- How to check os version in Linux command line
- Check os version in Linux
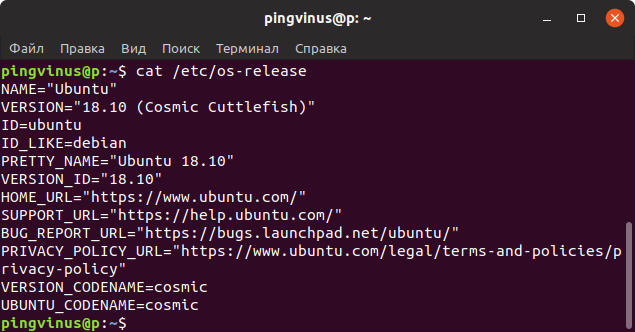
- The /etc/os-release file
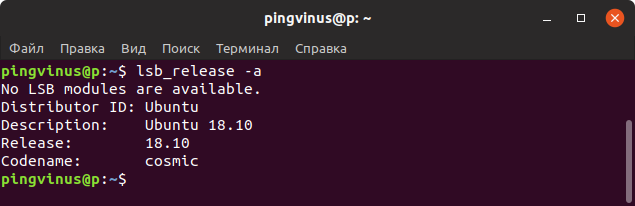
- Checking OS version on Linux using the lsb_release command
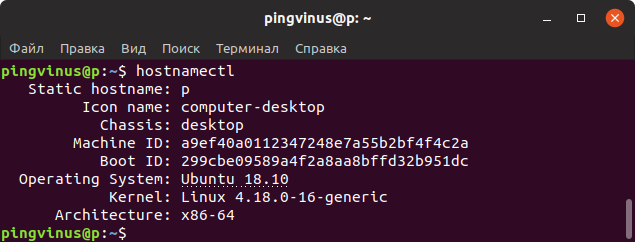
- hostnamectl command
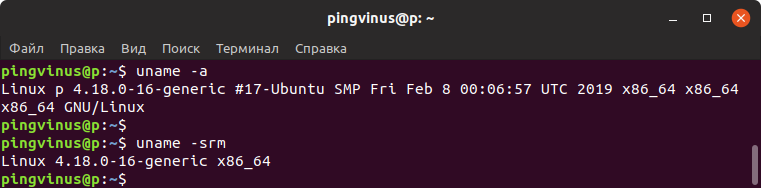
- uname command
- /etc/issue file
- Getting help
- Related media
- Conclusion
- How to Check OS Version in Linux
- Check Linux Version
- 1. From /etc/os-release
- 2. Using lsb_release command
- 3. Using Hostnamectl command
- 4. From /etc/issue file
- 5. From /etc/*release or /etc/*version
- Conclusion
- Как узнать версию Linux
- Команда lsb_release
- Команда hostnamectl
- Команда uname — версия ядра
- Файл /etc/os-release
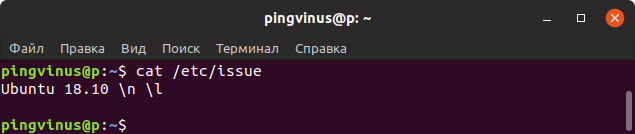
- Файл /etc/issue
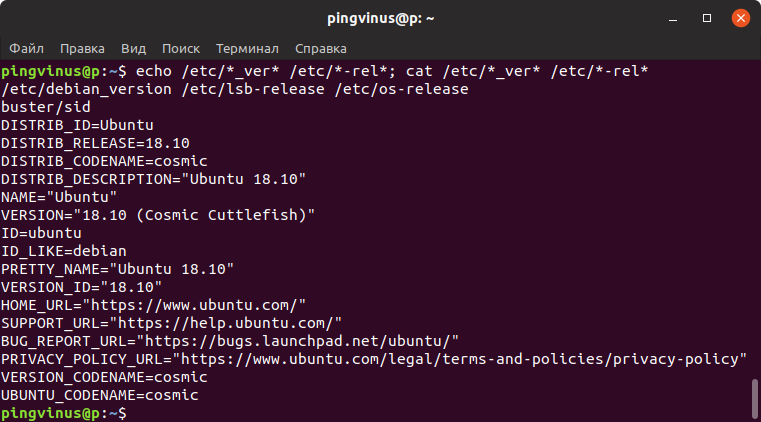
- Файлы /etc/***release и /etc/***version
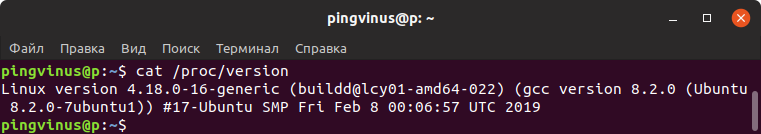
- Файл /proc/version
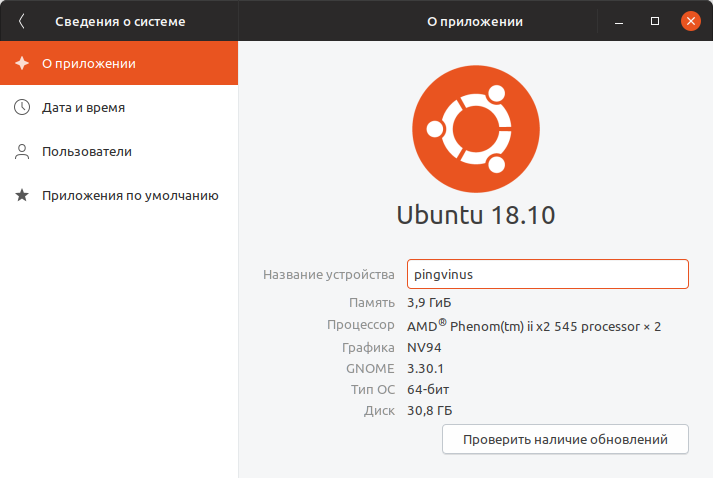
- Через графические утилиты
- Заключение
- How to check your Linux version: easy ways to view the distribution and version number
- Linux version: what do the distribution and version number mean?
- Checking the Linux version in the terminal
- Step 1: Distribution version number
- Step 2: Linux kernel version number
- Step 3: View everything at once with Inxi
- How to check Debian version: the quick and easy way
- How to check your Ubuntu version: a guide
- Remove a directory in Linux: a simple guide
- Deleting files in Linux: a how-to guide
- Linux find command: search and find files
How to check os version in Linux command line
Check os version in Linux
The procedure to find os name and version on Linux:
- Open the terminal application (bash shell)
- For remote server login using the ssh: ssh user@server-name
- Type any one of the following command to find os name and version in Linux:
cat /etc/os-release
lsb_release -a
hostnamectl - Type the following command to find Linux kernel version:
uname -r
Let us see all examples in details for common Linux distros.
The /etc/os-release file
Type the following cat command:
$ cat /etc/os-release
Sample outputs:
We can filter out information such as OS version and name using the grep command/egrep command as follows:
$ grep ‘^VERSION’ /etc/os-release
$ egrep ‘^(VERSION|NAME)=’ /etc/os-release
Here is what we see:
Even tiny Linux distro such as Alpine Linux provide the required OS (Operating system) information, including version:
Checking OS version on Linux using the lsb_release command
The lsb_release command gives LSB (Linux Standard Base) and distribution-specific information on the CLI. The syntax is:
$ lsb_release -a
Sample outputs:
hostnamectl command
Use hostnamectl command to query and change the system hostname and related settings. Just type the following command to check OS name and Linux kernel version:
$ hostnamectl
And it will give info as follows. Look out for “ Operating System ” and “ Kernel “:
Another outputs from my OpenSUSE Linux 15.2 server:
uname command
/etc/issue file
Use more command/less command as follows:
$ cat /etc/issue
$ more /etc/issue
$ less /etc/issue
Getting help
You can also view the manual page on uname using the following command:
$ man hostnamectl
$ man uname
$ man cat
Related media
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
Conclusion
We explained how to find and display the OS version on Linux. The safest option is to query /etc/os-release file using grep or cat command. Systemd based Linux distro users can use the hostnamectl command.
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
Источник
How to Check OS Version in Linux
Linux version can be checked using inbuilt commands or can read from specific files. It is important to determine the distribution name and version on many occasion like when doing package updates or OS update.
There are a lot of Linux distributions available like Debian, Ubuntu, CentOS, Mint, Arch, Fedora, RHEL, and more.
In this tutorial, I will show how to check the Linux version from the command line.
Check Linux Version
There are mainly 5 ways we can get Linux distribution name and its version.
1. From /etc/os-release
Use cat command to read the content of the file /etc/os-release , run the following command:
Output from CentOS
Output from Ubuntu
2. Using lsb_release command
The lsb_release -a displays the Linux version information from the command line. The output will display distribution ID, description, release and codename. To display only the description you can use lsb_release -d .
If you get «command not found» and then you need to install ‘lsb-core’ package.
Output of lsb_release -a
To display only the description, run:
3. Using Hostnamectl command
In modern Linux distributions which use systemd init systems, you can use hostnamectl command to display operating system version.
4. From /etc/issue file
You can get version information from /etc/issue file, to read file content use cat or less command:
5. From /etc/*release or /etc/*version
Some distribution use release and version file and those files are specific to that distro.
$ echo /etc/*version /etc/*release
/etc/debian_version /etc/ec2_version /etc/lsb-release /etc/os-release
To read the content from /etc/*release or /etc/*version, run the following command:
If you are interested to know the Linux kernel version and architecture then use uname command or you can read the content from /proc/version file.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we learned different ways to find Linux OS name and version from I hope you enjoyed reading and please leave your suggestion in the below comment section.
Источник
Как узнать версию Linux
Когда мы говорим о Linux, то обычно подразумеваем какой-либо дистрибутив Linux. Также под Linux мы можем иметь ввиду ядро Linux.
Иногда требуется определить версию Linux, в которой вы работаете. Пользователь может не знать или забыть, какая версия дистрибутива или какая версия ядра Linux используется. Если это чужая система, то может потребоваться узнать название используемого дистрибутива.
В данной статье рассматриваются различные способы, которые помогут нам определить используемую версию Linux. Рассматривается несколько команд для определения версии Linux. Приведенные команды универсальны и не зависят от дистрибутива. Возможно, некоторые из них могут не работать в каких-то дистрибутивах, в таком случае переходите к следующей команде и пробуйте ее.
Команда lsb_release
Команда lsb_release выводит информацию о дистрибутиве.
Префикс lsb в названии команды относится к проекту Linux Standard Base, который был создан с целью создания ряда стандартов для выпуска дистрибутивов Linux, чтобы уменьшить различия между отдельными дистрибутивами. Предполагается, что использование LSB снижает затраты, связанные с переносом приложений на разные дистрибутивы, а также снижает усилия, связанные с поддержкой этих приложений.
Чтобы отобразить информацию о дистрибутиве выполните команду:
Выводится название дистрибутива, номер версии и кодовое имя.
Можно использовать опцию -d , чтобы показать только строку Description, которая обычно содержит и название и версию дистрибутива.
Команда hostnamectl
Команда hostnamectl , выполненная без параметров или с ключом status , выводит текущую информацию о системе.
Помимо данных дистрибутива, выводится версия ядра и архитектура.
Команда uname — версия ядра
Команда uname выводит информацию о текущем ядре системы Linux, а также некоторые дополнительные данные.
Чтобы вывести всю информацию, используется ключ -a
Для удобства можно выводить только название ядра ( -s ) , версию ядра ( -r ) и архитектуру ( -m )
Файл /etc/os-release
В файле /etc/os-release содержится информация о дистрибутиве, включая URL-адреса сайт системы и некоторые дополнительные данные. Данный файл присутствует в дистрибутивах, использующих systemd.
Чтобы вывести содержимое файла /etc/os-release можно воспользоваться командой cat:
Файл /etc/issue
Файл /etc/issue содержит текст, который выводится в качестве приглашения ко входу в систему. Обычно текст представляет собой название дистрибутива и версию.
Выведем содержимое файла /etc/issue командой cat:
Файлы /etc/***release и /etc/***version
Если вы используете старый или какой-то специфический дистрибутив Linux, то информация о системе может хранится в файле /etc/abc-release или /etc/abc-version .
Вместо abc обычно указывается краткий идентификатор дистрибутива или lsb, если система совместима со стандартами LSB. Вместо символа — может быть символ _ . Например, для дистрибутива Fedora используется файл /etc/fedora-release
Необязательно знать названия этих файлов. Можно воспользоваться следующей командой, чтобы автоматически определить названия и вывести содержимое этих файлов:
Файл /proc/version
Информацию о ядре Linux также можно получить из файла /proc/version
Через графические утилиты
Многие дистрибутивы позволяют просмотреть некоторую информацию о системе, используя графические утилиты. Например, в Ubuntu это можно сделать из утилиты Параметров системы, на вкладке Сведения о системе .
Заключение
Мы рассмотрели различные способы получения информации о дистрибутиве и ядре системы Linux. Какие-то способы могут не работать в некоторых дистрибутивах Linux.
Источник
How to check your Linux version: easy ways to view the distribution and version number
When most people think of Linux, an open source operating system that serves as an alternative to Microsoft and Apple comes to mind. But unlike these market leaders that offer commercial operating systems, there is no single Linux operating system.
Instead, there is a whole series of free, open-source operating systems (referred to as “distributions”) that are built based on the Linux kernel. This means that Linux merely serves as the basis for potential operating systems, which are then built from the kernel and other programming elements. While Microsoft and Apple release closed-source, proprietary software products, the Linux kernel is open-source code that any member of the Linux community can use or modify to make their own applications and operating systems.
Since there exist countless Linux versions, it’s of utmost importance to know which version you’re running, especially when you run into technical problems, have questions, or want to do an update. Luckily, it’s very easy to find out. Keep reading for instructions on how tocheck your Linux version.
Linux version: what do the distribution and version number mean?
As of June 2020, there are now over 500 unique Linux distributions. The best-known are Ubuntu, Debian, Fedora, SUSE, Manjaro, and Linux Mint.
The family tree for Ubuntu alone contains over 65 software applications built on the basis of Ubuntu. The current distribution was released in 2020 with the version number 20.04. The first version of Ubuntu came out in 2004 and was based on the Debian operating system.
The various Linux distributions can be roughly divided into three basic family trees as well as countless other smaller branches and independent versions. For example, the entire Ubuntu family is based on Debian, the distribution Fedora is based on Red Hat Linux, and SUSE used Slackware.
Even though they’re all based on the Linux kernel, the various distributions serve as their own operating systems with different GNU toolchains and graphic interfaces. In order to find your way in the busy Linux landscape, it’s important to know which version of the Linux kernel and which distribution you’re using.
Checking the Linux version in the terminal
Whether you’re using Linux privately or professionally, it’s always important to know which Linux version and distribution you’re working with. That way you’ll know which package manager you’ll need for downloading new tools and updates, and which Linux forum you should turn to when you have questions or experience problems.
If you’re looking for details about your Linux version, there are two words which will be of particular significance:
- The version number of the distribution
- The version of the Linux kernel
To find out these two values, you’ll need to use Linux commands. In general, when working in Linux, user input is entered into so-called “shells”, which are interfaces between systems and users. Shells run using a graphic terminal that processes the commands in the relevant programming language. This will serve as your starting point in checking your Linux version.
Step 1: Distribution version number
Open the Linux terminal with the keys [Ctrl] + [Alt] + [T] or by using the search function. Type the following command into the terminal and then press enter:
The asterisk in the code ensures that the command will apply to all distributions and shows you the installed version. The data that you see now may look a bit messy, with some lines appearing twice or several ending in “release”. The most important line here is “PRETTY_NAME=”, which contains the name of the distribution and version number that you’re currently using.
Another command that works on all distributions without the need for a special tool is the following:
If you only need the name and version number of your current distribution, the following command will suffice:
In the following example, you can see that Ubuntu 20.04 LTS is currently running:
The command “lsb_release -d” shows the current distribution and its version number.
The following command lists more comprehensive information about the version:
The command “lsb_release -a” shows additional information about the distribution version you’re currently running.
This command should work on every Linux distribution, as long as you’ve installed the lsb-release package or it’s part of your Ubuntu version. If you haven’t already installed it, you can easily do so with the following command for Debian and Ubuntu:
Step 2: Linux kernel version number
If you’d like to know which version of the Linux kernel you’re using, type the following command into the terminal and press enter:
The command “uname -r” shows the version of the Linux kernel that you’re currently using.
You’ll now see which Linux kernel you’re using. In the above example, the Linux kernel is 5.4.0-26.
If you’d like to see more information (about computer architecture for example), you can enter the following command:
The command “uname -a” shows the version of the Linux kernel you’re using, as well as additional details.
Step 3: View everything at once with Inxi
With the tool Inxi, you can easily view all the information about your hardware, host, Linux kernel, desktop environment, and distribution. To install the program in Debian/Ubuntu, enter the following command into the terminal:
Once installed, you can view the above-mentioned data with this simple command:
- 16.10.20
- Know-how
- How did you like the article? 0
How to check Debian version: the quick and easy way
Knowing which Debian version you have not only helps you to choose the right install package for a program – you also need it to get appropriate support in forums. There are several different methods to check your Debian version. In this step-by-step guide, we’ll explain how to check your version using Terminal and Hardinfo.
How to check your Ubuntu version: a guide
Knowing which Ubuntu version you’re running is helpful for different things. You can use this information to check whether programs are compatible with your system. Or you can include the version number in troubleshooting searches. It’s thus of crucial importance to know how to check your Ubuntu version. Keep reading to find out how to do so in a few simple clicks.
Remove a directory in Linux: a simple guide
Sometimes you may need to delete an entire folder rather than just individual files. If you want to remove a Linux directory, there are several ways to do it. Here are a few basic solutions that use either File Manager or Terminal. We also explain what you can do if you don’t have the necessary rights.
Deleting files in Linux: a how-to guide
Deleting files in Linux couldn’t be easier. Whether you use the file manager or work directly in the terminal with the command “rm”, you can remove Linux files in just a few clicks. Keep reading to find out how to remove single files, multiple files, files of a certain type, or entire folders.
Linux find command: search and find files
While working on a Linux system the command line is frequently used. Many administrative tasks require you to find files and directories based on specific criteria. In doing so, Linux admins are accustomed to using the find command. Here, we’ll show you how the command works and how to use it as a handy tool.
Источник