- Your Own Linux.
- Linux How To’s | Bash Scripting | Python
- Sunday, 19 April 2015
- Sed Command in Linux — Append and Insert Lines to a File
- sed — Appending Lines to a File
- 1. Append a line after ‘N’th line
- 2. Append Line using Regular Expression/Pattern
- sed — Inserting Lines in a File
- 1. Insert line using the Line number
- 2. Insert lines using Regular expression
- Insert/Add String to Beginning of a File
- Inserting a String to Beginning of File
- Related Posts
- Recent Posts
- Recent Comments
- Latest Tweet
- 50 `sed` Command Examples
- 1. Basic text substitution using ‘sed’
- 2. Replace all instances of a text in a particular line of a file using ‘g’ option
- 3. Replace the second occurrence only of a match on each line
- 4. Replace the last occurrence only of a match on each line
- 5. Replace the first match in a file with new text
- 6. Replace the last match in a file with new text
- 7. Escaping backslash in replace commands to manage search and replace of file paths
- 8. Replace all files full path with just the filename no directory
- 9. Substitute text but only if some other text is found in the string
- 10. Substitute text but only if some other text is not found in the string
- 11. Add string before and after the matching pattern using ‘
’
- 12. Delete matching lines
- 13. Delete matching line and 2 lines after matching line
- 14. Delete all spaces at end of the line of text
- 15. Delete all lines that have a match two times on the line
- 16. Delete all lines that have only white-space
- 17. Delete all non-printable characters
- 18. If there is a match in line append something to end of line
- 19. If there is a match in the line insert a line before the text
- 20. If there is a match in the line insert a line after that line
- 21. If there is not a match append something to the end of line
- 22. If there is not a match delete the line
- 23. Duplicate matched text after adding a space after the text
- 24. Replace one list of strings with the new string
- 25. Replace the matched string with a string that contains newlines
- 26. Remove newlines from file and insert a comma at end of each line
- 27. Remove commas and add newline to split the text into multiple lines
- 28. Find case insensitive match and delete line
- 29. Find case insensitive match and replace with new text
- 30. Find case insensitive match and replace with all uppercase of the same text
- 31. Find case insensitive match and replace with all lowercase of same text
- 32. Replace all uppercase characters of the text with lowercase characters
- 33. Search for number in line and append any currency symbol before the number
- 34. Add commas to numbers that have more than 3 digits
- 35. Replaces tab character with 4 space characters
- 36. Replaces 4 consecutive space characters with tab character
- 37. Truncate all lines to first 80 characters
- 38. Search for a string regex and append some standard text after it
- 39. Search for string regex and append some text after the second match in each line
- 40. Running multi-line `sed` scripts from a file
- 41. Match a multi-line pattern and replace with new multi-line text
- 42. Replace order of two words in a text that match a pattern
- 43. Execute multiple `sed` commands from the command-line
- 44. Combine `sed` with other commands
- 45. Insert empty line in a file
- 46. Replace all alpha-numeric characters by space in each line of a file.
- 47. Use ‘&’ to print matched string
- 48. Switch pair of words in a file
- 49. Capitalize the first character of each word
- 50. Print line numbers of the file
- Conclusion:
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the sed command used for?
- What is S and G in sed command?
- How do I run a sed script?
- About the author
- Fahmida Yesmin
Your Own Linux.
Linux How To’s | Bash Scripting | Python
Sunday, 19 April 2015
Sed Command in Linux — Append and Insert Lines to a File
This is the second article of the «Super sed ‘ Series», in which we will learn how to append and insert lines to a file using line numbers and regular expressions. In the previous article in the series, we learned to print lines in a file using sed command.
Before we directly jump to the main content, every learner should know what sed is. Here is the brief introduction of the Super sed :
- sed stand for Stream EDitor and it being based on the ed editor, it borrows most of the commands from the ed . It was developed by Lee E. McMahon of Bell Labs.
- sed offers large range of text transformations that include printing lines, deleting lines, editing line in-place, search and replace, appending and inserting lines, etc.
- sed is useful whenever you need to perform common editing operations on multiple lines without using ‘vi’ editor.
- Whenever sed is executed on an input file or on the contents from stdin, sed reads the file line-by-line and after removing the trailing newline, places it in the «Pattern space», where the commands are executed on them after conditions (as in case of regex matching) are verified, and then printed on the stdout.
sed — Appending Lines to a File
For our better understanding, let us have a file sedtest.txt with contents as follows:
1. Append a line after ‘N’th line
This will add a line after ‘N’th line in the FILE.txt .
Example:
To append a line #This is just a commented line after 1st line,
While, to append a line after last line,
If you run above commands and inspect the file sedtest.txt , you would find that, the original contents of that file would not change. In case you wish to append lines in the file and save the changes (i.e. edit the file in place), you will have to use the option -i .
Lets check it for the latest command we have run to append lines after the last line of the file. Has it made any changes to the file?
No, the original file remains the same. But, I wanted to save the changes to the file. So, I should have used the option -i .
Yes, now changes are written to the file. Just remember this.
2. Append Line using Regular Expression/Pattern
This will append the line after the line where pattern match is found.
sed — Inserting Lines in a File
1. Insert line using the Line number
This will insert the line before the line at line number ‘N’.
While, to insert a line before last line,
2. Insert lines using Regular expression
This will insert the line before every line where pattern match is found.
That’s all about the second article on sed command. More articles on sed are coming soon. So, stay tuned. Of course, do not forget to share your feedback in the comment section below.
Источник
Insert/Add String to Beginning of a File
In a previous article, I showed you how to append a string to the end of file. Now I will show you how to insert a string to the beginning of a file in Linux. The solution is not as obvious as the former, but I will show you a quick and easy way using the standard Linux/Unix application sed.
Inserting a String to Beginning of File
- Suppose you had a text file with the contents and you wanted to insert a string to the beginning:
1st line
2nd line
3rd line - Run the command:
sed -i ‘1i Top of the file!’ - Now the file will look like this:
Top of the file!
1st line
2nd line
3rd line
A brief explanation of the sed command parameters that we used:
-i : This will update the contents of the file and automatically save it
1i : This means, insert to the 1st line of the file
Related Posts
Many thanks,
I was writing a script to automate the syslog installation with log analyzer and wanted to automate the editing of /etc/rsyslog.conf. So, I sued “sed -i ’22i $InputTCPServerRun 514′ /etc/rsyslog.conf”.
This sed work around is also useful for me to make editing easier.
Perfect little one liner! Thank you!
Excellent. Thank you!
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed.
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
- Valarie Walter on Basic Troubleshooting Steps for your Cell Phone
- John Mists on A Brief History of Android OS
- syarif on PostgreSQL: How to reload config settings without restarting database
- Raghu on How to SSH to a server using Ruby – Part I
- francisco clemente on Basic Troubleshooting Steps for your Cell Phone
Latest Tweet

@HeatwaredotNet
Источник
50 `sed` Command Examples
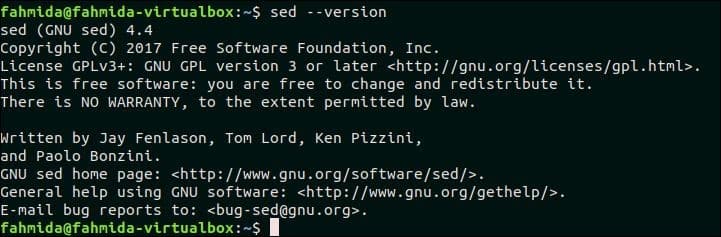
The following output shows that GNU Sed of version 4.4 is installed in the system.
Syntax:
If no filename is provided with `sed` command, then the script will work on standard input data. The `sed` script can be executed without any option.
Content:
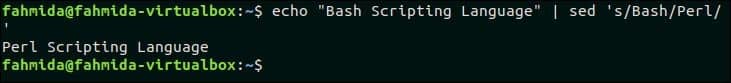
1. Basic text substitution using ‘sed’
Any particular part of a text can be searched and replaced by using searching and replacing pattern by using `sed` command. In the following example, ‘s’ indicates the search and replace task. The word ‘Bash’ will be searched in the text, “Bash Scripting Language” and if the word exists in the text then it will be replaced by the word ‘Perl’.
Output:
The word, ‘Bash’ exists in the text. So the output is ‘Perl Scripting Language’.
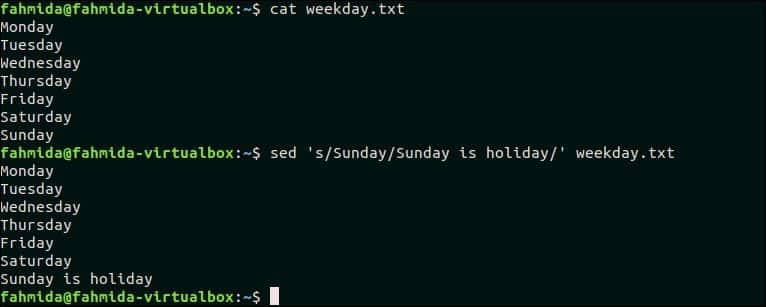
`sed` command can be used to substitution any part of a file content also. Create a text file named weekday.txt with the following content.
weekday.txt
The following command will search and replace the text ‘Sunday ‘, by the text ‘Sunday is holiday’.
Output:
‘Sunday’ exists in weekday.txt file and this word is replaced by the text, ‘Sunday is holiday’ after executing the above `sed` command.
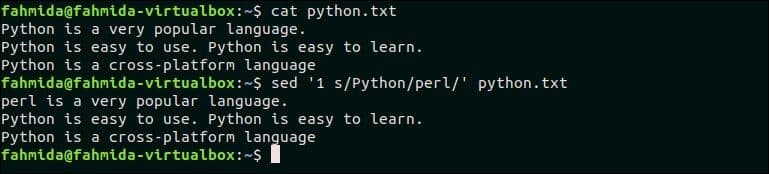
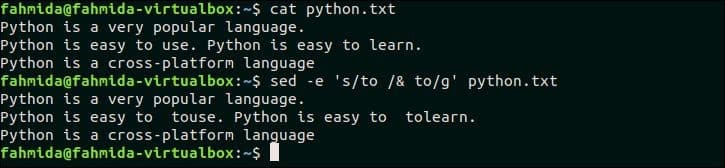
2. Replace all instances of a text in a particular line of a file using ‘g’ option
‘g’ option is used in `sed` command to replace all occurrences of matching pattern. Create a text file named python.txt with the following content to know the use of ‘g’ option. This file contains the word. ‘Python’ multiple times.
python.txt
Python is a very popular language.
Python is easy to use. Python is easy to learn.
Python is a cross-platform language
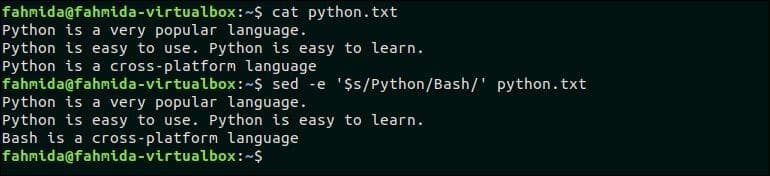
The following command will replace all occurrences of ‘Python’ in the second line of the file, python.txt. Here, ‘Python’ occurs two times in the second line.
Output:
The following output will appear after running the script. Here, All occurrence of ‘Python’ in the second line is replaced by ‘Perl’.
3. Replace the second occurrence only of a match on each line
If any word appears multiple times in a file then the particular occurrence of the word in each line can be replaced by using `sed` command with the occurrence number. The following `sed` command will replace the second occurrence of the searching pattern in each line of the file, python.txt.
Output:
The following output will appear after running the above command. Here, the searching text, ‘Python’ appears two times in the second line only and it is replaced by the text, ‘Perl‘.
4. Replace the last occurrence only of a match on each line
Create a text file named lang.txt with the following content.
lang.txt
Bash Programming Language. Python Programming Language. Perl Programming Language.
Hypertext Markup Language.
Extensible Markup Language.
5. Replace the first match in a file with new text
The following command will replace only the first match of the searching pattern, ‘Python‘ by the text, ‘perl‘. Here, ‘1’ is used to match the first occurrence of the pattern.
Output:
The following output will appear after running the above commands. Here. the first occurrence of ‘Python’ in the first line is replaced by ‘perl’.
6. Replace the last match in a file with new text
The following command will replace the last occurrence of the searching pattern, ‘Python‘ by the text, ‘Bash’. Here, ‘$’ symbol is used to match the last occurrence of the pattern.
Output:
The following output will appear after running the above commands.
7. Escaping backslash in replace commands to manage search and replace of file paths
It is necessary to escape the backslash in the file path for searching and replacing. The following command of `sed` will add backslash (\) in the file path.
Output:
The file path, ‘/home/ubuntu/code/perl/add.pl’ is provided as input in the `sed` command and the following output will appear after running the above command.
8. Replace all files full path with just the filename no directory
The filename can be retrieved from the file path very easily by using `basename` command. `sed` command can also be used to retrieve the filename from the file path. The following command will retrieve the filename only from the file path provided by `echo` command.
Output:
The following output will appear after running the above command. Here, the filename, ‘myfile.txt’ is printed as output.
9. Substitute text but only if some other text is found in the string
Create a file named ‘dept.txt’ with the following content to replace any text based on other text.
dept.txt
List of Total Students:
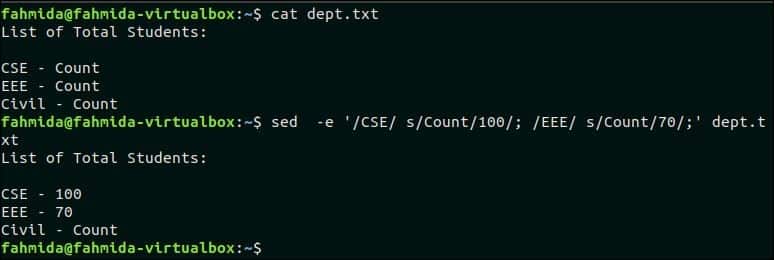
Two replace commands are used in the following `sed` command. Here, the text, ‘Count‘ will be replaced by 100 in the line that contains the text, ‘CSE‘ and the text, ‘Count’ will be replaced by 70 in the line that contains the searching pattern, ‘EEE’.
Output:
The following output will appear after the running the above commands.
10. Substitute text but only if some other text is not found in the string
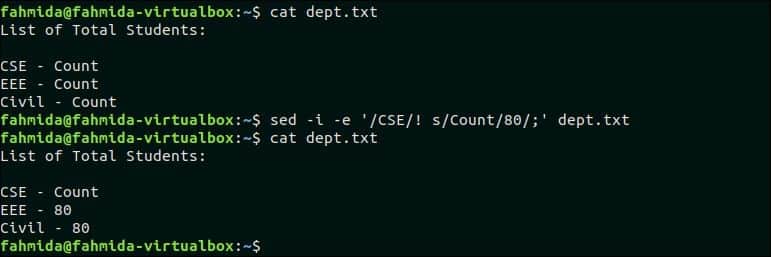
The following `sed` command will replace the ‘Count’ value in the line that does not contain the text, ‘CSE’. dept.txt file contains two lines that do not contain the text, ‘CSE’. So, the ‘Count‘ text will be replaced by 80 in two lines.
Output:
The following output will appear after running the above commands.
11. Add string before and after the matching pattern using ‘\1’
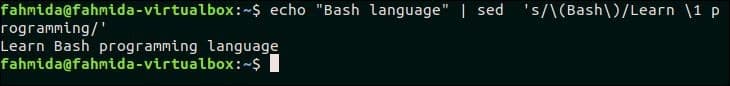
The sequence of matching patterns of `sed` command is denoted by ‘\1’, ‘\2’ and so on. The following `sed` command will search the pattern, ‘Bash’ and if the pattern matches then it will be accessed by ‘\1′ in the part of replacing text. Here, the text, ‘Bash’ is searched in the input text and, one text is added before and another text is added after ‘\1’.
Output:
The following output will appear after running the above command. Here, ‘Learn’ text is added before ‘Bash’ and ‘programming’ text is added after ‘Bash’.
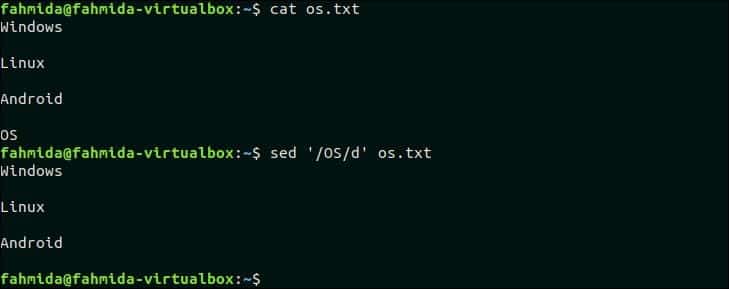
12. Delete matching lines
‘d’ option is used in `sed` command to delete any line from the file. Create a file named os.txt and add the following content to test the function of ‘d’ option.
cat os.txt
The following `sed` command will delete those lines from os.txt file that contains the text, ‘OS’.
Output:
The following output will appear after running the above commands.
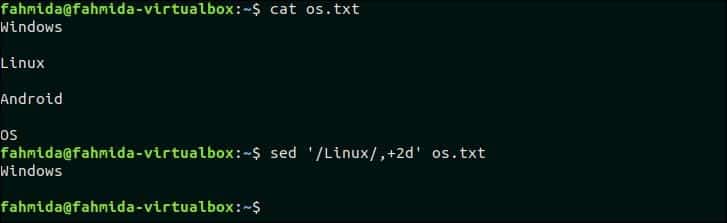
13. Delete matching line and 2 lines after matching line
The following command will delete three lines from the file os.txt if the pattern, ‘Linux’ is found. os.txt contains the text, ‘Linux‘ in the second line. So, this line and the next two lines will be deleted.
Output:
The following output will appear after running the above command.
14. Delete all spaces at end of the line of text
Using [:blank:] class can be used to remove spaces and tabs from the text or the content of any file. The following command will remove the spaces at the end of each line of the file, os.txt.
Output:
os.txt contains empty lines after each line those are deleted by the above `sed` command.
15. Delete all lines that have a match two times on the line
Create a text file named, input.txt with the following content and delete those lines of the file that contains the searching pattern two times.
input.txt
PHP is a server-side scripting language.
PHP is an open-source language and PHP is case-sensitive.
PHP is platform-independent.
‘PHP’ text contains two times in the second line of the file, input.txt. Two `sed` commands are used in this example to remove those lines that contain the pattern ‘php‘ two times. The first `sed` command will replace the second occurrence of ‘php’ in each line by ‘dl‘ and send the output into the second `sed` command as input. The second `sed` command will delete those lines that contain the text, ‘dl‘.
Output:
input.txt file has two lines that contain the pattern, ‘php’ two times. So, the following output will appear after running the above commands.
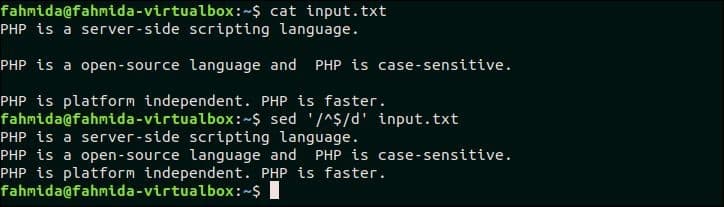
16. Delete all lines that have only white-space
Select any file that contains empty lines in the content to test this example. input.txt file that is created in the previous example, contains two empty lines that can be deleted by using the following `sed` command. Here, ‘^$’ is used to find out the empty lines in the file, input.txt.
Output:
The following output will appear after running the above commands.
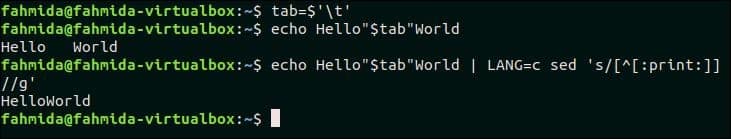
17. Delete all non-printable characters
Non-printable characters can be deleted from any text by replacing non-printable characters by none. [:print:] class is used in this example to find out the non-printable characters. ‘\t’ is a non-printable character and it can’t be parsed directly by the `echo` command. For this, ‘\t’ character is assigned in a variable, $tab that is used in an `echo` command. The output of the `echo` command is sent in the `sed` command that will remove the character, ‘\t’ from the output.
The following output will appear after running the above commands. The first `echo command will print the output with tab space and the `sed` command will print the output after removing the tab space.
18. If there is a match in line append something to end of line
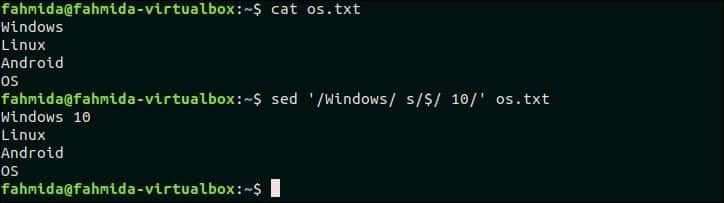
The following command will append ’10’ at the end of the line that contains the text, ‘Windows’ in the os.txt file.
Output:
The following output will appear after running the command.
19. If there is a match in the line insert a line before the text
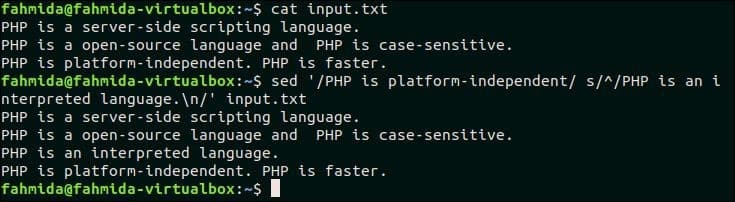
The following `sed` command will search the text, ‘PHP is platform-independent’ in the input.txt file that is created before. If the file contains this text in any line then, ‘PHP is an interpreted language’ will be inserted before that line.
Output:
The following output will appear after running the above commands.
20. If there is a match in the line insert a line after that line
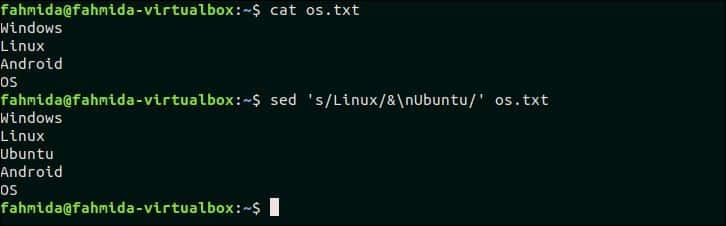
The following `sed` command will search the text, ‘Linux’ in the file os.txt and if the text exists in any line then a new text, ‘Ubuntu‘ will be inserted after that line.
Output:
The following output will appear after running the above commands.
21. If there is not a match append something to the end of line
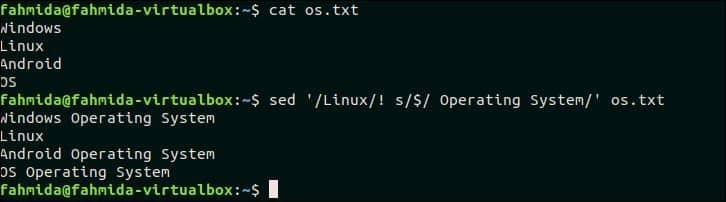
The following `sed` command will search those lines in os.txt that does not contain the text, ‘Linux’ and append the text, ‘Operating System‘ at the end of each line. Here, ‘$‘ symbol is used to identify the line where the new text will be appended.
Output:
The following output will appear after running the above commands. Three lines exist in the file os.txt that does not contain the text, ‘Linux’ and the new text s added at the end of these lines.
22. If there is not a match delete the line
Create a file named web.txt and add the following content and delete lines that do not contain the matching pattern. web.txt HTML 5JavaScriptCSSPHPMySQLJQuery The following `sed` command will search and delete those lines that do not contain the text, ‘CSS’. $ cat web.txt$ sed ‘/CSS/!d’ web.txt Output: The following output will appear after running the above commands. There is one line exists in the file that contains the text, ‘CSE’. So, the output contains just one line.
23. Duplicate matched text after adding a space after the text
The following `sed` command will search the word, ‘to’ in the file, python.txt and if the word exists then the same word will be inserted after the search word by adding space. Here, ‘&’ symbol is used to append the duplicate text.
Output:
The following output will appear after running the commands. Here, the word, ‘to’ is searched in the file, python.txt and this word exists in the second line of this file. So, ‘to’ with space is added after the matching text.
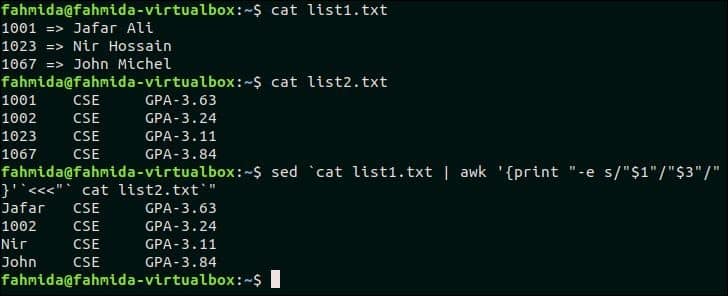
24. Replace one list of strings with the new string
You have to create two list files for testing this example. Create a text file named list1.txt and add the following content.
cat list1.txt
Create a text file named list2.txt and add the following content.
$ cat list2.txt
The following `sed` command will match the first column of the two text files shown above and replace the matching text with the value of the third column of the file list1.txt.
Output:
1001, 1023 and 1067 of list1.txt file match with the three data of list2.txt file and these values are replaced by corresponding names of the third column of list1.txt.
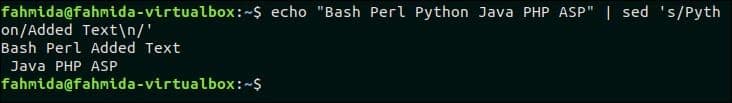
25. Replace the matched string with a string that contains newlines
The following command will take input from the `echo` command and search the word, ‘Python’ in the text. If the word exists in the text then a new text, ‘Added Text’ will be inserted with newline. $ echo “Bash Perl Python Java PHP ASP” | sed ‘s/Python/Added Text\n/’ Output: The following output will appear after running the above command.
26. Remove newlines from file and insert a comma at end of each line
The following `sed` command will replace each newline by a comma in the file os.txt. Here, -z option is used to separate the line by NULL character.
Output:
The following output will appear after running the above command.
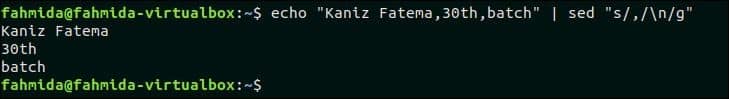
27. Remove commas and add newline to split the text into multiple lines
The following `sed` command will take the comma-separated line from the `echo` command as input and replace the comma by newline.
Output:
The following output will appear after running the above command. The input text contains three comma-separated data that are replaced by newline and printed in three lines.
28. Find case insensitive match and delete line
‘I’ is used in `sed` command for the case-insensitive match that indicates ignore case. The following `sed` command will search the line that contains the word, ‘linux‘ and delete the line from os.txt file.
Output:
The following output will appear after running the above command. os.txt contains the word, ‘Linux’ that matched with the pattern, ‘linux’ for case-insensitive search and deleted.
29. Find case insensitive match and replace with new text
The following `sed` command will take the input from the `echo` command and replace the word, ‘bash’ by the word, ‘PHP’.
Output:
The following output will appear after running the above command. Here, the word, ‘Bash’ matched with the word, ‘bash’ for case-insensitive search and replaced by the word, ‘PHP’.
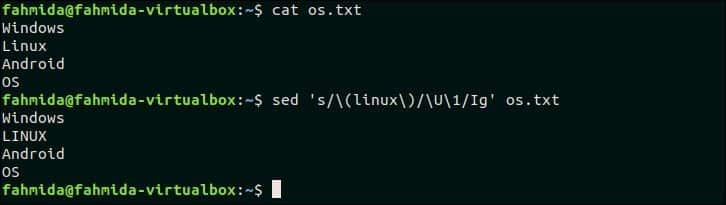
30. Find case insensitive match and replace with all uppercase of the same text
‘\U’ is used in `sed` to convert any text to all uppercase letter. The following `sed` command will search the word, ‘linux‘ in the os.txt file and if the word exists then it will replace the word with all uppercase letters.
Output:
The following output will appear after running the above commands. The word, ‘Linux’ of os.txt file is replaced by the word, ‘LINUX’.
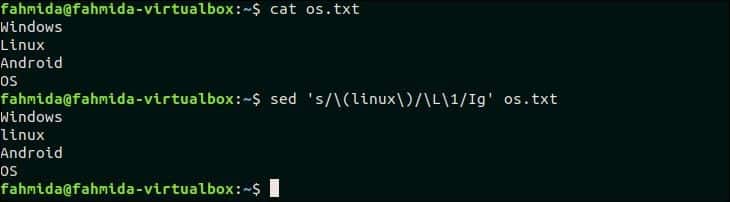
31. Find case insensitive match and replace with all lowercase of same text
‘\L’ is used in `sed` to convert any text to all lowercase letters. The following `sed` command will search the word, ‘Linux’ in the os.txt file and replace the word by all lowercase letters.
Output:
The following output will appear after running the above commands. The word, ‘Linux’ is replaced by the word, ‘linux’ here.
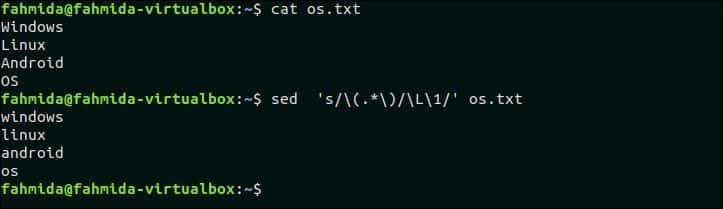
32. Replace all uppercase characters of the text with lowercase characters
The following `sed` command will search all uppercase characters in the os.txt file and replace the characters by lowercase letters by using ‘\L’.
Output:
The following output will appear after running the above commands.
33. Search for number in line and append any currency symbol before the number
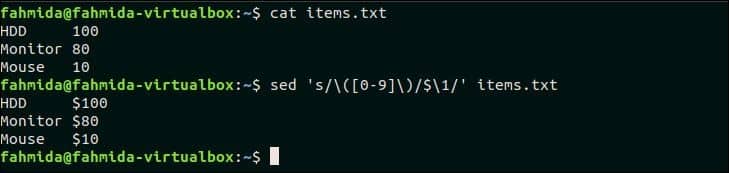
Create a file named items.txt with the following content.
items.txt
The following `sed` command will search the number in each line of items.txt file and append the currency symbol, ‘$’ before each number.
Output:
The following output will appear after running the above commands. Here, ‘$’ symbol is added before the number of each line.
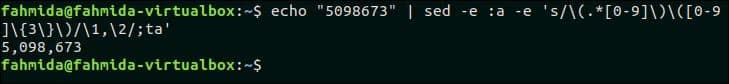
34. Add commas to numbers that have more than 3 digits
The following `sed` command will take a number as input from `echo` command and add comma after each group of three digits counting from the right. Here, ‘:a’ indicates the label and ‘ta’ is used to iterate grouping process.
Output:
The number 5098673 is given in the `echo` command and the `sed` command generated the number 5,098,673 by adding comma after each group of three digits.
35. Replaces tab character with 4 space characters
The following `sed` command will replace each tab (\t) character by four space characters. ‘$’ symbol is used in the `sed` command to match the tab character and ‘g’ is used to replace all tab characters.
Output:
The following output will appear after running the above command.
36. Replaces 4 consecutive space characters with tab character
The following command will replace 4 consecutive characters with tab (\t) character.
Output:
The following output will appear after running the above command.
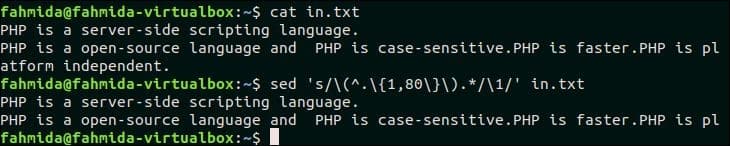
37. Truncate all lines to first 80 characters
Create a text file named in.txt that contains the lines more than 80 characters to test this example.
in.txt
PHP is a server-side scripting language.
PHP is an open-source language and PHP is case-sensitive. PHP is platform-independent.
The following `sed` command will truncate each line of in.txt file into 80 characters.
Output:
The following output will appear after running the above commands. The second line of in.txt file contains more than 80 characters and this line is truncated in the output.
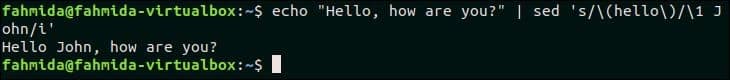
38. Search for a string regex and append some standard text after it
The following `sed` command will search the text, ‘hello‘ in the input text and append the text, ‘ John‘ after that text.
Output:
The following output will appear after running the above command.
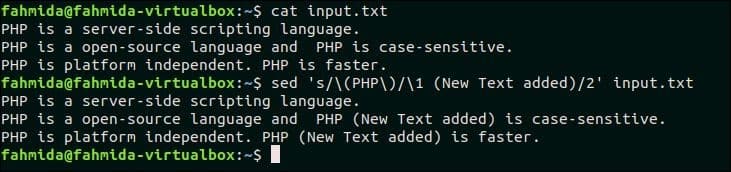
39. Search for string regex and append some text after the second match in each line
The following `sed` command will search the text, ‘PHP‘ in each line of input.txt and replace the second match in each line with the text, ‘New Text Added’.
Output:
The following output will appear after running the above commands. The searching text, ‘PHP’ appears for two times in the second and third lines of input.txt file. So, the text, ‘New Text added’ is inserted in the second and third lines.
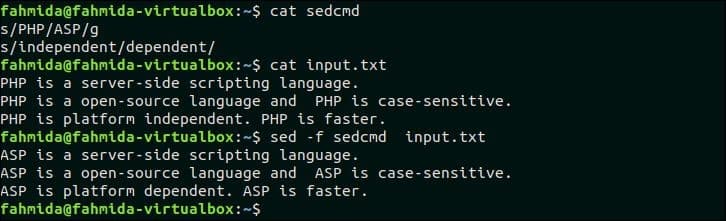
40. Running multi-line `sed` scripts from a file
Multiple `sed` scripts can be stored in a file and all the scripts can be executed together by running `sed` command. Create a file named ‘sedcmd‘ and add the following content. Here, two `sed` scripts are added in the file. One script will replace the text, ‘PHP‘ by ‘ASP‘ another script will replace the text, ‘independent‘ by the text, ‘dependent‘.
sedcmd
The following `sed` command will replace all ‘PHP’ and ‘independent’ text by ‘ASP’ and ‘dependent’. Here, ‘-f’ option is used in the `sed` command to execute `sed` script from the file.
Output:
The following output will appear after running above commands.
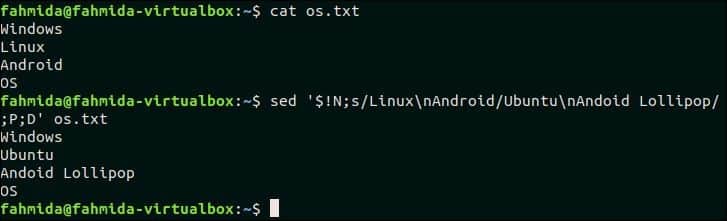
41. Match a multi-line pattern and replace with new multi-line text
The following `sed` command will search the multi-line text, ‘Linux\nAndroid’ and if the pattern matches then the matching lines will be replaced by the multi-line text, ‘Ubuntu\nAndroid Lollipop‘. Here, P and D are used for multiline processing.
Output:
The following output will appear after running the above commands.
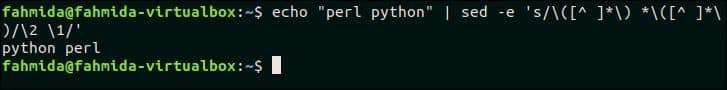
42. Replace order of two words in a text that match a pattern
The following `sed` command will take the input of two words from `echo` command and replace the order of these words.
Output:
The following output will appear after running the above command.
43. Execute multiple `sed` commands from the command-line
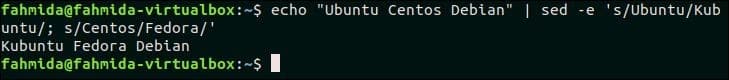
‘-e’ option is used in `sed` command to run multiple `sed` scripts from the command line. The following `sed` command will take a text as input from `echo` command and replaces ‘Ubuntu‘ by ‘Kubuntu‘ and ‘Centos‘ by ‘Fedora‘.
Output:
The following output will appear after running the above command. Here, ‘Ubuntu’ and ‘Centos’ are replaced by ‘Kubuntu’ and ‘Fedora’.
44. Combine `sed` with other commands
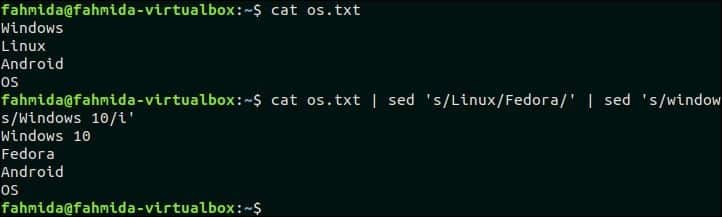
The following command will combine the `sed` command with `cat` command. The first `sed` command will take input from os.txt file and send the output of the command to second `sed` command after replacing the text’ ‘Linux’ by ‘Fedora’. The second `sed` command will replace the text, ‘Windows’ by ‘Windows 10’.
Output:
The following output will appear after running the above command.
45. Insert empty line in a file
Create a file named stdlist with the following content.
stdlist
‘G’ option is used to insert empty line in a file. The following `sed` command will insert empty lines after each line of stdlist file.
Output:
The following output will appear after running the above commands. An empty line is inserted after each line of the file.
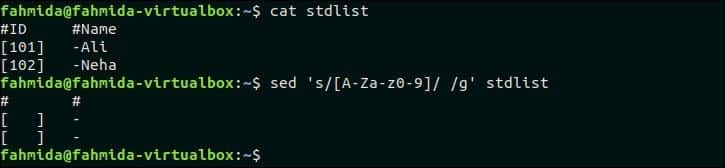
46. Replace all alpha-numeric characters by space in each line of a file.
The following command will replace all alpha-numeric characters by space in the stdlist file.
Output:
The following output will appear after running the above commands.
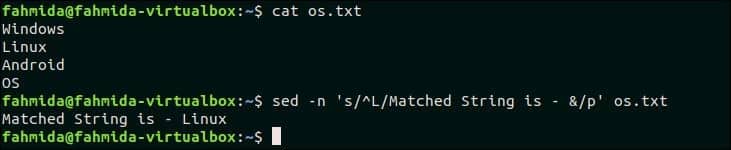
47. Use ‘&’ to print matched string
The following command will search the word starting with ‘L’ and replace the text by appending ‘Matched String is –‘ with the matched word by using ‘&’ symbol. Here, ‘p’ is used to print the modified text.
Output:
The following output will appear after running the above command.
48. Switch pair of words in a file
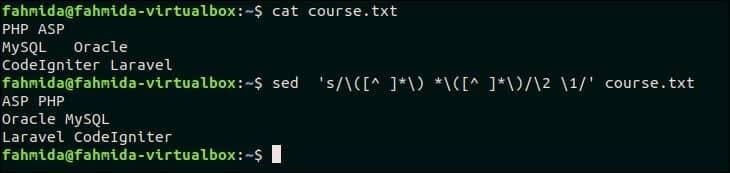
Create a text file named course.txt with the following content that contains the pair of words in each line.
course.txt
The following command will switch the pair of words in each line of the file, course.txt.
Output:
The following output will appear after switching the pair of words in each line.
49. Capitalize the first character of each word
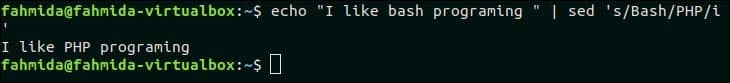
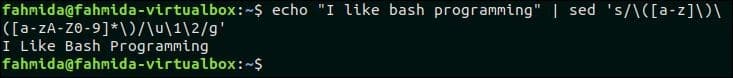
The following `sed` command will take input text from the `echo` command and convert the first character of each word to a capital letter.
Output:
The following output will appear after running the above command. The input text, “I like bash programming” is printed as “I Like Bash Programming” after capitalizing the first word.
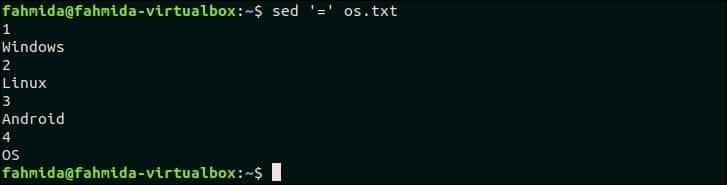
50. Print line numbers of the file
‘=’ symbol is used `sed` command to print the line number before each line of a file. The following command will print the content of os.txt file with line number.
Output:
The following output will appear after running the above command. There are four lines in os.txt file. So, the line number is printed before each line of the file.
Conclusion:
Different uses of `sed` command are explained in this tutorial by using very simple examples. The output of all `sed` scripts mentioned here are generated temporary and the content of the original file remained unchanged. But if you want you can modify the original file by using –i or –in-place option of `sed command. If you are a new Linux user and want to learn the basic uses of `sed` command to perform various types of string manipulation tasks, then this tutorial will help you. After reading this tutorial, hope, any user will get the clear concept about the functions of `sed` command.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the sed command used for?
The sed command has a number of different uses. That being said, the main usage is for substituting words in a file, or finding and replacing.
The great thing about sed is that you can search for a word in a file and replace it, but you never even have to open the file – sed just does it all for you!
As well as this, it can be used for deletion. All you need to do is type the word you want to find, replace or delete into sed, and it brings it up for you – you can then choose to replace that word or delete all traces of the word from your file.
sed is a fantastic tool to be able to replace things like IP addresses and anything that is highly sensitive that you would not otherwise want to put in a file. sed is a must-know for any software engineer!
What is S and G in sed command?
In its most simple terms, the S function that can be used in sed simply means ‘substitute’. After typing the S you can replace or substitute anything you wish – just typing S will only replace the first occurrence of the word on a line.
Therefore, if you have a sentence or line that mentions it more than once, the S function is not ideal as it will only substitute the first occurrence. You can specify a pattern to make S replace words every two occurrences as well.
Specifying G at the end of the sed command will do a global replacement (that is what the G stands for). With this in mind, if you specify G it will replace every occurrence of the word you have chosen, rather than just the first occurrence that the S does.
How do I run a sed script?
You can run a sed script in a number of ways but the most common is on the command line. Here you can just specify sed and the file you want to use the command on.
This allows you to use sed on that file, allowing you to find, delete and substitute as needed.
You can also use it in a shell script, and this way you can pass whatever you want to the script, and it will run the find and replace command for you. This is useful for not wanting to specify highly sensitive data inside a script, so instead, you can pass it in as a variable
Bear in mind that this is of course only available on Linux, and so you will need to ensure you have a Linux command line in order to run your sed script.
About the author
Fahmida Yesmin
I am a trainer of web programming courses. I like to write article or tutorial on various IT topics. I have a YouTube channel where many types of tutorials based on Ubuntu, Windows, Word, Excel, WordPress, Magento, Laravel etc. are published: Tutorials4u Help.
Источник