device definition and select Next.
- Select one or more system images for the Android versions you want to emulate, and select Next. An x86 or x86_64 image is recommended.
- Under Emulated Performance, select Hardware — GLES 2.0 to enable hardware acceleration.
Verify the AVD configuration is correct, and select Finish.
For details on the above steps, see Managing AVDs.
Agree to Android Licenses
Before you can use Flutter, you must agree to the licenses of the Android SDK platform. This step should be done after you have installed the tools listed above.
Make sure that you have a version of Java 8 installed and that your JAVA_HOME environment variable is set to the JDK’s folder.
Android Studio versions 2.2 and higher come with a JDK, so this should already be done.
Open an elevated console window and run the following command to begin signing licenses.
Linux setup
Warning: Beta! This area covers desktop support, which is available as a beta release. Beta support still has notable feature gaps, including accessibility support. You can try a beta snapshot of desktop support on the stable channel, or you can keep up with the latest changes to desktop on the beta channel. For more information, see the Desktop section in What’s new in Flutter 2, a free article on Medium.
Additional Linux requirements
For Linux desktop development, you need the following in addition to the Flutter SDK:
Run the following command
Enable desktop support
At the command line, perform the following command to enable desktop support
Web setup
Flutter has support for building web applications in the stable channel. Any app created in Flutter 2 automatically builds for the web. To add web support to an existing app, follow the instructions on Building a web application with Flutter when you’ve completed the setup above.
Next step
Set up your preferred editor.
Except as otherwise noted, this work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, and code samples are licensed under the BSD License.
Источник











