- How to check if port is in use on Linux or Unix
- How to check if port is in use in
- Option #1: lsof command
- Option #2: netstat command
- Linux netstat syntax
- FreeBSD/MacOS X netstat syntax
- OpenBSD netstat syntax
- Option #3: nmap command
- A note about Windows users
- Conclusion
- How do I check if a port is in use on Linux?
- Popular port numbers in Linux
- How to check if a port is in use on Linux
- How can you find out which process is listening on a port on Linux
- Getting a list of all open port in production
- How to check open ports in Linux using the CLI
- What the hell are a TCP and UDP ports?
- Port numbers
- Check open ports in Linux
- Using netstat to list open ports
- Use ss to list open ports
- Listening ports and applications using lsof command
- nmap command
- The open port doesn’t mean anyone from outside can access those ports
- Conclusion
- 4 способа узнать, какие порты прослушиваются в Linux
- 1. Используя команду netstat
- 2. Используя команду ss
- 3. Используя программу Nmap
- 4. Используя команду lsof
How to check if port is in use on Linux or Unix
H ow do I determine if a port is in use under Linux or Unix-like system? How can I verify which ports are listening on Linux server? How do I check if port is in use on Linux operating system using the CLI?
It is important you verify which ports are listening on the server’s network interfaces. You need to pay attention to open ports to detect an intrusion. Apart from an intrusion, for troubleshooting purposes, it may be necessary to check if a port is already in use by a different application on your servers. For example, you may install Apache and Nginx server on the same system. So it is necessary to know if Apache or Nginx is using TCP port # 80/443. This quick tutorial provides steps to use the netstat, nmap and lsof command to check the ports in use and view the application that is utilizing the port.
| Tutorial details | |
|---|---|
| Difficulty level | Easy |
| Root privileges | Yes |
| Requirements | lsof, ss, and netstat on Linux |
| Est. reading time | 3 minutes |
How to check if port is in use in
To check the listening ports and applications on Linux:
- Open a terminal application i.e. shell prompt.
- Run any one of the following command on Linux to see open ports:
sudo lsof -i -P -n | grep LISTEN
sudo netstat -tulpn | grep LISTEN
sudo ss -tulpn | grep LISTEN
sudo lsof -i:22 ## see a specific port such as 22 ##
sudo nmap -sTU -O IP-address-Here - For the latest version of Linux use the ss command. For example, ss -tulw
Let us see commands and its output in details.
Option #1: lsof command
The syntax is:
$ sudo lsof -i -P -n
$ sudo lsof -i -P -n | grep LISTEN
$ doas lsof -i -P -n | grep LISTEN ### [OpenBSD] ###
Sample outputs:
Fig.01: Check the listening ports and applications with lsof command
Option #2: netstat command
You can check the listening ports and applications with netstat as follows.
Linux netstat syntax
Run netstat command along with grep command to filter out port in LISTEN state:
$ netstat -tulpn | grep LISTEN
The netstat command deprecated for some time on Linux. Therefore, you need to use the ss command as follows:
sudo ss -tulw
sudo ss -tulwn
sudo ss -tulwn | grep LISTEN
Where, ss command options are as follows:
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
- -t : Show only TCP sockets on Linux
- -u : Display only UDP sockets on Linux
- -l : Show listening sockets. For example, TCP port 22 is opened by SSHD server.
- -p : List process name that opened sockets
- -n : Don’t resolve service names i.e. don’t use DNS
FreeBSD/MacOS X netstat syntax
$ netstat -anp tcp | grep LISTEN
$ netstat -anp udp | grep LISTEN
OpenBSD netstat syntax
$ netstat -na -f inet | grep LISTEN
$ netstat -nat | grep LISTEN
Option #3: nmap command
The syntax is:
$ sudo nmap -sT -O localhost
$ sudo nmap -sU -O 192.168.2.13 ##[ list open UDP ports ]##
$ sudo nmap -sT -O 192.168.2.13 ##[ list open TCP ports ]##
Sample outputs:
Fig.02: Determines which ports are listening for TCP connections using nmap
A note about Windows users
You can check port usage from Windows operating system using following command:
netstat -bano | more
netstat -bano | grep LISTENING
netstat -bano | findstr /R /C:»[LISTEING]»
Conclusion
This page explained command to determining if a port is in use on Linux or Unix-like server. For more information see the nmap command and lsof command page online here
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
Источник
How do I check if a port is in use on Linux?
I am a new Linux system user. I need to find out which process is listening on a port on Linux using the command line. How do you find out which process is listening on a port on Linux operating systems?
A network port in Linux is nothing but a number that identifies one side of a connection between two systems. All networked devices use port numbers to determine to which process a message should be delivered. The domain name and IP address are like a street address, and port numbers are like room numbers.
| Tutorial details | |
|---|---|
| Difficulty level | Easy |
| Root privileges | Yes |
| Requirements | Linux |
| Est. reading time | 2 minutes |
Popular port numbers in Linux
- HTTP – TCP 80
- HTTPS – TCP 443
- POP3 – TCP 110
- SMTP – TCP 25
- SSH – TCP 22
- DNS/DOMAIN – TCP/UDP 53
Use the cat command or grep command/egrep command to query port numbers as follows:
cat /etc/services
grep -w 80 /etc/services
egrep -w ’53/(tcp|udp)’ /etc/services
How to check if a port is in use on Linux
The procedure is as follows:
- Open the terminal application on Linux.
- Type any one of the following command to check if a port is in use on Linux
sudo lsof -i -P -n | grep LISTEN
sudo netstat -tulpn | grep LISTEN
sudo netstat -tulpn | grep :443
sudo ss -tulpn | grep LISTEN
sudo ss -tulpn | grep ‘:22’ - Search for the TCP or UDP port description in /etc/services file on Linux:
grep -E -w ‘PORT_NUMBER_HERE/(tcp|udp)’ /etc/services
Let us see some examples and sample commands in details.
How can you find out which process is listening on a port on Linux
Type the ss command or netstat command to see if a TCP port 443 is in use on Linux?
sudo netstat -tulpn | grep :443
sudo ss -tulpn | grep :443
If a port is open, you should see the output as follows:
The port 443 is in use and opened by nginx service. Where,
- -t : Display TCP sockets/port
- -u : Show UDP sockets/port
- -l : See only listening sockets i.e. open port
- -p : Also display process name that opened port/socket
- -n : View addresses and port numbers in numerical format. Do not use DNS to resolve names.
Getting a list of all open port in production
Simply run:
sudo lsof -i -P -n | grep LISTEN
sudo ss -tulpn
sudo netstat -tulpn
Sample outputs:
Источник
How to check open ports in Linux using the CLI
I need to list all open ports in Linux cloud server. How do I check open ports in Linux using the CLI? Can you give me the command to check open ports in Linux operating system?
To troubleshoot server problems and to avoid security issue, one needs to find out open TCP and UDP ports. In this tutorial, you will learn the different Linux commands to check open ports in Linux for auditing and securing the server.
| Tutorial details | |
|---|---|
| Difficulty level | Easy |
| Root privileges | Yes |
| Requirements | Linux command line |
| Est. reading time | 5 minutes |
What the hell are a TCP and UDP ports?
A port is nothing but a 16-bit number between 0 to 65535. For example, TCP port number 22 may be forwarded to the OpenSSH server. Therefore, 22 port number is a way to identify the sshd (OpenSSH server) process.
Port numbers
- The Well Known Ports are those from 0 through 1023.
- The Registered Ports are those from 1024 through 49151.
- The Dynamic and Private Ports are those from 49152 through 65535.
A registered port is a network port assigned by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) and stored in /etc/services file. Use the cat command or grep command/egrep command to view port numbers and service mappings:
Display a list of applications and their ports assigned by IANA
Check open ports in Linux
The procedure to monitor and display open ports in Linux is as follows:
- Open a Linux terminal application
- Use ss command to display all open TCP and UDP ports in Linux.
- Another option is to use the netstat command to list all ports in Linux.
- Apart from ss / netstat one can use the lsof command to list open files and ports on Linux based system.
- Finally, one can use nmap command to check TCP and UDP ports too.
Let us see all commands and examples in details.
Using netstat to list open ports
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
- -t : All TCP ports
- -u : All UDP ports
- -l : Display listening server sockets
- -p : Show the PID and name of the program to which each socket belongs
- -n : Don’t resolve names
- | grep LISTEN : Only display open ports by applying grep command filter.
Use ss to list open ports
The ss command is used to dump socket statistics. It allows showing information similar to netstat. It can display more TCP and state information than other tools. The syntax is:
sudo ss -tulpn
Sample outputs:
Listening ports and applications using lsof command
Let us run the following to check open TCP and UDP ports using the lsof command:
sudo lsof -i -P -n | grep LISTEN
Where,
- -i : Look for listing ports
- -P : Inhibits the conversion of port numbers to port names for network files. Inhibiting the conversion may make lsof run a little faster. It is also useful when port name lookup is not working properly.
- -n : Do not use DNS name
- | grep LISTEN : Again only show ports in LISTEN state using the grep command as filter.
nmap command
In addition, to above commands one can use the nmap command which is an open source tool for network exploration and security auditing. We are going to use nmap to find and list open ports in Linux:
$ sudo nmap -sT -O localhost
$ sudo nmap -sU -O 192.168.2.254 ##[ list open UDP ports ]##
$ sudo nmap -sT -O 127.0.0.1 ##[ list open TCP ports ]##
$ sudo nmap -sTU -O 192.168.2.24
Sample outputs:
The open port doesn’t mean anyone from outside can access those ports
So far, you know how to find and list open TCP and UDP ports on Linux. However, those ports can still be blocked by software, cloud, or hardware firewall. Hence, you need to verify that your corporate firewall is not blocking incoming or outgoing access. For instance on Linux server we list or dump firewall rules using the following syntax:
sudo iptables -S
# IPv6
sudo ip6tables -S
Conclusion
In conclusion, finding out open ports is one of the most fundamental duties of a Linux system administrator for security reasons. Therefore, close down all unwanted ports and configure firewall such as UFW and FirewallD to open or block ports as per your requirements. After reading this tutorial, you should have a good understanding of how to check for open ports in Linux. See IANA’s offical list of TCP, UDP and other ports here for more information.
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
Источник
4 способа узнать, какие порты прослушиваются в Linux
Порт может в одном из следующих состояний: открыт (open), фильтруется (filtered), закрыт (closed), без фильтрации (unfiltered). Порт называется открытым если какое-либо приложение, служба на целевой машине прослушивает (listening) его в ожидании соединений/пакетов. Также по отношению к службе часто употребляют термин «привязка» (bind), который означает, что служба назначена к определённому порту, то есть после её запуска она будет прослушивать его, чтобы ответить на входящие запросы.
Термин «привязка» используют по отношению к службам, которые прослушивают порт на постоянной основе и готовы принять входящие соединения. Примером таких служб являются SSH, MySQL, веб-сервер. Некоторые приложения (например, веб-браузер) делают исходящие соединения. Для этих исходящих соединений обычно используется порт с номером в десятки тысяч, например, 37830 или 46392 или 54284 или что-то подобное. Но они используют порт на короткое время — только чтобы отправить запрос и получить ответ. Сразу после получения ответа программа освобождает порт. Если ей понадобится вновь сделать запрос, то она может выбрать любой другой незанятый порт — необязательно тот же самый. Такие порты не являются прослушивающими, то есть они не принимают внешние запросы на инициализацию соединения. Это состояние сокета называется ESTABLISHED, его нужно отличать от прослушивания порта (LISTENING), то есть от открытых портов.
В этой статье будут рассмотрены четыре способа проверить открытые порты, точнее говоря, какие порты прослушиваются в системе, а также показано вам как найти приложение (службу) прослушивающие определённый порт в Linux.
1. Используя команду netstat
Netstat — это широко применяемый инструмент для запроса информации о сетевой подсистеме Linux. Вы можете использовать её для показа всех открытых портов примерно так:

Флаг -l говорит netstat вывести все прослушивающие сокеты, -t означает показать все TCP соединения, -u для показа всех UDP соединений и -p включает показывать PID и имя программы/приложения, которое прослушивает порт.
Обратите внимание, что вместо номеров портов программа выводит имена популярных служб. Если вы хотите, чтобы порты были показаны как числа, то добавьте флаг -n.
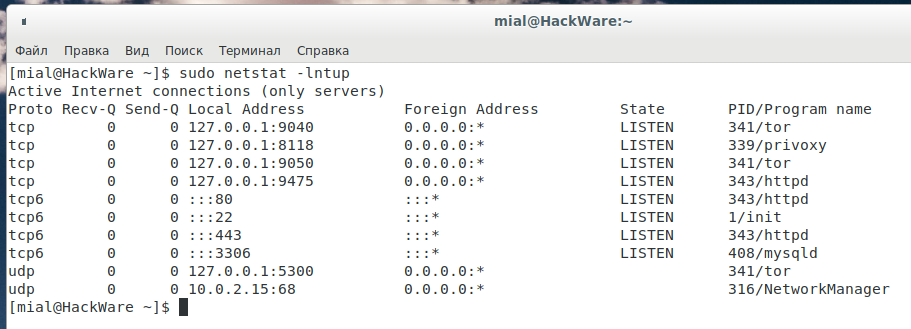
Вы также можете использовать команду grep для определения, какое приложение прослушивает определённый порт, например:
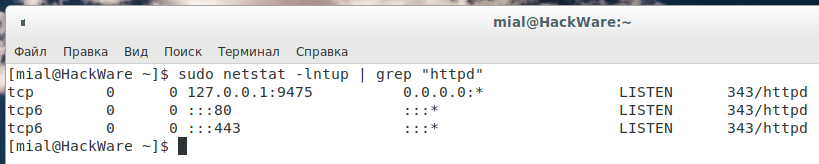
Можно искать не по имени службы, а по номеру порта, с помощью этого можно определить, какая служба привязана к определённому порту:

Если вам нужно чтобы данные постоянно обновлялись, то используйте ключ -c, тогда новые данные будут выводиться каждую секунду.
2. Используя команду ss
ss — это другой полезный инструмент для отображения информации о сокетах. Её вывод выглядит похоже с тем, какую информацию даёт netstat. В документации netstat сказано, что она в основном устарела и её заменой является как раз ss.
Следующая команда покажет все прослушиваемые порты для TCP и UDP соединений в виде цифровых значений:

Опции имеют такое же значение:
- -l означает показать только прослушивающие сокеты (по умолчанию они опускаются);
- -t означает показать TCP сокеты;
- -u означает показать UDP сокеты.
Если добавить ключ -p, то программа дополнительно покажет процессы, использующие сокет:
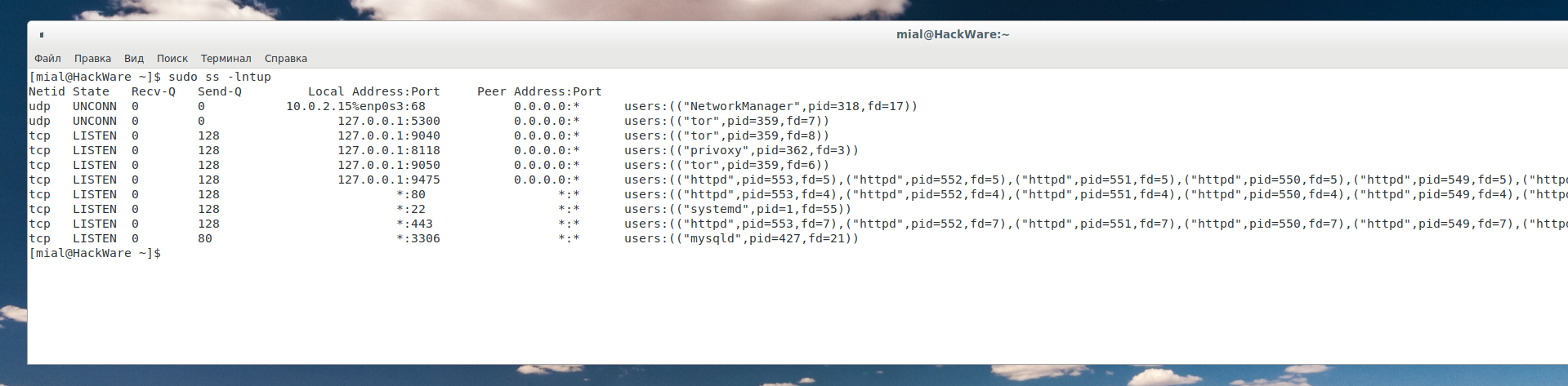
Программа очень детально показывает информацию по каждому процессу, в том числе выводит все подпроцессы, связанные с родительским. С одной стороны, это хорошо, так как информация исчерпывающая, но с другой, данных о процессах может быть слишком много и вывод становится трудно читаемым.
3. Используя программу Nmap
Nmap — это мощный и популярный инструмент исследования сети и сканер портов. Для установки nmap в вашу систему используйте стандартный менеджер пакетов как показано ниже.
На Debian/Ubuntu/Linux Mint:
На CentOS/RHEL:
На Fedora 22+:
На Arch Linux:
Для сканирования открытых/прослушиваемых портов на вашей системе Linux, запустите следующую команду (она может занять долгое время для завершения):
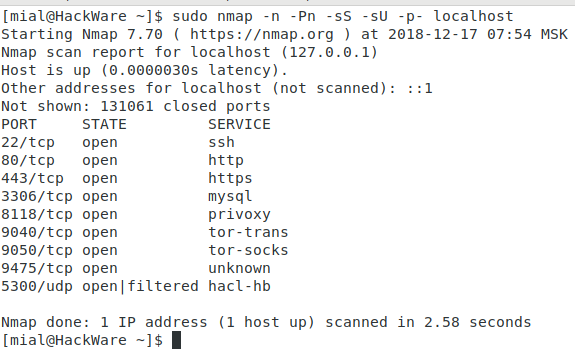
4. Используя команду lsof
Последний инструмент, который мы рассмотрим в этой статье, это команда lsof, которая используется для вывода списка открытых файлов в Linux. Поскольку в Unix/Linux всё является файлом, открытый файл может быть потоком или сетевым файлом.
Для вывода списка всех Интернет и сетевых файлов, используйте опцию -i. Помните, что эта команда показывает смесь имён служб и цифровых портов.
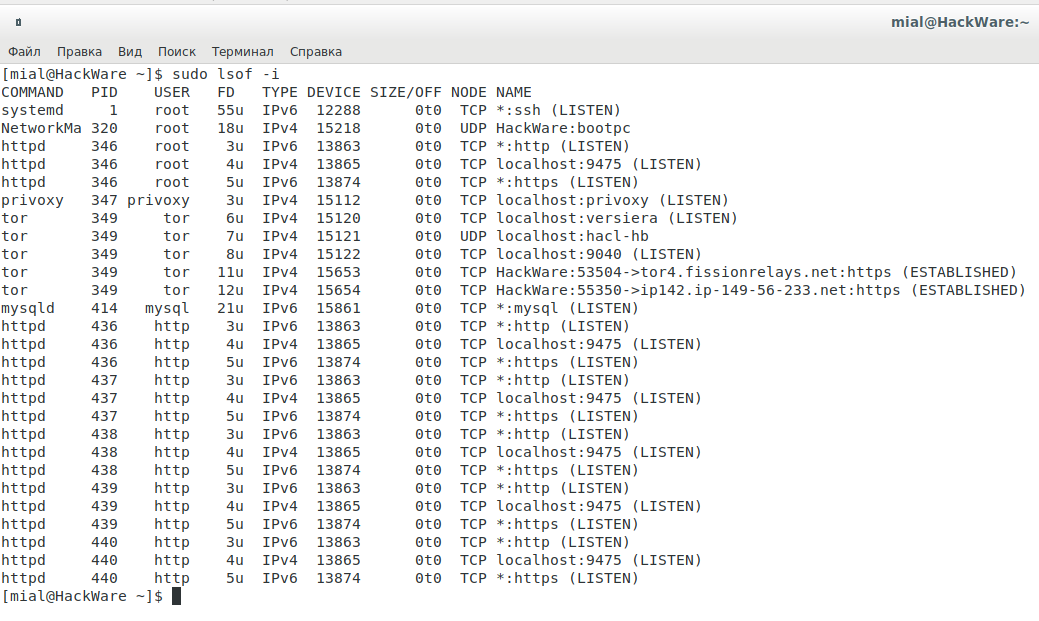
Чтобы найти, какое приложение прослушивает определённый порт, запустите lsof в следующей форме:
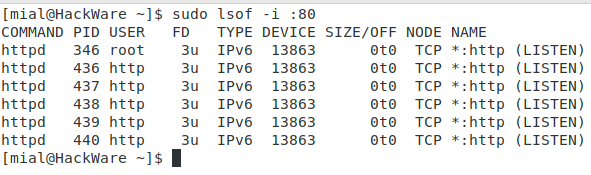
Вот и всё! В этой статье мы узнали четыре способа проверить открытые порты в Linux. Мы также показали, как проверить, какой процесс привязан к определённому порту.
О том, как правильно понимать вывод этих команд, смотрите статью «Что означают 0.0.0.0, :*, [::], 127.0.0.1. Как понять вывод NETSTAT».
Источник




