- How to execute .bin and .run files in Debian
- Executing .bin and .run files
- Karim Buzdar
- Execute Binary Files In Linux
- ‘sudo’ Command
- Running Binary Types (.bin and .run)
- User Interface Option
- Terminal Option
- Conclusion
- How to Install or Execute a .bin File in Ubuntu Linux
- What is Bin file?
- Install Or Execute Bin File
- Conclusion
- How to execute .bin and .run files in Debian
- Executing .bin and .run files
- Karim Buzdar
- How to execute a .run or .bin file in CentOS 8
- Execute .bin/.run file in CentOS 8
- Conclusion
- Karim Buzdar
How to execute .bin and .run files in Debian
Before explaining how to execute .bin and .run files on your Debian, let us first define what exactly these file extensions are:
Bin File: A Binary or BIN file in Debian refers to installation packages that are mostly self-extracting executables for installing software on your system. Although most software can be installed through the Debian Software Manager, from .deb packages, and .tar.xz packages, there is software that is not available in these formats. These mostly include newer software and newer versions, mostly beta, of software that is not available otherwise. The bin packages can easily be executed/run using the Debian command line, the Terminal.
Run File: These are also executable files typically used for Linux program installers. Run Files contain program data and instructions for making the installation; often used for distributing device drivers and software applications.
In this article, we will explain how to execute/run the file with .run and .bin extensions on Debian Linux.
We have run the commands and procedures mentioned in this article on a Debian 10 Buster system. We will be using the Debian command line, the Terminal, in explaining how to run bin and run files. You can open the Terminal application easily through the system application launcher search. Simply click the Super/Windows key and then enter Terminal in the search bar as follows:
Note: Please make sure your .run and .bin files come from a reliable source, as executing an insecure file can damage your system and even compromise your system security.
Executing .bin and .run files
The process of running both the .run and .bin files is pretty simple and straightforward in Debian.
We are assuming that your bin/run file is already downloaded in a known location on your system.
Open the Terminal application and move to the location where you have saved the executable file.
For example, I would use the following command to move to my Downloads folder:
Now use the following command to make your .bin/,run file executable: Advertisement
In this example, I will be making a sample .run file named samplefile.run executable.
If your .run/.bin file does not exist in the current location, you can specify the exact file path/location in the above commands.
Please enter the password for sudo if your system asks for it.
My file will now be marked as executable. This is indicated by a change in the color of the filename when listed through the ls command:
Once your .bin/.run file has become executable, you can use the following command to execute it:
You can specify the path of the executable file in the above command if it does not exist in the current folder you are in.
My sample file is pretty much an empty file. In case of a proper installation package, the installation process will begin after you execute the file.
This is the power of the Debian command line. You can install rare software packages available in the .run and .bin formats easily on your system.
Karim Buzdar
About the Author: Karim Buzdar holds a degree in telecommunication engineering and holds several sysadmin certifications. As an IT engineer and technical author, he writes for various web sites. You can reach Karim on LinkedIn
Источник
Execute Binary Files In Linux
Linux has many format options for running applications from deb to rpm and the new formats snap and flatpak. Binary files can be in .bin or .run formats and although this can be easy to install it can be hard to remove and need an extra trick and a little experience to complete the removal.
Some of the .bin and .run files need root privileges to install or run the applications. For being able to install the applications you need to run it with sudo command.
‘sudo’ Command
Sudo permits the user to execute a command as a superuser (with higher privileges or root permissions).
On the example below, you can notice that trying to update using the terminal without root privileges gives you a permission error message. 
Running Binary Types (.bin and .run)
There are two ways to run binary applications, one is through the user interface and the other is going to the terminal.
User Interface Option
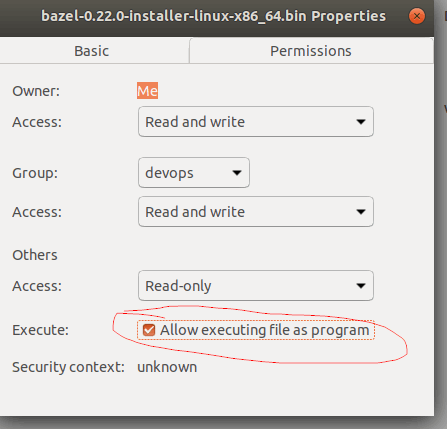
To Install using the user interface, first, you need to make the file executable. To make the file executable first, right-click on the binary file and then properties and go to permissions. On Permissions thick the checkbox with the option allows executing the file as program close the program and double click on the binary. If the file doesn’t run, just right-click on it and select run on the terminal to execute it.
Sometimes when you run the binary it takes a while to execute it if the file size is big. So be patient and wait for it. If it doesn’t try running it from terminal.
Terminal Option
To run it through terminal it’s not a hard task either. For being able to run it just make the file executable using chmod +x app-name.bin command and then execute it with ./app-name.bin.
Note that if the application doesn’t run with an error message permission denied with normal privileges you may need to use sudo ./app-name.bin 
Conclusion
Linux has many options for running or installing applications which is one of the good things of Open Source, binary files are just one out there. There are snap packages, Flatpak, deb and many more, some applications are available on these formats so it’s up to choose which one you prefer.
Источник
How to Install or Execute a .bin File in Ubuntu Linux
This post will guide you how to install .bin file on Ubuntu 14.04/16.04/18.04 Linux. How do I execute a .bin file using SSH on Ubuntu Linux server. How to execute binary files on Ubuntu Linux.
What is Bin file?
Binary Files can be in .bin or .run files under Ubuntu Linux. and the .bin or .run is the only file types, and you need to mark as executable permission to install it on your Ubuntu system. You can install it either in terminal or through GUI.
Install Or Execute Bin File
This guide will introduce two methods to install executable file under Ubuntu Linux. And executable files can also be recognized by the extension .bin and .run.
Terminall Installation
Here are the steps to install .bin files via terminal on Ubuntu:
#1 you need to download the .bin file that you want to install.
#2 Open a terminal window by clicking the Ubuntu terminal icon located on the Launcher taskbar. and then searching for “Terminal” and then clicking Terminal icon on the result page. or you can right click on the desktop, and select Terminal from the popup menu list to open one terminal window.
#3 change the current directory to your directory where the executable file is stored. for example, you have downloaded .bin files into the /tmp directory. Then type the following command:
#4 You need to mark the file permission as executable with the following chmod command, type:
Then type the required password for root, and press Enter key. And the file can be executed by the current user with root privileges now.
#5 the bin file can be run in the terminal by typing the following command:
If you hit an error message such as “permission denied”, and you can try to execute the file by adding sudo before the above command.
GUI Installation
You can also install the executable binary files via Ubuntu Desktop GUI. Here are the steps:
#1 Click the Files icon on the Ubuntu Launcher to start the File Manger and then change to the directory in which the executable file is stored.
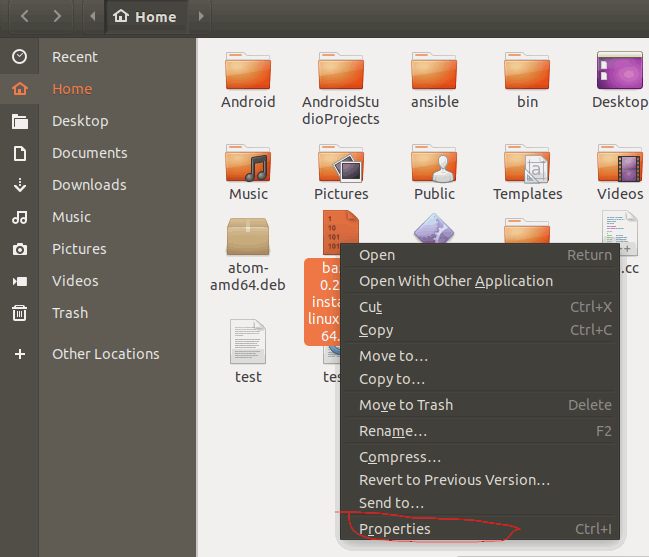
#2 right click on the BIN file and select Properties from the popup menu list, and the Properties dialog will appear. then switch to Permissions tab, and check the Allow Executing File as Program. then click the Close button.
#3 double-click on the .run or .bin file. and if there is no any action appears to be happening, and you need to run it in the terminal.
Conclusion
You should know that how to install the executable binary file (.bin or .run) on your Ubuntu 14.04 or 16.04 or 18.04 Linux from this guide.
Источник
How to execute .bin and .run files in Debian
Before explaining how to execute .bin and .run files on your Debian, let us first define what exactly these file extensions are:
Bin File: A Binary or BIN file in Debian refers to installation packages that are mostly self-extracting executables for installing software on your system. Although most software can be installed through the Debian Software Manager, from .deb packages, and .tar.xz packages, there is software that is not available in these formats. These mostly include newer software and newer versions, mostly beta, of software that is not available otherwise. The bin packages can easily be executed/run using the Debian command line, the Terminal.
Run File: These are also executable files typically used for Linux program installers. Run Files contain program data and instructions for making the installation; often used for distributing device drivers and software applications.
In this article, we will explain how to execute/run the file with .run and .bin extensions on Debian Linux.
We have run the commands and procedures mentioned in this article on a Debian 10 Buster system. We will be using the Debian command line, the Terminal, in explaining how to run bin and run files. You can open the Terminal application easily through the system application launcher search. Simply click the Super/Windows key and then enter Terminal in the search bar as follows:
Note: Please make sure your .run and .bin files come from a reliable source, as executing an insecure file can damage your system and even compromise your system security.
Executing .bin and .run files
The process of running both the .run and .bin files is pretty simple and straightforward in Debian.
We are assuming that your bin/run file is already downloaded in a known location on your system.
Open the Terminal application and move to the location where you have saved the executable file.
For example, I would use the following command to move to my Downloads folder:
Now use the following command to make your .bin/,run file executable: Advertisement
In this example, I will be making a sample .run file named samplefile.run executable.
If your .run/.bin file does not exist in the current location, you can specify the exact file path/location in the above commands.
Please enter the password for sudo if your system asks for it.
My file will now be marked as executable. This is indicated by a change in the color of the filename when listed through the ls command:
Once your .bin/.run file has become executable, you can use the following command to execute it:
You can specify the path of the executable file in the above command if it does not exist in the current folder you are in.
My sample file is pretty much an empty file. In case of a proper installation package, the installation process will begin after you execute the file.
This is the power of the Debian command line. You can install rare software packages available in the .run and .bin formats easily on your system.
Karim Buzdar
About the Author: Karim Buzdar holds a degree in telecommunication engineering and holds several sysadmin certifications. As an IT engineer and technical author, he writes for various web sites. You can reach Karim on LinkedIn
Источник
How to execute a .run or .bin file in CentOS 8
There are some files that we are downloaded from the internet that have extensions of .bin or .run. To run such files, we have to set the permission to execute those files. A .bin or .run file is a self-extracting binary file in Linux and Unix Operating systems. For example, Java and Flash are two examples of such files. In this tutorial, we will learn how to run .bin and .run extension files. So let’s get started.
Execute .bin/.run file in CentOS 8
Firstly, set the permission of the file which you have downloaded. For this open up the terminal and type the following command:
I have downloaded a file from the internet (file.run), to execute that file. Firstly, we need to set the permission to execute, as shown in the figure.
You can also set the executable permission, by navigating to the properties of that file, as shown in the figures:
In the properties, click on the permissions tab appear at the top and click on the checkbox (Allow executing file as program) as shown below.
To run/execute this file open up the terminal and type the following command:
The same method described above is used to execute the .bin file.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we learned how to set the permissions of .bin and .run files and how to execute these files in CentOS 8. I hope this tutorial will help you to set the permission of such executable files and how to execute them.
Karim Buzdar
About the Author: Karim Buzdar holds a degree in telecommunication engineering and holds several sysadmin certifications. As an IT engineer and technical author, he writes for various web sites. You can reach Karim on LinkedIn
Источник