- 3 Command Line Tools to Install Local Debian (.DEB) Packages
- 1. Install Software Using Dpkg Command
- 2. Install Software Using Apt Command
- 3. Install Software Using Gdebi Command
- If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
- Linux how to install deb package
- Install/Uninstall .deb files
- Convert .rpm files to .deb files
- Установка deb пакетов в Ubuntu
- Где взять deb пакеты?
- Установка deb пакетов Ubuntu
- Выводы
- 3 Ways to Install Deb Files on Ubuntu [& How to Remove Them Later]
- Installing .deb files on Ubuntu and Debian-based Linux Distributions
- Method 1: Use the default Software Center
- Troubleshoot: Double clicking deb file doesn’t open in software center in Ubuntu 20.04
- Method 2: Use Gdebi application for installing deb packages with dependencies
- Method 3: Install .deb files in command line using dpkg
- How to remove deb packages
- Method 1: Remove deb packages using apt command
- Method 2: Remove deb packages using dpkg command
3 Command Line Tools to Install Local Debian (.DEB) Packages
In this tutorial we will learn how to install local software packages (.DEB) in Debian and its derivatives such as Ubuntu and Linux Mint using three different command line tools and they are dpkg, apt and gdebi.
This is useful to those new users who have migrated from Windows to Ubuntu or Linux Mint. The very basic problem they face is installing local software on system.
However, Ubuntu and Linux Mint has its own Graphical Software Center for easy software installation, but we will be looking forward to installing packages through terminal way.
1. Install Software Using Dpkg Command
Dpkg is a package manager for Debian and its derivatives such as Ubuntu and Linux Mint. It is used to install, build, remove and manage .deb packages. but unlike other Linux package management systems, it cannot automatically download and install packages with their dependencies.
To install a local package, use the dpkg command with the -i flag along with package name as shown.

If you get any dependency errors while installing or after installing and launching a program, you can use the following apt command to resolve and install dependencies using the -f flag, which tells the program to fix broken dependencies.
To remove a package use -r option or if you want to remove all its files including configuration files, you can purge it using the —purge option as shown.

To know more about installed packages, read our article that shows how to list all files installed from a .deb package.
2. Install Software Using Apt Command
The apt command is a advanced command-line tool, which offers new software package installation, existing software package upgradation, updating of the package list index, and even upgrading the whole Ubuntu or Linux Mint system.
It also offers apt-get and apt-cache command-line tools for managing packages more interactively on Debian and its derivatives such as Ubuntu and Linux Mint systems.
Essentially, apt-get or apt do not understand .deb files, they are designed to primarily handle package names (for example teamviewer, apache2, mariadb etc..) and they retrieve and install .deb archives associated with a package name, from a source specified in the /etc/apt/sources.list file.
The only trick to installing a local Debian package using apt-get or apt is by specifying a local relative or absolute path ( ./ if in current dir) to the package, otherwise it will try to retrieve the package from remote sources and the operation will fail.


To remove a package use remove option or if you want to remove all its files including configuration files, you can purge it using the purge option as shown.
3. Install Software Using Gdebi Command
gdebi is a tiny command-line tool for installing local deb packages. It resolves and installs package dependencies on the fly. To install a package, use the following command.

To remove a package installed from gdebi, you can use apt, apt-get or dpkg commands using purge option as shown.
That’s It! In this tutorial, we have explained three different command line tools for installing or removing local Debian packages in Ubuntu and Linux Mint.
If you know any other way of installing local packages, do share with us using our comment section below.
If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
TecMint is the fastest growing and most trusted community site for any kind of Linux Articles, Guides and Books on the web. Millions of people visit TecMint! to search or browse the thousands of published articles available FREELY to all.
If you like what you are reading, please consider buying us a coffee ( or 2 ) as a token of appreciation.
We are thankful for your never ending support.
Источник
Linux how to install deb package
Although the preferred method of installing programs is via the package managers described in ChapterВ 3, Adding, Removing and Updating Applications, you can also download and install individual package files containing software. There are many different kinds of Linux package files. Most of these are associated with the package managers of specific Linux distributions.
If you find a packaged application that you wish to install, it is recommended that you check if there is a native Kubuntu package of the application available through a package manager, and that you install that version instead. This guarantees that the program is completely compatible with your system. If there is no package available through the package manager, you can install it manually. The installation procedure depends on the type of package file.
Install/Uninstall .deb files
The package files associated with Kubuntu have the .deb suffix because of Kubuntu’s close relation to the Debian GNU/Linux distribution. You can download and install individual .deb files. You will need administrative privileges to do this (see the section called “Root And Sudo”).
To install a .deb file, simply Right click on the .deb file, and choose Kubuntu Package Menu -> Install Package .
Alternatively, you can also install a .deb file by opening a terminal and typing:
To uninstall a .deb file, remove it using Adept , or type:
Convert .rpm files to .deb files
Another type of package files is Red Hat Package Manager Files which have the .rpm suffix. It is not recommended to install these on an Kubuntu system. In almost all cases, a native Kubuntu .deb package is available. However, if absolutely necessary, an .rpm file can be converted to a .deb package using the program alien .
Run the following command in a terminal, with administrative privileges:
Источник
Установка deb пакетов в Ubuntu
Установка новых программ — один из самых важных моментов при работе с вашей системой. Раньше мы уже рассматривали добавление PPA в систему и установку программ из исходников. Но даже в PPA есть далеко не все пакеты, а установка из исходников слишком сложна для новичков.
Нередко возникает необходимость поставить программу, для которой уже есть собранные deb пакеты в интернете. Это может быть какая-нибудь не очень популярная программа или даже драйвера, которые вы скачали и хотите установить на компьютер где нет сети. На компьютере без сети установка программ с флешки ubuntu может стать единственным решением. В этой статье будет рассмотрена установка deb пакетов в ubuntu. Мы рассмотрим где их взять и как установить deb в ubuntu.
Где взять deb пакеты?
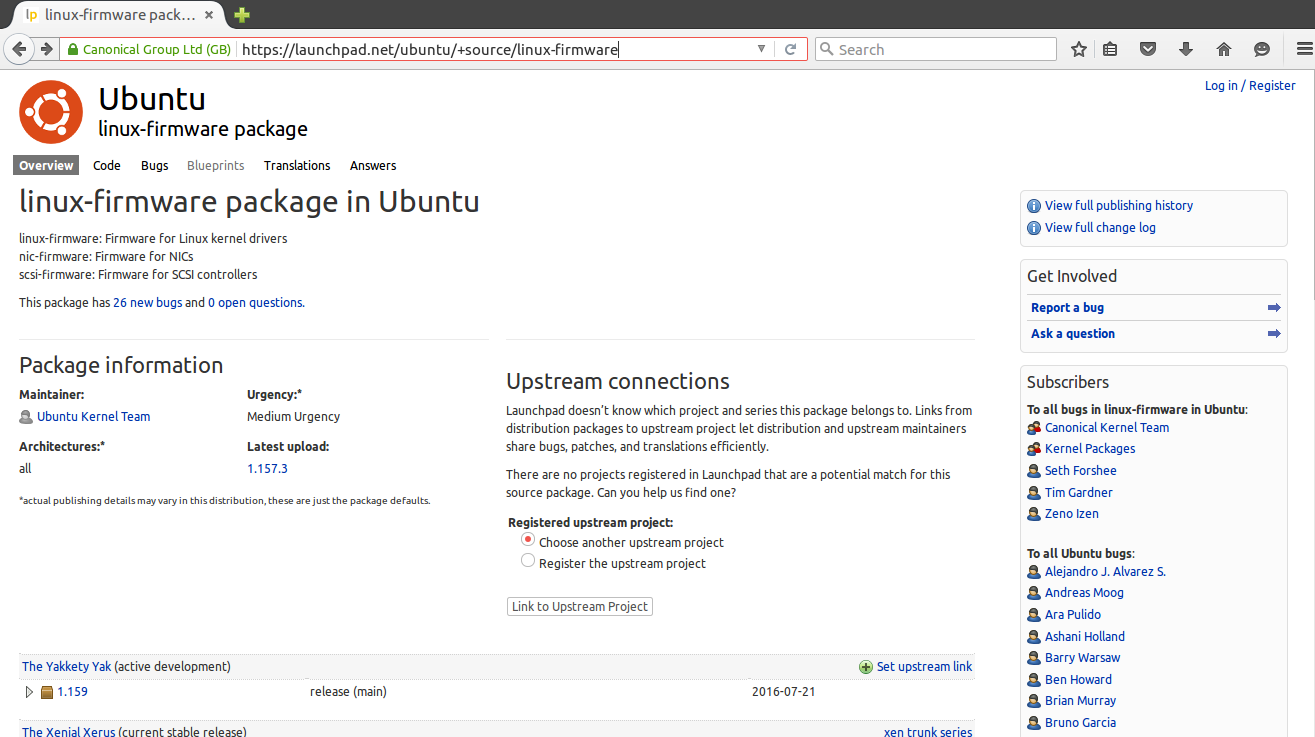
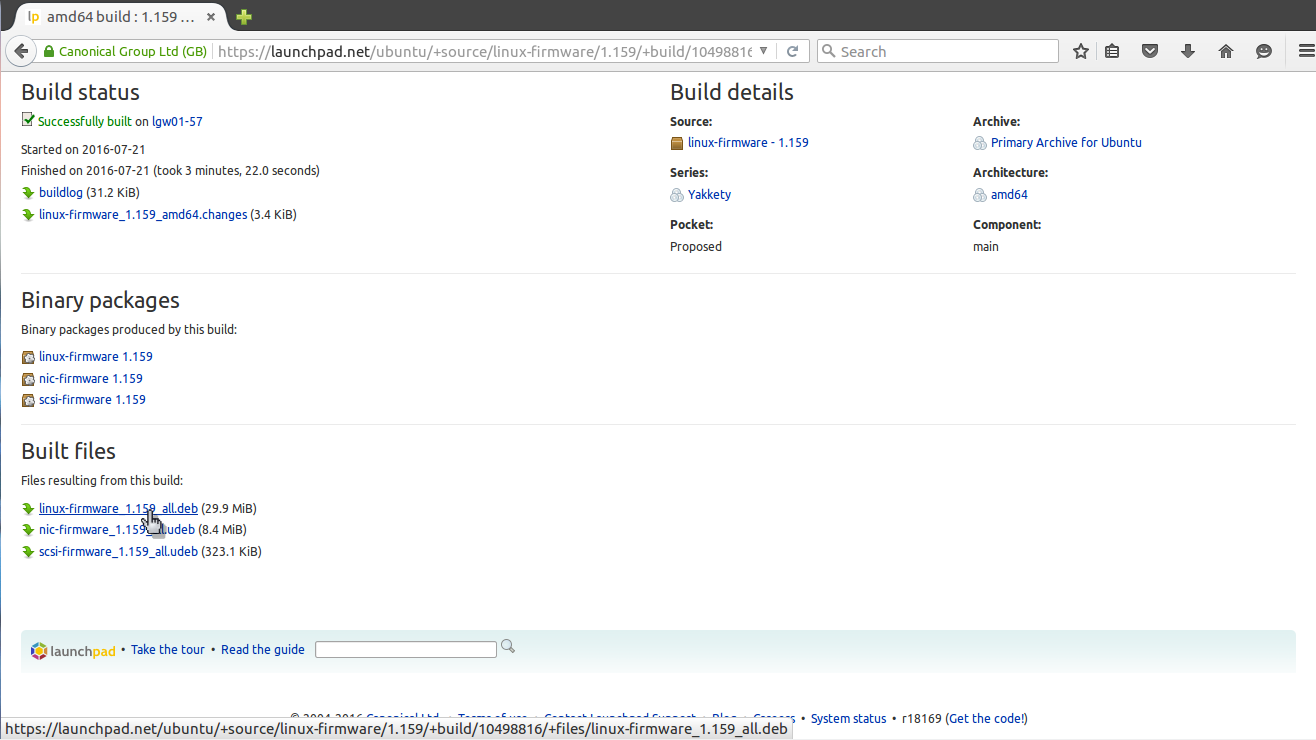
Ответ прост — на просторах интернета. Если это нужная вам программа, то вы уже знаете где взять для ее пакет. В случае с драйверами ситуация немного сложнее. Все программы и драйвера, которые находятся в официальных репозиториях Ubuntu вы можете найти на сайте launchpad.net, это очень удобно, если на машине, где они должны быть установлены нет интернета. Например, ищем linux-firmware и открываем ее страницу на Launchpad, внизу выбираем версию программы:
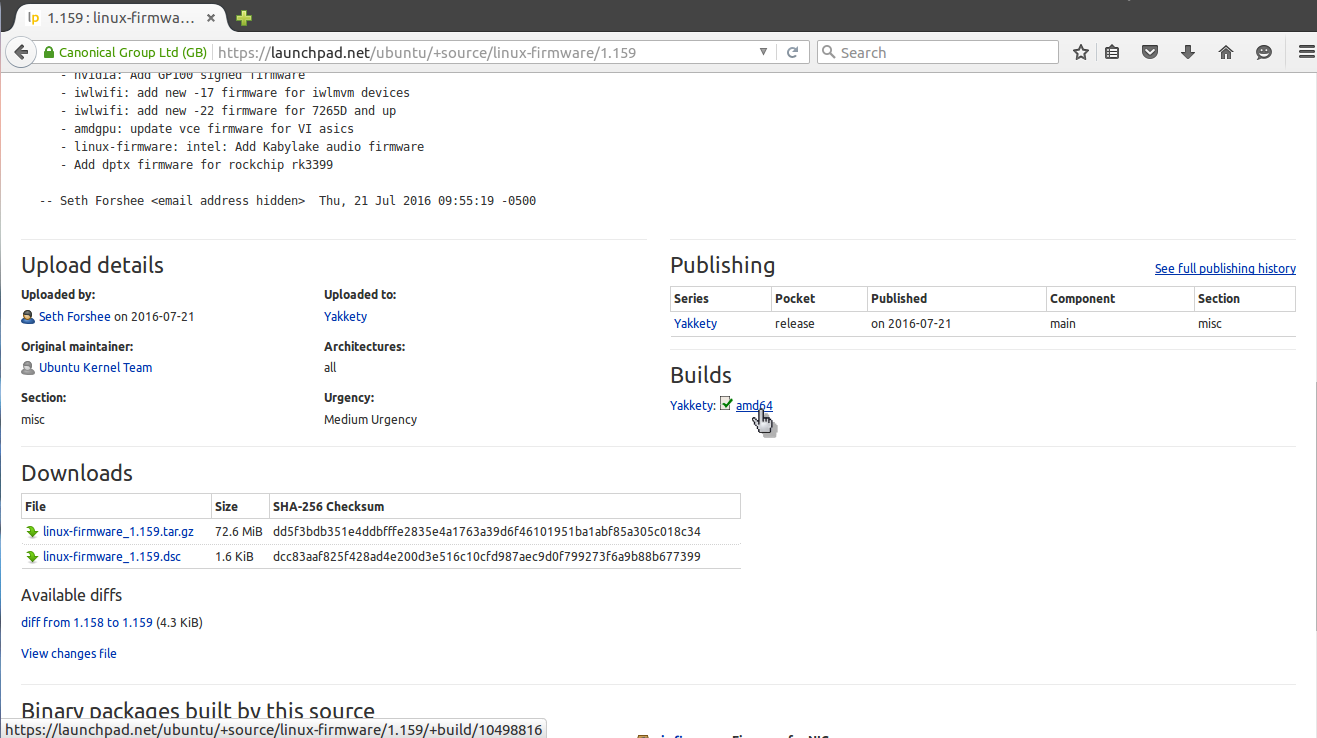
Дальше выбираем архитектуру:
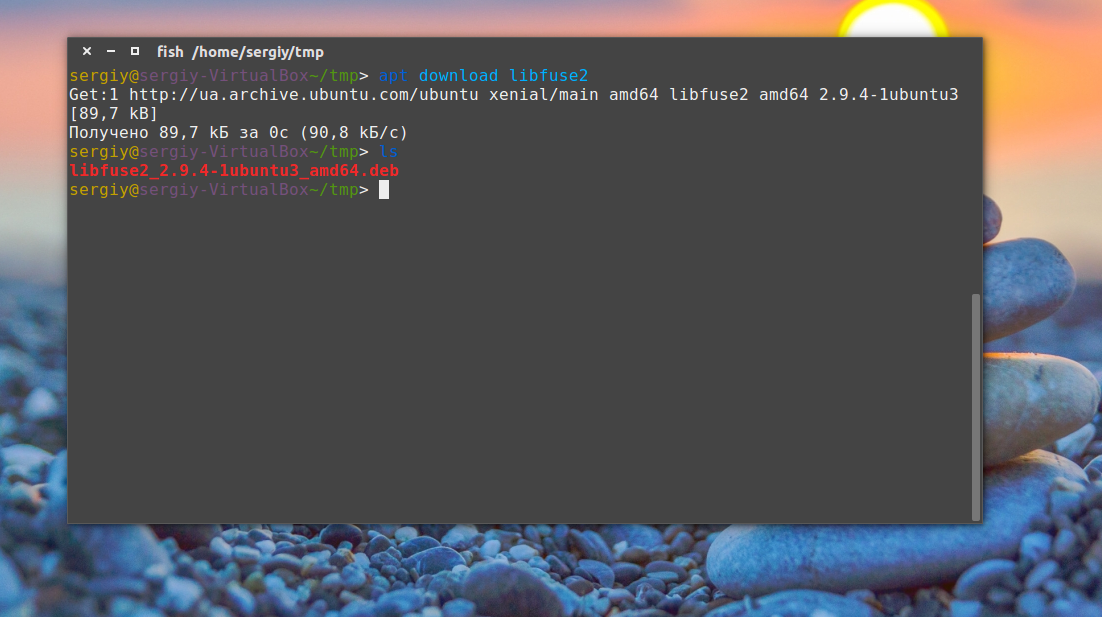
И осталось получить deb файл для нашей системы:
apt download имя_пакета
Пакет будет сохранен в текущей папке и дальше вы сможете все без проблем установить. Но будет скачан только сам пакет, без его зависимостей. Зависимости мы можем получить только в системе с интернетом используя команду apt-rdepends:
apt download имя_пакета $(apt-rdepends имя_пакета|grep -v «^ «)
Теперь у вас есть не только пакет, но и все его зависимости.
Установка deb пакетов Ubuntu
Установить Deb пакет Ubuntu не так уж сложно, для этого даже есть несколько утилит. Можно устанавливать как с помощью графического интерфейса, так и в терминале.
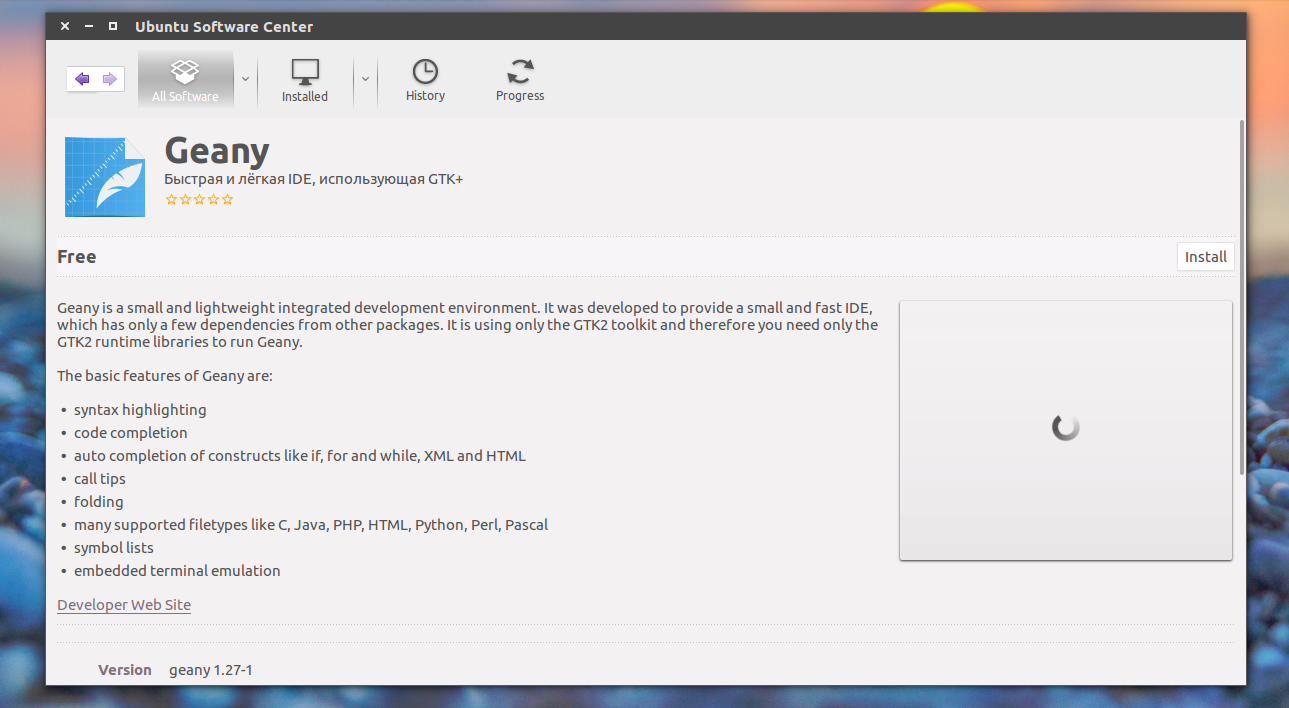
Самый простой способ установки — в графическом интерфейсе, с помощью центра приложений, с него и начнем. Откройте файловый менеджер в папке с пакетом:
Выполните двойной клик по deb пакету, далее откроется центр приложений, где вы посмотреть информацию о пакете и запустить установку нажав кнопку установить.
Установка программ Ubuntu с помощью центра приложений мне не очень нравится, он обычно очень долго думает и не всегда правильно открывает программу, но можно воспользоваться другой графической утилитой — gdebi. Сначала ее нужно установить:
sudo apt-get install gdebi
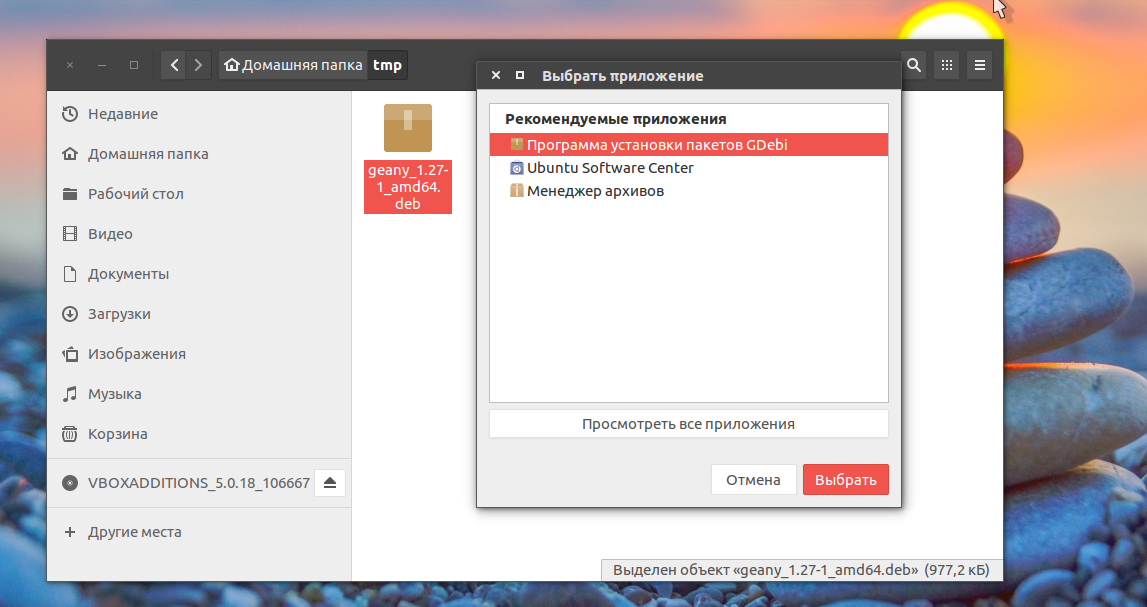
Теперь кликаем правой кнопкой мыши по файлу, выбираем открыть с помощью и gdebi:
Дальше осталось нажать кнопку установить и дождаться завершения установки пакета ubuntu. Программа автоматически установит все зависимости, если есть доступ к сети.
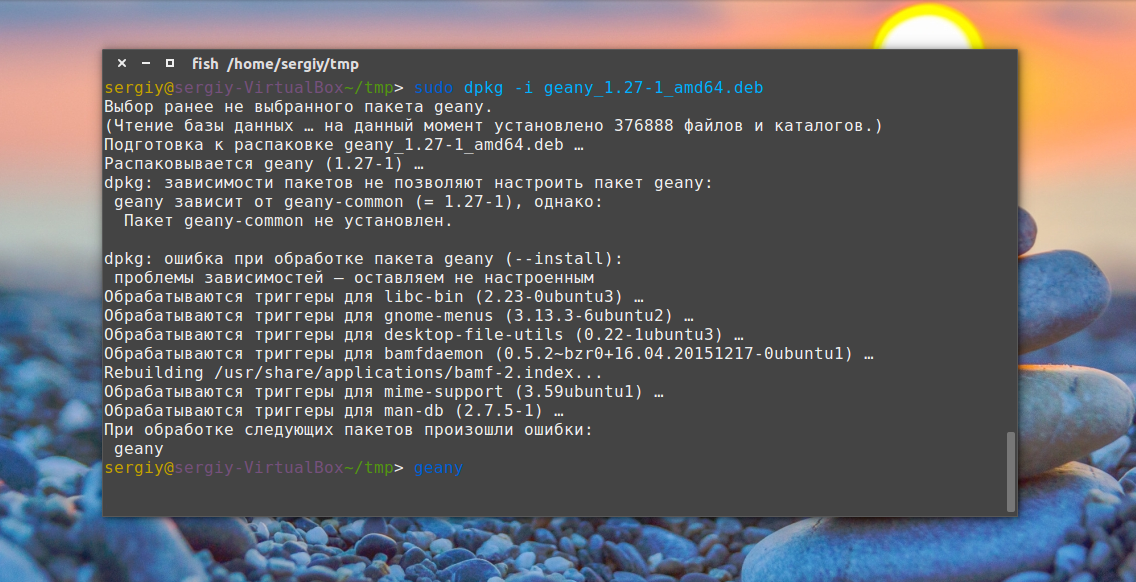
Установка deb из консоли Ubuntu выполняется не намного сложнее. Для этого используется утилита dpkg. Сначала переходим в папку куда был загружен deb пакет:
sudo dpkg -i имя_пакета.deb
Для этой команды доступны символы сокращений, например, можно написать вот так, чтобы установить все deb пакеты из этой директории:
$ sudo dpkg -i *.deb
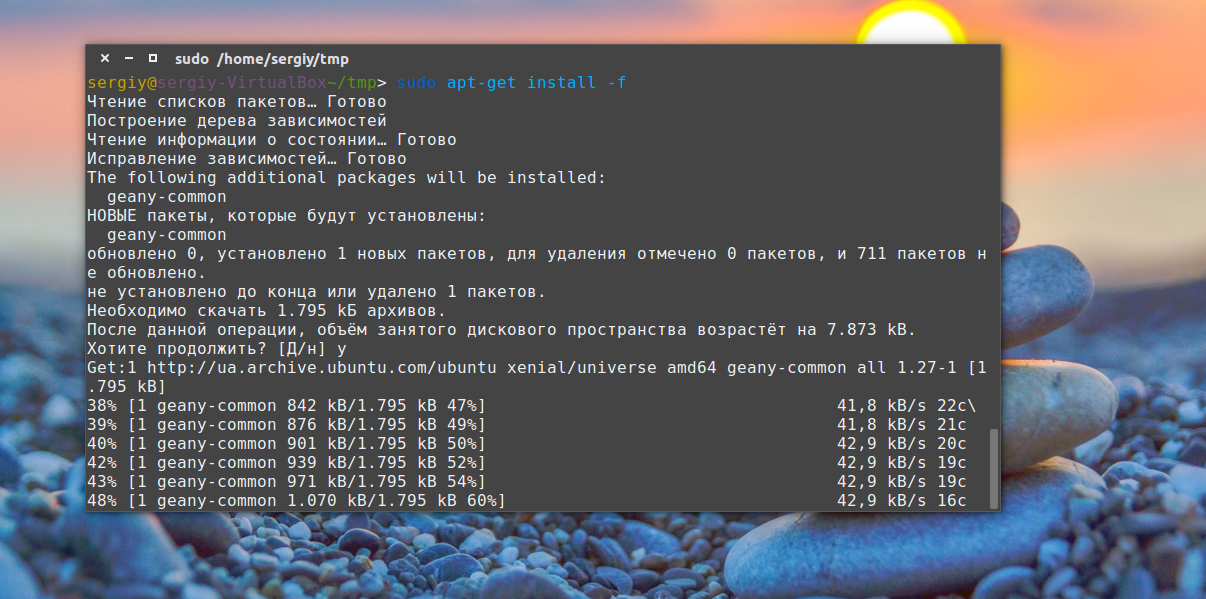
Программа не умеет разрешать зависимости, даже если есть доступ к сети, она только устанавливает пакет, поэтому для установки зависимостей после установки deb ubuntu выполните:
$ sudo apt-get -f install
Теперь, когда зависимости были загружены, вы можете запускать и использовать программу.
Это не единственный способ установки пакетов ubuntu через терминал, утилиту gdebi тоже можно запустить таким способом:
sudo gdebi имя_пакета.deb
Возможно, вы не знали, но apt тоже умеет устанавливать deb пакеты и даже более чем успешно разрешает зависимости. Только утилите нужно передать полный путь к файлу для установки. Если вы находитесь в папке с deb пакетом выполните:
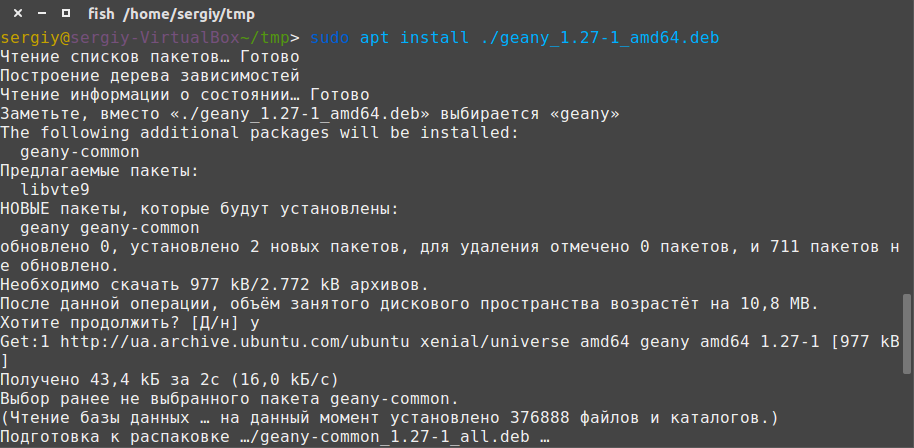
sudo apt install ./имя_пакета.deb
Программа автоматически установит все зависимости и больше ничего не придется выполнять.
Выводы
Вот и все. Теперь установка deb пакетов в Ubuntu не вызовет у вас проблем. Оказывается, есть несколько способов установки программ в ubuntu и все они имеют свои преимущества. Если у вас остались вопросы, спрашивайте в комментариях!
Источник
3 Ways to Install Deb Files on Ubuntu [& How to Remove Them Later]
Last updated June 15, 2020 By Abhishek Prakash 44 Comments
This beginner article explains how to install deb packages on Ubuntu. It also shows you how to remove those deb packages afterwards.
This is another article in our Ubuntu beginner series. If you’re completely new to Ubuntu, you might be wondering about how to install applications.
The easiest way is to use the Ubuntu Software Center. Search for an application by name and install it from there.
Life would be too simple if you could find all the applications in the Software Center. That’s not the case, unfortunately .
Some software is available via ‘deb’ packages. These are archived files that end with the .deb extension.
You can think of .deb files as like .exe files in Windows. You double click on the .exe file and it starts the installation procedure in Windows. Deb packages are pretty much the same.
You can find these deb packages in the download section of a software provider’s website. For example, if you want to install Google Chrome on Ubuntu, you can download the Chrome deb package from its website.
Now the question arises, how do you install deb files? There are multiple ways of installing deb packages on Ubuntu. I’ll show them to you one by one in this tutorial.
Installing .deb files on Ubuntu and Debian-based Linux Distributions
You can choose a GUI tool or a command line tool for installing a deb package. The choice is yours.
Let’s go on and see how to install deb files.
Method 1: Use the default Software Center
The simplest method is to use the default software center in Ubuntu. There’s nothing special to do here. Simply go to the folder where you downloaded the .deb file (usually the Downloads folder) and double click on the file.
It will open the software center, where you should see the option to install the software. All you have to do is to hit the install button and enter your login password.
See, it’s even more simple than installing from a .exe file on Windows, isn’t it?
Troubleshoot: Double clicking deb file doesn’t open in software center in Ubuntu 20.04
This is weird but can easily be fixed. All you have to do is to right click on the deb file and go for Open With option. In here, choose open with Software Install as the default choice.
Method 2: Use Gdebi application for installing deb packages with dependencies
Again, life would be a lot simpler if things always went smoothly. But that’s not life as we know it.
Now that you know .deb files can be easily installed via the Software Center, let me tell you about the dependency error that you may encounter with some packages.
What happens is that a program may be dependent on another piece of software (such as libraries). When the developer is preparing the deb package for you, he/she may assume that your system already has that piece of software.
But if that’s not the case and your system doesn’t have those required pieces of software, you’ll encounter the infamous ‘dependency error’.
The Software Center cannot handle such errors on its own so you have to use another tool called gdebi.
gdebi is a lightweight GUI application with the sole purpose of installing deb packages.
It identifies the dependencies and tries to install these along with the .deb files.
Personally, I prefer gdebi over the software center for installing deb files. It is a lightweight application so the installation seems quicker. You can read in detail about using gDebi and making it the default for installing DEB packages.
You can install gdebi from the software center or using the command below:
Method 3: Install .deb files in command line using dpkg
If you want to install deb packages in the command lime, you can use either the apt command or the dpkg command. The apt command actually uses the dpkg command underneath it, but apt is more popular and easier to use.
If you want to use the apt command for deb files, use it like this:
If you want to use the dpkg command for installing deb packages, here’s how to do it:
In both commands, you should replace path_to_deb_file with the path and name of the deb file you’ve downloaded.
If you get a dependency error while installing the deb packages, you can use the following command to fix it:
How to remove deb packages
Removing a deb package isn’t a big deal either. And no, you don’t need the original deb file that you used to install the program.
Method 1: Remove deb packages using apt command
All you need is the name of the program that you’ve installed and then you can use apt or dpkg to remove that program.
Now the question comes, how do you find the exact program name that you need to use in the remove command? The apt command has a solution for that as well.
You can find the list of all installed files with the apt command, but manually going through this will be a pain. So you can use the grep command to search for your package.
For example, I installed the AppGrid application in the previous section but if I want to find out the exact program name, I can use something like this:
This will give me all the packages that have grid in their name, and from there I can get the exact program name.
As you can see, a program called appgrid is installed. Now you can use this program name with the apt remove command.
Method 2: Remove deb packages using dpkg command
You can use dpkg to find the installed program’s name:
The output will give all the packages installed that have grid in their names.
ii in the above command output means that the package has been correctly installed.
Now that you have the program name, you can use the dpkg command to remove it:
Tip: Updating deb packages
Some deb packages (like Chrome) provide updates through system updates, but for most other software you’ll have to remove the existing program and install the newer version.
I hope this beginner’s guide helped you install deb packages on Ubuntu. I added the remove part so you can have better control over the programs you installed.
Like what you read? Please share it with others.
Источник