- How to open Ubuntu file manager as root user
- Open Ubuntu Nautilus File Manager as root
- Edit or Open Ubuntu Files and Folders as root Administrative
- Warning: Running File Manager as Admin
- 5 Commands to View the Content of a File in Linux Command Line
- 5 commands to view files in Linux
- 1. Cat
- 3. Less
- 4. Head
- 5. Tail
- Bonus: Strings command
How to open Ubuntu file manager as root user
By default, the File Manager in Ubuntu or in any other Linux distro uses a non-root user. I mean a user that doesn’t have Administrative rights can access them graphically. It improves overall system security. However, if you want to run File manager as the root user or want to open & edit files and folder with administrative rights that are possible as well. However, you have to use the command terminal to enable that. The following tutorial carried out on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS focal fossa. However, the steps will be the same for earlier versions such as Ubuntu 19.10/19.04; 18.10/18.04 including Debian, Linux Mint, or any similar OS running Nautilus File manager.
Open Ubuntu Nautilus File Manager as root
- Open command terminal either from Applications or using keyboard shortcut- Ctrl+Alt+T.
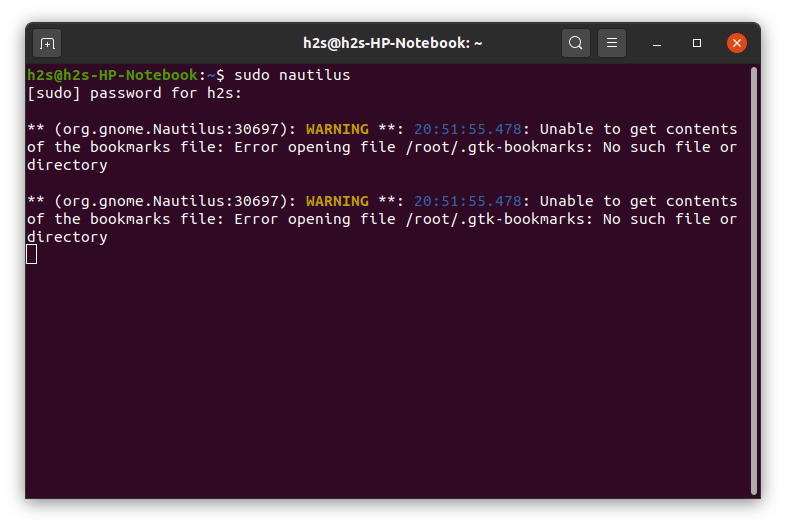
- Run Nautilus file manager with sudo. Here is the syntax:
- It will ask for your current non-root user’s password that is present in the sudo group.
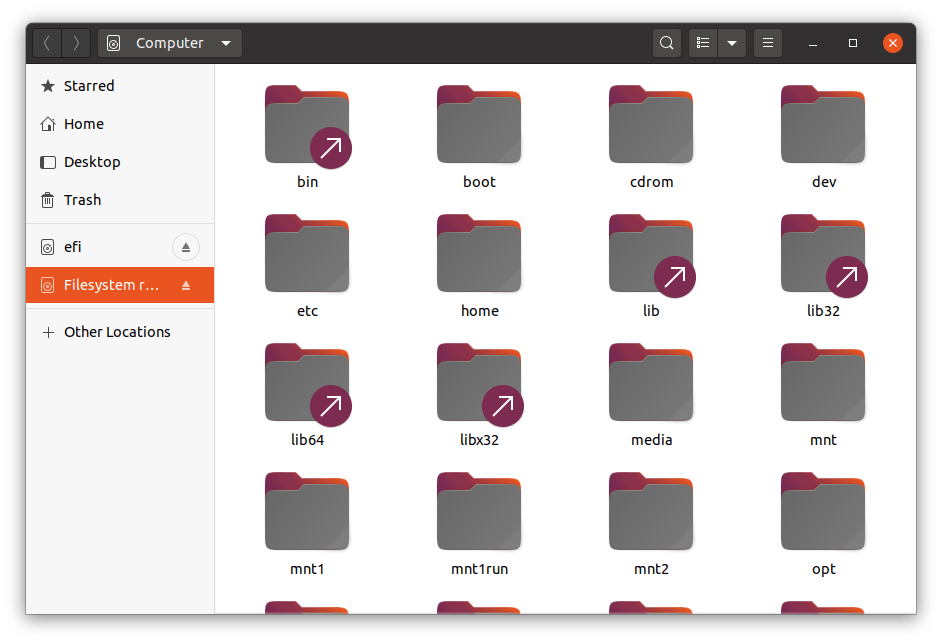
- Ubuntu File manager will open under administrative rights. Now you can navigate to any folder and files that can only be accessed by the root user via the graphical user interface.
Edit or Open Ubuntu Files and Folders as root Administrative
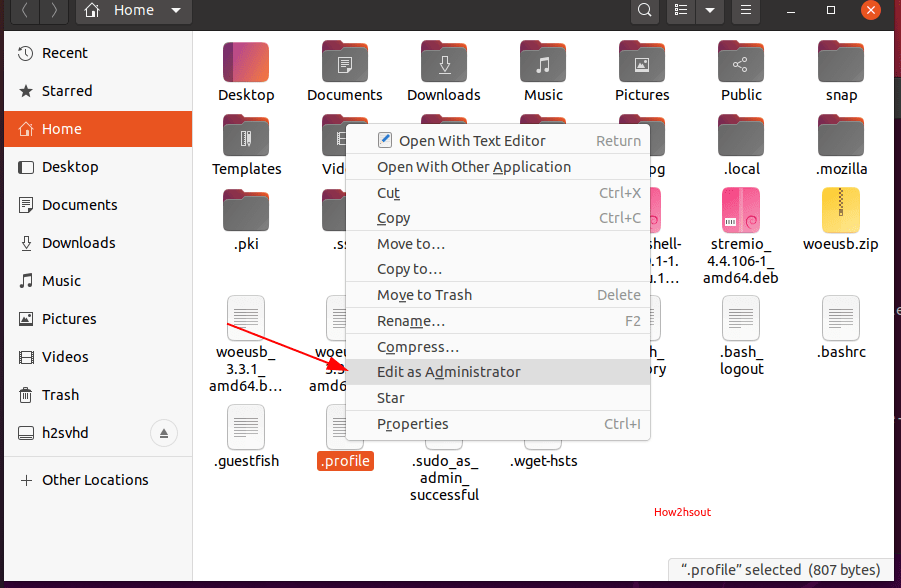
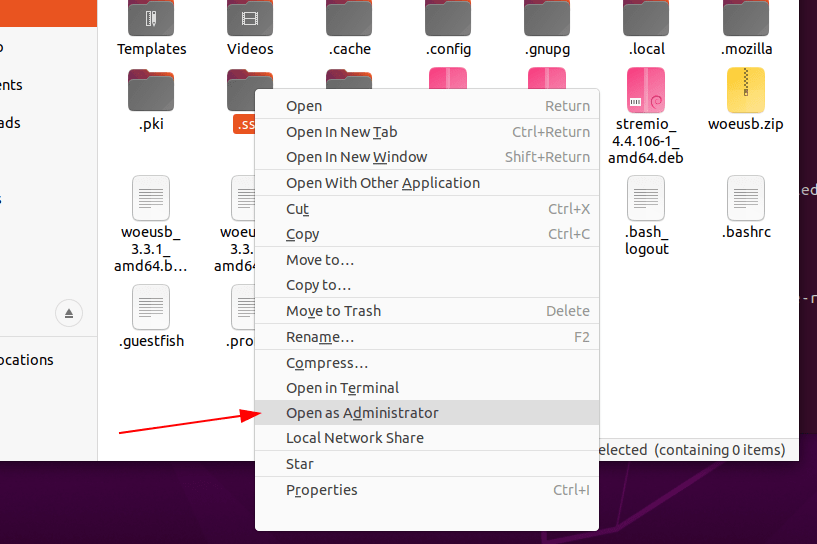
If you want to edit any file or open folder as root user directly from the Nautilus file manager’s graphical user interface. Then, we can embed an option “Edit as Administrator” or “Open as Administrator” privileges in its contextual menu.
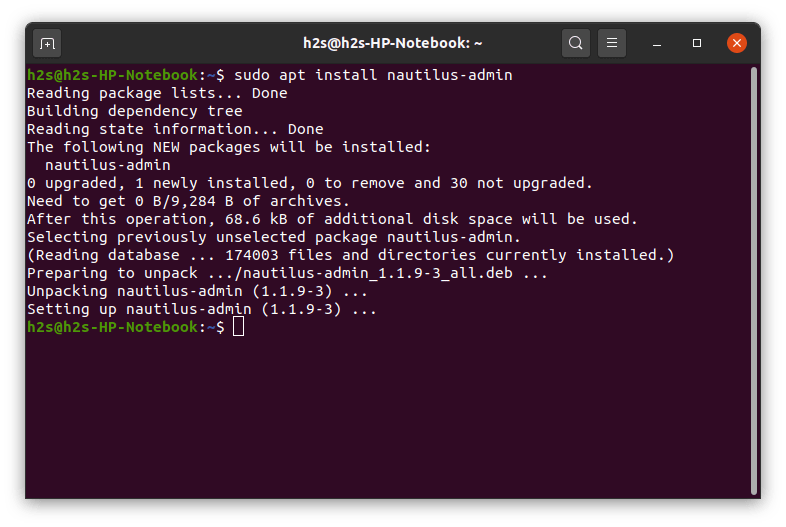
- Again open command terminal, if you already have not.
- Install the Nautilus Admin package.
- Enter the current user password and press the Y key to accept the packages for downloading and installing.
- Restart Nautilus File manager instances.
- Type exit and hit the Enter key to close the Terminal window.
- Now, to edit any file as the root user, open file manager, or right-click on that particular wherever it resides. And select the option “Edit as Administrator”.
- To open folders as root, same just like above right click on that and select “Open as Administrator’.
Warning: Running File Manager as Admin
Although, the above tutorial is useful in case you are not a well-experienced command terminal user, however, be cautious. Make sure you wouldn’t alter or edit some core configuration files that could leave your Ubuntu unstable or un-bootable.
Источник
5 Commands to View the Content of a File in Linux Command Line
If you are new to Linux and you are confined to a terminal, you might wonder how to view a file in the command line.
Reading a file in Linux terminal is not the same as opening file in Notepad. Since you are in the command line mode, you should use commands to read file in Linux.
Don’t worry. It’s not at all complicated to display a file in Linux. It’s easy as well essential that you learn how to read files in the line.
Here are five commands that let you view the content of a file in Linux terminal.
5 commands to view files in Linux
Before you how to view a file in Unix like systems, let me clarify that when I am referring to text files here. There are different tools and commands if you want to read binary files.
1. Cat
This is the simplest and perhaps the most popular command to view a file in Linux.
Cat simply prints the content of the file to standard display i.e. your screen. It cannot be simpler than this, can it?
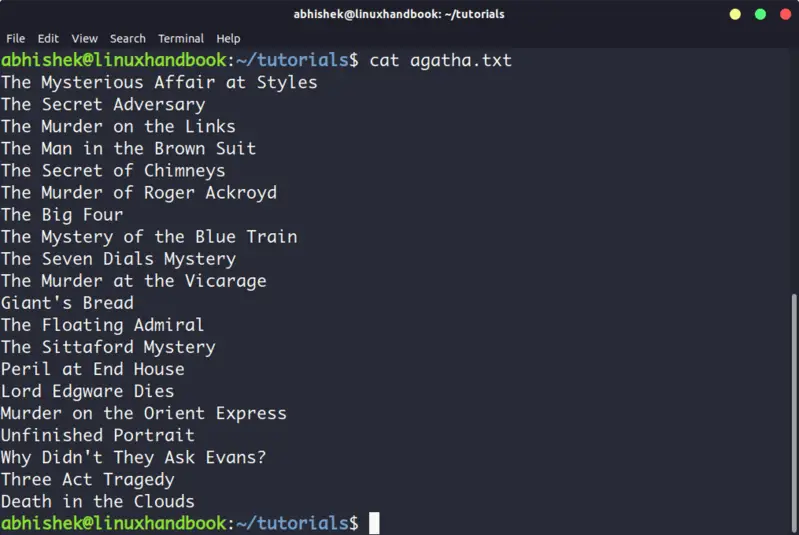
Cat becomes a powerful command when used with its options. I recommend reading this detailed tutorial on using cat command.
The problem with cat command is that it displays the text on the screen. Imagine if you use cat command with a file that has 2000 lines. Your entire screen will be flooded with the 200 lines and that’s not the ideal situation.
So, what do you do in such a case? Use less command in Linux (explained later).
The nl command is almost like the cat command. The only difference is that it prepends line numbers while displaying the text in the terminal.
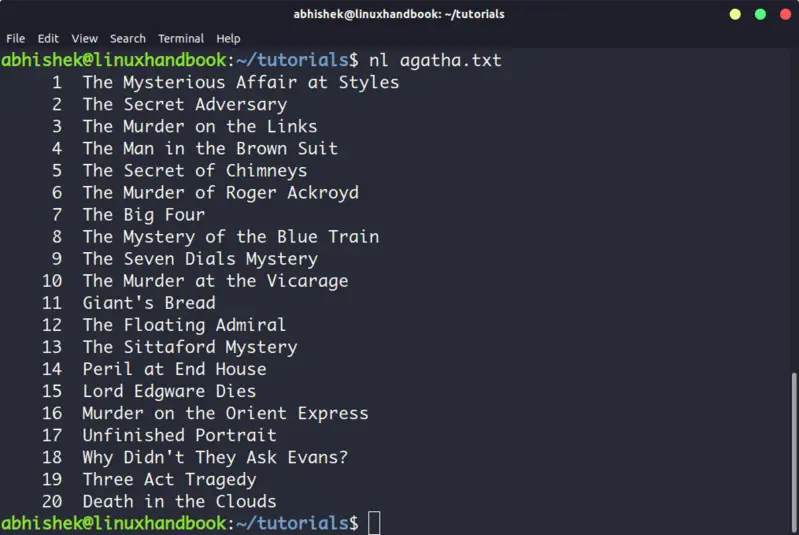
There are a few options with nl command that allows you to control the numbering. You can check its man page for more details.
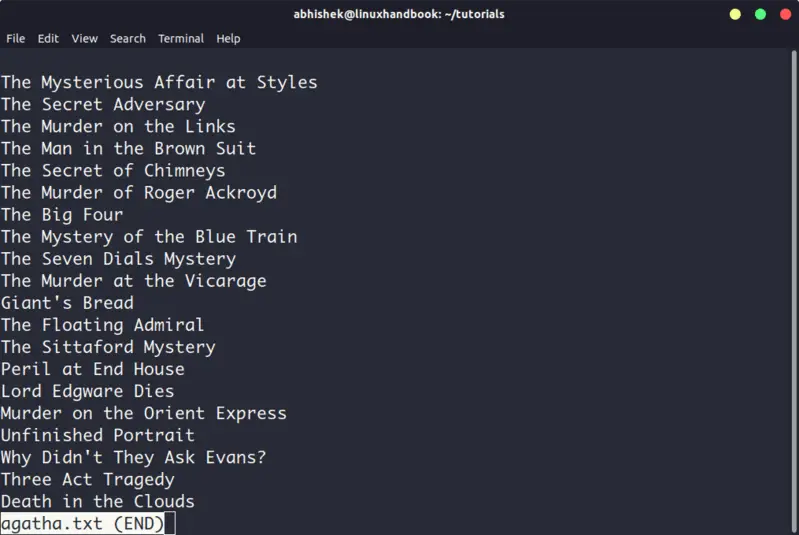
3. Less
Less command views the file one page at a time. The best thing is that you exit less (by pressing q), there are no lines displayed on the screen. Your terminal remains clean and pristine.
I strongly recommend learning a few options of the Less command so that you can use it more effectively.
There is also more command which was used in olden days but less command has more friendly features. This is why you might come across the humorous term ‘less is more’.
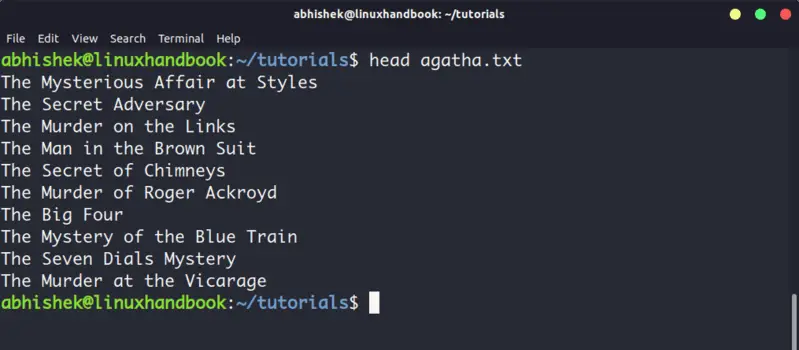
4. Head
Head command is another way of viewing text file but with a slight difference. The head command displays the first 10 lines of a text file by default.
You can change this behavior by using options with head command but the fundamental principle remains the same: head command starts operating from the head (beginning) of the file.
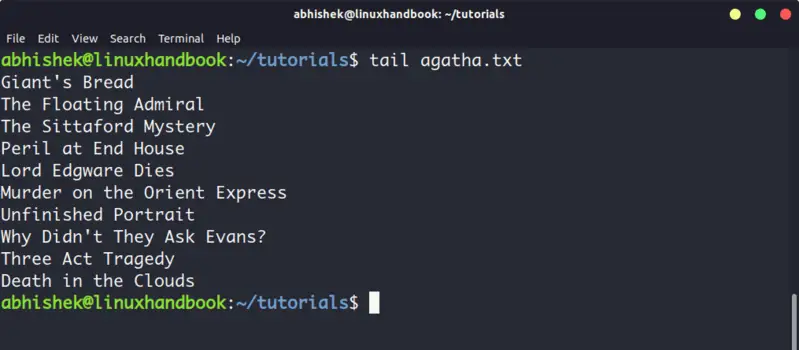
5. Tail
Tail command in Linux is similar and yet opposite to the head command. While head command displays file from the beginning, the tail command displays file from the end.
By default, tail command displays the last 10 lines of a file.
Head and Tail commands can be combined to display selected lines from a file. You can also use tail command to see the changes made to a file in real time.
Bonus: Strings command
Okay! I promised to show only the commands for viewing text file. And this one deals with both text and binary files.
Strings command displays the readable text from a binary file.
No, it doesn’t convert binary files into text files. If the binary file consists of actual readable text, strings command displays those text on your screen. You can use the file command to find the type of a file in Linux.
Conclusion
Some Linux users use Vim to view the text file but I think that’s overkill. My favorite command to open a file in Linux is the less command. It leaves the screen clear and has several options that makes viewing text file a lot easier.
Since you now know ways to view files, maybe you would be interested in knowing how to edit text files in Linux. Cut and Paste are two such commands that you can use for editing text in Linux terminal. You may also read about creating files in Linux command line.
Источник