- How To Start, Stop, Restart Networking On Linux?
- Get Status Of Network Service
- Debian, Ubuntu, Kali
- Fedora, CentOS
- Stop Network Service
- Ubuntu, Debian, Kali
- Fedora,CentOS
- Start Network
- Ubuntu, Debian, Kali
- Fedora,CentOS
- Restart Network
- How to Restart Network Interface in Linux
- Restart Network Interface Using Command Lines in Linux (generic method)
- Debian / Ubuntu Linux restart network interface
- Redhat (RHEL) / CentOS / Fedora / Suse / OpenSuse Linux – Restart network interface in Linux
- Slackware Linux restart commands
- How to see status of network/networking service
- Ubuntu Restart Networking Command
- Task: Restart networking under Ubuntu Linux
- How to restart the networking service ( Ubuntu version 14.04LTS or older )?
- To start networking service, enter :
- To stop networking service, enter:
- A note about desktop users
- How to Restart Networking in Debian Linux
- Restarting Networking on Debian 8 Wheezy and Older:
- Installing Network Manager on Debian 9 Stretch:
- Using Network Manager to Configure Networking:
- Restarting a Single Connection Using Network Manager:
- Restarting Network Manager:
How To Start, Stop, Restart Networking On Linux?
I have changed my network configuration and want to restart to make changes effective. Or there are some problems with my network and I think restarting it will solve my problems. Here we will look at how to restart networking service in various network distributions like Ubuntu, Debian, Fedora, CentOS.
Get Status Of Network Service
We will get status of network with the following command.
Debian, Ubuntu, Kali
For deb based distributions we will use init.d system. We will provide status option to the networking script.
As we cab see that networking service is active from given date. Its PID is 897 .
Fedora, CentOS
For distributions like CentOS, RedHat, Fedora we will use systemctl command. We will provide the options status and network which is the networking service.
Stop Network Service
We can stop network like below. Bu keep in mind for remote connection it can be create problems with ssh
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali
We will use stop option with networking command in order to stop network services in Ubuntu, Debian, Kali, Mint etc.
Fedora,CentOS
We will use systemctl again with stop option which will stop network services. We also require root privileges that will beget with sudo command.
Start Network
We can start network like below.
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali
We will provide start option in order to start network services in deb based distributions.
Fedora,CentOS
We will use start network option in order to start network services in rpm based distributions.
Restart Network
Now we can restart our network or network services.
Источник
How to Restart Network Interface in Linux
Restart Network Interface Using Command Lines in Linux (generic method)
The procedure to to turn off eth0 interface is as follows. Run:
# ifdown eth0
To turn on eth0 interface run:
# ifup eth0
See ip address info using the ip command:
# ip a show eth0

Debian / Ubuntu Linux restart network interface
To restart network interface, enter:
sudo /etc/init.d/networking restart
To stop and start use the following option (do not run them over remote ssh session as you will get disconnected):
sudo /etc/init.d/networking stop
sudo /etc/init.d/networking start
Debian/Ubuntu Linux with systemd, run:
$ sudo systemctl restart networking
Redhat (RHEL) / CentOS / Fedora / Suse / OpenSuse Linux – Restart network interface in Linux
To restart network interface, enter:
# /etc/init.d/network restart
To stop and start use the following option (do not run them over remote ssh session as you will get disconnected):
# /etc/init.d/network stop
# /etc/init.d/network start
Fedora/RHEL/CentOS/Suse Linux with systemd, run:
$ sudo systemctl restart network
Slackware Linux restart commands
Type the following command:
/etc/rc.d/rc.inet1 restart
You can take down or restart particular interface such as eth1 as follows:
# /etc/rc.d/rc.inet1 eth1_restart
# /etc/rc.d/rc.inet1 eth1_start ### start eth1 ###
# /etc/rc.d/rc.inet1 eth1_stop ### stop eth1 ###
How to see status of network/networking service
Run command:
$ sudo systemctl status network #CentOS/RHEL/Fedora/Suse
$ sudo systemctl status network #Debian/Ubuntu
Sample outputs:
Источник
Ubuntu Restart Networking Command
| Tutorial details | |
|---|---|
| Difficulty level | Easy |
| Root privileges | Yes |
| Requirements | None |
| Est. reading time | 1m |
How to restart network in Ubuntu Server:
- /etc/init.d/networking restart script based command.
- service restart networking – Use service to run a System V init script such as networking.
- systemctl restart networking – Restart networking for the latest version of Ubuntu server.
The syntax is as follows to restart the networking on Ubuntu or Debian based operating systems.
Task: Restart networking under Ubuntu Linux
Open the terminal (bash shell command line) and type the following commands on the latest version of Ubuntu 16.04 or above :
$ sudo systemctl restart networking
OR
$ sudo systemctl restart networking.service
To verify status and connectivity, enter:
$ sudo systemctl status networking.service
$ ip r ## show routing info ##
$ ip a show eth0 ## show info for eth0 interface ##
$ ip a show br0 ## show info for br0 interface replace br0 with your actual interface ##
$ ping cyberciti.biz
Sample session from above commands:
Fig.01: How to restart network service in Ubuntu server
How to restart the networking service ( Ubuntu version 14.04LTS or older )?
You can use the service command following as well:
$ sudo service networking restart
Warning : Do not stop networking service over ssh session.
To start networking service, enter :
$ sudo /etc/init.d/networking start
OR
$ sudo service networking start
To stop networking service, enter:
$ sudo /etc/init.d/networking stop
OR
$ sudo service networking stop
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
A note about desktop users
If above command failed, try the following command:
$ sudo service network-manager restart
OR systemd based Ubuntu system (latest version:
$ sudo systemctl restart network-manager
See also:
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
| Category | List of Unix and Linux commands |
|---|---|
| Documentation | help • mandb • man • pinfo |
| Disk space analyzers | df • duf • ncdu • pydf |
| File Management | cat • cp • less • mkdir • more • tree |
| Firewall | Alpine Awall • CentOS 8 • OpenSUSE • RHEL 8 • Ubuntu 16.04 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Linux Desktop Apps | Skype • Spotify • VLC 3 |
| Modern utilities | bat • exa |
| Network Utilities | NetHogs • dig • host • ip • nmap |
| OpenVPN | CentOS 7 • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Debian 8/9 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Package Manager | apk • apt |
| Processes Management | bg • chroot • cron • disown • fg • glances • gtop • jobs • killall • kill • pidof • pstree • pwdx • time • vtop |
| Searching | ag • grep • whereis • which |
| Shell builtins | compgen • echo • printf |
| Text processing | cut • rev |
| User Information | groups • id • lastcomm • last • lid/libuser-lid • logname • members • users • whoami • who • w |
| WireGuard VPN | Alpine • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Firewall • Ubuntu 20.04 |
Comments on this entry are closed.
Interestingly enough, this command now says it is deprecated (due to a change in Debian code[1]). I think it still works, though probably for a limited time.
I like this site , really rich collection of solutions
i am from bangladesh , working as Project Manager
My wish to developed myself as a High level linux administrator
this site help me a lot daily
slam i want to learn networking configuration in ubuntu using terminal
i cannot execute the “service network restart”
it”ll display network unrecogonized service.
And also my apache is not working well.
after restarting apache ,apache page is not displaying after typing the localhost in my ubuntu system.
please help me guys.
thanks in advance.
thnq.
such a helpfull site!!
The correct syntax to restart network in Ubuntu Server for the second option is:
2. service networking restart
Источник
How to Restart Networking in Debian Linux
In this article, I will show you how to configure the network easily and restart them properly on Debian Linux. Let’s get started.
Restarting Networking on Debian 8 Wheezy and Older:
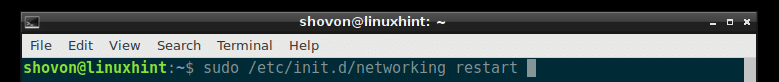
On Debian Linux, the network configuration is stored in /etc/network/interfaces file. On older version of Debian, when you make changes to /etc/network/interfaces file, you can restart networking with the following command:
The network service should be restarted. But on Debian 9 Stretch, that no longer works due to a bug.
Installing Network Manager on Debian 9 Stretch:
You can directly configure a network interface using /etc/network/interfaces file manually if you like. But the good news is, you don’t have to do that. On recent Linux distributions such as Debian 9 Stretch, networking can be managed by the Network Manager. It makes configuring a network really easy. Network Manager has command line utilities for network configuration.
If you have minimal server version of Debian 9 Stretch installed, you may not have Network Manager installed. In that case, you have to install Network Manager.
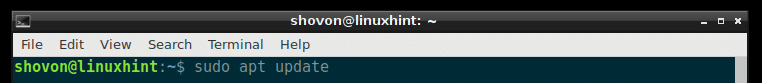
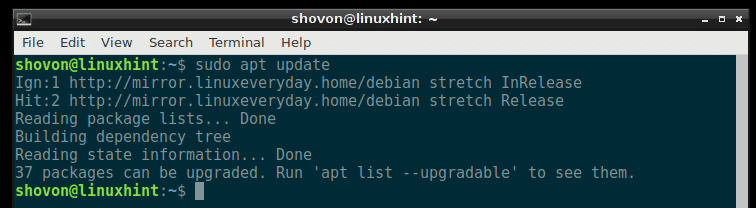
First update the package repository cache with the following command
The package repository cache should be updated.
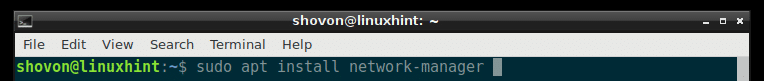
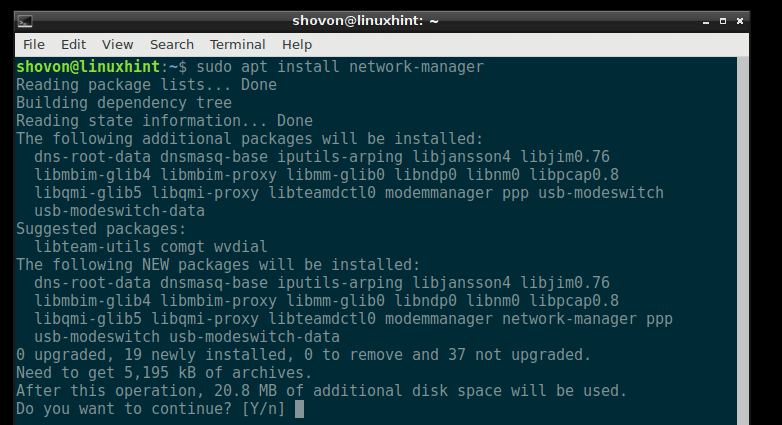
Now install Network Manager with the following command:
Press y and then press to continue.
Network Manager should be installed.
Using Network Manager to Configure Networking:
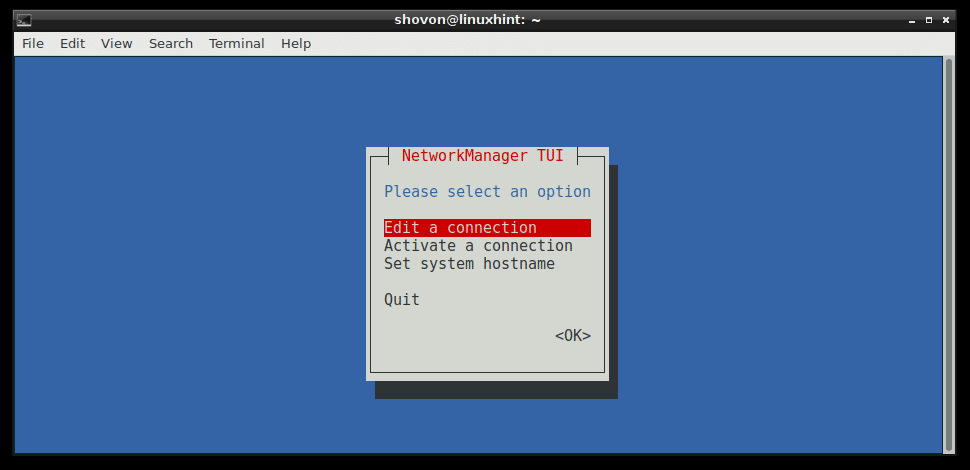
Network Manager has nmtui terminal based interactive tool that you can use to configure networking on Debian 9 Stretch.
To start nmtui, run the following command:
You should see the following window. From here you can set hostname, edit/add network connection, and active/deactivate network connections that you created.
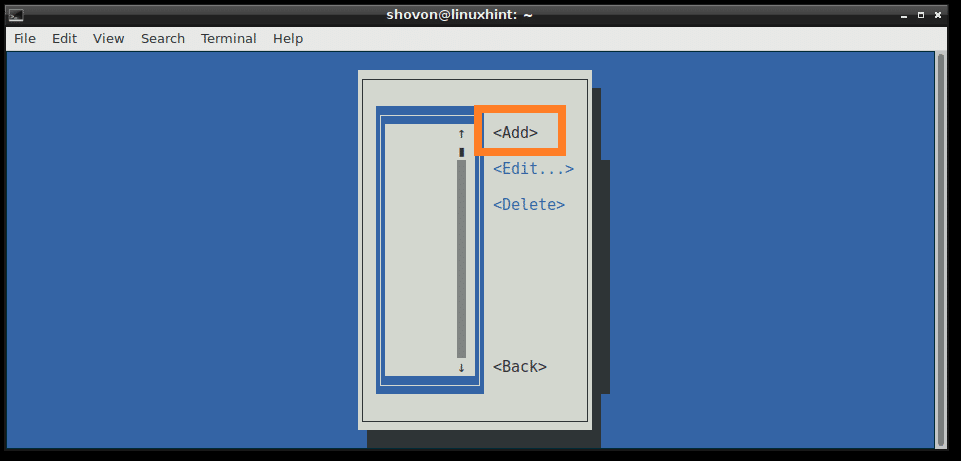
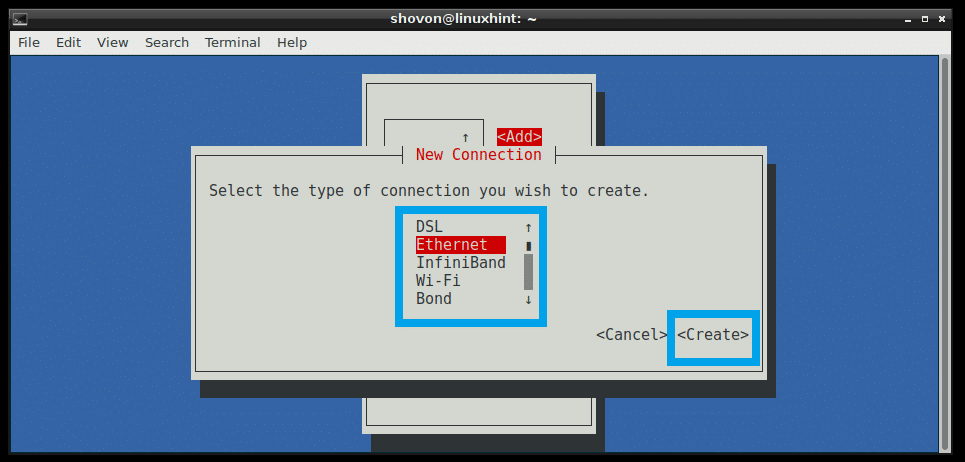
To create a connection, go to Edit a connection. Then press to select and then press .
Now select your connection method. I am going for Ethernet as I have a wired connection. Now press and select and then press .
Now type in a Profile name. It can be anything you want. I recommend you make it short and easy. Now type in a Device identified. I have only one physical Ethernet cable connected to my computer and is recognized as ens33, so I typed that. You can run ip link show command to find out your Device identifier.
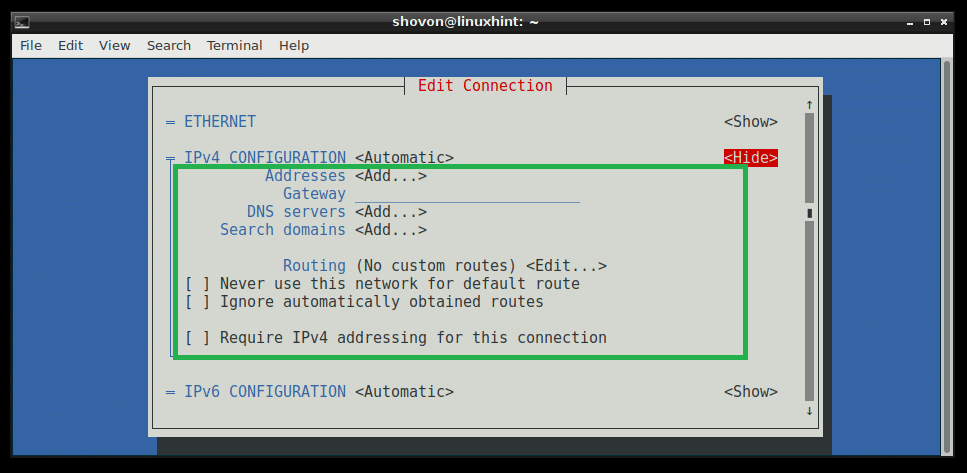
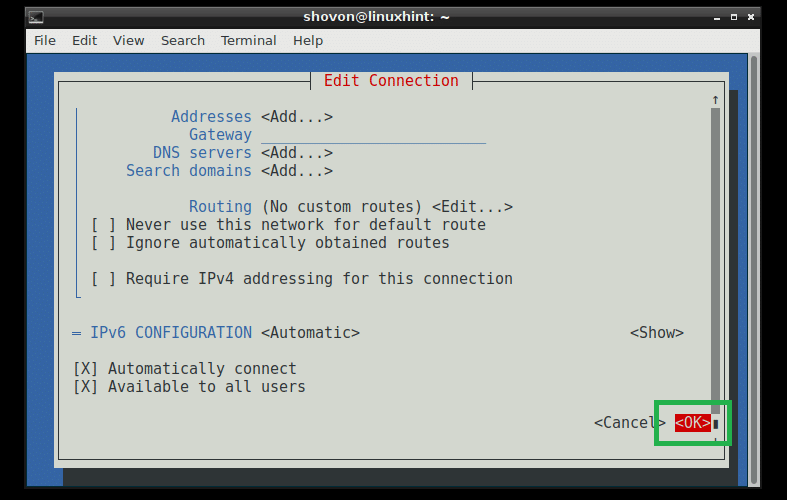
If you want to use DHCP to get the IP address for this network interface, then that’s pretty much everything you need to do. But if you want to assign a static IPv4 or IPv6 address, then you have to press to go to for IPv4 CONFIGURATION or IPv6 CONFIGURATION or both depending on your need. Then press . Then you should see something like this. Type in your IP Address, Gateway, DNS servers information, Routing and other information.
Once you’re done, scroll down using the and go to and then press .
Your connection should be created and activated.
NOTE: Network Manager do not manage interfaces defined in /etc/network/interfaces file. So if the interface you’re configuring with Network Manager is also configured using the /etc/network/interfaces file, then be sure to comment it out or remove it from the /etc/network/interfaces file for Network Manager to work with that interface.
Restarting a Single Connection Using Network Manager:
In the earlier section, I showed you how to create a connection using Network Manager. In this section I will show you how to restart the connection.
When you edit a connection, you must restart the connection for the changes to take effect.
You can use the nmtui utility to restart a connection using the Terminal based user interface.
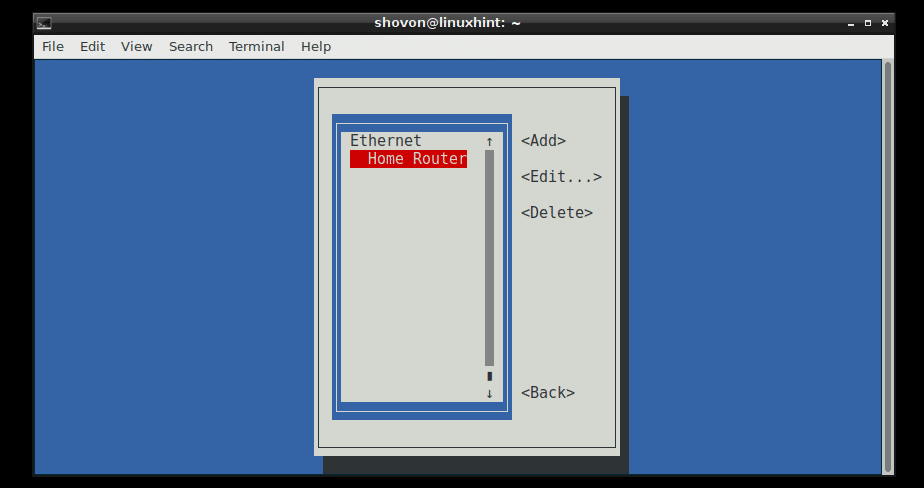
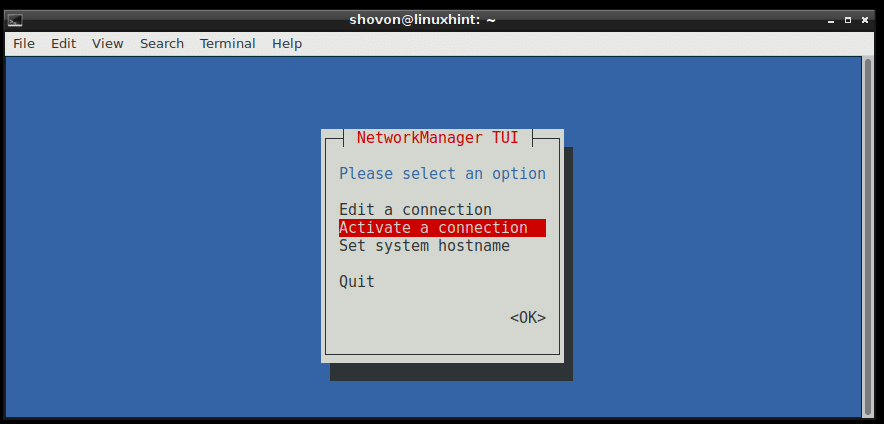
Run nmtui and go to Activate a connection.
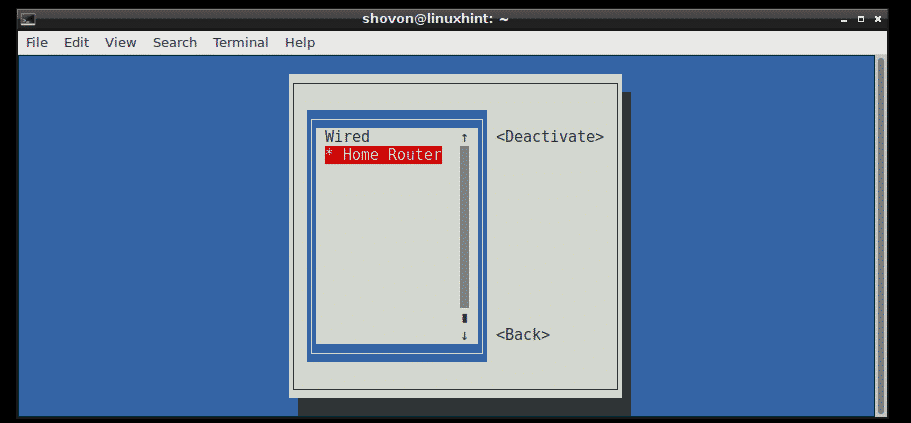
Now select your Connection from the list, in my case the Home Router, then press .
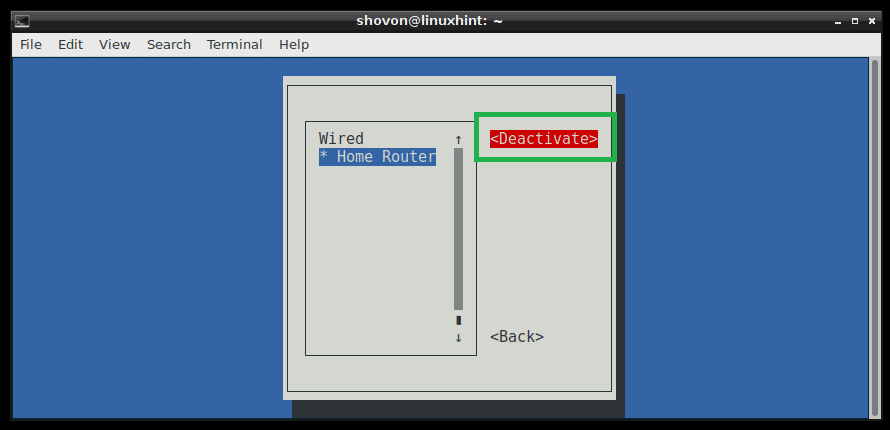
Now while is selected, press to deactivate the connection first.
Now while is selected, press to activate the connection again. Your changes should be applied.
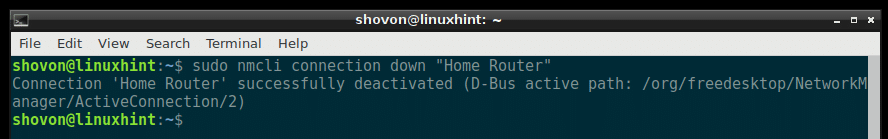
You can do the same thing from the terminal using the nmcli command.
Deactivate the Home Router connection with the following command:
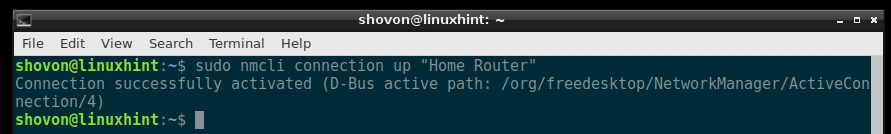
To Activate the Home Router connection again, run the following command:
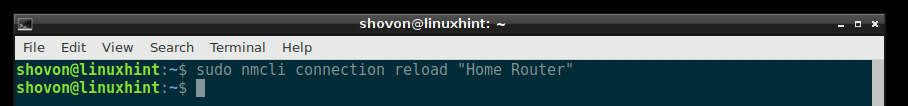
You can also Restart the connection with a single command:
Restarting Network Manager:
If you have a lot of connection, which may take a lot of time to restart one by one, then you can just restart the Network Manager service with the following command:
The Network Manager service should restart.
That’s how you Restart Networking Properly on Debian Linux. Thanks for reading this article.
Источник