- Как в Linux монтировать шару CIFS
- Подготовка
- Установка пакетов
- Сетевые порты
- Синтаксис
- Ручное монтирование
- Автоматическое монтирование CIFS через fstab
- Примеры использования опций
- Версии SMB
- Монтирование от гостевой учетной записи
- Права на примонтированные каталоги
- How to Mount Windows Share on Ubuntu Linux
- Installing CIFS
- Mounting a Windows Share
- Secure CIFS credential
- Auto mount the shares
- Unmount the shares
- Conclusion
- More Articles You May Like
- 6 Comments. add one
- Как монтировать общие папки Windows в системах Linux
- How to Mount Windows Share on Linux using CIFS
- В этом руководстве мы расскажем, как вручную и автоматически монтировать общие папки Windows в системах Linux.
- Установка пакетов утилит CIFS
- Монтирование CIFS Windows Share
- Авто монтаж
- Размонтирование Windows Share
- Вывод
- How to Mount a Windows Share in Linux
- SMB vs CIFS vs SAMBA
- Mount a Windows Share Using GUI (Files / Nautilus)
- Mount A Windows Share Using Command Line
- Using the mount.cifs Command
- Automatically Mount CIFS Share at Boot
- Mount CIFS Share at Boot Using /etc/fstab
- Mount CIFS Share using AutoFS
- Installing autofs Package
- Create Credentials File
- Get UID for User
- Edit auto.master Map File
- Create the Shares File
- Restart the Service
- Test and Verify
- Conclusion
Как в Linux монтировать шару CIFS
Что такое Linux и CIFS простыми словами.
Работа с общими папками Windows происходит с использованием протокола CIFS (SMB). Все примеры в данном руководстве выполняются на Linux Ubuntu и CentOS.
Подготовка
Установка пакетов
Для монтирования общей папки необходимо установить набор утилит для работы с CIFS.
yum install cifs-utils
apt-get install cifs-utils
Сетевые порты
Если мы будем монтировать сетевую папку, сервер которой находится за брандмауэром, необходимо открыть следующие порты:
Синтаксис
* вместо mount.cifs можно написать mount -t cifs.
mount.cifs //192.168.1.1/public /mnt
* простой пример монтирования папки public на сервере 192.168.1.1 в локальный каталог /mnt.
Ручное монтирование
Теперь монтирование можно выполнить следующей командой:
mount.cifs //192.168.1.10/share /mnt -o user=dmosk
* в данном примере будет примонтирован каталог share на сервере 192.168.1.10 в локальную папку /mnt под учетной записью dmosk.
То же самое, с использованием домена:
mount.cifs //192.168.1.10/share /mnt -o user=dmosk,domain=dmosk.local
Автоматическое монтирование CIFS через fstab
Для начала создаем файл, в котором будем хранить данные авторизации при подключении к общей папке:
И добавляем в него данные следующего вида:
username=dmosk
password=dPassw0rd
domain=dmosk.local
* в этом примере создана пара логин/пароль — dmosk/dPassw0rd; domain указывать не обязательно, если аутентификация выполняется без него.
Теперь открываем конфигурационный файл fstab:
и добавляем в него следующее:
//192.168.1.10/share /mnt cifs user,rw,credentials=/root/.smbclient 0 0
* в данном примере выполняется монтирование общей папки share на сервере с IP-адресом 192.168.1.10 в каталог /mnt. Параметры для подключения — user: позволяет выполнить монтирование любому пользователю, rw: с правом на чтение и запись, credentials: файл, который мы создали на предыдущем шаге.
Чтобы проверить правильность настроек, вводим следующую команду:
Примеры использования опций
Версии SMB
Если на стороне Windows используется старая или слишком новая версия протокола SMB, при попытке монтирования мы можем получить ошибку mount error(112): Host is down. Чтобы это исправить, указываем версию:
mount.cifs //192.168.1.10/share /mnt/ -o vers=1.0
* монтирование по протоколу SMB1.0
Монтирование от гостевой учетной записи
Если сервер принимает запросы без логина и пароля, то клиент подключается, как гость:
mount.cifs //192.168.1.10/share /mnt -o guest
//192.168.1.10/share /mnt cifs guest 0 0
Права на примонтированные каталоги
При монтировании папки мы можем указать определенные права:
mount.cifs //192.168.1.10/share /mnt -o file_mode=0777,dir_mode=0777
Для указания владельца, который будет назначен для примонтированного каталога, используем:
mount.cifs //192.168.1.10/share /mnt -o uid=33,gid=33
* чтобы посмотреть идентификаторы пользователя, вводим id -u и id -g .
Источник
How to Mount Windows Share on Ubuntu Linux
CIFS (Common Internet File System) is a popular file sharing protocol on Internet. It allows users on a Linux system access to a particular mount point on a windows share.
CIFS is an implementation of SMB (Server Message Block) — a protocol used for network file sharing.
This tutorial will go through all steps of installing and configuring relevant utilities in order to mount windows share on Linux system.
Installing CIFS
Install cifs-utils package on Ubuntu Linux by using the following command line
Mounting a Windows Share
In this section, the tutorial will show you the way to manually and automatically mount windows share on Linux systems.
Creating a directory on your Ubuntu Linux machine, the name of directory is arbitrary. In the below command line, I created a folder named winshare under /mnt
/mnt/winshare is the mount point of the remote windows share.
Windows share can be mounted on your Ubuntu Linux system mount point using cifs option of mount command
WIN_SHARE_IP is the IP address of windows machine.
If the $windows_user is in a windows domain, specify the domain as the following command line
By default, linux mount windows share with the full permission (rwx or 777). If you want to change the permission on your own, please use the dir_mode and file_mode options to set permission for directory and file.
You also can change the default ownership of user and group by specify the uid (user id) and gid (group id) options.
Once the windows share is successfully mounted, using command df -h for verifying the mounting windows share in Linux. In the following example, WIN_SHARE_IP = 192.168.1.8 and $shared_name = sharefolder
Secure CIFS credential
This section will explain how to use a credential file when your Ubuntu Linux mount the share using command.
Create a cifs credentials file: /etc/cifs-credentials. The file contains the below information:
Grant permission read and write to credentials file:
Now, we can mount the share using credentials with command as follows:
Auto mount the shares
If you manually mount the shares using mount command, when you reboot your Linux machine, the shares will be lost.
The file /etc/fstab contains the necessary configuration that allows automatically mount cifs permanently.
Edit the /etc/fstab file with your favorite editors (vim, nano. )
Then add the following line to the file.
Run the command to mount all the entries listed in /etc/fstab
Since then, the mount cifs will be persistent across reboots.
Unmount the shares
In order to unmount a share, you have to determine the mount point. In the above example, mount point is /mnt/winshare. Use the umount command:
If the mount point is in a busy process and the above command failed, run command with option -l (—lazy)
Conclusion
The tutorial has gone through all steps to mount a windows share on Ubuntu Linux using CIFS. If you have any questions, feel free to reach out to us.
More Articles You May Like
6 Comments. add one
I do not understand why you need to specify the Windows machine IP adress. These are constantly changing when using DHCP, which almost everyone uses. Does that mean that one has to go through the above procedure every day if one wants to connect to a Windows machine whose IP address has changed (people shut off their computers at night, likely getting a new IP address asigned the next day when turned on)? Is there a way that automatically detects the target Windows machine, as Windows does in its own networking system?
If IP address changes, use DNS names
This doesn’t appear to work in the latest ubuntu release.
If I do it from the command line, it requires the «vers=2.0» option.
Not sure how to fix it in the fstab. All I get is error(22) invalid argument.
What does tail -f /var/log/kern.log shows when you mount?
I’m not sure if it’s the cause of your error, but there’s a typo in the fstab line — where it says «dir_node=0755», it should say «dir_mode=0755». Double check that’s correct in your fstab.
Источник
Как монтировать общие папки Windows в системах Linux
How to Mount Windows Share on Linux using CIFS
В этом руководстве мы расскажем, как вручную и автоматически монтировать общие папки Windows в системах Linux.
В операционных системах Linux и UNIX общий ресурс Windows можно смонтировать в определенной точке монтирования в дереве локальных каталогов, используя cifs параметр mount команды.
Общая файловая система Интернета (CIFS) — это сетевой протокол обмена файлами. CIFS является формой SMB.
Установка пакетов утилит CIFS
Чтобы смонтировать общий ресурс Windows в системе Linux, сначала необходимо установить пакет утилит CIFS.
Установка утилит CIFS в Ubuntu и Debian:
Установка утилит CIFS в CentOS и Fedora:
Имя пакета может отличаться в разных дистрибутивах Linux.
Монтирование CIFS Windows Share
Монтирование удаленного общего ресурса Windows аналогично монтированию обычных файловых систем.
Сначала создайте каталог, который будет служить точкой монтирования для удаленного общего ресурса Windows:
Запустите следующую команду как пользователь root или пользователь с правами sudo для монтирования общего ресурса:
Вам будет предложено ввести пароль:
В случае успеха не выводится.
Чтобы убедиться, что удаленный общий ресурс Windows успешно смонтирован, используйте команду mount или df -h .
После монтирования общего ресурса точка монтирования становится корневым каталогом смонтированной файловой системы. Вы можете работать с удаленными файлами, как если бы они были локальными файлами.
Пароль также можно указать в командной строке:
Если пользователь находится в рабочей группе или домене Windows, вы можете установить его следующим образом:
Для большей безопасности рекомендуется использовать файл учетных данных, который содержит имя пользователя, пароль и домен общего ресурса.
Файл учетных данных имеет следующий формат:
Файл не должен быть доступен для чтения пользователям. Чтобы установить правильные разрешения и владельца , запустите:
Чтобы использовать файл учетных данных, определите его следующим образом:
По умолчанию подключенный общий ресурс принадлежит пользователю root, а разрешения установлены на 777.
Используйте dir_mode опцию, чтобы установить разрешение каталога и file_mode установить разрешение файла:
Пользователь по умолчанию и группа собственность могут быть изменены с uid и gid опциями:
Чтобы установить дополнительные параметры , добавьте их в виде списка через запятую после -o параметра. Чтобы получить список всех опций монтирования, введите man mount ваш терминал.
Авто монтаж
Когда общий ресурс монтируется вручную с помощью mount команды, он не сохраняется после перезагрузки.
/etc/fstab Файл содержит список записей , которые определяют , где , как и то , что файловая система будет смонтирована на старте системы.
Чтобы автоматически смонтировать общий ресурс Windows при запуске вашей системы Linux, определите монтирование в /etc/fstab файле. Строка должна содержать имя хоста или IP-адрес ПК с Windows, имя общего ресурса и точку монтирования на локальном компьютере.
Откройте /etc/fstab файл в текстовом редакторе :
Добавьте следующую строку в файл:
Выполните следующую команду для монтирования общего ресурса:
mount Команда, будет читать содержание /etc/fstab и установить долю.
При следующей перезагрузке системы общий ресурс Windows будет смонтирован автоматически.
Размонтирование Windows Share
Команда umount отсоединяет (размонтирует) смонтированную файловую систему от дерева каталогов.
Чтобы отсоединить подключенный общий ресурс Windows, используйте umount команду с указанием либо каталога, в котором он был подключен, либо удаленного общего ресурса:
Если в fstab файле CIFS есть запись в файле, удалите ее.
Команда umount не сможет отсоединить общий ресурс, когда он используется. Чтобы узнать, какие процессы обращаются к общему ресурсу Windows, используйте fuser команду:
Найдя процессы, вы можете остановить их с помощью kill команды и размонтировать общий ресурс.
Если у вас по-прежнему возникают проблемы с размонтированием общего ресурса, используйте параметр -l ( —lazy ), который позволяет размонтировать занятую файловую систему, как только она больше не будет занята.
Вывод
В Linux вы можете смонтировать общий доступ к Windows, используя mount команду с cifs параметром.
Источник
How to Mount a Windows Share in Linux
In this tutorial we will be discussing different ways to connect to a Microsoft share form Linux. Before we dive in I think it is important to understand the different terminology used when talking about Samba, SMB and CIFS shares.
Table of Contents
SMB vs CIFS vs SAMBA
SMB (Server Message Block) is a protocol used for network file sharing. It was originally designed at IBM in the 1980’s.
CIFS (Common Internet File System) is a implementation of SMB that was created by Microsoft.
SAMBA is an open source software suite and set of utilities used by UNIX/Linux to communicate with Microsoft Windows systems.
From the average user stand point SMB and CIFS can be used interchangeably. As you will see below, we will connect to the same share using both SMB and CIFS.
Mount a Windows Share Using GUI (Files / Nautilus)
You can easily connect to a Windows share using the Files application (formerly known as Nautilus) that ships with Gnome. For the sake of clarity, we will call it Nautilus.
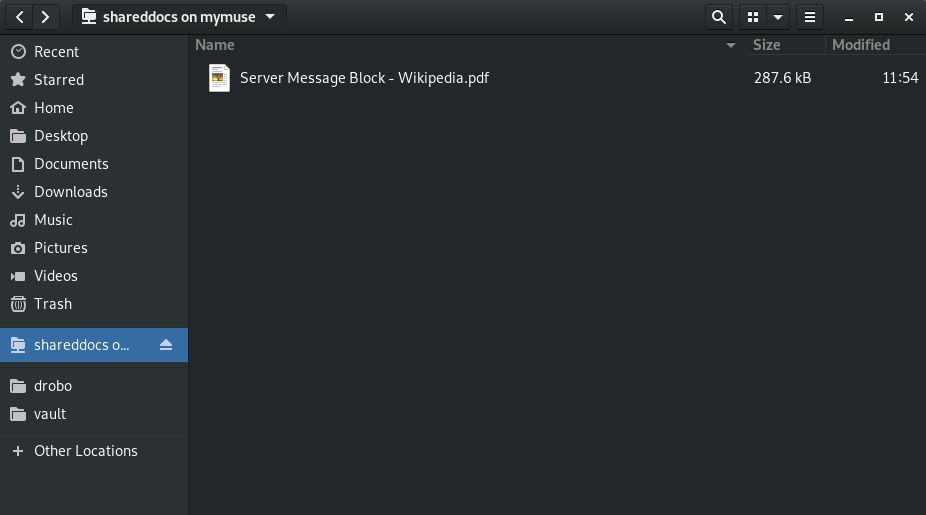
Open the Nautilus application and select “Other Location” from the left places panel.
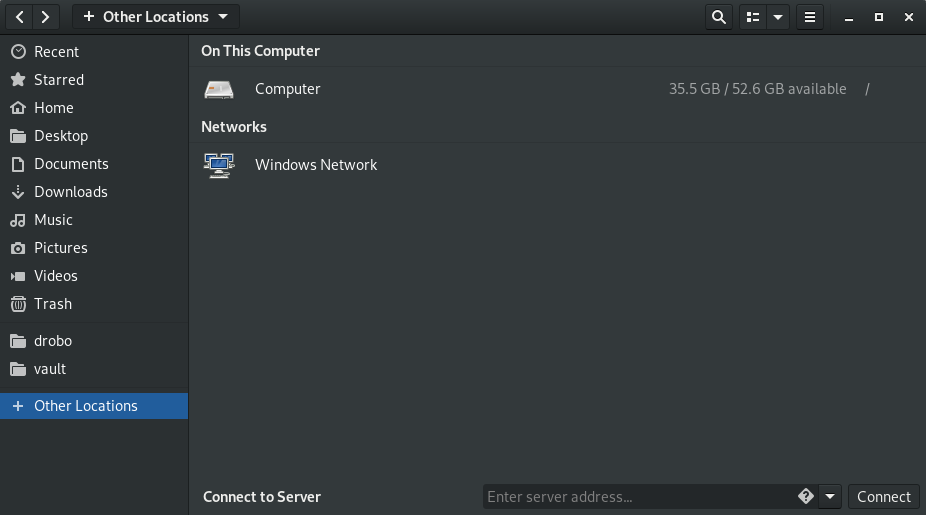
At the bottom of the screen you will see “Connect to Server” with a box asking for you to enter the server address. Inside that box is a diamond with a question mark in it that you can click for some help.
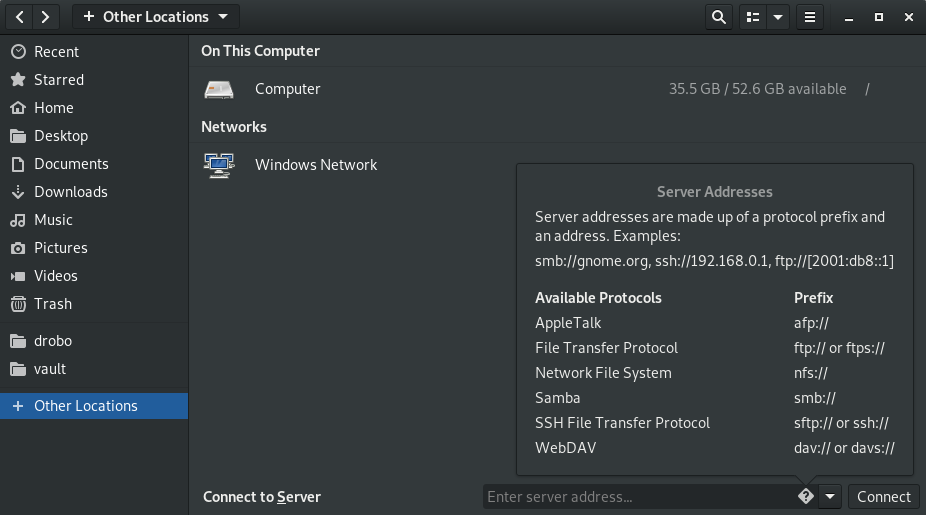
As you can see in the pop-up, server addresses are made up of a protocol prefix and an address. On my Windows machine named “MyMuse” I created a share called “SharedDocs”. So inside that entry box we will use:
We can also use the IP address:
This will bring up a dialog box asking for authentication credentials.
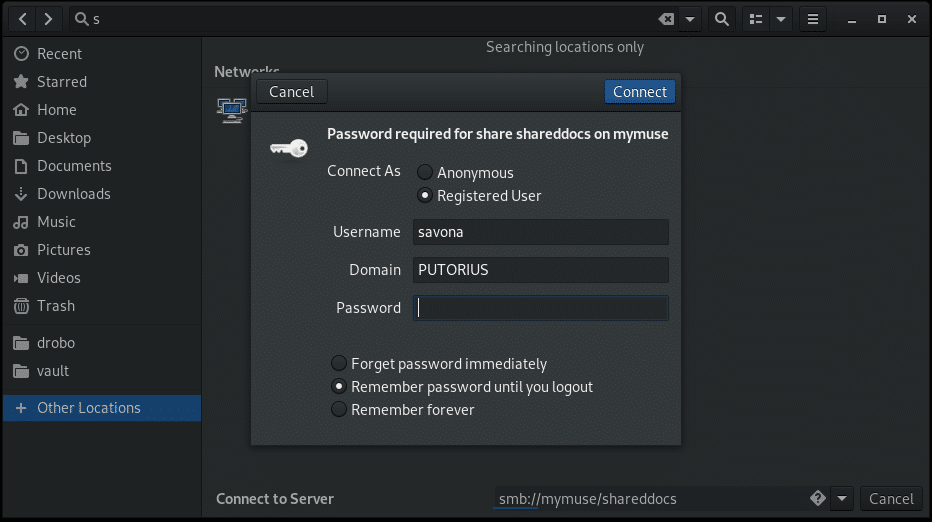
Select the “Registered User” radio button and enter your details. You have three options for storing your password.
- Forget password immediately – This will log you in and and soon as your session is over you will be required to provide your credentials again.
- Remember password until you logout – Remember your password until you explicitly logout.
- Remember forever – This option will store the credentials and allow you to easily return to the share.
Once you are connected, Nautilus will show the location on the left panel allowing easy access to the share.
Be aware that once that connection is closed you will have to go back to “Other Locations” and use the drop down box to reconnect. If you want to make the share persistently accessible from the left menu you will need to add a bookmark.
NOTE: If you do not want to type your credentials every time ensure that you select “Remember Forever” when authenticating to the share.
To add a bookmark, connect to the share then right click it in the left panel and select “Add Bookmark”.
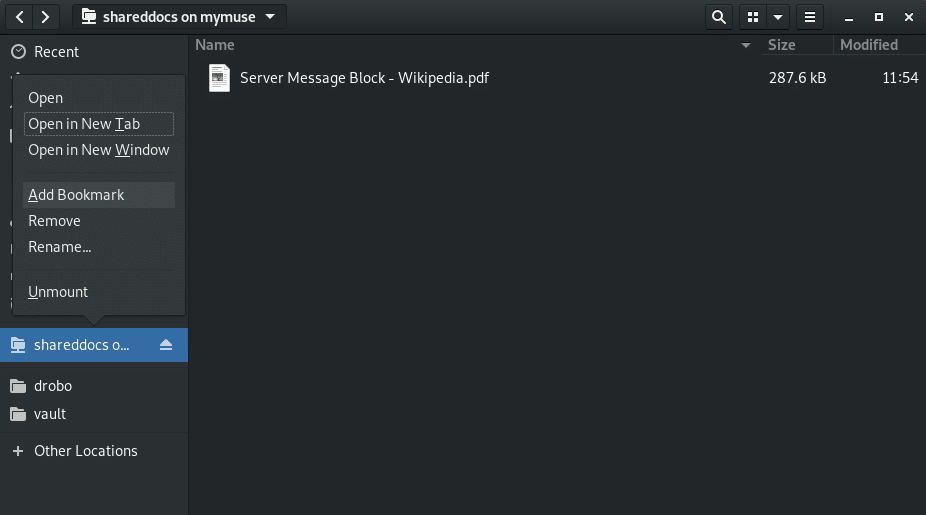
If you have a lot of shares, or multiple shares on the same device, it will be hard to differentiate them. You can rename them to something more user friendly by right clicking on the bookmark and selecting “Rename…”.
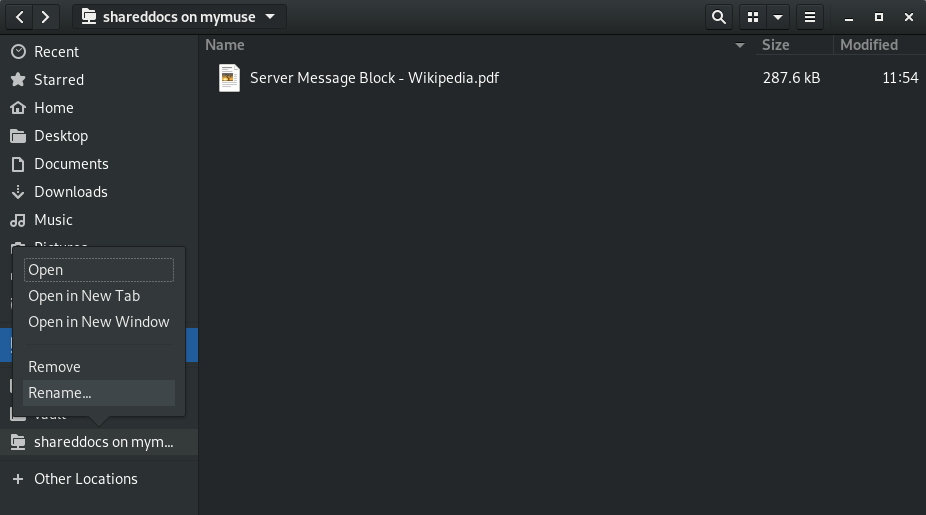
Now we can easily navigate to our share as the name is clearly visible and easy to identify.
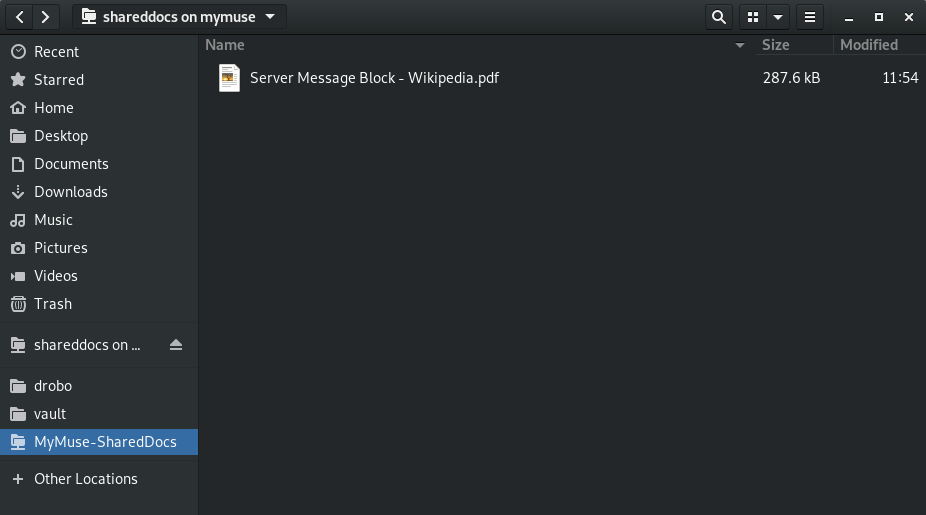
Mount A Windows Share Using Command Line
Using the mount.cifs Command
You can easily mount a cifs share from the command line using the mount.cifs command. Using the mount command requires root privileges.
First, create a directory to mount the share:
Use the mount.cifs command to mount the share at the created directory.
You can use the IP address as well.
Alternatively, you can use mount -t cifs with the same syntax.
Automatically Mount CIFS Share at Boot
Mount CIFS Share at Boot Using /etc/fstab
You can add your CIFS mount point in /etc/fstab and have the system mount it during boot. However, there are some considerations to make. If the share is not available at boot time the system will hang until the mount attempt times out, or worse, refuse to boot. This will cause a delay in accessing the system. To avoid this you can use autofs (next section). Also mounting it via fstab requires you to put your credentials somewhere in plain text. You have two options when using fstab to mount a CIFS share.
- Put the credentials in the fstab file itself – This is a huge security risk as fstab is readable by any user. Someone can simply cat the file and see your credentials. IT IS NOT RECOMMENDED!
- Use a credentials file – This entails saving your credentials in a separate file which can then be protected by permissions. Although your credentials will still be saved in plain text, someone would need root permissions to read them.
Because of the high risk of the first option, we will not even discuss how to do it. It is easy enough to use a credentials file.
First, create a hidden file in root’s home directory (/root/). You can call this file whatever you like. Most people call it .smbcreds or similar. In this file you need two lines, one containing “username= ” and one containing “password= ”.
Now set the permissions so it is only readable by root:
Now edit the /etc/fstab file and add the following information:
- Remote server share address (//mymuse/shareddocs)
- Local mount point (/mnt/cifs)
- Filesystem type (cifs)
- options (credentials file=/root/.smbcreds)
- dump option (0)
- check option (0)
Example fstab, last line showing the CIFS mount point.
Mount CIFS Share using AutoFS
The most obvious benefit of using autofs is that the share is only mounted when being accessed. If it is unavailable it will not effect your system when it boots.
Using autofs has the same credentials issues described above with fstab. It is also necessary to store your password in plain text when using autofs for cifs shares.
Installing autofs Package
Install autofs in CentOS 7, or Red Hat 7:
Install autofs in Ubuntu 18:
Let’s configure autofs to mount our Windows share.
Create Credentials File
First, ensure you create the credentials file as described above:
DO NOT forget to set the permissions:
Get UID for User
Now, let’s get our user accounts uid so we can tell autofs to mount the share as our user instead of root.
Edit auto.master Map File
Edit the /etc/auto.master configuration file. In this file we will provide a map of directories to shares for autofs to use. Add the following line to the file:
The first part of the above line is the directory we are using as a mount point (you can create a custom directory if you wish). The second is the file that autofs should look in for instructions on how to connect to the resource and mount it.
Create the Shares File
Next edit or create the /etc/auto.shareddocs file and add the following:
Restart the Service
Now we must restart the autofs service so it reads the new configuration.
Test and Verify
Now, let’s look in the /mnt directory.
The shareddocs directory doesn’t exist until you try to access it (auto fs). If everything above was followed, we should be to cd into that directory even though we do not see it. The directory will be dynamically created as it is accessed.
Bob’s your uncle.
Conclusion
In this article we covered 3 different ways to mount your Windows shares in Linux. You should now be able to mount an SMB share via the GUI, manually on the command line, automatically on boot and with autofs.
An important point I would like to stress is make sure you protect your credentials. I hope you enjoyed this tutorial, please leave feedback or questions in the comments below.
Источник