- How To Find Out Hard Disk Specs / Details on Linux
- Using lsblk command to find out hard disk information
- Linux show block device such as hard disk drive attributes
- hdparm Command
- lshw Command
- Finding Out Linux Disks Names Only
- Linux GUI Disk Utility
- The smartctl command
- A Note About RAID and SCSI Disks
- Conclusion
- 6 Different Ways to List Hard Drives in Linux
- Listing Hard Drives in Linux
- 2. fdisk
- 3. lsblk
- 4. cfdisk
- 5. parted
- 6. sfdisk
- How To Find Hard Disk Drive Details In Linux
- 1. Hdparm
- 1.1. Install hdparm on Linux
- 1.2. Find Hard Disk Drive details in Linux using Hdparm
- 2. lshw
- 2.1. Install lshw in Linux
- 2.2. Find Hard Disk Drive Details In Linux Using lshw
- 3. inxi
- 3.1. Install inxi in Linux
- 3.2. Find Hard Disk Drive Details In Linux Using Inxi
- 4. Smartctl
- 4.1. Find Hard Disk Drive Details In Linux Using Smartctl
- 5. Find Hard Disk Drive Details In Linux Using Lsblk
- 6. Find Hard Disk Drive Details In Linux Using Fdisk and Sfdisk Commands
- 7. Find Hard Disk Drive Details In Linux Using /proc
- 8. Hwinfo
- 8.1. Install Hwinfo In Linux
- 8.2. Find Hard Disk Drive Details In Linux Using Hwinfo
- 9. GNOME Disks
- 9.1. Find Hard Disk Drive Details In Linux Using GNOME Disks
How To Find Out Hard Disk Specs / Details on Linux
Using lsblk command to find out hard disk information
Run the lsblk command as follows to lists information about all available or the specified block devices:
# lsblk
# lsblk /dev/DISK
# lsblk /dev/sda
So I have two NVMe SSD in RAID-1 mode with encrypted partitions:
Another option is to run the following command to list all disks and their names:
# ls -lF /dev/disk/by-id/
Linux show block device such as hard disk drive attributes
Open the terminal app and then type the blkid command:
# blkid
hdparm Command
Open the terminal and type the following command to find information about /dev/sda:
# hdparm -I /dev/sda
OR
$ sudo hdparm -I /dev/sda
Sample outputs:
lshw Command
You need to install lshw command using apt-get or yum command. To display all disks and storage controllers in the system, enter:
# lshw -class disk -class storage
Sample outputs:
Finding Out Linux Disks Names Only
The following lshw command will quickly list installed disks including CD/DVD/BD drivers:
# lshw -short -C disk
Sample outputs:
Another option so to run the fdisk command as follows:
# fdisk -l
Use the grep command/egrep command to filter out loopback and other unwanted devices:
# fdisk -l | grep ‘^Disk /dev/’
# fdisk -l | grep ‘^Disk /dev/’ | egrep -v ‘/dev/(loop|mapper|md)’
Linux GUI Disk Utility
Gnome users can use the gnome-disk-utility/gnome-disks for the following purposes:
- Get information about installed disks and its current health.
- Manage and configure disk drives.
- Configure media.
- Set up software RAID devices and more.
Type the following command or start Disk utility by visiting Applications > System Tools > Disk Utility :
$ palimpsest
OR
$ gnome-disks
Sample outputs:
Fig.01: Linux List Hard Drives GUI Tool & Command — Click to enlarge
Fig.02: Samrtdata about hard disk
The smartctl command
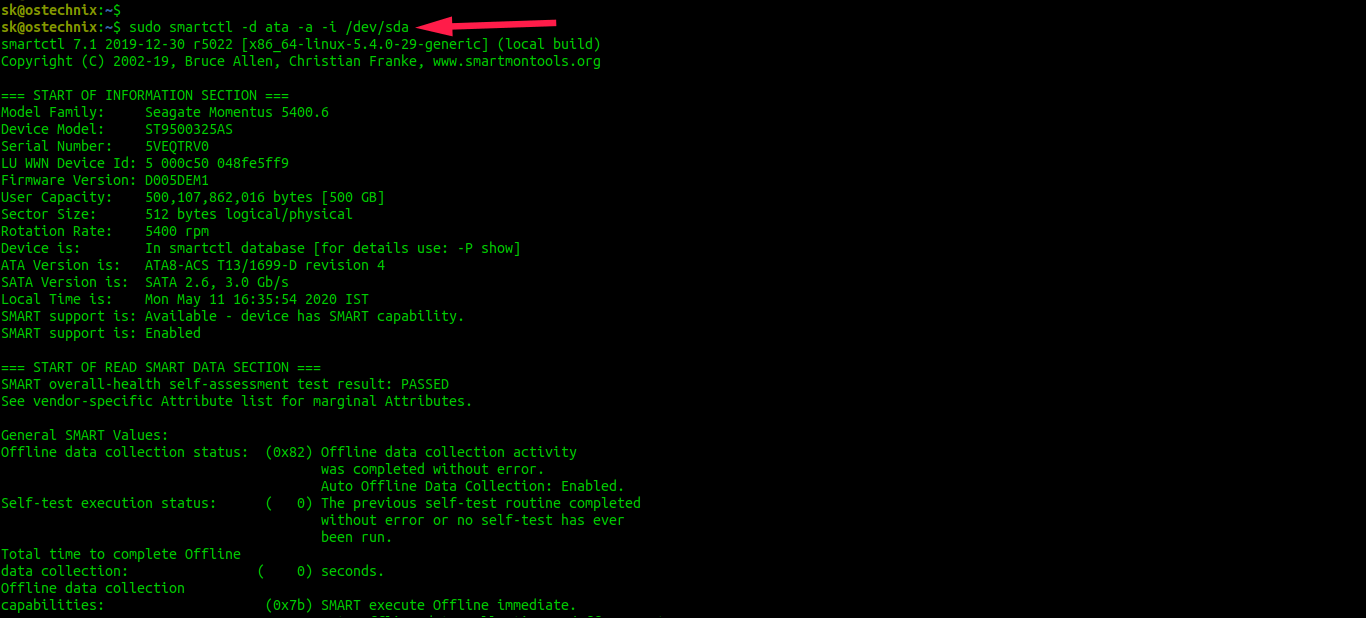
The smartctl command act as a control and monitor Utility for SMART disks under Linux and Unix like operating systems. Type the following command to get information about /dev/sda (SATA disk):
# smartctl -d ata -a -i /dev/sda
Sample outputs:
A Note About RAID and SCSI Disks
Try the following commands for SCSI and hardware RAID based devices:
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
- sdparm Command – fetch SCSI / SATA device information.
- scsi_id Command – queries a SCSI device via the SCSI INQUIRY vital product data (VPD).
- Use smartctl To Check Disk Behind Adaptec RAID Controllers
- Use smartctl Check Hard Disk Behind 3Ware RAID Card
Conclusion
You learned about finding hard disk drive infromation on Linux. To get more information about your hard disk, refer to our other articles and tutorials:
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
Источник
6 Different Ways to List Hard Drives in Linux
There are several ways to list all the hard drives present in a system through Linux command lines.
Keep in mind a hard drive could be physically connected, virtually connected or even emulated (for example: when you use storage devices such as EMC, Sun or IBM).
Here are some different commands which can list the hard drives, keep in mind there are others but these are probably the most commonly used and easy to get the job done.
Listing Hard Drives in Linux
Please note that some of these commands are actually disk partitioning tools and listing disk partition is one of their features.
Let’s see what commands you can use to show disk info in Linux.
The df command in Linux is probably one of the most commonly used. It lists the actual “disk space usage” and it can give you information about what hard disks (or current disk space) is being used in the entire system.
The most common way to use it is with the -h argument which means “human readable” (because we are not machines, right?):
As you can see, the first column is the current logic name (or the name you can find it within your system), the second column is how big is each of them, the third column is how much is currently used (in bytes), the fourth column is how much is currently available in each for usage (in bytes), the fifth column is how much is used (in %) and the sixth and last column is where is it physically mounted in your Linux system.
2. fdisk
fdisk is another common option among sysops. It currently lists the different partitions (which is related to hard drives as a hard drive can be divided into several partitions) in your system.
This will return the entire amount of space (in GB or MB), the entire amount of bytes and the entire amount of sectors per each partition and as a summary, it also gives you the start and end sectors, the amount of disk space (in Bytes) and the type of partition.
Tip: Usually a SATA disk is labelled with sd.
3. lsblk
This one is a little more sophisticated but gets the job done as it lists all block devices. It will give you a very simple list of all devices:
It is probably more visual than the others as it even shows the partitions per each disk in a visual way (like the sda in the example above). It also gives information about the total size per each partition and disk and the physical location for each. This is very commonly used when you need to mount things to be used (like a USB stick or similar) so you can know where is it in order to proceed to mount it.
4. cfdisk
cfdisk is probably the most advanced one in GUI (Graphical User Interface), as it is absolutely visual and interactive. It allows at first to list all disks/partitions in your system but it also allows you to manage them by selecting them and then applying actions such as “Delete”, “Resize”, “Type” (to change partition Type) and “Write” changes done to partitions.
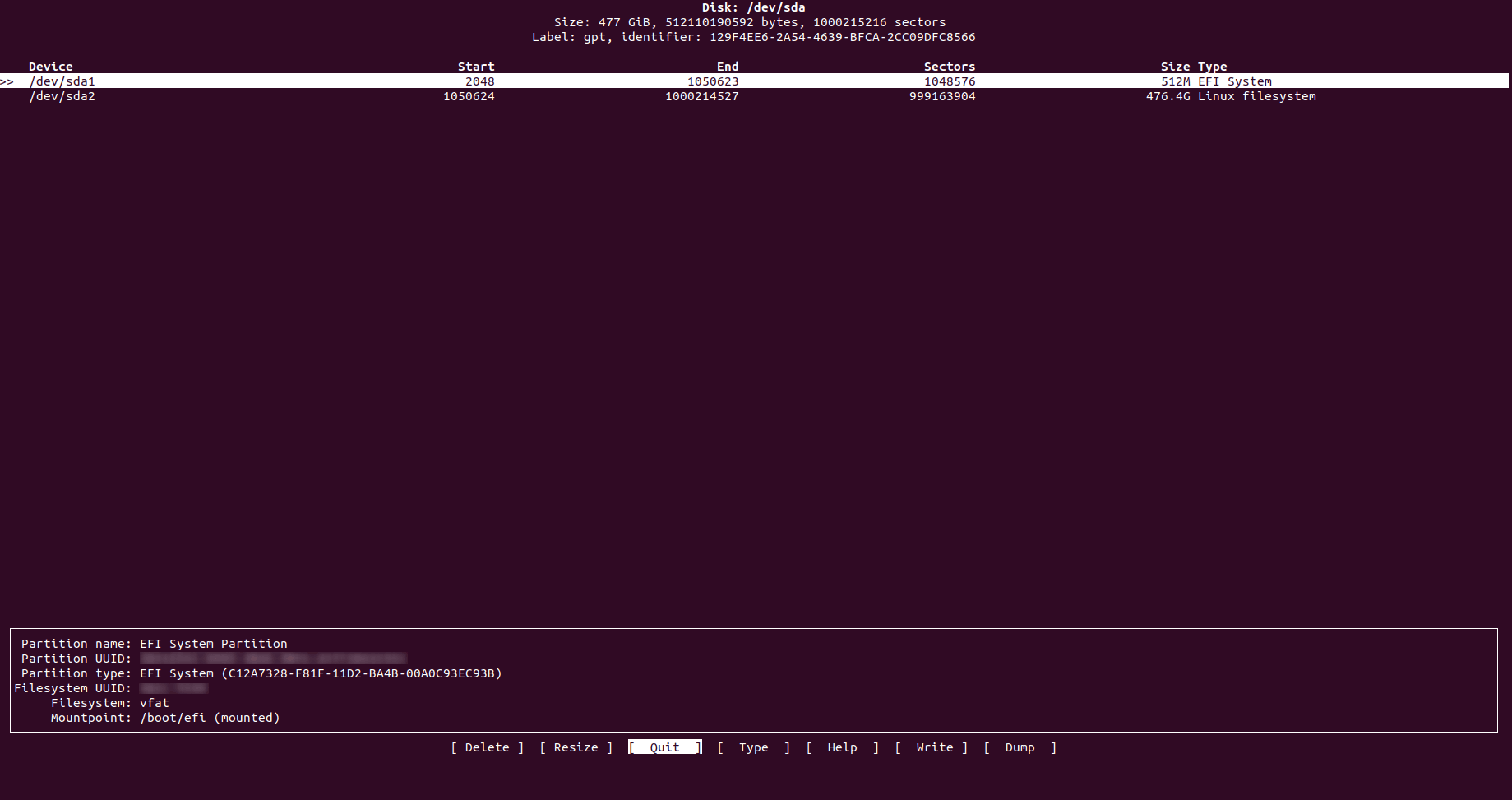
It also gives you very friendly information about each partition and disk as it gives you where does each partition cylinders start and ends, amount of sectors used by each one and the full size of each one with its type. It won’t give you for example how much is used or free to use.
5. parted
This one is similar to previous ones mentioned, it lists all partitions and allows to manage them. Its main difference is that it also informs you the brand and model of your hard disks and even the type of connectivity used in it (scsi, sata, etc) and total disk size.
6. sfdisk
This is very similar to fdisk, however sfdisk allows you to see both physical and logical volumes and also gives you a “summary” of the actual physical volumes’ partitions with the cylinders (start and end), sectors, size and type.
Probably the “s” is for “super”, as it is a fdisk with super powers:
These commands should allow you to at least see what logical volumes, partitions and hard drives you have in your system and make use of this information for whatever reason you need it, being this just to know more or manipulate any of these.
Most of these commands also give you managing capabilities to modify and manipulate partitions at your will, so make sure to use them with responsibility.
If you like checking system information, do read the article about getting processor information in Linux command line.
If you have any questions or suggestions, do let me know in the comment section.
Источник
How To Find Hard Disk Drive Details In Linux
This guide lists various methods to find Hard disk drive details in Linux operating systems. Using the below methods, you can able to find the hard disk make, hard disk type, size, firmware version, partition tables and other hardware parameters. First, we will see how to display hard disk details with hdparm command line utility.
1. Hdparm
Hdparm is a command line program to get or set hardware parameters for PATA, SATA, SAS and SSD devices.
It accepts any device as mass storage that is connected to IDE, SATA, SAS interfaces, so we can even retrieve information about CD/DVD drives as well.
Using hdparm utility, we can tune the hard disk or DVD drive, test the HDD or SSD speed, reduce noise level by activating acoustic mode, turn energy-saving mode on or off, enable or disable sleep mode, enable/disable drive cache and even erase drives securely.
Hdparm is written by Mark Lord, the lead developer and maintainer of the (E)IDE driver for Linux, and current contributor to the «libata» subsystem.
A word of caution
Even though hdparm offers significant advantages to increase disk performance, it is also EXTREMELY DANGEROUS . It will very likely lead to massive data loss when some parameters are misused. The hdparm documentation suggests that YOU SHOULD NOT USE SOME COMMANDS AT ANY CIRCUMSTANCES . So I’ve excluded such dangerous commands in this guide. More importantly, It is always recommended to backup your hard drive before testing hdparm on your Linux system.
1.1. Install hdparm on Linux
Hdparm comes pre-installed in most Linux distributions. If it is not included for any reason, install hdparm on your Linux system using the default package manager.
On Arch Linux, Manjaro Linux:
On Debian, Ubuntu, Linux Mint:
On Fedora, CentOS, RHEL:
1.2. Find Hard Disk Drive details in Linux using Hdparm
To display detailed information of the hard disk, simply run hdparm with sudo or root privileges as shown below:
Here, sda is my hard disk. Replace it with your own device. Here I have used «less» command for interactive reading. Press ENTER key or hit UP/DOWN arrows to go through the rest of the output. Press q to exit when done.
Sample output from my Ubuntu system:
As you can see, the hdparm displays the hard disk’s model number, serial number, firmware revision followed by hard disk configuration (no of cylinders, heads, sectors), DMA settings, list of enabled features, security parameters etc. All functions found under «Commands/features» section and marked with an asterisk are currently active.
Similarly, you can check information of other devices.
When running hdparm with no options, -acdgkmur is assumed. Refer man pages to know what each option is for.
For more details, refer man pages.
2. lshw
Lshw (Hardware Lister) is a simple, yet full-featured utility that provides detailed information on the hardware configuration of a Linux system. It can report exact memory configuration, firmware version, mainboard configuration, CPU version and speed, Hard disk drive details, cache configuration, bus speed and a lot more.
2.1. Install lshw in Linux
lshw comes pre-installed with some Linux distributions like Ubuntu by default. If it is not installed by any chance, install lshw in your Linux box using the default package manager like below.
On Arch Linux and its variants like Manjaro Linux, run:
On Debian, Ubuntu, Linux Mint:
On Fedora, CentOS, RHEL:
2.2. Find Hard Disk Drive Details In Linux Using lshw
After installing lshw, simply run the following command to get the details of your hard disk drive in Linux:
Sample output:
To display only the name of the disks, run:
Sample output:
For more details, check man pages.
3. inxi
Inxi is yet another full-featured command line system information tool. It shows system hardware, CPU, drivers, Xorg, Desktop, Kernel, GCC version(s), Processes, RAM usage, and a wide variety of other useful information. Be it a hard disk or CPU, mother board or the complete detail of the entire system, inxi will get them for you more accurately in seconds.
3.1. Install inxi in Linux
Inxi is also available in the default repositories of most Linux distributions.
For Arch Linux, it is available in AUR. You can install it using any AUR helper programs, for example Yay.
On Debian, Uubntu:
On CentOS and RHEL:
Enable [EPEL] repository using the following command:
3.2. Find Hard Disk Drive Details In Linux Using Inxi
To get the details of the installed hard disk drives in your Linux system, run:
Sample output:
You can also display more disk details like disk controller speed, serial no and temperature using the following command:
Sample output:
Unlike Hdparm and lshw programs, it will only display the hard disk drive details. The hdparm and lshw utilities will display all drive details including CD/DVD ROM.
For more details, refer man pages.
Suggested read:
4. Smartctl
Smartclt is a command line, control and monitor utility for SMART disks. It controls the Self-Monitoring, Analysis and Reporting Technology (shortly SMART) system built into most ATA/SATA and SCSI/SAS hard drives and solid-state drives. Smartclt command is part of the smartmontools package, which comes pre-installed in most Linux versions.
4.1. Find Hard Disk Drive Details In Linux Using Smartctl
To fetch the complete details about the hard disk drive in your Linux box, run:
Sample output:
For more details, refer man pages.
5. Find Hard Disk Drive Details In Linux Using Lsblk
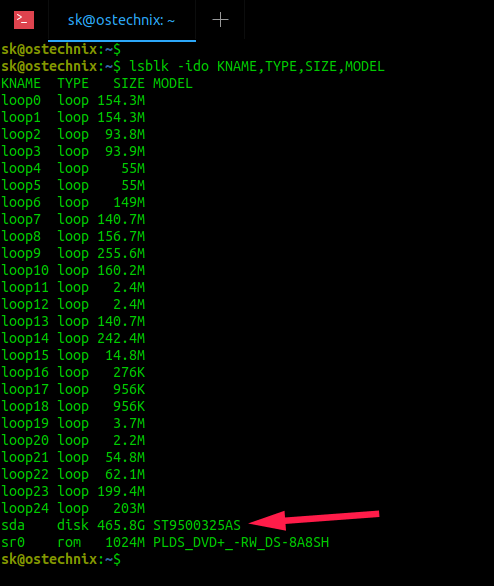
Lsblk is a command line utility to display all available or the specified block devices in Unix-like operating systems. It reads the «sysfs» filesystem and «udev db» to gather information. The lsblk command is part of the «util-linux» package, which comes pre-installed in most Linux distributions.
To display all block devices using lsblk command, run:
Sample output:
You can even display more details including filesystem type, UUID, Mountpoint etc., like below:
Sample output:
If you want to display only the physical devices, use «-d» flag.
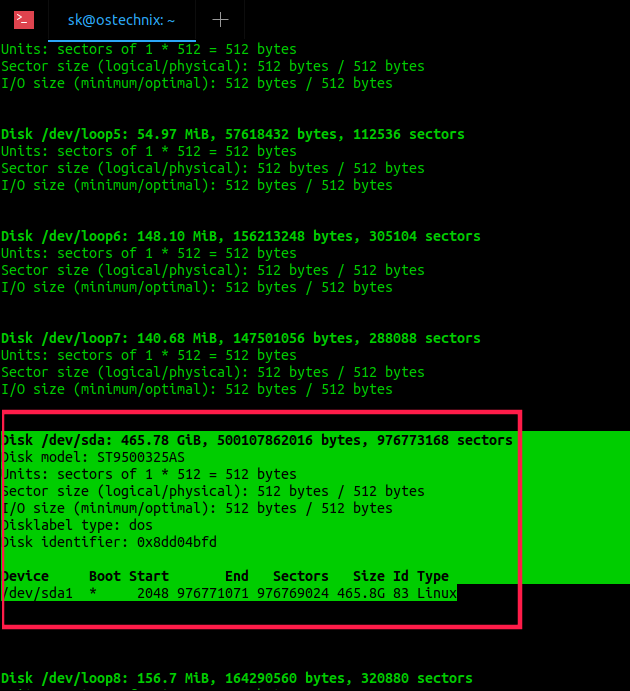
6. Find Hard Disk Drive Details In Linux Using Fdisk and Sfdisk Commands
Fdisk and Sfdisk commands are used to create and manipulate partition tables. fdisk is a dialog-driven program for creating and manipulating partition tables whereas sfdisk is a script-oriented tool for partitioning any block device. Both are part of util-linux package which comes pre-installed in all Linux distros.
To get the HDD details, run fdisk as root or sudo user with «-l» flag:
Sample output:
The usage of Sfdisk is same as fdisk. To list HDD details using Sfdisk, run it with -l flag with root or sudo privileges:
To exclude the details of dm (device mapper) devices from the output, run:
Sample output:
7. Find Hard Disk Drive Details In Linux Using /proc
The /proc is a special virtual filesystem in Unix-like distributions. It is also known as process information pseudo-file system. It doesn’t contain any ‘real’ files but runtime system information such as processes, system memory, mounted devices and hardware configuration etc. Each device details are stored in a separate directory under /proc directory. The storage devices’ details will be available in «/proc/scsi/scsi» file.
Sample output:
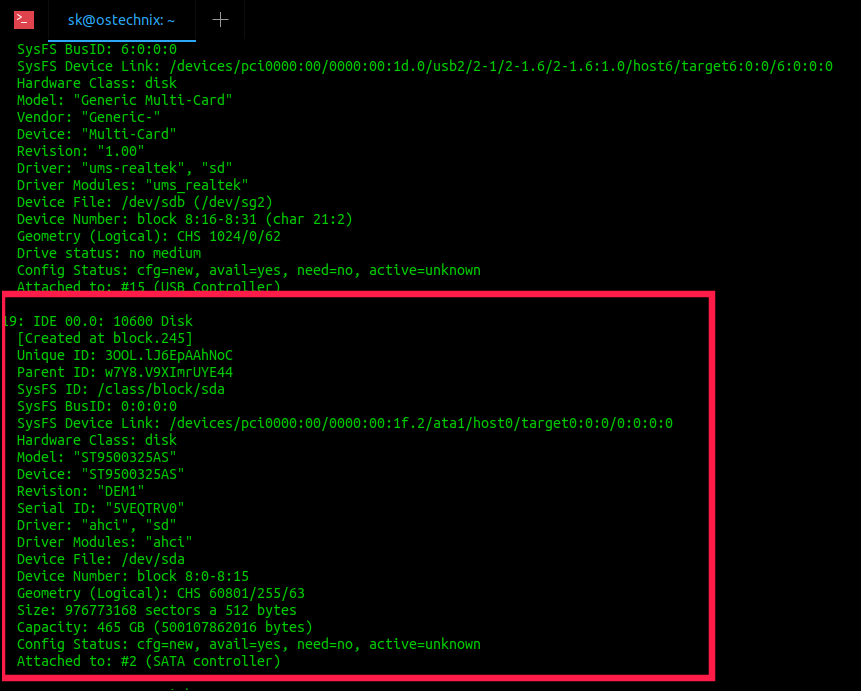
8. Hwinfo
Hwinfo is a free, open source and command line utility to find Linux system hardware information. It probes for the hardware present in a Linux system and displays the extensive details of each hardware device. It uses libhd.so library to gather details of almost all hardware such as BIOS, CPU, Architecture, Memory, Hard Disk(s), Partitions, Camera, Bluetooth, CD/DVD drives, Keyboard/Mouse, Graphics card, Monitor, Modem, Scanner, Printer, PCI, IDE, SCSI, Sound card, Network interface card, USB and a lot more.
8.1. Install Hwinfo In Linux
Refer the following link to install Hwinfo in your Linux system.
8.2. Find Hard Disk Drive Details In Linux Using Hwinfo
To find Hard disk drive details using Hwinfo, run:
Sample output:
Or you can display the short summary of the disk details:
Sample output:
9. GNOME Disks
Disks or Gnome-disk-utility is a graphical user interface program to view, modify and configure available storage devices and media in a Linux system. If you are not comfortable with command line way, you can use use GNOME Disks to create and restore disk images, partition and format drives, inspect drive speed, benchmark drives and check health status etc. It comes pre-installed in all Linux distributions that has GNOME desktop environment.
9.1. Find Hard Disk Drive Details In Linux Using GNOME Disks
Launch Disks either from Menu or Dash. It lists all available disks and media in your Linux system.
Источник