- Ethical hacking and penetration testing
- InfoSec, IT, Kali Linux, BlackArch
- How to add Kali Linux repositories to another Linux distribution
- What will the Kali Linux repository give?
- What happens when adding repositories of other Linux distributions
- What distributions can Kali Linux repositories be added to
- Manual for adding Kali Linux repositories (using Linux Mint as an example)
- Complete system conversion to Kali Linux
- Linux mint репозитории kali
- Default Network Repository Value
- Switching Branches/Regular Repositories
- Sources.list Format
- Default Offline Install Values
- Non-Kali Repositories
- Mirrors
- Source Repositories
- Как обновить Kali Linux
- Обновление системы Kali Linux
- Репозиторий kali-last-snapshot
- Репозиторий kali-experimental
- Репозиторий kali-rolling
- Выводы
Ethical hacking and penetration testing
InfoSec, IT, Kali Linux, BlackArch
How to add Kali Linux repositories to another Linux distribution
I’ll start with the most important thing, with a serious warning: this operation may kill your distribution and make it unusable! This is a very real opportunity to break everything due to incompatibility of packages!
What will the Kali Linux repository give?
After all these terrible warnings, the question arises, why take this risk? If you add the repository of another distribution, you can install its packages. For example, if you add Kali Linux repositories to Linux Mint, you can install Kali Linux programs on Linux Mint.
What happens when adding repositories of other Linux distributions
When adding any new repositories, after updating the package cache, packages from new repositories become available for installation, as well as for updating existing packages in the system.
Repositories may contain the same packages, but different versions. When performing updates, newer packages will replace packages of previous versions in the system. Since the source packages of the distribution kit may not be compatible with the packages of another distribution kit, the system may stop working normally after the upgrade. Moreover, if the first upgrade went fine, this does not mean that as a result of any subsequent upgrade something bad will not happen.
You can significantly reduce the danger from Kali Linux repositories, but at the same time take advantage of this Linux distribution. We will achieve this by setting a lower priority for Kali Linux repository; this will be described below.
What distributions can Kali Linux repositories be added to
Only distributions based on Debian are suitable for this, that is, Debian itself, as well as Linux Mint, Ubuntu, etc.
Manual for adding Kali Linux repositories (using Linux Mint as an example)
We will not only correctly add repositories, but also configure the low priority of Kali Linux repositories, thanks to this:
- with automatic updates, Kali Linux packages will not replace the main distribution packages, even if Kali Linux has newer versions
- it will be possible to install any Kali Linux programs
- when new versions of Kali Linux programs are released, they will be automatically updated along with other packages in the system
That is, we get the benefits of Kali Linux, but we do not risk spoiling our distribution (although anything can happen).
Start with a complete upgrade of your system:
Then reboot it; that is, we got a completely updated system in which the command
should output the following:
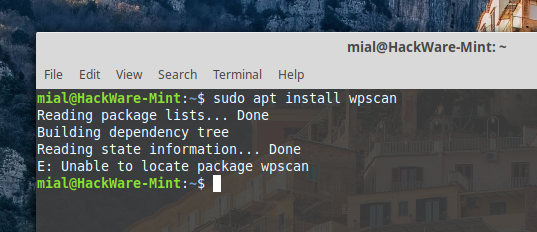
Run the test — try installing the WPScan program on Linux Mint:
This package is missing, so the expected failure:
Add Kali Linux repositories:
To make sure that new repositories are added, try again to update the apt cache:
The operation should fail:
This is normal – it should be so.
For the next operation, we need the gnupg package, install it:
Now, in order for the system to verify Kali Linux packages, you need to add the public key of this distribution. Download it and add it with the following commands:
Now you update the cache again (but at the moment DO NOT upgrade the system – otherwise everything will break and you will not be able to boot anymore):
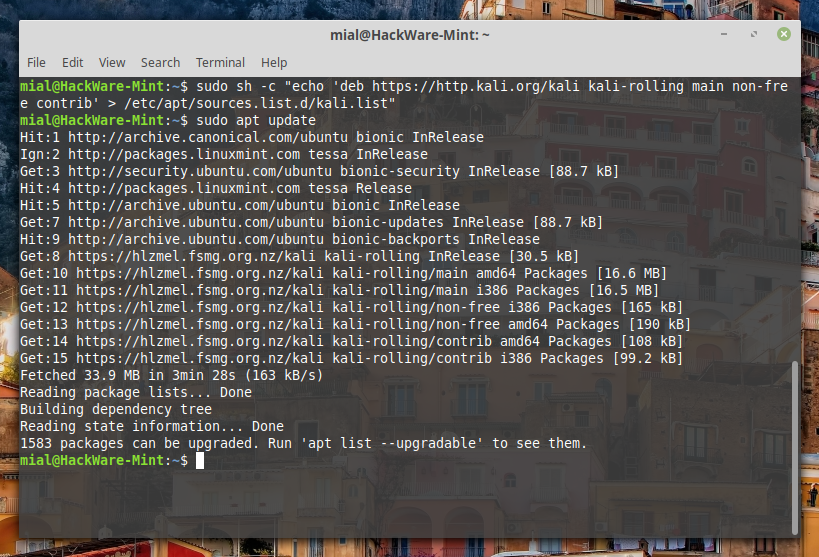
As you can see, we are invited to upgrade more than one and a half thousand packages – DO NOT do this.
Now we need to set the correct priority for packages from Kali Linux repositories: they will have a lower priority than the others, as a result, Kali Linux packages (for example, kernels) will not be installed automatically, but manually you can install any packages that you need.
Run the command:
Or simply create the file /etc/apt/preferences.d/kali.pref with the following contents:
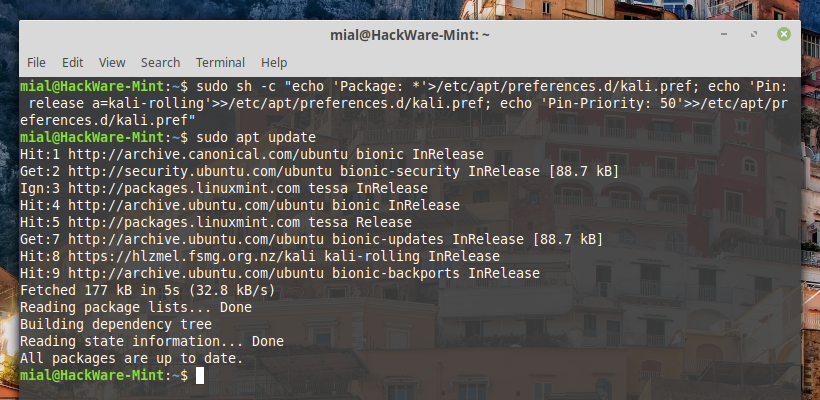
Updating the package cache again:
As you can see, now the Kali Linux repository does not affect the system when it is updated:
But if we try to install WPScan, which we could not find in the repositories earlier, then now everything will be successful. Although there are nuances – the apt program will not cope with this task:
The problem will be that the wpscan package has dependencies, these dependencies are present in the Kali Linux repositories, but something prevents the apt program from installing them.
Therefore, to install Kali Linux packages, we will use aptitude in a command of the form:
For example, to install wpscan:

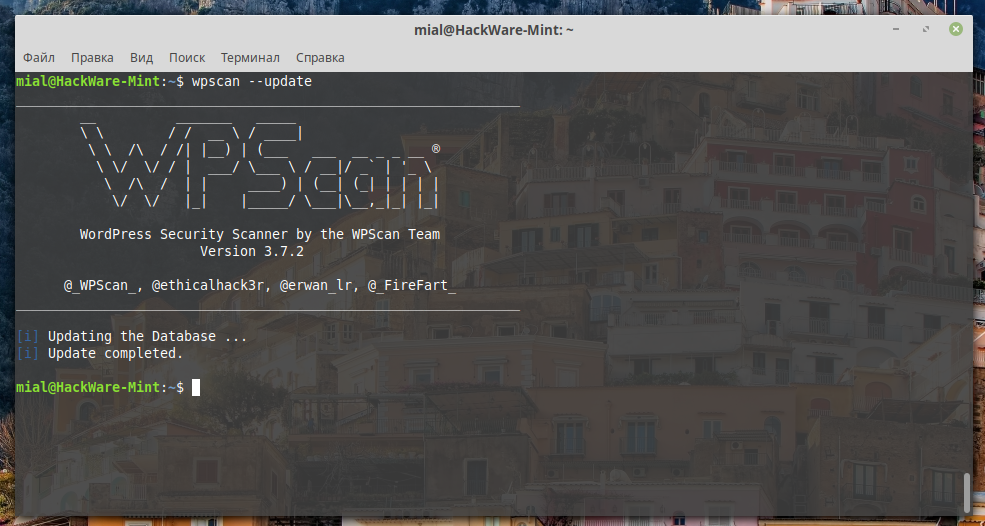
This is the effect of Kali Linux repositories (the ability to install its programs) with minimal risk of breaking the Linux distribution into which you add new repositories.
Nevertheless, the risks remain: when installing packages, in the dependencies of which important components of the system, such as the kernel, may be present. Therefore, it is not recommended to install drivers and kernel modules from the Kali Linux repository (you can install anything from the main repositories of your Linux distribution, including video drivers and new kernels). With the vast majority of other programs should not be a problem.
Complete system conversion to Kali Linux
If you need Kali Linux, then just download the Live distribution and install it for yourself.
But there are situations when it is impossible to ‘just download and install’ — for example, when deploying Kali Linux on VPS hosting. I had to solve this problem when deploying the system to DigitalOcean. I’ll talk about this example in the next article about my experience with DigitalOcean.
Источник
Linux mint репозитории kali
The topic of repositories is always a large one, and comes up frequently. It is an item which people often get wrong and confused with. Please take the time to read the information below and any references which is linked to before acting on anything.
Default Network Repository Value
On a standard, clean install of Kali Linux, with network access, you should have the following entry present in /etc/apt/sources.list :
If the output doesn’t exactly match up to the above output, you may not be able to install any new additional packages or receive updates. This may happen for any number of reasons, such as:
- You have switched your branch.
- Using a different hardcoded mirror.
You will probably want to read the “switching branches” section to alter this.
Since Kali 2020.3, after Kali’s setup is complete, network repositories will be enabled by default, even if there was no network access during installation.
Switching Branches/Regular Repositories
Kali has various different branches to choose from (please take the time to read which one would be the best option for your setup), and you may be able to switch or include additional repositories.
kali-rolling (Default & frequently updated):
kali-last-snapshot (Point release so more “stable” & the “safest”):
kali-experimental (Packages which are under testing — often used with the rolling repository):
Sources.list Format
- Archive is going to be deb (Regular Binary) or deb-src (Source), depending if you want a package or the source of the package.
- Mirror should be http.kali.org/kali as this is our load balancer, which will direct you to best mirror.
- Branch is what version of Kali you wish to use.
- Component is what packages you wish to use, based on the Debian Free Software Guidelines (DFSG). Kali defaults to everything.
Default Offline Install Values
During the Kali setup process, if you don’t have access to a network connection to reach a repository, you will perform an offline installation of Kali Linux. You will be limited to the packages & the version which is on the medium you installed Kali from. This will then configure Kali to continue to use this medium to install packages from, even after Kali has been installed.
This means you will not get any updates to packages, or any new additional tools, which can be frustrating. You can see if you the offline media enabled if your values match up with whats below (or if you want to enable this option):
If your output matches whats above, please see the switching branch section, if you wish to receive updates.
However, if you do have network connection, which has access to network repositories, it will be enabled for you. You don’t need to do anything.
Non-Kali Repositories
If you want to install additional tools and software (such as signal) outside of what Kali has to offer, you may need to include an extra repository for this to happen. Please do not alter /etc/apt/sources.list , as this is used for the Kali Linux Operating System. Any extra tools and software needs to be placed into their own file in the directory /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ (such as /etc/apt/sources.list.d/repo-name.list , replacing repo-name with the mirror name). It is highly recommended that each mirror should be in its own file.
By adding Kali’s repository to a non-Kali OS (such as trying to add Kali to Ubuntu), this will highly increase the chance of your system not working. It may not happen straight away, but without any warning, it may break. We will not be able to offer support (and based on what we have seen over the years, most other OS will not help too).
Likewise, adding other operating system’s repositories into Kali (such as trying to put Ubuntu on Kali), will break your installation. This is the single most common reason why Kali Linux systems break.
If any guides are telling you to do anything else than the above, this is unofficial advice, and completely not supported by Kali Linux. More often than not, users in this case end up doing a reinstall after learning this lesson.
Mirrors
We have a list of official Kali Linux mirrors, as well as a guide on how to setup your own. This may be kept as a local repository which is only accessible on a LAN, or a remote private one, or if you have the ability to, you may wish to share back to the community and make it public allowing for anyone else in your geographical area to benefit from it.
Source Repositories
By using a deb in the repositories, it will allow for binary packages to be downloaded. However, should you require the source to a package (so you can compile the package yourself if you so wish, or look into debugging a problem with a package), you can add deb-src as a extra line in the repositories.
We used kali-rolling for the branch above, but you can select any value you wish.
Updated on: 2021-Sep-27
Author: g0tmi1k
Источник
Как обновить Kali Linux
Kali Linux, на сегодняшний день одна из самых популярных операционных систем используемых для аудита безопасности корпоративных и домашних локальных сетей, периферийного оборудования, серверов, рабочих станций и различного ПО.
Программное обеспечение, поставляемое в рамках дистрибутива Kali Linux, периодически обновляется, получая при этом новые возможности или исправление ошибок в старых версиях ПО. Дальше мы рассмотрим как обновить Kali Linux из разных веток его репозитория.
Обновление системы Kali Linux
Kali Linux имеет три официальные ветки репозиториев. И каждая отличается своим набором пакетов для обновления операционной системы.
Репозиторий kali-last-snapshot
kali-last-snapshot (Kali последний снимок) самая стабильная ветка репозитория. Обновления для ПО и ОС в ней не публикуются, за исключением критических заплаток, исправляющих нестабильную работу или закрывающих бреши в безопасности операционной системы. Все новые возможности появятся только в новой версии операционной системы Kali Linux.
Чтобы применить этот репозиторий по умолчанию в вашей ОС, измените файл /etc/apt/sources.list:
sudo nano /etc/apt/sources.list
Впишите в него следующую строку (убрав все остальные если таковые есть):
deb http://http.kali.org/kali kali-last-snapshot main non-free contrib
Затем обновите список пакетов доступных из вашего репозитория:
sudo apt update
Обновление пакетов Kali Linux выполняется командой:
sudo apt upgrade
Репозиторий kali-experimental
kali-experimental (экспериментальная Kali) ветка репозитория которая подойдёт энтузиастам готовым получать самые новые версии ПО, находящиеся на стадии тестирования. Разработчики не гарантируют стабильность работы программ и операционной системы при обновлении из этой ветки.
Чтобы использовать данный репозиторий по умолчанию, обновите конфиг в файле /etc/apt/sources.list.
Вместо kali-last-snapshot вставьте kali-experimental. Должна получится такая строка:
deb http://http.kali.org/kali kali-experimental main non-free contrib
Обновить пакеты из этой экспериментальной ветки можно командами:
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgrade
Репозиторий kali-rolling
kali-rolling (дословно прокатывание, катание или обкатка) — репозиторий который используется по умолчанию во всех дистрибутивах Kali Linux. В данной ветке периодически выкладываются относительно стабильные новые версии ПО и компонентов операционной системы.
Если вы хотите использовать этот репозиторий по умолчанию в файле /etc/apt/sources.list должна быть следующая строка:
deb https://http.kali.org/kali kali-rolling main non-free contrib
Затем нужно поочерёдно выполнить ряд команд:
sudo apt update
Теперь обновить Kali Linux через терминал можно командой:
sudo apt upgrade
Если вы хотите обновить всё, включая и компоненты ОС, выполните команду
sudo apt full-upgrade
Выводы
Обновление Kali Linux по большому счету мало чем отличается от обновления других операционных систем на основе Debian или Ubuntu. Однако следует с осторожностью относится к обновлению из экспериментальной ветки репозитория Kali Linux. В случае необходимости можно установить отдельные пакеты из этого репозитория, не обновляя всю операционную систему целиком, даже если что-то пойдёт не так, всегда проще удалить одну нестабильную программу, чем исправлять целый ряд возможных проблем.
Источник






