- UNIX / Linux List Current Logged In Users
- Linux Command To List Current Logged In Users
- How to find currently logged in users in Linux
- Using w command to list current logged in users under Unix or Linux
- Understanding w command outputs
- Display all logged in users using who command
- Getting help with the whois command
- users command
- Vieing logged in users with last command
- Лог файлы Linux по порядку
- Основные лог файлы
- И другие журналы
- Чем просматривать — lnav
- Viewing Linux Logs from the Command Line
- /var/log
- Viewing logs with less
- Viewing logs with dmesg
- Viewing logs with tail
- There are other tools
UNIX / Linux List Current Logged In Users
H ow do I print the user names of users currently logged in to the current UNIX / Linux host / server from a command prompt?
You need to use any one of the following command line tools to list currently logged in users on Linux or Unix-like systems.
| Tutorial details | |
|---|---|
| Difficulty level | Easy |
| Root privileges | Yes |
| Requirements | w or who command on Linux and Unix |
| Est. reading time | 5m |
The following two file keep login records on Linux and Unix-like systems:
- /var/run/utmp – Keeps and allows us to discover information about who is currently using the system. Please note that there may be more L inux and Unix users currently using the system, because not all programs use utmp logging . In other words, poorly written app, hidden programs, malware, and other bad stuff will not be useful to list logged in users.
- /var/log/wtmp – Keeps records all logins and logouts.
We simply cannot read these files using cat command/grep command/egrep command as file is in binary database format. Hence, we use the following commands to find currently logged in users in Linux and Unix-like systems.
Linux Command To List Current Logged In Users
- w command – Shows information about the users currently on the machine, and their processes.
- who command – Display information about users who are currently logged in.
- users command – See the login names of the users currently on the system, in sorted order, space separated, on a single line. It reads all information from /var/run/utmp file.
How to find currently logged in users in Linux
Open a terminal (or login into remote server using ssh command) and type the following commands.
Using w command to list current logged in users under Unix or Linux
Open the terminal application and then type the w command:
$ w
Fig.01: w command in action.
Understanding w command outputs
From Fig.01 we see the following for each user:
- USER – Linux or Unix login name.
- TTY – The tty name.
- FROM The remote host or IP address.
- @Login – Login time.
- IDEL – Idle time.
- JCPU – The JCPU time is the time used by all processes attached to the tty. However, it does not include past background jobs, but does include currently running background jobs.
- PCPU – The PCPU time is the time used by the current process, named in the “what” field.
- WHAT – The command line of that users current process.
To see info about a user named tom, enter:
$ w tom
Tell w command not print header:
$ w -h
$ w —no-header
We can also ignore current process username by passing the -u or —no-current to the w command:
$ w -u
$ w —no-current
Want to see remote hostname field? Try:
$ w -f
Show IP address instead of hostname for from field:
$ w -i
We can also old style output. In other words old outputs prints blank space for idle times less than one minute:
$ w -o
Display all logged in users using who command
The who command works on all Unix like operating systems such as macOS, *BSD, Linux and so on. The syntax is pretty simple:
# who
Here is what we see:
The who command displays the following information:
- root – The username
- pts/0 – Type of the terminal device. In this example, we see pseudoterminal pts/0 used by root user.
- 2013-03-12 15:10 – User login date and time stamp.
- (10.1.3.177) – The remote IP address from which the user logged into this server.
We can pass the -a option to who command as follows to see time of last system boot, display dead processes, system login processes, active processes spawned by init/systemd, print current runlevel, print last system clock change, show user’s message status, and list users logged in to Linux or Unix box:
# who -a
Here is output from older Linux system (pre Systemd):
Sample outputs from Systemd based Linux sysetem:
Getting help with the whois command
You can pass the following options to the who command (taken from the who command man page):
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
users command
Open a terminal or login over the ssh session and enter the following users command:
$ users
Output who is currently logged:
Vieing logged in users with last command
Want to see a listing of last logged in users? Use the last command to lookup binary database called /var/log/wtmp and displays a list of all users logged in (and out) since that file was created. For instance see history for user named ‘vivek’:
$ last vivek
Источник
Лог файлы Linux по порядку
Невозможно представить себе пользователя и администратора сервера, или даже рабочей станции на основе Linux, который никогда не читал лог файлы. Операционная система и работающие приложения постоянно создают различные типы сообщений, которые регистрируются в различных файлах журналов. Умение определить нужный файл журнала и что искать в нем поможет существенно сэкономить время и быстрее устранить ошибку.

Журналирование является основным источником информации о работе системы и ее ошибках. В этом кратком руководстве рассмотрим основные аспекты журналирования операционной системы, структуру каталогов, программы для чтения и обзора логов.
Основные лог файлы
Все файлы журналов, можно отнести к одной из следующих категорий:
Большинство же лог файлов содержится в директории /var/log .
- /var/log/syslog или /var/log/messages содержит глобальный системный журнал, в котором пишутся сообщения с момента запуска системы, от ядра Linux, различных служб, обнаруженных устройствах, сетевых интерфейсов и много другого.
- /var/log/auth.log или /var/log/secure — информация об авторизации пользователей, включая удачные и неудачные попытки входа в систему, а также задействованные механизмы аутентификации.
- /var/log/dmesg — драйвера устройств. Одноименной командой можно просмотреть вывод содержимого файла. Размер журнала ограничен, когда файл достигнет своего предела, старые сообщения будут перезаписаны более новыми. Задав ключ —level= можно отфильтровать вывод по критерию значимости.
- /var/log/alternatives.log — Вывод программы update-alternatives , в котором находятся символические ссылки на команды или библиотеки по умолчанию.
- /var/log/anaconda.log — Записи, зарегистрированные во время установки системы.
- /var/log/audit — Записи, созданные службой аудита auditd .
- /var/log/boot.log — Информация, которая пишется при загрузке операционной системы.
- /var/log/cron — Отчет службы crond об исполняемых командах и сообщения от самих команд.
- /var/log/cups — Все, что связано с печатью и принтерами.
- /var/log/faillog — Неудачные попытки входа в систему. Очень полезно при проверке угроз в системе безопасности, хакерских атаках, попыток взлома методом перебора. Прочитать содержимое можно с помощью команды faillog .
- var/log/kern.log — Журнал содержит сообщения от ядра и предупреждения, которые могут быть полезны при устранении ошибок пользовательских модулей встроенных в ядро.
- /var/log/maillog/ или /var/log/mail.log — Журнал почтового сервера, используемого на ОС.
- /var/log/pm-powersave.log — Сообщения службы экономии заряда батареи.
- /var/log/samba/ — Логи файлового сервера Samba , который используется для доступа к общим папкам Windows и предоставления доступа пользователям Windows к общим папкам Linux.
- /var/log/spooler — Для представителей старой школы, содержит сообщения USENET. Чаще всего бывает пустым и заброшенным.
- /var/log/Xorg.0.log — Логи X сервера. Чаще всего бесполезны, но если в них есть строки начинающиеся с EE, то следует обратить на них внимание.
Для каждого дистрибутива будет отдельный журнал менеджера пакетов.
- /var/log/yum.log — Для программ установленных с помощью Yum в RedHat Linux.
- /var/log/emerge.log — Для ebuild -ов установленных из Portage с помощью emerge в Gentoo Linux.
- /var/log/dpkg.log — Для программ установленных с помощью dpkg в Debian Linux и всем семействе родственных дистрибутивах.
И немного бинарных журналов учета пользовательских сессий.
- /var/log/lastlog — Последняя сессия пользователей. Прочитать можно командой last .
- /var/log/tallylog — Аудит неудачных попыток входа в систему. Вывод на экран с помощью утилиты pam_tally2 .
- /var/log/btmp — Еже один журнал записи неудачных попыток входа в систему. Просто так, на всякий случай, если вы еще не догадались где следует искать следы активности взломщиков.
- /var/log/utmp — Список входов пользователей в систему на данный момент.
- /var/log/wtmp — Еще один журнал записи входа пользователей в систему. Вывод на экран командой utmpdump .
И другие журналы
Так как операционная система, даже такая замечательная как Linux, сама по себе никакой ощутимой пользы не несет в себе, то скорее всего на сервере или рабочей станции будет крутится база данных, веб сервер, разнообразные приложения. Каждое приложения или служба может иметь свой собственный файл или каталог журналов событий и ошибок. Всех их естественно невозможно перечислить, лишь некоторые.
- /var/log/mysql/ — Лог базы данных MySQL.
- /var/log/httpd/ или /var/log/apache2/ — Лог веб сервера Apache, журнал доступа находится в access_log , а ошибки — в error_log .
- /var/log/lighthttpd/ — Лог веб сервера lighttpd.
В домашнем каталоге пользователя могут находится журналы графических приложений, DE.
/.xsession-errors — Вывод stderr графических приложений X11.
/.xfce4-session.verbose-log — Сообщения рабочего стола XFCE4.
Чем просматривать — lnav
Почти все знают об утилите less и команде tail -f . Также для этих целей сгодится редактор vim и файловый менеджер Midnight Commander. У всех есть свои недостатки: less неважно обрабатывает журналы с длинными строками, принимая их за бинарники. Midnight Commander годится только для беглого просмотра, когда нет необходимости искать по сложному шаблону и переходить помногу взад и вперед между совпадениями. Редактор vim понимает и подсвечивает синтаксис множества форматов, но если журнал часто обновляется, то появляются отвлекающие внимания сообщения об изменениях в файле. Впрочем это легко можно обойти с помощью .
Недавно я обнаружил еще одну годную и многообещающую, но слегка еще сыроватую, утилиту — lnav, в расшифровке Log File Navigator.

Установка пакета как обычно одной командой.
Навигатор журналов lnav понимает ряд форматов файлов.
- Access_log веб сервера.
- CUPS page_log
- Syslog
- glog
- dpkg.log
- strace
- Произвольные записи с временными отметками
- gzip, bzip
- Журнал VMWare ESXi/vCenter
Что в данном случае означает понимание форматов файлов? Фокус в том, что lnav больше чем утилита для просмотра текстовых файлов. Программа умеет кое что еще. Можно открывать несколько файлов сразу и переключаться между ними.
Программа умеет напрямую открывать архивный файл.
Показывает гистограмму информативных сообщений, предупреждений и ошибок, если нажать клавишу . Это с моего syslog-а.
Кроме этого поддерживается подсветка синтаксиса, дополнение по табу и разные полезности в статусной строке. К недостаткам можно отнести нестабильность поведения и зависания. Надеюсь lnav будет активно развиваться, очень полезная программа на мой взгляд.
Источник
Viewing Linux Logs from the Command Line
Learn how to easily check Linux logs in this article from our archives.
At some point in your career as a Linux administrator, you are going to have to view log files. After all, they are there for one very important reason…to help you troubleshoot an issue. In fact, every seasoned administrator will immediately tell you that the first thing to be done, when a problem arises, is to view the logs.
And there are plenty of logs to be found: logs for the system, logs for the kernel, for package managers, for Xorg, for the boot process, for Apache, for MySQL… For nearly anything you can think of, there is a log file.
Most log files can be found in one convenient location: /var/log . These are all system and service logs, those which you will lean on heavily when there is an issue with your operating system or one of the major services. For desktop app-specific issues, log files will be written to different locations (e.g., Thunderbird writes crash reports to ‘
/.thunderbird/Crash Reports’). Where a desktop application will write logs will depend upon the developer and if the app allows for custom log configuration.
We are going to be focus on system logs, as that is where the heart of Linux troubleshooting lies. And the key issue here is, how do you view those log files?
Fortunately there are numerous ways in which you can view your system logs, all quite simply executed from the command line.
/var/log
This is such a crucial folder on your Linux systems. Open up a terminal window and issue the command cd /var/log . Now issue the command ls and you will see the logs housed within this directory ( Figure 1 ).
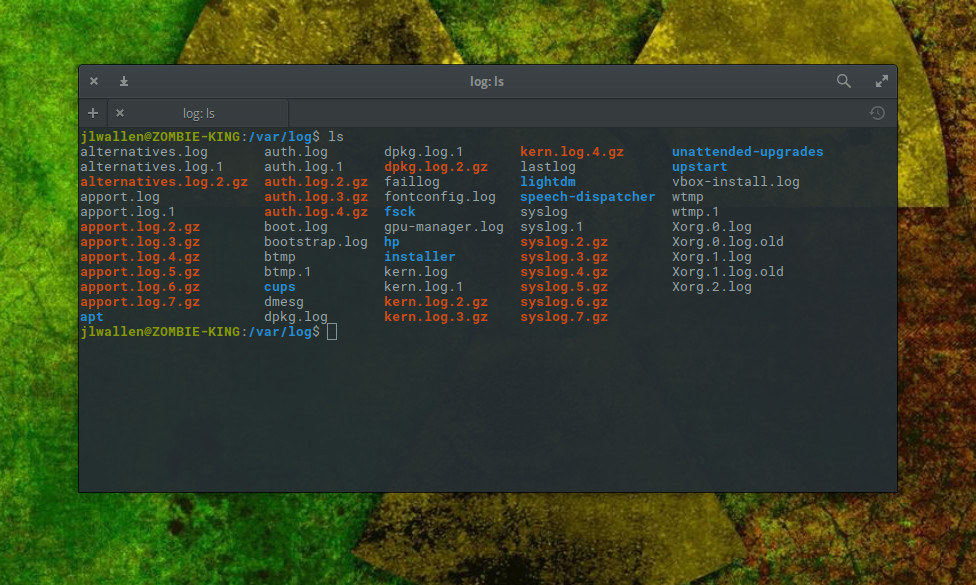
Now, let’s take a peek into one of those logs.
Viewing logs with less
One of the most important logs contained within /var/log is syslog. This particular log file logs everything except auth-related messages. Say you want to view the contents of that particular log file. To do that, you could quickly issue the command less /var/log/syslog . This command will open the syslog log file to the top. You can then use the arrow keys to scroll down one line at a time, the spacebar to scroll down one page at a time, or the mouse wheel to easily scroll through the file.
The one problem with this method is that syslog can grow fairly large; and, considering what you’re looking for will most likely be at or near the bottom, you might not want to spend the time scrolling line or page at a time to reach that end. Will syslog open in the less command, you could also hit the [Shift]+[g] combination to immediately go to the end of the log file. The end will be denoted by (END). You can then scroll up with the arrow keys or the scroll wheel to find exactly what you want.
This, of course, isn’t terribly efficient.
Viewing logs with dmesg
The dmesg command prints the kernel ring buffer. By default, the command will display all messages from the kernel ring buffer. From the terminal window, issue the command dmesg and the entire kernel ring buffer will print out ( Figure 2 ).
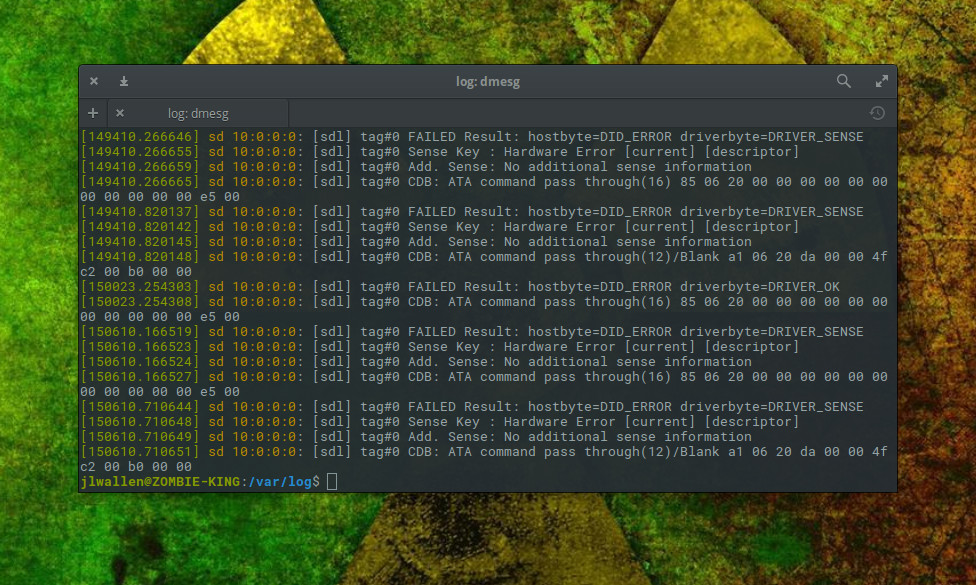
Fortunately, there is a built-in control mechanism that allows you to print out only certain facilities (such as daemon ).
Say you want to view log entries for the user facility. To do this, issue the command dmesg –facility=user . If anything has been logged to that facility, it will print out.
Unlike the less command, issuing dmesg will display the full contents of the log and send you to the end of the file. You can always use your scroll wheel to browse through the buffer of your terminal window (if applicable). Instead, you’ll want to pipe the output of dmesg to the less command like so:
The above command will print out the contents of dmesg and allow you to scroll through the output just as you did viewing a standard log with the less command.
Viewing logs with tail
The tail command is probably one of the single most handy tools you have at your disposal for the viewing of log files. What tail does is output the last part of files. So, if you issue the command tail /var/log/syslog, it will print out only the last few lines of the syslog file.
Using tail in this manner is invaluable for troubleshooting issues.
To escape the tail command (when following a file), hit the [Ctrl]+[x] combination.
You can also instruct tail to only follow a specific amount of lines. Say you only want to view the last five lines written to syslog ; for that you could issue the command:
The above command would follow input to syslog and only print out the most recent five lines. As soon as a new line is written to syslog, it would remove the oldest from the top. This is a great way to make the process of following a log file even easier. I strongly recommend not using this to view anything less than four or five lines, as you’ll wind up getting input cut off and won’t get the full details of the entry.
There are other tools
You’ll find plenty of other commands (and even a few decent GUI tools) to enable the viewing of log files. Look to more, grep, head, cat, multitail, and System Log Viewer to aid you in your quest to troubleshooting systems via log files.
Advance your career with Linux system administration skills. Check out the Essentials of System Administration course from The Linux Foundation.
Источник



