- 5 commands to check memory usage on Linux
- Memory Usage
- 1. free command
- 2. /proc/meminfo
- 3. vmstat
- 4. top command
- 5. htop
- RAM Information
- Summary
- 66 thoughts on “ 5 commands to check memory usage on Linux ”
- Команда Free (свободная оперативная память) в Linux
- Free Command in Linux
- Сколько свободной оперативной памяти мне доступно в моей системе Linux? Достаточно ли свободной памяти для установки и запуска новых приложений?
- Как использовать Free команду
- Отображение использования памяти в удобочитаемом формате
- Отображение использования памяти в других метриках
- Отображение итогов в столбце
- Постоянно печатать вывод
- Вывод
- Find Ram Size in Linux Using free And top Commands
- Use /proc/meminfo file to find ram size in Linux
- Use free Command to check RAM size
- The free command options
- Finding free and used ram info using the vmstat command
- The top Command
- GUI system information tool
- Say hello to dmidecode Command
- Related media
- Conclusion
- Информация об оперативной памяти в Linux. Свободная, занятая и тип памяти
- Свободная и занятая оперативная память
- Команда free
- Команда vmstat
- Команда top
- Команда htop
- Файл /proc/meminfo
- Тип памяти и частота
- Заключение
5 commands to check memory usage on Linux
Memory Usage
On linux, there are commands for almost everything, because the gui might not be always available. When working on servers only shell access is available and everything has to be done from these commands. So today we shall be checking the commands that can be used to check memory usage on a linux system. Memory include RAM and swap.
It is often important to check memory usage and memory used per process on servers so that resources do not fall short and users are able to access the server. For example a website. If you are running a webserver, then the server must have enough memory to serve the visitors to the site. If not, the site would become very slow or even go down when there is a traffic spike, simply because memory would fall short. Its just like what happens on your desktop PC.
1. free command
The free command is the most simple and easy to use command to check memory usage on linux. Here is a quick example
The m option displays all data in MBs. The total os 7976 MB is the total amount of RAM installed on the system, that is 8GB. The used column shows the amount of RAM that has been used by linux, in this case around 6.4 GB. The output is pretty self explanatory. The catch over here is the cached and buffers column. The second line tells that 4.6 GB is free. This is the free memory in first line added with the buffers and cached amount of memory.
Linux has the habit of caching lots of things for faster performance, so that memory can be freed and used if needed.
The last line is the swap memory, which in this case is lying entirely free.
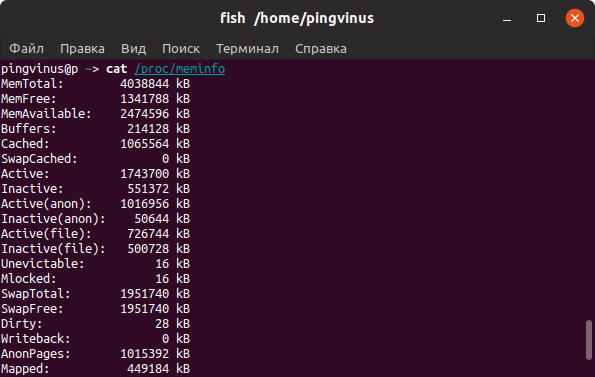
2. /proc/meminfo
The next way to check memory usage is to read the /proc/meminfo file. Know that the /proc file system does not contain real files. They are rather virtual files that contain dynamic information about the kernel and the system.
Check the values of MemTotal, MemFree, Buffers, Cached, SwapTotal, SwapFree.
They indicate same values of memory usage as the free command.
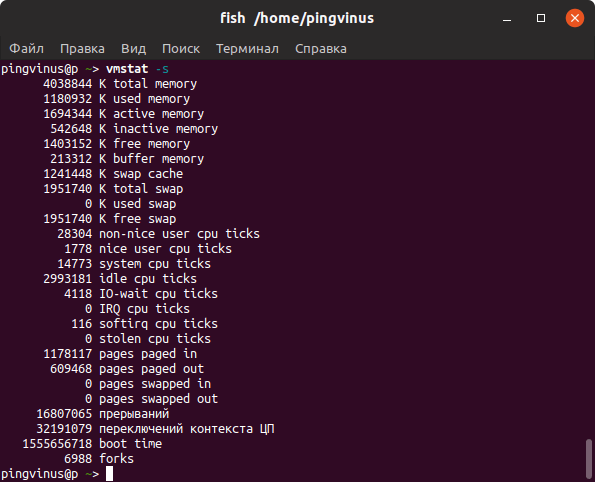
3. vmstat
The vmstat command with the s option, lays out the memory usage statistics much like the proc command. Here is an example
The top few lines indicate total memory, free memory etc and so on.
4. top command
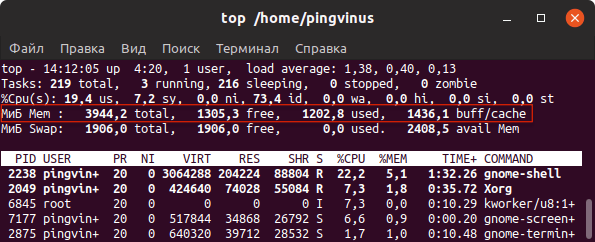
The top command is generally used to check memory and cpu usage per process. However it also reports total memory usage and can be used to monitor the total RAM usage. The header on output has the required information. Here is a sample output
Check the KiB Mem and KiB Swap lines on the header. They indicate total, used and free amounts of the memory. The buffer and cache information is present here too, like the free command.
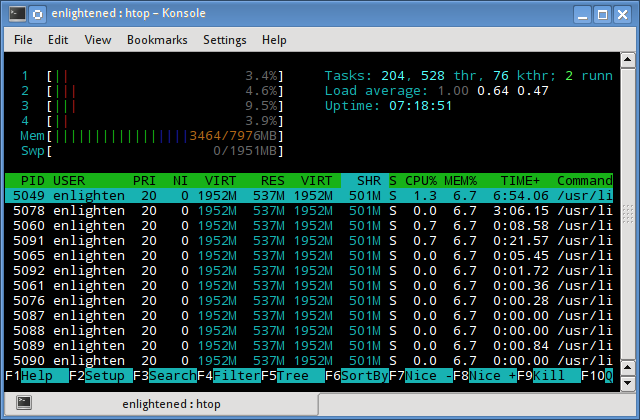
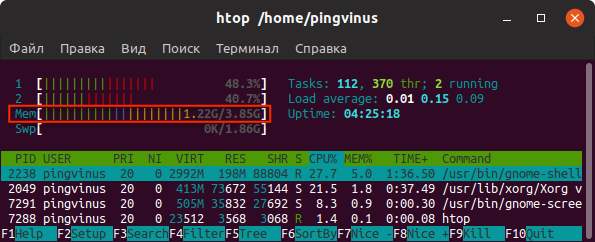
5. htop
Similar to the top command, the htop command also shows memory usage along with various other details.
The header on top shows cpu usage along with RAM and swap usage with the corresponding figures.
RAM Information
To find out hardware information about the installed RAM, use the demidecode command. It reports lots of information about the installed RAM memory.
Provided information includes the size (2048MB), type (DDR2) , speed(667 Mhz) etc.
Summary
All the above mentioned commands work from the terminal and do not have a gui. When working on a desktop with a gui, it is much easier to use a GUI tool with graphical output. The most common tools are gnome-system-monitor on gnome and
ksysguard on KDE. Both provide resource usage information about cpu, ram, swap and network bandwidth in a graphical and easy to understand visual output.
A Tech Enthusiast, Blogger, Linux Fan and a Software Developer. Writes about Computer hardware, Linux and Open Source software and coding in Python, Php and Javascript. He can be reached at [email protected] .
66 thoughts on “ 5 commands to check memory usage on Linux ”
You have explained the topic very well. Thanks for sharing a nice article.
Thanks for these commands. It saved a lots of time.
How about explaining what we are looking for? Most people would know these commands. Waste of time.
Please correct the typo in “RAM Information” section. The command for viewing hardware info about RAM is “dmidecode” and not “demidecode”.
And it also requires root privileges.
Источник
Команда Free (свободная оперативная память) в Linux
Free Command in Linux
Сколько свободной оперативной памяти мне доступно в моей системе Linux? Достаточно ли свободной памяти для установки и запуска новых приложений?
В системах Linux вы можете использовать free команду для получения подробного отчета об использовании памяти системой.
Команда free предоставляет информацию об общем объеме физической и подкачки памяти, а также о свободной и используемой памяти и пространстве подкачки в системе.
Как использовать Free команду
Синтаксис free команды следующий:
При использовании без какой-либо опции, free команда отобразит информацию о памяти и поменяет местами в кибибайтах. 1 кибибайт (КиБ) составляет 1024 байта.
Вывод будет включать три строки, заголовок, одну строку для памяти и одну для подкачки:
В старых версиях Linux выходные данные могут немного отличаться.
- total — это число представляет собой общий объем памяти, который может использоваться приложениями.
- used — использованная память Он рассчитывается как: used = total — free — buffers — cache
- free — Свободная / Неиспользуемая память.
- shared — этот столбец можно игнорировать, так как он не имеет смысла. Это здесь только для обратной совместимости.
- buff / cache — объединенная память, используемая буферами ядра, кешем страниц и слэбами. / эта память может быть восстановлена в любое время, если это необходимо приложениям. Если вы хотите, чтобы буферы и кеш отображались в двух отдельных столбцах, используйте эту -w опцию.
- available — оценка объема памяти, доступной для запуска новых приложений без замены.
Отображение использования памяти в удобочитаемом формате
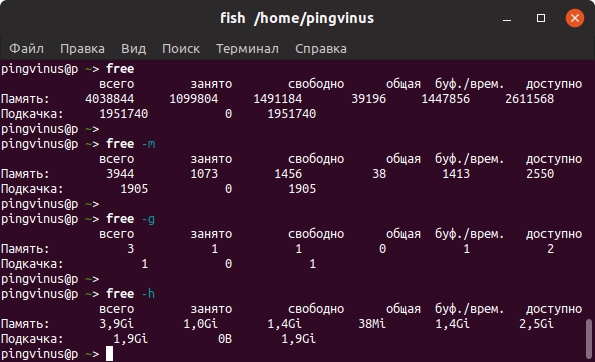
Как мы видели в приведенном выше примере, по умолчанию free команда отображает информацию о памяти в кибибайтах. Чтобы просмотреть информацию в удобочитаемом формате (обычно мегабайты и гигабайты), используйте -h параметр:
Отображение использования памяти в других метриках
Команда free также позволяет указать единицу измерения памяти. Допустимые варианты:
- -b , —bytes — Вывести вывод в байтах.
- —kilo — Отображение вывода в килобайтах (1 КБ = 1000 байт).
- —mega — Показать вывод в мегабайтах.
- —giga — Отображение вывода в гигабайтах.
- —tera — Отображение вывода в терабайтах.
- -k , —kibi — Вывести вывод в кибибайтах. (1 КБ = 1024 байт). Это единица по умолчанию.
- -m , —mebi — выход дисплея в Mebibytes.
- -g , —gibi — выход дисплея в gibytes.
- —tebi — Отображать вывод в тебибайтах.
- —peti — Выводить вывод в пебибайтах.
- —si — Вместо 1024 используйте полномочия 1000. Например —mebi —si , равно —mega .
Например, чтобы показать вывод в мегабайтах, вы должны набрать:
Отображение итогов в столбце
Чтобы отобразить строку, отображающую итоги столбца, используйте -t параметр. Это даст вам сумму памяти и поменяет местами общие, использованные и свободные столбцы.
Постоянно печатать вывод
Для того, чтобы непрерывно отображать информацию о памяти об использовании экрана с -s , —seconds варианты с последующим номером , который определяет задержку.
Например, чтобы печатать информацию о памяти каждые пять секунд, вы должны выполнить:
Команда free будет продолжать отображать результат, пока вы не нажмете CTRL+C . Это похоже на поведение watch команды .
Для отображения результата для определенного числа раз использовать -c , —count вариант. В приведенном ниже примере команда напечатает результат десять раз:
Вывод
К настоящему времени вы должны хорошо понимать, как использовать и интерпретировать free команду. Для просмотра всех доступных параметров free командной строки введите man free в своем терминале.
Источник
Find Ram Size in Linux Using free And top Commands
Use /proc/meminfo file to find ram size in Linux
| Tutorial details | |
|---|---|
| Difficulty level | Easy |
| Root privileges | Yes |
| Requirements | None |
| Est. reading time | 5m |
The /proc/meminfo file tells you about memory usage on the server. This file is used by the free command and many other Linux commands to display the amount of free and used memory (both physical and swap) on the system as well as the shared memory and buffers used by the kernel. Type the following cat command/less command to view total installed ram and used ram, enter:
$ less /proc/meminfo
OR
$ cat /proc/meminfo
Sample outputs:
Of course, we can use the grep command/egrep command as follows to filter out information:
Use free Command to check RAM size
Free command is a frontend to /proc/meminfo file. It provides more human-readable output to show you the total amount of free and used physical and swap memory in the system, as well as the buffers used by the kernel, run:
$ free -m
OR
$ free -g
Sample outputs:
The free command options
From the free(1) man page:
Hence, we try those options too:
$ free
$ free -m
$ free -g -t -o
$ free -t
$ free -o
Finding free and used ram info using the vmstat command
The vmstat command can display memory statistics including additional information about processes, paging, block IO, traps, and cpu activity. Pass the -s option to the vmstat to show us memory statistics as follows:
$ vmstat -s
Sample outputs:
The top Command
The top command provides a dynamic real-time view of a running system including a quick summary information about RAM, CPU as well as a list of tasks currently being managed by the Linux kernel. Type the following command:
$ top
Sample outputs:
Fig.01: Display Linux RAM Size with the top commad
GUI system information tool
The System Monitor Gnome or KDE application enables you to display basic system information and monitor system processes, usage of system resources, and file systems. You can start System Monitor in the following ways:
Click on System menu > Choose Administration > System Monitor
Alternatively, type the following command:
$ gnome-system-monitor
Sample outputs:
Linux view installed memory with the System Monitor application
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
Say hello to dmidecode Command
The dmidecode command is used for dumping a computer’s DMI (some say SMBIOS) table contents in a human-readable format. This table contains a description of the system’s hardware components, as well as other useful pieces of information such as serial numbers and BIOS revision. Thanks to this table, you can retrieve this information without having to probe for the actual hardware. To see complete information about memory, enter:
$ sudo dmidecode —type memory
Sample outputs:
Related media
This tutorial is also available in a quick video format:
Conclusion
In this tutorial, you learned how to use the various command line and GUI tools amount of free and used memory in the Linux system. See free and vmstat command man page here and here:
man free
man vmstat
man top
man htop
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
Источник
Информация об оперативной памяти в Linux. Свободная, занятая и тип памяти
В этой статье мы рассмотрим, как получить информацию об оперативной памяти (RAM) в Linux.
Мы воспользуемся утилитами командной строки доступными для большинства Linux дистрибутивов.
Свободная и занятая оперативная память
Для получения информации о количестве свободной и занятой оперативной памяти в Linux можно использовать различные утилиты и команды. Рассмотрим несколько распространенных способов.
Команда free
Команда free очень простая, она выводит информацию о общем количестве оперативной памяти, о количестве занятой и свободной памяти, а также об использовании файла подкачки.
По умолчанию объем памяти выводится в килобайтах. Используя опции, можно выводить объем памяти в других форматах. Некоторые опции:
- -m — в мегабайтах
- -g — в гигабайтах
- -h — автоматически определить формат
Команда vmstat
Команда vmstat выводит различную статистику по использованию памяти. Используя ключ -s можно вывести подробную статистику в табличном виде.
Команда top
top — это утилита командной строки, которая используется для мониторинга процессов и используемых ресурсов компьютера.
Запуск утилиты top :
В заголовке выводится информация об использованной оперативной памяти.
Команда htop
Утилита htop, также как и top, используется для мониторинга ресурсов и процессов.
Для установки утилиты htop в Ubuntu Linux (Linux Mint и других Ubuntu/Debian-дистрибутивах) выполните команду:
Запуск утилиты htop :
Файл /proc/meminfo
Описанные выше команды, в качестве источника информации используют системные файлы из файлов, хранящихся в виртуальной файловой системе /proc . В файле /proc/meminfo содержится информация об использовании памяти. Выведем содержимое файла /proc/meminfo :
Тип памяти и частота
Рассмотрим, как получить информацию об установленных в компьютер модулях оперативной памяти. Воспользуемся командной dmidecode
Используем следующую команду:
В выводе команды будет информация о слотах оперативной памяти. Для каждого слота отображается установленный модуль оперативной памяти, его тип (поле Type ), размер (поле Size ), скорость/частота (поле Speed ) и другая информация.
В зависимости от системы и оборудования не всегда удается получить все данные, поэтому некоторые поля могут быть пустыми или иметь надписи Not provided/Unknown.
Заключение
Мы рассмотрели различные способы для просмотра информации о доступной и занятой оперативной памяти, а также показали, как вывести информацию об установленных модулях оперативной памяти.
Для отслеживания использования ресурсов компьютера существует множество графических программ. Найти их можно в нашем каталоге программ для Linux в разделе Система/Мониторинг.
Источник