- SambaAD start
- Содержание
- Установка [ править ]
- Управление пользователями [ править ]
- Подключение компьютера [ править ]
- AD/Samba-клиент и клонирование рабочей станции [ править ]
- GUI для управления Samba [ править ]
- Особенности [ править ]
- Управления пользователями и компьютерами [ править ]
- Правки ADSI [ править ]
- Управление DNS [ править ]
- Управления групповой политикой [ править ]
- Вторичный контроллер [ править ]
- Репликация [ править ]
- Ошибки [ править ]
- Прочее [ править ]
- Ручное обновление кэша SSSD [ править ]
- How to add or delete a samba user under Linux
- Adding a Linux user account
- Adding Samba user
- Allowing user to access samba share
- Deleting the Samba user
- Linux list samba users
- Synopsis
- DESCRIPTION
- OPTIONS
- COMMANDS
- computer
- computer add computername [options]
- computer create computername [options]
- computer delete computername [options]
- computer edit computername
- computer list
- computer move computername new_parent_dn [options]
- computer show computername [options]
- contact
- contact add [ contactname ] [options]
- contact create [ contactname ] [options]
- contact delete contactname [options]
- contact edit contactname
- contact list [options]
- contact move contactname new_parent_dn [options]
- contact show contactname [options]
- contact rename contactname [options]
- dbcheck
- delegation
- delegation add-service accountname principal [options]
- delegation del-service accountname principal [options]
- delegation for-any-protocol accountname [(on|off)] [options]
- delegation for-any-service accountname [(on|off)] [options]
- delegation show accountname [options]
- dns add server zone name A|AAAA|PTR|CNAME|NS|MX|SRV|TXT data
- dns delete server zone name A|AAAA|PTR|CNAME|NS|MX|SRV|TXT data
- dns query server zone name A|AAAA|PTR|CNAME|NS|MX|SRV|TXT|ALL [options] data
- dns roothints server [ name ] [options]
- dns serverinfo server [options]
- dns update server zone name A|AAAA|PTR|CNAME|NS|MX|SRV|TXT olddata newdata
- dns zonecreate server zone [options]
- dns zonedelete server zone [options]
- dns zoneinfo server zone [options]
- dns zonelist server [options]
- domain
- domain backup
- domain backup offline
- domain backup online
- domain backup rename
- domain backup restore
- domain classicupgrade [options] classic_smb_conf
- domain dcpromo dnsdomain [DC|RODC] [options]
- domain demote
- domain exportkeytab keytab [options]
- domain info ip_address [options]
- domain join dnsdomain [DC|RODC|MEMBER|SUBDOMAIN] [options]
- domain level show|raise options [options]
- domain passwordsettings show|set options [options]
- domain passwordsettings pso
- domain passwordsettings pso apply pso-name user-or-group-name [options]
- domain passwordsettings pso create pso-name precedence [options]
- domain passwordsettings pso delete pso-name [options]
- domain passwordsettings pso list [options]
- domain passwordsettings pso set pso-name [options]
- domain passwordsettings pso show user-name [options]
- domain passwordsettings pso show-user pso-name [options]
- domain passwordsettings pso unapply pso-name user-or-group-name [options]
- domain provision
- domain trust
- domain trust create DOMAIN options [options]
- domain trust delete DOMAIN options [options]
- domain trust list options [options]
- domain trust namespaces [ DOMAIN ] options [options]
- domain trust show DOMAIN options [options]
- domain trust validate DOMAIN options [options]
- drs bind
- drs kcc
- drs options
- drs replicate destination_DC source_DC NC [options]
- drs showrepl
- dsacl
- dsacl set
- forest
- forest directory_service
- forest directory_service dsheuristics VALUE
- forest directory_service show
SambaAD start
SambaAD(DC) — реализация службы каталогов на Samba. В данной статье будет рассмотрена в роли домена.
Содержание
Установка [ править ]
Вводим имя компьютера и домена:
Копируем файл настроек krb5:
Перед строчкой nameserver добавляем строку nameserver с адресом 127.0.0.1, первую по очередности.
Т.к. Samba использует свой DNS-сервер удаляем bind:
(адрес должен иметь адрес 127.0.0.1)
4)Проверяем имена хостов:
адрес _kerberos._udp.*адрес домена с точкой
адрес _ldap._tcp.*адрес домена с точкой
адрес хоста.*адрес домена с точкой
Password for administrator@PETR.RU: Warning: Your password will expire in 41 days on Чт 29 апр 2021 18:25:49
6)Просмотр полученного билета:
Управление пользователями [ править ]
Создать пользователя с паролем[1], :
Просмотреть доступных пользователей:
Изменить пароль пользователя:
Не забудьте разблокировать пользователя:
Если компьютер с таким именем заведён, удалить его можно командой:
Добавить пользователя в группу:
Удалить пользователя из группы:
Смотрим значение memberOf
Подключение компьютера [ править ]
Идем в /etc/net/ifaces/eth0
Правим настройки IPv4:
Правим настройки шлюза:
Домены по-умолчанию и DNS-сервера:
Т.к. Samba использует свой DNS-сервер удаляем bind:
Применяем настройки DNS:
Проверяем, пингуется ли домен:
Если не пингуется, проверяйте настройки сети и DNS и перезапускайте еще раз их.
И дописываем после:
Запускаем службы wicd:
Удаляем Network Manager:
- ЦУС-Пользователи-Аутентификация
- Домен AD:
- домен petr.ru
- рабочая группа: PETR
- имя компьютера: вводим свое
- Вводим пароль доменного администратора
- Перезагружаемся
- в файл options настраиваемого интерфейса добавляем:
- включаем его загрузку через systemd:
в нашем примере:
AD/Samba-клиент и клонирование рабочей станции [ править ]
Если вы настроили на одном компьютере ALT Linux с AD/Samba доменом и хотите развернуть образ на другом компьютере, приготовьтесь потом сделать следующее. Каждый компьютер введенный в домен получает keytab-файл от Kerberos. И если вы уже введенную в домен систему развернете на другом компьютере, она будет конфликтовать из-за Kerberos-билета.
Чтобы не было конфликта:
- введите систему в домен
- клонируйте акронимом/подобным (склонируйте-разверните)
- выведите систему из домена
- переименуйте компьютер
- удалите файл /etc/krb5.keytab
- введите в домен[3]
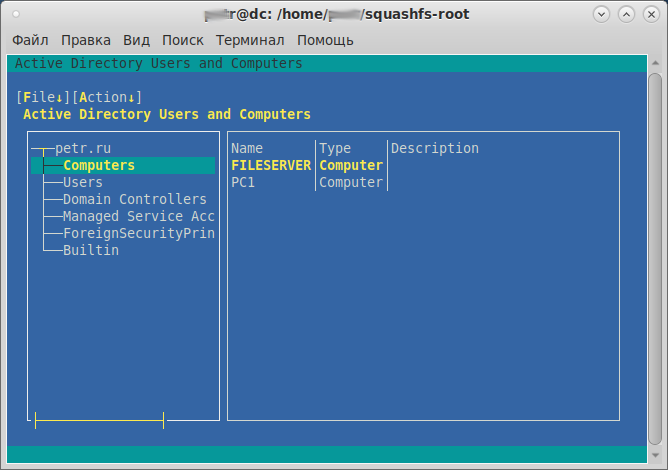
GUI для управления Samba [ править ]
- управления пользователями и компьютерами
- Правки ADSI
- Управления DNS
- Управления групповой политикой
можно использовать утилиту Admin Tools.
Переходи в каталог со скачанной программой, распаковываем ее из архива и распаковываем:
Потом переходим в каталог с программой и запускаем в консоли:
Для управления используйте Tab, пробел и Esc.
- username: Administrator
- password: ваш пароль
- domain: домен с точкой, вида DOMAIN.RU
Особенности [ править ]
Управления пользователями и компьютерами [ править ]
- Табом, стрелками и Enter выбираем элемент, потом табом переходим в Action и выбираем Propereties.
- Затем Edit.
Правки ADSI [ править ]
- Делаем Action-Connect to-Computer-Select or type a domain or server-вводим имя домена (DOMAIN.RU)
- username: Administrator
- password: ваш пароль
- domain: домен с точкой, вида DOMAIN.RU
- Табом, стрелками и Enter выбираем элемент, потом табом переходим в Action и выбираем Propereties.
- Затем Edit.
Управление DNS [ править ]
- Делаем Action-Connect to DNS-server-The following computer-Select or type a domain or server-вводим имя домена (DOMAIN.RU)
- username: Administrator
- password: ваш пароль
- domain: домен с точкой, вида DOMAIN.RU
- Табом, стрелками и Enter выбираем элемент, потом табом переходим в Action и выбираем Propereties.
- Затем Edit.
Здесь же можно создать всякие A, AAA и пр. записи и т.п.
Управления групповой политикой [ править ]
- username: Administrator
- password: ваш пароль
- domain: домен с точкой, вида DOMAIN.RU
Но править политики там нельзя.
Вторичный контроллер [ править ]
2.Ставим на него samba-dc.
4.Присваиваем имя DC2
5.Заводим IP-адрес для DC2 на основном домене:
6.На DC2 правим /etc/krb5.conf
7. Перезапускаем сеть и самбу
8. Получаем билет и убеждаемся, что билет получен:
9. Вводим в домен:
Если всё нормально, в конце видим:
10. После успешного ввода в домен в resolvconf необходимо сменить адрес PDC на адрес вторичного DC (в нашем примере 10.0.2.7).
Для этого правим файл /etc/net/ifaces/eth0/resolv.conf
11. Включаем и запускаем службу samba:
12. На DC2 выполняем:
13. Правим hosts Samba
Правим файл /etc/samba/lmhosts (на обоих контроллерах) — это локальный hosts файл используемый Samba.
Прописываем туда оба домена.
- в файл options настраиваемого интерфейса добавляем:
- включаем его загрузку через systemd:
в нашем примере:
Репликация [ править ]
Репликация выполняется на вторичном контроллере.
1. Реплицируем с первичного (1-й приемник, 2-й источник)
2. Реплицируем на первичный (1-й приемник, 2-й источник)
3. Просмотр статуса репликации
Чтобы сделать репликацию в планировщике заданий, добавьте параметр пароля:
Ошибки [ править ]
Рассинхронизация времени на контроллерах домена. Сделайте время на контроллерах одинаковым.
2.Ошибка при репликации на второй:
Выполните на вторичном контроллере:
где dc2.petr.ru — ваш вторичный контроллер домена
3.Ошибка при репликации на первый:
Не прописаны домены в /etc/samba/lmhosts.
Прочее [ править ]
Ручное обновление кэша SSSD [ править ]
Необходимое удалить его базы и перезапустить.[4]
Источник
How to add or delete a samba user under Linux
To add a new user to access a samba share you need to first create a server user account using “useradd” command and then use the same account to add the samba user. Follow the steps givenbelow to add user john and give him the access to a samba share.
Adding a Linux user account
One way for a user to browse a Samba share is have a UNIX account on the Samba server. This is done via the commands ‘useradd [username]‘ and ‘passwd [username]‘. If you already have the user account created on the system, skip the part below and proceed to add samba user directly.
Set the password for the new user created.
Adding Samba user
Once the user has a local account their corresponding Samba samba user can be added using smbpasswd -a command. The smbpasswd command when used with -a option adds the new samba user and also allows you to set the password for the new samba user. For example for the user john, use the command below:
The -a switch adds john to the Samba password list.
To modify an existing Samba user’s Samba password (using the example john user again):
Allowing user to access samba share
Configure the Samba share in the /etc/samba/smb.conf configuration file to allow the new user to browse the share:
Use testparm to show your updated share. Reload the smb.conf configuration file with below command.
For RHEL/CentOS 6
For RHEL/CentOS 7
Deleting the Samba user
In order to delete the samba user, use the steps below. make sure you delete the corresponding UNIX user from the server as well if required.
1. delete samba user(john) using smbpasswd command with -x option.
2. You can now delete the UNIX OS user john along with all the files associated with the user like home directory, using the ‘userdel -r’ command.
Источник
Linux list samba users
samba-tool — Main Samba administration tool.
Synopsis
samba-tool [-h] [-W myworkgroup] [-U user] [-d debuglevel] [—v]
DESCRIPTION
This tool is part of the samba (7) suite.
OPTIONS
Show this help message and exit
Set the realm for the domain.
Note that specifying this parameter here will override the realm parameter in the smb.conf file.
DN to use for a simple bind.
Specify the password on the commandline.
Be cautious about including passwords in scripts or passing user-supplied values onto the command line. For security it is better to let the Samba client tool ask for the password if needed, or obtain the password once with kinit .
If —password is not specified, the tool will check the PASSWD environment variable, followed by PASSWD_FD which is expected to contain an open file descriptor (FD) number.
Finally it will check PASSWD_FILE (containing a file path to be opened). The file should only contain the password. Make certain that the permissions on the file restrict access from unwanted users!
While Samba will attempt to scrub the password from the process title (as seen in ps), this is after startup and so is subject to a race.
Sets the SMB username or username and password.
If %PASSWORD is not specified, the user will be prompted. The client will first check the USER environment variable (which is also permitted to also contain the password seperated by a %), then the LOGNAME variable (which is not permitted to contain a password) and if either exists, the value is used. If these environmental variables are not found, the username found in a Kerberos Credentials cache may be used.
A third option is to use a credentials file which contains the plaintext of the username and password. This option is mainly provided for scripts where the admin does not wish to pass the credentials on the command line or via environment variables. If this method is used, make certain that the permissions on the file restrict access from unwanted users. See the -A for more details.
Be cautious about including passwords in scripts or passing user-supplied values onto the command line. For security it is better to let the Samba client tool ask for the password if needed, or obtain the password once with kinit .
While Samba will attempt to scrub the password from the process title (as seen in ps), this is after startup and so is subject to a race.
Set the SMB domain of the username. This overrides the default domain which is the domain defined in smb.conf. If the domain specified is the same as the servers NetBIOS name, it causes the client to log on using the servers local SAM (as opposed to the Domain SAM).
Note that specifying this parameter here will override the workgroup parameter in the smb.conf file.
If specified, this parameter suppresses the normal password prompt from the client to the user. This is useful when accessing a service that does not require a password.
Unless a password is specified on the command line or this parameter is specified, the client will request a password.
If a password is specified on the command line and this option is also defined the password on the command line will be silently ignored and no password will be used.
This parameter determines whether Samba client tools will try to authenticate using Kerberos. For Kerberos authentication you need to use dns names instead of IP addresses when connnecting to a service.
Note that specifying this parameter here will override the client use kerberos parameter in the smb.conf file.
Specifies the credential cache location for Kerberos authentication.
This will set —use-kerberos=required too.
IP address of the server
level is an integer from 0 to 10. The default value if this parameter is not specified is 1 for client applications.
The higher this value, the more detail will be logged to the log files about the activities of the server. At level 0, only critical errors and serious warnings will be logged. Level 1 is a reasonable level for day-to-day running — it generates a small amount of information about operations carried out.
Levels above 1 will generate considerable amounts of log data, and should only be used when investigating a problem. Levels above 3 are designed for use only by developers and generate HUGE amounts of log data, most of which is extremely cryptic.
Note that specifying this parameter here will override the log level parameter in the smb.conf file.
This will redirect debug output to STDOUT. By default all clients are logging to STDERR.
COMMANDS
computer
Manage computer accounts.
computer add computername [options]
Add a new computer to the Active Directory Domain.
The new computer name specified on the command is the sAMAccountName, with or without the trailing dollar sign.
DN of alternative location (with or without domainDN counterpart) to default CN=Computers in which new computer object will be created. E.g. ‘OU=OUname’.
The new computers’s description.
IPv4 address for the computer’s A record, or IPv6 address for AAAA record, can be provided multiple times.
Computer’s Service Principal Name, can be provided multiple times.
Prepare enabled machine account for oldjoin mechanism.
computer create computername [options]
Add a new computer. This is a synonym for the samba-tool computer add command and is available for compatibility reasons only. Please use samba-tool computer add instead.
computer delete computername [options]
Delete an existing computer account.
The computer name specified on the command is the sAMAccountName, with or without the trailing dollar sign.
computer edit computername
Edit a computer AD object.
The computer name specified on the command is the sAMAccountName, with or without the trailing dollar sign.
Specifies the editor to use instead of the system default, or ‘vi’ if no system default is set.
computer list
List all computers.
computer move computername new_parent_dn [options]
This command moves a computer account into the specified organizational unit or container.
The computername specified on the command is the sAMAccountName, with or without the trailing dollar sign.
The name of the organizational unit or container can be specified as a full DN or without the domainDN component.
computer show computername [options]
Display a computer AD object.
The computer name specified on the command is the sAMAccountName, with or without the trailing dollar sign.
Comma separated list of attributes, which will be printed.
contact
contact add [ contactname ] [options]
Add a new contact to the Active Directory Domain.
The name of the new contact can be specified by the first argument ‘contactname’ or the —given-name, —initial and —surname arguments. If no ‘contactname’ is given, contact’s name will be made up of the given arguments by combining the given-name, initials and surname. Each argument is optional. A dot (‘.’) will be appended to the initials automatically.
DN of alternative location (with or without domainDN counterpart) in which the new contact will be created. E.g. ‘OU=OUname’. Default is the domain base.
The new contacts’s description.
Contact’s given name.
Contact’s display name.
Contact’s job title.
Contact’s email address.
Contact’s home page.
Contact’s phone number.
Contact’s mobile phone number.
Contact’s office location.
contact create [ contactname ] [options]
Add a new contact. This is a synonym for the samba-tool contact add command and is available for compatibility reasons only. Please use samba-tool contact add instead.
contact delete contactname [options]
Delete an existing contact.
The contactname specified on the command is the common name or the distinguished name of the contact object. The distinguished name of the contact can be specified with or without the domainDN component.
contact edit contactname
Modify a contact AD object.
The contactname specified on the command is the common name or the distinguished name of the contact object. The distinguished name of the contact can be specified with or without the domainDN component.
Specifies the editor to use instead of the system default, or ‘vi’ if no system default is set.
contact list [options]
List all contacts.
Display contact’s full DN instead of the name.
contact move contactname new_parent_dn [options]
This command moves a contact into the specified organizational unit or container.
The contactname specified on the command is the common name or the distinguished name of the contact object. The distinguished name of the contact can be specified with or without the domainDN component.
contact show contactname [options]
Display a contact AD object.
The contactname specified on the command is the common name or the distinguished name of the contact object. The distinguished name of the contact can be specified with or without the domainDN component.
Comma separated list of attributes, which will be printed.
contact rename contactname [options]
Rename a contact and related attributes.
This command allows to set the contact’s name related attributes. The contact’s CN will be renamed automatically. The contact’s new CN will be made up by combining the given-name, initials and surname. A dot (‘.’) will be appended to the initials automatically, if required. Use the —force-new-cn option to specify the new CN manually and —reset-cn to reset this change.
Use an empty attribute value to remove the specified attribute.
The contact name specified on the command is the CN.
Specify a new CN (RDN) instead of using a combination of the given name, initials and surname.
Set the CN to the default combination of given name, initials and surname.
New display name.
New email address.
dbcheck
Check the local AD database for errors.
delegation
delegation add-service accountname principal [options]
Add a service principal as msDS-AllowedToDelegateTo.
delegation del-service accountname principal [options]
Delete a service principal as msDS-AllowedToDelegateTo.
delegation for-any-protocol accountname [(on|off)] [options]
Set/unset UF_TRUSTED_TO_AUTHENTICATE_FOR_DELEGATION (S4U2Proxy) for an account.
delegation for-any-service accountname [(on|off)] [options]
Set/unset UF_TRUSTED_FOR_DELEGATION for an account.
delegation show accountname [options]
Show the delegation setting of an account.
Manage Domain Name Service (DNS).
dns add server zone name A|AAAA|PTR|CNAME|NS|MX|SRV|TXT data
Add a DNS record.
dns delete server zone name A|AAAA|PTR|CNAME|NS|MX|SRV|TXT data
Delete a DNS record.
dns query server zone name A|AAAA|PTR|CNAME|NS|MX|SRV|TXT|ALL [options] data
dns roothints server [ name ] [options]
Query root hints.
dns serverinfo server [options]
Query server information.
dns update server zone name A|AAAA|PTR|CNAME|NS|MX|SRV|TXT olddata newdata
Update a DNS record.
dns zonecreate server zone [options]
dns zonedelete server zone [options]
dns zoneinfo server zone [options]
Query zone information.
dns zonelist server [options]
domain
domain backup
Create or restore a backup of the domain.
domain backup offline
Backup (with proper locking) local domain directories into a tar file.
domain backup online
Copy a running DC’s current DB into a backup tar file.
domain backup rename
Copy a running DC’s DB to backup file, renaming the domain in the process.
domain backup restore
Restore the domain’s DB from a backup-file.
domain classicupgrade [options] classic_smb_conf
Upgrade from Samba classic (NT4-like) database to Samba AD DC database.
domain dcpromo dnsdomain [DC|RODC] [options]
Promote an existing domain member or NT4 PDC to an AD DC.
domain demote
Demote ourselves from the role of domain controller.
domain exportkeytab keytab [options]
Dumps Kerberos keys of the domain into a keytab.
domain info ip_address [options]
Print basic info about a domain and the specified DC.
domain join dnsdomain [DC|RODC|MEMBER|SUBDOMAIN] [options]
Join a domain as either member or backup domain controller.
domain level show|raise options [options]
Show/raise domain and forest function levels.
domain passwordsettings show|set options [options]
Show/set password settings.
domain passwordsettings pso
Manage fine-grained Password Settings Objects (PSOs).
domain passwordsettings pso apply pso-name user-or-group-name [options]
Applies a PSO’s password policy to a user or group.
domain passwordsettings pso create pso-name precedence [options]
Creates a new Password Settings Object (PSO).
domain passwordsettings pso delete pso-name [options]
Deletes a Password Settings Object (PSO).
domain passwordsettings pso list [options]
Lists all Password Settings Objects (PSOs).
domain passwordsettings pso set pso-name [options]
Modifies a Password Settings Object (PSO).
domain passwordsettings pso show user-name [options]
Displays a Password Settings Object (PSO).
domain passwordsettings pso show-user pso-name [options]
Displays the Password Settings that apply to a user.
domain passwordsettings pso unapply pso-name user-or-group-name [options]
Updates a PSO to no longer apply to a user or group.
domain provision
Promote an existing domain member or NT4 PDC to an AD DC.
domain trust
Domain and forest trust management.
domain trust create DOMAIN options [options]
Create a domain or forest trust.
domain trust delete DOMAIN options [options]
Delete a domain trust.
domain trust list options [options]
List domain trusts.
domain trust namespaces [ DOMAIN ] options [options]
Manage forest trust namespaces.
domain trust show DOMAIN options [options]
Show trusted domain details.
domain trust validate DOMAIN options [options]
Validate a domain trust.
Manage Directory Replication Services (DRS).
drs bind
Show DRS capabilities of a server.
drs kcc
Trigger knowledge consistency center run.
drs options
Query or change options for NTDS Settings object of a domain controller.
drs replicate destination_DC source_DC NC [options]
Replicate a naming context between two DCs.
drs showrepl
Show replication status. The [—json] option results in JSON output, and with the [—summary] option produces very little output when the replication status seems healthy.
dsacl
Administer DS ACLs
dsacl set
Modify access list on a directory object.
forest
Manage Forest configuration.
forest directory_service
Manage directory_service behaviour for the forest.
forest directory_service dsheuristics VALUE
Modify dsheuristics directory_service configuration for the forest.
forest directory_service show
Show current directory_service configuration for the forest.
Manage Flexible Single Master Operations (FSMO).
Источник