- Linux mint звук наушники
- Как исправить отсутствие звука в Ubuntu и Linux Mint
- Различные способы исправить отсутствие звука в Ubuntu
- Исправление фиктивного вывода в настройках звука
- Первый альтернативный способ исправить отсутствие звука в Ubuntu
- Второй альтернативный способ исправить отсутствие звука в Ubuntu
- Третий альтернативный метод: попробуйте alsamixer
- Четвертый альтернативный способ исправить отсутствие звука в Ubuntu
- Пятый альтернативный метод (специально для Lenovo Carbon X1)
- Linux mint звук наушники
Linux mint звук наушники
16 июн 2017, 12:05
Здравствуйте, уважаемые любители Linux Lint!
Помогите, пожалуйста, у меня странная проблема, решить самостоятельно не удается (Мучаюсь уже 3 месяца 
Проблема такая вот, раньше стояла Ubuntu 14.04 x32, проблем никаких не было. Ну как и все любящие новинок, решил я себе обновить систему до 16.04, но решил поставить x64, вот поставил вроде бы все нормально, но через некоторое время заметил проблему, а именно, почему-то звука в наушниках вообще нету.
Ну и я пошел лазить в настройки alsa (
$ alsamixer).
Обнаружил, что headphon стоит MM (Mute), а что же мне делать, я снял MM поднял до конца и вуаля, работает!
Но, что самое интересное, то что после перезагрузки все возвращается на свои места(То есть, опять нету звука в наушниках).
Через несколько месяцев поставил Linux Mint 18.1, и та же проблема здесь.
PS: и в PavControl так же, сбрасываются настройки.
Что мне делать? Как быть? Может есть знающие люди, которым все же не лень будет помогать мне, отзовитесь, пожалуйста.
Немного технической информации: Audio device: Intel Corporation NM10/ICH7 Family High Definition Audio Controller (rev 01)
LevonX , в alsamixer ‘e правей есть еще такой пункт как Auto-Mute Mode
И вот здесь еще можно почитать по смене дефолтного канала на уровне пульсы — помогите настроить выход на наушники
Источник
Как исправить отсутствие звука в Ubuntu и Linux Mint
Нет звука в свежей установке Ubuntu? Видите только фиктивный вывод? Без проблем. Вот несколько методов, с помощью которых вы можете попробовать пофиксить проблему отсутствия звука в Ubuntu и других дистрибутивах Linux
Как это происходит с каждым новым выпуском Ubuntu, вы устанавливаете или обновляете свою ось до свежей версии Ubuntu и сталкиваетесь с рядом проблем. Но всегда есть способ преодолеть эти не большие, но досадные неприятности.
Одна из наиболее распространенных проблем — отсутствие звука после установки Ubuntu. Есть несколько причин отсутствия звука в Ubuntu, но я расскажу о тех приемах, которые сработали в моем случае.
Давайте же пристальнее рассмотрим те шаги, с помощью которых я исправил подобную проблему и как можете исправить ее вы.
Различные способы исправить отсутствие звука в Ubuntu
Причины отсутствия звука в Ubuntu могут быть совершенно разными. И, так как решение зависит от типа проблемы, я предлагаю получить некоторую информацию о вашей системе, особенно об оборудовании, связанным со звуком.
Сначала установите инструмент inxi:
Теперь проверьте информацию о системе, машине и аудио с помощью этой команды:
Вы должны увидеть примерно такую информацию:
Присмотритесь к аудио части вышеприведенного вывода. Он сообщает, что это Intel Sunrise Point-LP HD Audio, и у него есть драйвер Linux snd_hda_intel, и звук обслуживается Alsa. Эта информация может быть полезна на некоторых этапах устранения неполадок со звуком.
Исправление фиктивного вывода в настройках звука
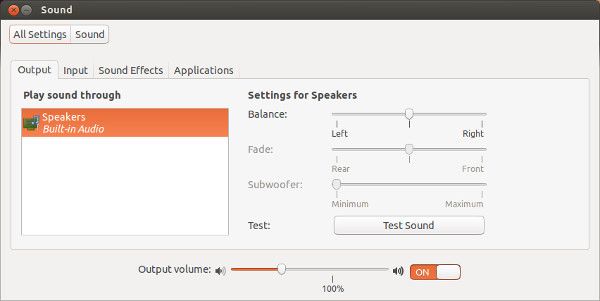
Первый шаг, чисто, что называется, «для отчистки совести», проверьте, не замьючен ли звук. Убедившись в этом, перейдите в Настройки звука:
В настройках звука вы обнаружите, что здесь практически ничего нет, кроме фиктивного выхода. Довольно неприятно. Это означает, что ваша звуковая карта даже не распознается. Ба-дум-тс!
Без паники. Единственное решение, которое устранило проблему со звуком на моем Dell Inspiron с процессором Intel, — это принудительная перезагрузка Alsa. Для этого используйте в терминале следующую команду (Ctrl + Alt + T):
Вывод будет таким:
Вы можете подумать, что процесс подвис или все еще обрабатывается, но сам процесс занимает всего пару секунд. Вы можете просто закрыть террминал, нажав Ctrl + C.
Теперь вам нужно перезагрузить компьютер. А после: либо воспроизвести музыкальные или видеофайлы, либо заглянуть в настройки системы, что бы выяснить сработал ли этот способ.
Первый альтернативный способ исправить отсутствие звука в Ubuntu
Если прошлый способ не помог вам в устранении проблемы, попробуйте переустановить Alsa и Pulse audio следующим образом.
И снова принудительно перезагрузите Alsa:
Перезагрузитесь и проверьте, вернулся ли звук.
Второй альтернативный способ исправить отсутствие звука в Ubuntu
Перейдите в свой домашнюю директорию, а затем перейдите в скрытый каталог конфигурации. Переименуйте здесь каталог с именем pulse:
Теперь перезагрузите вашу систему. Каталог Pulse будет создан заново, и у вас должен восстановиться звук.
Третий альтернативный метод: попробуйте alsamixer
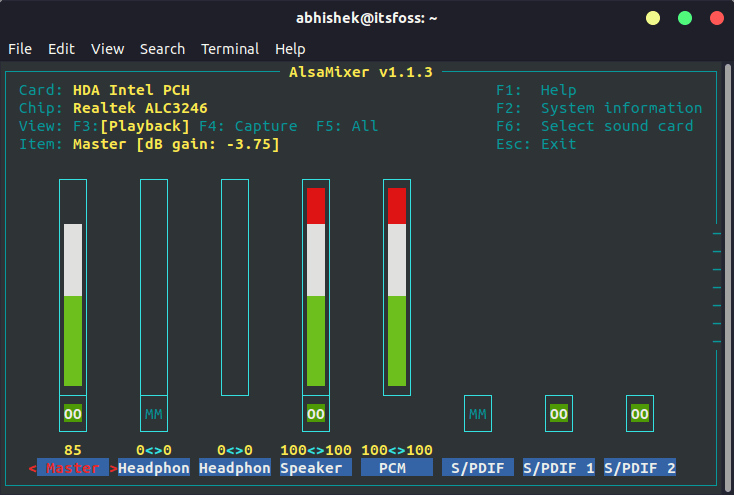
Откройте терминал и используйте следующую команду, чтобы открыть alsamixer:
Вы должны увидеть такой экран:
Проверьте, отключены ли здесь динамики или желаемый аудиовыход. MM означает отключение звука, а OO означает включение. Если желаемый аудиовыход (в основном это динамики) или мастер отключен, включите его.
Вы можете закрыть экран alsamixer, нажав клавишу Esc.
Обратите внимание: если команда alsamixer возвращает ошибку, возможно, это связано с тем, что у вас более одной звуковой карты. В этом случае вам нужно указать номер звуковой карты (см. Вывод inxi, который я упоминал в начале) следующим образом:
Четвертый альтернативный способ исправить отсутствие звука в Ubuntu
Диспетчер скорости (speed dispatcher) — это функция, которая позволяет вашей системе преобразовывать текст в речь. Иногда она конфликтует с другими настройками звука. Если вам не нужна эта функция, вы можете попробовать отключить ее, возможно это вернет вам звук.
Откройте терминал и отредактируйте файл диспетчера речи с помощью следующей команды:
Здесь измените RUN = yes на RUN = no. Перезагрузитесь и наслаждайтесь звуком.
Пятый альтернативный метод (специально для Lenovo Carbon X1)
Некоторые из наших читателей отметили, что ни один из вышеперечисленных методов не помог их ноутбуку Lenovo Thinkpad Carbon X1 7-го поколения.
Я изучил проблему и обнаружил следующее. У этой модели есть проблемы с Linux. Хотя в ядре Linux 5.5 и более поздних версиях улучшена поддержка этой модели, но для пользователей Ubuntu 18.04 и Mint 19, в которых используется ядро более ранней версии — 5.3, все еще остаются проблемы.
Проверьте версию ядра Linux, и если она 5.4 или ниже, попробуйте следующий обходной путь, предложенный разработчиками Arch Linux и Ubuntu.
Откройте файл конфигурации alsa (команда может быть другой для Mint, потому что текстовый редактор Gedit не используется в Mint):
Добавьте в конец этого файла следующую строку:
Сохраните и закройте файл и перезагрузите систему. После этих действий звук должен вернуться.
Устранение проблемы со звуком, безусловно, является одним из обязательных действий после установки Ubuntu.
Если один из вышеупомянутых методов сработал для вас, оставьте комментарий ниже, указав метод, который сэкономил вам время. Также приветствуются любые другие предложения и отзывы.
Источник
Linux mint звук наушники
30 ноя 2016, 18:49
#!/usr/bin/pulseaudio -nF
#
# This file is part of PulseAudio.
#
# PulseAudio is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it
# under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by
# the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or
# (at your option) any later version.
#
# PulseAudio is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but
# WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
# MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
# General Public License for more details.
#
# You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License
# along with PulseAudio; if not, see .
# This startup script is used only if PulseAudio is started per-user
# (i.e. not in system mode)
### Load something into the sample cache
#load-sample-lazy x11-bell /usr/share/sounds/freedesktop/stereo/bell.oga
#load-sample-lazy pulse-hotplug /usr/share/sounds/freedesktop/stereo/device-added.oga
#load-sample-lazy pulse-coldplug /usr/share/sounds/freedesktop/stereo/device-added.oga
#load-sample-lazy pulse-access /usr/share/sounds/freedesktop/stereo/message.oga
### Automatically restore the volume of streams and devices
load-module module-device-restore
load-module module-stream-restore
load-module module-card-restore
### Automatically augment property information from .desktop files
### stored in /usr/share/application
load-module module-augment-properties
### Should be after module-*-restore but before module-*-detect
load-module module-switch-on-port-available
### Load audio drivers statically
### (it’s probably better to not load these drivers manually, but instead
### use module-udev-detect — see below — for doing this automatically)
#load-module module-alsa-sink
#load-module module-alsa-source device=hw:1,0
#load-module module-oss device=»/dev/dsp» sink_name=output source_name=input
#load-module module-oss-mmap device=»/dev/dsp» sink_name=output source_name=input
#load-module module-null-sink
#load-module module-pipe-sink
### Automatically load driver modules depending on the hardware available
.ifexists module-udev-detect.so
load-module module-udev-detect
.else
### Use the static hardware detection module (for systems that lack udev support)
load-module module-detect
.endif
### Automatically connect sink and source if JACK server is present
.ifexists module-jackdbus-detect.so
.nofail
load-module module-jackdbus-detect channels=2
.fail
.endif
### Automatically load driver modules for Bluetooth hardware
#.ifexists module-bluetooth-policy.so
#load-module module-bluetooth-policy
#.endif
#.ifexists module-bluetooth-discover.so
#load-module module-bluetooth-discover
#.endif
### Load several protocols
.ifexists module-esound-protocol-unix.so
load-module module-esound-protocol-unix
.endif
load-module module-native-protocol-unix
### Network access (may be configured with paprefs, so leave this commented
### here if you plan to use paprefs)
#load-module module-esound-protocol-tcp
#load-module module-native-protocol-tcp
#load-module module-zeroconf-publish
### Load the RTP receiver module (also configured via paprefs, see above)
#load-module module-rtp-recv
### Load the RTP sender module (also configured via paprefs, see above)
#load-module module-null-sink sink_name=rtp format=s16be channels=2 rate=44100 #sink_properties=»device.description=’RTP Multicast Sink'»
#load-module module-rtp-send source=rtp.monitor
### Load additional modules from GConf settings. This can be configured with the paprefs tool.
### Please keep in mind that the modules configured by paprefs might conflict with manually
### loaded modules.
.ifexists module-gconf.so
.nofail
load-module module-gconf
.fail
.endif
### Automatically restore the default sink/source when changed by the user
### during runtime
### NOTE: This should be loaded as early as possible so that subsequent modules
### that look up the default sink/source get the right value
#load-module module-default-device-restore
### Automatically move streams to the default sink if the sink they are
### connected to dies, similar for sources
#load-module module-rescue-streams
### Make sure we always have a sink around, even if it is a null sink.
#load-module module-always-sink
### Honour intended role device property
load-module module-intended-roles
### Automatically suspend sinks/sources that become idle for too long
load-module module-suspend-on-idle
### If autoexit on idle is enabled we want to make sure we only quit
### when no local session needs us anymore.
.ifexists module-console-kit.so
load-module module-console-kit
.endif
.ifexists module-systemd-login.so
load-module module-systemd-login
.endif
### Enable positioned event sounds
load-module module-position-event-sounds
### Cork music/video streams when a phone stream is active
#load-module module-role-cork
### Modules to allow autoloading of filters (such as echo cancellation)
### on demand. module-filter-heuristics tries to determine what filters
### make sense, and module-filter-apply does the heavy-lifting of
### loading modules and rerouting streams.
load-module module-filter-heuristics
load-module module-filter-apply
# X11 modules should not be started from default.pa so that one daemon
# can be shared by multiple sessions.
### Load X11 bell module
#load-module module-x11-bell sample=x11-bell
### Register ourselves in the X11 session manager
#load-module module-x11-xsmp
### Publish connection data in the X11 root window
.ifexists module-x11-publish.so
.nofail
load-module module-x11-publish
.fail
.endif
### Make some devices default
#set-default-sink output
#set-default-source input
# This file is part of PulseAudio.
#
# PulseAudio is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
# it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by
# the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or
# (at your option) any later version.
#
# PulseAudio is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but
# WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
# MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
# General Public License for more details.
#
# You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License
# along with PulseAudio; if not, see .
## Configuration file for the PulseAudio daemon. See pulse-daemon.conf(5) for
## more information. Default values are commented out. Use either ; or # for
## commenting.
; daemonize = no
; fail = yes
; allow-module-loading = yes
; allow-exit = yes
; use-pid-file = yes
; system-instance = no
; local-server-type = user
; enable-shm = yes
; shm-size-bytes = 0 # setting this 0 will use the system-default, usually 64 MiB
; lock-memory = no
; cpu-limit = no
; high-priority = yes
; nice-level = -11
; realtime-scheduling = yes
; realtime-priority = 5
; exit-idle-time = 20
; scache-idle-time = 20
; dl-search-path = (depends on architecture)
; load-default-script-file = yes
; default-script-file = /etc/pulse/default.pa
; log-target = auto
; log-level = notice
; log-meta = no
; log-time = no
; log-backtrace = 0
; resample-method = speex-float-1
; enable-remixing = yes
; enable-lfe-remixing = yes
; lfe-crossover-freq = 120
; rlimit-fsize = -1
; rlimit-data = -1
; rlimit-stack = -1
; rlimit-core = -1
; rlimit-as = -1
; rlimit-rss = -1
; rlimit-nproc = -1
; rlimit-nofile = 256
; rlimit-memlock = -1
; rlimit-locks = -1
; rlimit-sigpending = -1
; rlimit-msgqueue = -1
; rlimit-nice = 31
; rlimit-rtprio = 9
; rlimit-rttime = 200000
; default-sample-format = s16le
; default-sample-rate = 44100
alternate-sample-rate = 48000
; default-sample-channels = 2
; default-channel-map = front-left,front-right
; default-fragments = 4
; default-fragment-size-msec = 25
; enable-deferred-volume = yes
deferred-volume-safety-margin-usec = 1
; deferred-volume-extra-delay-usec = 0
resample-method = speex-float-5
default-sample-format = float24le
analog-output-headphones: Аналоговые наушники (priority 9000, latency offset 0 usec, available: no)
properties:
device.icon_name = «audio-headphones»
active port:
$ aplay -l
**** Список PLAYBACK устройств ****
карта 0: NVidia [HDA NVidia], устройство 0: Generic Analog [Generic Analog]
Подустройства: 0/1
Подустройство №0: subdevice #0
карта 0: NVidia [HDA NVidia], устройство 1: Generic Digital [Generic Digital]
Подустройства: 1/1
Подустройство №0: subdevice #0
карта 1: HDMI [HDA ATI HDMI], устройство 3: HDMI 0 [HDMI 0]
Подустройства: 1/1
Подустройство №0: subdevice #0
Источник