- How To Find Out Hard Disk Specs / Details on Linux
- Using lsblk command to find out hard disk information
- Linux show block device such as hard disk drive attributes
- hdparm Command
- lshw Command
- Finding Out Linux Disks Names Only
- Linux GUI Disk Utility
- The smartctl command
- A Note About RAID and SCSI Disks
- Conclusion
- 10 Commands to Check Disk Partitions and Disk Space on Linux
- 1. fdisk
- 2. sfdisk
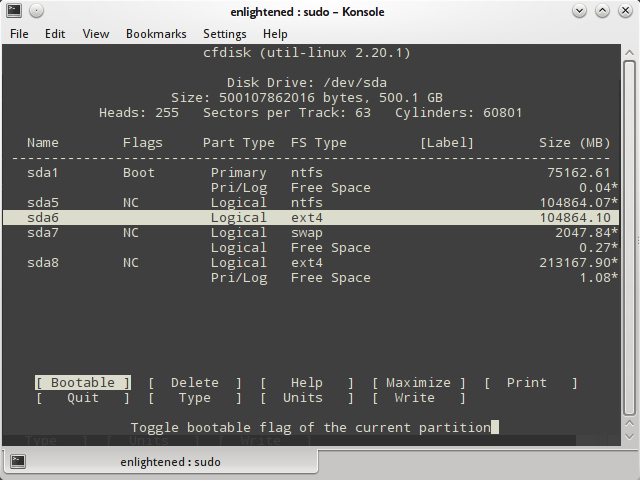
- 3. cfdisk
- 4. parted
- 6. pydf
- 7. lsblk
- 8. blkid
- 9. hwinfo
- 10. Inxi
- Summary
- 47 thoughts on “ 10 Commands to Check Disk Partitions and Disk Space on Linux ”
- Как посмотреть диски в Linux
- 1. lsblk
- 2. df -h
- 3. fdisk -l
- 4. parted -l
- 5. cfdisk
- 6. sfdisk -l
- 7. ls -l /dev/disk/by-id
- 8. lshw -class disk
- Заключение
How To Find Out Hard Disk Specs / Details on Linux
Using lsblk command to find out hard disk information
Run the lsblk command as follows to lists information about all available or the specified block devices:
# lsblk
# lsblk /dev/DISK
# lsblk /dev/sda
So I have two NVMe SSD in RAID-1 mode with encrypted partitions:
Another option is to run the following command to list all disks and their names:
# ls -lF /dev/disk/by-id/
Linux show block device such as hard disk drive attributes
Open the terminal app and then type the blkid command:
# blkid
hdparm Command
Open the terminal and type the following command to find information about /dev/sda:
# hdparm -I /dev/sda
OR
$ sudo hdparm -I /dev/sda
Sample outputs:
lshw Command
You need to install lshw command using apt-get or yum command. To display all disks and storage controllers in the system, enter:
# lshw -class disk -class storage
Sample outputs:
Finding Out Linux Disks Names Only
The following lshw command will quickly list installed disks including CD/DVD/BD drivers:
# lshw -short -C disk
Sample outputs:
Another option so to run the fdisk command as follows:
# fdisk -l
Use the grep command/egrep command to filter out loopback and other unwanted devices:
# fdisk -l | grep ‘^Disk /dev/’
# fdisk -l | grep ‘^Disk /dev/’ | egrep -v ‘/dev/(loop|mapper|md)’
Linux GUI Disk Utility
Gnome users can use the gnome-disk-utility/gnome-disks for the following purposes:
- Get information about installed disks and its current health.
- Manage and configure disk drives.
- Configure media.
- Set up software RAID devices and more.
Type the following command or start Disk utility by visiting Applications > System Tools > Disk Utility :
$ palimpsest
OR
$ gnome-disks
Sample outputs:
Fig.01: Linux List Hard Drives GUI Tool & Command — Click to enlarge
Fig.02: Samrtdata about hard disk
The smartctl command
The smartctl command act as a control and monitor Utility for SMART disks under Linux and Unix like operating systems. Type the following command to get information about /dev/sda (SATA disk):
# smartctl -d ata -a -i /dev/sda
Sample outputs:
A Note About RAID and SCSI Disks
Try the following commands for SCSI and hardware RAID based devices:
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
- sdparm Command – fetch SCSI / SATA device information.
- scsi_id Command – queries a SCSI device via the SCSI INQUIRY vital product data (VPD).
- Use smartctl To Check Disk Behind Adaptec RAID Controllers
- Use smartctl Check Hard Disk Behind 3Ware RAID Card
Conclusion
You learned about finding hard disk drive infromation on Linux. To get more information about your hard disk, refer to our other articles and tutorials:
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
Источник
10 Commands to Check Disk Partitions and Disk Space on Linux
In this post we are taking a look at some commands that can be used to check up the partitions on your system.
The commands would check what partitions there are on each disk and other details like the total size, used up space and file system etc.
Commands like fdisk, sfdisk and cfdisk are general partitioning tools that can not only display the partition information, but also modify them.
1. fdisk
Fdisk is the most commonly used command to check the partitions on a disk. The fdisk command can display the partitions and details like file system type. However it does not report the size of each partitions.
Each device is reported separately with details about size, seconds, id and individual partitions.
2. sfdisk
Sfdisk is another utility with a purpose similar to fdisk, but with more features. It can display the size of each partition in MB.
3. cfdisk
Cfdisk is a linux partition editor with an interactive user interface based on ncurses. It can be used to list out the existing partitions as well as create or modify them.
Here is an example of how to use cfdisk to list the partitions.
Cfdisk works with one partition at a time. So if you need to see the details of a particular disk, then pass the device name to cfdisk.
4. parted
Parted is yet another command line utility to list out partitions and modify them if needed.
Here is an example that lists out the partition details.
Df is not a partitioning utility, but prints out details about only mounted file systems. The list generated by df even includes file systems that are not real disk partitions.
Here is a simple example
Only the file systems that start with a /dev are actual devices or partitions.
Use grep to filter out real hard disk partitions/file systems.
To display only real disk partitions along with partition type, use df like this
Note that df shows only the mounted file systems or partitions and not all.
6. pydf
Improved version of df, written in python. Prints out all the hard disk partitions in a easy to read manner.
Again, pydf is limited to showing only the mounted file systems.
7. lsblk
Lists out all the storage blocks, which includes disk partitions and optical drives. Details include the total size of the partition/block and the mount point if any.
Does not report the used/free disk space on the partitions.
If there is no MOUNTPOINT, then it means that the file system is not yet mounted. For cd/dvd this means that there is no disk.
Lsblk is capbale of displaying more information about each device like the label and model. Check out the man page for more information
Display UUID and Model of device
The «-o» option can be used to specify the columns to display. The following example shows the UUID and model name column along with other columns.
The above output has all the necessary information about all the storage devices present on the system or connected via usb. You can see the device name, size, mount point, uuid, model name etc.
This is the best command to see all information about storage devices together in one place.
8. blkid
Prints the block device (partitions and storage media) attributes like uuid and file system type. Does not report the space on the partitions.
9. hwinfo
The hwinfo is a general purpose hardware information tool and can be used to print out the disk and partition list.
The output however does not print details about each partition like the above commands.
To learn more about the Hwinfo command check this post:
Check hardware information on Linux with hwinfo command
10. Inxi
Inxi is a very useful command line program that can display information about various hardware components present on the system. To display information about the disk drives and storage devices use the «-D» option with inxi.
The «-x» option prints extra available information.
The output from inxi does not contains details like UUID and mount directory.
To learn more about the inxi command check out this post:
Inxi is an amazing tool to check hardware information on Linux
Summary
The output of parted is concise and complete to get an overview of different partitions, file system on them and the total space. Pydf and df are limited to showing only mounted file systems and the same on them.
Fdisk and Sfdisk show a whole lot of information that can take sometime to interpret whereas, Cfdisk is an interactive partitioning tool that display a single device at a time.
So try them out, and do not forget to comment below.
A Tech Enthusiast, Blogger, Linux Fan and a Software Developer. Writes about Computer hardware, Linux and Open Source software and coding in Python, Php and Javascript. He can be reached at [email protected] .
47 thoughts on “ 10 Commands to Check Disk Partitions and Disk Space on Linux ”
Thank you for this great summary of relevant commands and also showing whether SU privileges are needed or not.
Good article. Thanks for writing this .
I’d also suggest including “ncdu” (stands for ncurses du) – https://dev.yorhel.nl/ncdu – in this as it’s quite useful in knowing the disk usage on the terminal in a graphical way
pydf hands down the best alternative if you want a quick glance at disk usage!
Very useful, thank you!
very useful,
How about GUI tools?
Hardinfo is a GUI tool that shows hardware information including disk drives and partitions..
On ubuntu it can be installed with the following command
sudo apt-get install hardinfo
Another tool is gparted.
It is a partition management tool, but can also be used to list the disk drives and partitions
Well done — I learned something!
glad to know that.
thanks for the comment.
Very useful. Thank you for your effort.
Detailed and to the point post. Thanks A Ton!
Источник
Как посмотреть диски в Linux
Системные администраторы ОС Linux обычно просматривают диски, чтобы проверить все дисковое пространство и его использование. Список дисков также помогает увидеть подключенные диски к системе, разделы и файловую систему, используемую дисками.
В системе Linux существует несколько способов посмотреть все жесткие диски. Из этой статьи вы узнаете, как посмотреть диски в Linux с помощью командной строки.
1. lsblk
lsblk (list block devices) используется для просмотра информации обо всех доступных блочных устройствах, таких как жесткий диск и флэш-накопители.
Просто набрав команду lsblk, вы получите список всех блочных устройств в виде древовидного формата. Это удобный и простой способ посмотреть диски.
sda 8:0 0 238.5G 0 disk
├─sda1 8:1 0 529M 0 part
├─sda2 8:2 0 100M 0 part /boot/efi
├─sda3 8:3 0 16M 0 part
├─sda4 8:4 0 165.8G 0 part
├─sda5 8:5 0 70G 0 part /
└─sda6 8:6 0 2G 0 part [SWAP]
zram0 252:0 0 8G 0 disk [SWAP]
2. df -h
Команда df используется для просмотра объема доступного дискового пространства. Так же команда df отобразит имя устройства, общее количество блоков, используемое дисковое пространство, доступное дисковое пространство, процент используемого пространства, точку монтирования файловой системы, а также покажет удаленно смонтированные файловые системы, такие как NFS.
Команда df -h покажет доступное пространство всех дисков в удобочитаемом виде.
Ответ в терминале:
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
devtmpfs 5.8G 0 5.8G 0% /dev
tmpfs 5.8G 90M 5.7G 2% /dev/shm
tmpfs 2.4G 11M 2.4G 1% /run
tmpfs 4.0M 0 4.0M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/sda5 69G 62G 3.1G 96% /
tmpfs 5.8G 4.7M 5.8G 1% /tmp
/dev/sda2 96M 41M 56M 43% /boot/efi
tmpfs 1.2G 200K 1.2G 1% /run/user/1000
3. fdisk -l
Команда fdisk — это текстовая утилита, используемая для управления разделами диска. С помощью fdisk вы можете отобразить разделы диска, создать новый раздел, удалить существующий раздел жесткого диска и просмотреть размер раздела.
Для этого используется команда fdisk -l отобразит все доступные разделы диска
Ответ в терминале:
Disk /dev/sda: 238.47 GiB, 256060514304 bytes, 500118192 sectors
Disk model: SK hynix SC300B
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 4096 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 4096 bytes / 4096 bytes
Disklabel type: gpt
Disk identifier: FF57C955-D98A-49C4-B1ED-835A44F2A0A4
Device Start End Sectors Size Type
/dev/sda1 2048 1085439 1083392 529M Windows recovery environment
/dev/sda2 1085440 1290239 204800 100M EFI System
/dev/sda3 1290240 1323007 32768 16M Microsoft reserved
/dev/sda4 1323008 349122559 347799552 165.8G Microsoft basic data
/dev/sda5 349122560 495923199 146800640 70G Linux filesystem
/dev/sda6 495923200 500117503 4194304 2G Linux swap
Disk /dev/zram0: 8 GiB, 8589934592 bytes, 2097152 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 4096 = 4096 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 4096 bytes / 4096 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 4096 bytes / 4096 bytes Disk /dev/loop0: 207.15 MiB, 217214976 bytes, 424248 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/loop1: 99.18 MiB, 103993344 bytes, 203112 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
4. parted -l
Parted — это полезный и мощный инструмент используемый для управления разделами жесткого диска из терминала (командной строки). Обладает способностями такими как список, создание, сжатие, удаление, поиск и восстановление разделов диска. С помощью команды parted вы можете легко управлять всеми разделами жесткого диска.
команда parted-l покажет расположение разделов дисков.
Ответ в терминале:
Model: ATA SK hynix SC300B (scsi)
Disk /dev/sda: 256GB
Sector size (logical/physical): 512B/4096B
Partition Table: gpt
Disk Flags:
Number Start End Size File system Name Flags
1 1049kB 556MB 555MB ntfs Basic data partition hidden, diag
2 556MB 661MB 105MB fat32 EFI System Partition boot, esp
3 661MB 677MB 16.8MB Microsoft reserved partition msftres
4 677MB 179GB 178GB ntfs Basic data partition msftdata
5 179GB 254GB 75.2GB ext4
6 254GB 256GB 2147MB linux-swap(v1) swap
Model: Unknown (unknown)
Disk /dev/zram0: 8590MB
Sector size (logical/physical): 4096B/4096B
Partition Table: loop
Disk Flags:
Number Start End Size File system Flags
1 0.00B 8590MB 8590MB linux-swap(v1)
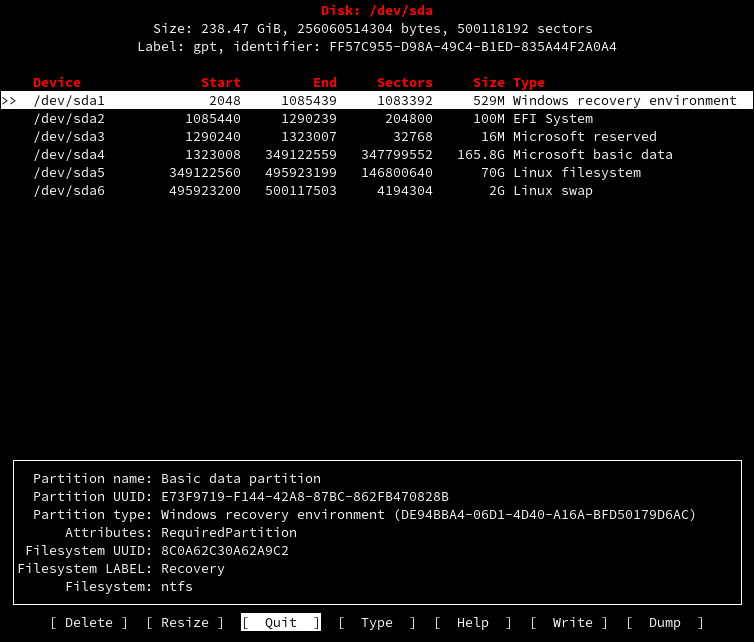
5. cfdisk
Cfdisk немного отличается от вышеприведенных команд, эта команда обеспечивает графическое представление в терминальном интерфейсе. С помощью cfdisk вы можете просматривать, создавать, удалять и изменять разделы.
Disk: /dev/sda Size: 238.47 GiB, 256060514304 bytes, 500118192 sectors Label: gpt, identifier: FF57C955-D98A-49C4-B1ED-835A44F2A0A4 Device Start End Sectors Size Type
/dev/sda1 2048 1085439 1083392 529M Windows recovery environment
/dev/sda2 1085440 1290239 204800 100M EFI System
/dev/sda3 1290240 1323007 32768 16M Microsoft reserved
/dev/sda4 1323008 349122559 347799552 165.8G Microsoft basic data
/dev/sda5 349122560 495923199 146800640 70G Linux filesystem
/dev/sda6 495923200 500117503 4194304 2G Linux swap
┌──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Partition name: Basic data partition │
│ Partition UUID: E73F9719-F144-42A8-87BC-862FB470828B │
│ Partition type: Windows recovery environment (DE94BBA4-06D1-4D40-A16A-BFD50179D6AC) │
│ Attributes: RequiredPartition │
│ Filesystem UUID: 8C0A62C30A62A9C2 │
│Filesystem LABEL: Recovery │
│ Filesystem: ntfs │
└──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
[ Delete ] [ Resize ] [ Quit ] [ Type ] [ Help ] [ Write ] [ Dump ]
6. sfdisk -l
sfdisk — это редактор таблиц разделов. Он может показать разделы, показать размер раздела, проверить разделы на устройстве и подготовить устройство.
Команда sfdisk -l покажет разделы каждого диска.
Ответ в терминале:
Disk /dev/sda: 238.47 GiB, 256060514304 bytes, 500118192 sectors
Disk model: SK hynix SC300B
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 4096 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 4096 bytes / 4096 bytes
Disklabel type: gpt
Disk identifier: FF57C955-D98A-49C4-B1ED-835A44F2A0A4
Device Start End Sectors Size Type
/dev/sda1 2048 1085439 1083392 529M Windows recovery environment
/dev/sda2 1085440 1290239 204800 100M EFI System
/dev/sda3 1290240 1323007 32768 16M Microsoft reserved
/dev/sda4 1323008 349122559 347799552 165.8G Microsoft basic data
/dev/sda5 349122560 495923199 146800640 70G Linux filesystem
/dev/sda6 495923200 500117503 4194304 2G Linux swap
Disk /dev/zram0: 8 GiB, 8589934592 bytes, 2097152 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 4096 = 4096 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 4096 bytes / 4096 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 4096 bytes / 4096 bytes
Disk /dev/loop0: 207.15 MiB, 217214976 bytes, 424248 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/loop1: 99.18 MiB, 103993344 bytes, 203112 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
7. ls -l /dev/disk/by-id
команда ls — это очень простая, но мощная команда, используемая для отображения файлов и каталогов. Мы можем посмотреть диски, посмотреть каталог /dev/disk/by-id.
$ ls -l /dev/disk/by-id
Ответ в терминале:
total 0
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 9 Jun 20 23:26 ata-SK_hynix_SC300B_HFS256G39MND-3510B_FI68N023911308NC9 -> ../../sda
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 Jun 20 23:26 ata-SK_hynix_SC300B_HFS256G39MND-3510B_FI68N023911308NC9-part1 -> ../../sda1
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 Jun 20 23:26 ata-SK_hynix_SC300B_HFS256G39MND-3510B_FI68N023911308NC9-part2 -> ../../sda2
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 Jun 20 23:26 ata-SK_hynix_SC300B_HFS256G39MND-3510B_FI68N023911308NC9-part3 -> ../../sda3
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 Jun 20 23:26 ata-SK_hynix_SC300B_HFS256G39MND-3510B_FI68N023911308NC9-part4 -> ../../sda4
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 Jun 20 23:26 ata-SK_hynix_SC300B_HFS256G39MND-3510B_FI68N023911308NC9-part5 -> ../../sda5
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 Jun 20 23:26 ata-SK_hynix_SC300B_HFS256G39MND-3510B_FI68N023911308NC9-part6 -> ../../sda6
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 9 Jun 20 23:26 wwn-0x5ace42e0900dd482 -> ../../sda
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 Jun 20 23:26 wwn-0x5ace42e0900dd482-part1 -> ../../sda1
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 Jun 20 23:26 wwn-0x5ace42e0900dd482-part2 -> ../../sda2
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 Jun 20 23:26 wwn-0x5ace42e0900dd482-part3 -> ../../sda3
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 Jun 20 23:26 wwn-0x5ace42e0900dd482-part4 -> ../../sda4
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 Jun 20 23:26 wwn-0x5ace42e0900dd482-part5 -> ../../sda5
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 Jun 20 23:26 wwn-0x5ace42e0900dd482-part6 -> ../../sda6
Вы также можете посмотреть:
8. lshw -class disk
lshw — это инструмент Linux, который используется для получения подробной информации об аппаратной конфигурации системы.
Используйте -class disk для просмотра информации о диске.
Ответ в терминале:
*-disk
description: ATA Disk
product: SK hynix SC300B
physical id: 0.0.0
bus info: scsi@1:0.0.0
logical name: /dev/sda
version: 0P00
serial: FI68N023911308NC9
size: 238GiB (256GB)
capabilities: gpt-1.00 partitioned partitioned:gpt
configuration: ansiversion=5 guid=ff57c955-d98a-49c4-b1ed-835a44f2a0a4 logicalsectorsize=512 sectorsize=4096
Кроме того, можно вывести class disk as-json или -html или-xml.
Ответ в терминале:
<
«id» : «disk»,
«class» : «disk»,
«claimed» : true,
«handle» : «GUID:ff57c955-d98a-49c4-b1ed-835a44f2a0a4»,
«description» : «ATA Disk»,
«product» : «SK hynix SC300B»,
«physid» : «0.0.0»,
«businfo» : «scsi@1:0.0.0»,
«logicalname» : «/dev/sda»,
«dev» : «8:0»,
«version» : «0P00»,
«serial» : «FI68N023911308NC9»,
«units» : «bytes»,
«size» : 256060514304,
«configuration» : <
«ansiversion» : «5»,
«guid» : «ff57c955-d98a-49c4-b1ed-835a44f2a0a4»,
«logicalsectorsize» : «512»,
«sectorsize» : «4096»
>,
«capabilities» : <
«gpt-1.00» : «GUID Partition Table version 1.00»,
«partitioned» : «Partitioned disk»,
«partitioned:gpt» : «GUID partition table»
>,
«children» : [
]
>
Заключение
Для всех команд, кроме lsblk и ls-l dev/disk, требуется root — доступ или разрешения суперпользователя для его запуска.
В этой статье мы узнали, как посмотреть диски в Linux с помощью командной строки.
Источник