- Set Time, Date Timezone in Linux from Command Line or Gnome | Use ntp
- Set Time/Date/Timezone in Ubuntu Linux
- Check Current Time
- Using the date command
- Using timedatectl command
- Changing Time
- using date command
- Change Date
- Create custom date format
- List/Change time zone
- Set the Local-rtc
- Check/Change CMOS Time
- Conclusion
- 11 Useful Linux date command examples (How to set date and time in Linux)
- Syntax
- Linux date command Examples
- Example 1: How to check current date and time using date command
- Example 2: How to check future date using date command
- Example 3: How to check version of date command
- Example 4: How to Check current UTC Time using date command
- Example 5: How to Set date and time in Linux
- Example 6: How to Set only time in Linux using date command
- Example 7: How to Set only date in Linux using date command
- Example 8: How to Check the Last Modification date timestamp of a file
- Example 9: How to Display date in RFC Format
- Example 10: Using Format Specifiers with date command
- Example 11: Check Other date command options
- HowTo: UNIX Set Date and Time Command
- HP-UX UNIX Set Date Example Using Various Formats
Set Time, Date Timezone in Linux from Command Line or Gnome | Use ntp
Written by Guillermo Garron
Date: 2012-04-19 15:55:00 00:00
To have the correct time and date in Linux is very important, a lot of things depends on it. It does not matter if you are using Linux to power your personal computer or you have a Linux server. The server and system clock needs to be on time.
Set date from the command line
Set time from the command line
Set time and date from the command line
Linux check date from command line
Will show you something like this:
Set hardware clock
The hardware clock is the clock that runs in you PC hardware even if you disconnect it from the main power supply. This is because it has a lithium battery in the modern computers and another type of battery in the old ones.
We’ll see differences between hardware clock and system clock
Will output something like this:
Now check the system clock
Will output something like this:
Let’s set the hardware clock to local time:
If you want to set it to UTC time use:
Set the timezone
To set the timezone of your system clock do the following:
Choose the right timezone for you.
Automatically adjust your computer clock
To have your system to automatically adjust time we need to install ntp . Get it from your repository. Once installed you can configure it this way:
Edit the file /etc/ntpd.conf . It will look like this:
Be sure to start the daemon, and to make it start automatically when the system boots.
On Arch Linux is: /etc/rc.d/ntpd start on Debian and derivatives /etc/init.d/ntpd start
Update from the command line against a time server
You can update the clock manually, without the need of the daemon with ntpdate
You will get something like this:
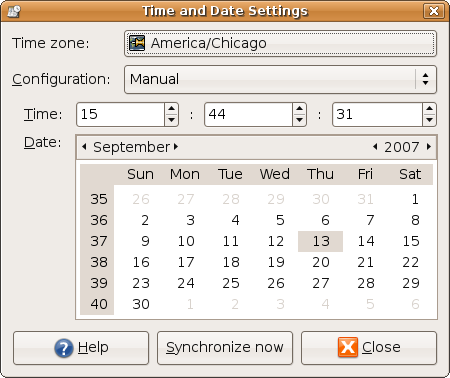
Bonus: Set the time and Date on Gnome
If you are using Gnome right click on the clock and select adjust, or go to: System > Administration > Time and Date (You may be asked for root password)
You will see a window similar to this one:
If you enjoyed the article, please share it
Источник
Set Time/Date/Timezone in Ubuntu Linux
Time is an important aspect in Linux systems especially in critical services such as cron jobs. Having the correct time on the server ensures that the server operates in a healthy environment that consists of distributed systems and maintains accuracy in the workplace.
In this tutorial, we will focus on how to set time/date/time zone and to synchronize the server clock with your Ubuntu Linux machine.
Check Current Time
You can verify the current time and date using the date and the timedatectl commands. These linux commands can be executed straight from the terminal as a regular user or as a superuser. The commands are handy usefulness of the two commands is seen when you want to correct a wrong time from the command line.
Using the date command
Log in as a root user and use the command as follows
Output
You can also use the same command to check a date 2 days ago
Output
Using timedatectl command
Checking on the status of the time on your system as well as the present time settings, use the command timedatectl as shown
Changing Time
We use the timedatectl to change system time using the format HH:MM: SS. HH stands for the hour in 24-hour format, MM stands for minutes and SS for seconds.
Setting the time to 09:08:07 use the command as follows (using the timedatectl)
using date command
Changing time means all the system processes are running on the same clock putting the desktop and server at the same time. From the command line, use date command as follows
Where,
• 10: Hour (hh)
• 13: Minute (mm)
• 13: Second (ss)
To change the locale to either AM or PM use the %p in the following format.
Change Date
Generally, you want your system date and time is set automatically. If for some reason you have to change it manually using date command, we can use this command :
It will set your current date and time of your system into ‘January 25, 2014′ and ’09:17:00 AM’. Please note, that you must have root privilege to do this.
You can use timedatectl to set the time and the date respectively. The accepted format is ‘YYYY-MM-DD’, ‘YYYY’ represents the year, ‘MM’ the month in two digits and ‘DD’ for the day in two digits.
Changing the date to ’15 January 2019′, you should use the following command:
Create custom date format
To create custom date format, use a plus sign (+)
%D format follows Year/Month/Day format.
You can also put the day name if you want. Here are some examples :
List/Change time zone
Changing the time zone is crucial when you want to ensure that everything synchronizes with the Network Time Protocol. The first thing to do is to list all the region’s time zones using the list-time zones option or grep to make the command easy to understand
The above command will present a scrollable format.
Recommended timezone for servers is UTC as it doesn’t have daylight savings. If you know, the specific time zones set it using the name using the following command
To display timezone execute
Set the Local-rtc
The Real-time clock (RTC) which is also referred to as the hardware clock is independent of the operating system and continues to run even when the server is shut down.
Use the following command
In addition, the following command for the local time
Check/Change CMOS Time
The computer CMOS battery will automatically synchronize time with system clock as long as the CMOS is working correctly.
Use the hwclock command to check the CMOS date as follows
To synchronize the CMOS date with system date use the following format
Conclusion
To have the correct time for your Linux environment is critical because many operations depend on it. Such operations include logging events and cron jobs as well.
If you have any questions or feedback, feel free to leave a comment.
Источник
11 Useful Linux date command examples (How to set date and time in Linux)
Table of Contents
In this article, I will take you through 11 Useful Linux date command examples. date is an important Linux command frequently used to set System date and time. You might have encountered few cluster based set up where each and every node needs to be in date and time sync with each other to be able to run successfully. Once it goes out of date or time sync beyond few seconds or minutes, cluster goes down. Hence it is very important to set the date and time correctly in the System. In this session we will look at how to set date and time in Linux using date command examples.
Syntax
date [OPTION]. [+FORMAT]
date [-u|—utc|—universal] [MMDDhhmm[[CC]YY][.ss]]
Linux date command Examples
Example 1: How to check current date and time using date command
If you want to check current date and time of your System then you need to simple run date command as shown below.
Example 2: How to check future date using date command
If you want to check date of some future day then you can check it by using —date option.
To check Next Tueday date you can use below command.
To check Next Sunday date you can use below command.
To check tomorrow date you can use below command.
To check yesterday date you can use below command.
To check after 2 Years date you can use below command.
To check after 2 months date you can use below command.
—date : display time described by STRING, not ‘now’. More info on date command Man page.
Example 3: How to check version of date command
If you want to check the version of date command then you need to use —version option as shown below. As you can see from below output current version is 8.22
—version : output version information and exit. More info on date command Man page.
Example 4: How to Check current UTC Time using date command
You can check the current Coordinated Universal Time by using date -u command.
-u : print or set Coordinated Universal Time (UTC)
Example 5: How to Set date and time in Linux
If you want to change both data and time then you can use —set option with date command to change that as shown below.
—set : set time described by STRING
Example 6: How to Set only time in Linux using date command
If you want to only change the time then you can use the same —set option as shown in above example and set the time only instead of setting both date and time.
Example 7: How to Set only date in Linux using date command
If you want to change only date but not the time then you need to first check the current time and then set accordingly. For example, if you check the current date and time you can see that current date is 16th May 2020 and current time is 13:16:04 EDT .
So, if you want to change the date only say to 17 May,2020 in this example keeping the time same then you need to use below date command.
Example 8: How to Check the Last Modification date timestamp of a file
If you want to check the last modification date timestamp of a file then you need to use -r option with date command as shown below. In this example we are checking the last modification date timestamp of a file file1.txt using date -r file1.txt command.
-r : display the last modification time of FILE
Example 9: How to Display date in RFC Format
If you want to display date in RFC format then you need to use date -R command as shown below.
-R : output date and time in RFC 2822 format
Example 10: Using Format Specifiers with date command
There are lot of format specifiers available to use with date command as per the needs. You can check and find its usages below.
%a locale’s abbreviated weekday name (e.g., Sun)
%A locale’s full weekday name (e.g., Sunday)
%b locale’s abbreviated month name (e.g., Jan)
%B locale’s full month name (e.g., January)
%c locale’s date and time (e.g., Thu Mar 3 23:05:25 2005)
%C century; like %Y, except omit last two digits (e.g., 20)
%d day of month (e.g., 01)
%D date; same as %m/%d/%y
%e day of month, space padded; same as %_d
%F full date; same as %Y-%m-%d
%g last two digits of year of ISO week number (see %G)
%G year of ISO week number (see %V); normally useful only with %V
%h same as %b
%H hour (00..23)
%I hour (01..12)
%j day of year (001..366)
%k hour, space padded ( 0..23); same as %_H
%l hour, space padded ( 1..12); same as %_I
%m month (01..12)
%M minute (00..59)
%n a newline
%N nanoseconds (000000000..999999999)
%p locale’s equivalent of either AM or PM; blank if not known
%P like %p, but lower case
%r locale’s 12-hour clock time (e.g., 11:11:04 PM)
%R 24-hour hour and minute; same as %H:%M
%s seconds since 1970-01-01 00:00:00 UTC
%S second (00..60)
%t a tab
%T time; same as %H:%M:%S
%u day of week (1..7); 1 is Monday
%U week number of year, with Sunday as first day of week (00..53)
%V ISO week number, with Monday as first day of week (01..53)
%w day of week (0..6); 0 is Sunday
%W week number of year, with Monday as first day of week (00..53)
%x locale’s date representation (e.g., 12/31/99)
%y last two digits of year (00..99)
%Y year
%z +hhmm numeric time zone (e.g., -0400)
Example 11: Check Other date command options
If you want to check all the other options available with date command you can use date —help command as shown below.
—help : display this help and exit
Источник
HowTo: UNIX Set Date and Time Command
I recently noticed that one of my UNIX servers was about 4 hours behind the correct time. I wanted to correct the date and time manually. How do I set date and/or time under UNIX operating systems using command line options?
The date command displays the current day, date, time, and year as well as it can set both the date and time for you. To see the current date and time, enter:
$ date
You must be login as root to set / change date under UNIX. The syntax to set date and time under UNIX and UNIX like operating system is as follows:
- MM : Month (two-digit numeric month)
- dd : Day (two-digit numeric day i.e. day of month)
- hh : Hour
- mm : Minutes (30)
- cc : First two digits of the year (10)
- yy : Last two digits of the year (2010).
To set date to April 27, 2010 8:00am under HP-UX, AIX, Sun Solaris or UNIX like operating system, enter:
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
HP-UX UNIX Set Date Example Using Various Formats
Using the mmddHHMM[[cc]yy][.ss] format, set date:
Источник