- Команда screen Linux
- Установка утилиты screen
- Основы работы команды screen
- Возможности программы
- Основные команды screen
- Как пользоваться screen Linux
- Выводы
- Screen Command Examples: Get Control of Linux / Unix Terminal
- Screen Command Example 1: Execute a command (or shell-script), and detach the screen
- Screen Detach Method 1: Detach the screen using CTRL+A d
- Screen Detach Method 2: Detach the screen using -d option
- Screen Command Example 2: List all the running screen processes
- Screen Command Example 3: Attach the Screen when required
- Screen Command Usage Scenario 1
- Screen Command Usage Scenario 2
- If you enjoyed this article, you might also like..
Команда screen Linux
Эффективность администрирования систем GNU/Linux напрямую зависит от используемых утилит. Возможность выполнять максимум задач в минимальный срок — приоритетная цель этого процесса. Команда screen Linux является одним из основных инструментов системного администратора.
По умолчанию screen не является стандартной утилитой в большинстве дистрибутивов, но работает везде одинаково. Поэтому сначала рассмотрим её инсталляцию, а затем — возможности и основные команды.
Установка утилиты screen
Разница в инсталляции программы на разных дистрибутивах заключается в программах управления пакетами и их командами.
Чтобы установить screen в Ubuntu, Linux Mint, Deepin и других систем семейства Debian, используйте команду apt:
sudo apt install screen
В Manjaro, Antergos и других Arch-подобных ОС screen располагается в AUR, поэтому используйте соответствующую программу управления пакетами, например aurman:
aurman -S screen
Для инсталляции screen в системах на основе Red Hat (например Fedora и CentOS) используйте утилиту dnf:
dnf install screen
Основы работы команды screen
Принцип работы GNU/Linux в целом заключается в использовании небольших утилит, которые делают что-то одно, но хорошо. И эта программа — не исключение.
Команда screen Linux является консольной программой и имеет однозначное определение, соответствующее названию, — это оконный менеджер, разделяющий один физический терминал между несколькими процессами. Подходит для прямого либо удалённого администрирования.
Возможности программы
Screen позволяет переключаться между терминалами, в которых выполняются процессы, не прерывая их. Это особенно эффективно, когда необходимо производить сборку/установку ПО и мониторить дисковое пространство или использовать аппаратные ресурсы.
Screen может разделять текущий терминал на меньшее количество окон с возможностью запуска в них того же или других терминалов. Это ещё больше упрощает вышеописанную задачу, особенно при использовании больших мониторов.
Также к одной сессии screen может подключаться несколько пользователей. Это эффективно при обучении персонала.
Основные команды screen
Откройте терминал. Для запуска первого окна наберите:—
Создастся новая сессия программы и появится приветственное сообщение. Для его закрытия нужно нажать Space или Enter.
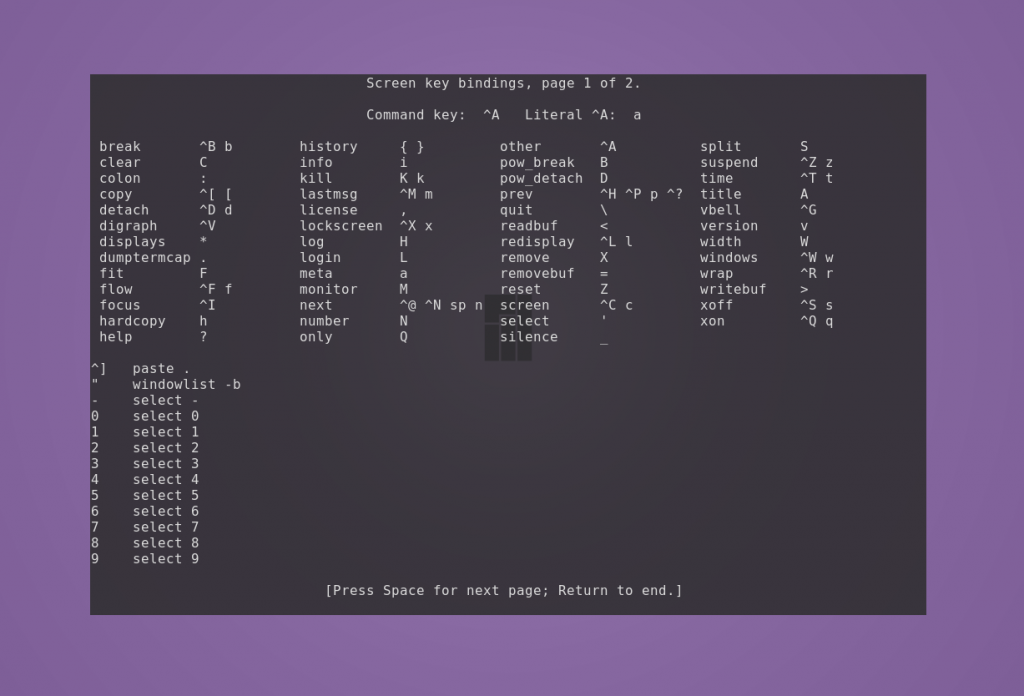
Все управляющие команды начинаются с комбинации клавиш Ctrl + a, затем следует буква или сочетание клавиш. Буквы разных регистров выполняют разные команды. Также сочетания можно заменять текстом. Для его ввода нажмите Ctrl + a и :, после чего вводите текст.
Например, чтобы создать новое окно, нажмите по очереди сочетание Ctrl + a и затем c. Для просмотра списка созданных окон нажмите Ctrl + a и w.
Для перехода в любое из созданных окон сессии используется комбинация Ctrl + a и номер, который за ним закреплён, или Ctrl + a и «, после чего нужно выбрать стрелками необходимое. Для последовательного перехода используйте Ctrl + a и n (следующее окно) или p (предыдущее окно).
Чтобы разделить экран по горизонтали, нажмите Ctrl + a и S. Например, для разделения окна по горизонтали напишите split.
Будет создано новое окно снизу от текущего, и оно не становится активным. Чтобы разделить по вертикали, нажмите Ctrl + a и | (или введите split -v).
Были созданы новые пустые окна. Для переключения между ними используйте Ctrl + a и Tab (или напишите focus). Положение курсора указывает, какое окно является активным в данный момент. Для скрытия окна используйте Ctrl + a и X (или введите remove).
Чтобы запустить в новом окне терминал, нажмите Ctr + a и c (или наберите screen).
Чтобы скрыть все окна и оставить только текущее, используйте Ctrl + a и Q (или напишите only).
Переименовать окно можно с помощью Ctrl + a и A. Внизу появится строка с возможностью заменить старое название.
Чтобы скрыть все окна сессии, нажмите Ctrl + a и \. Подтвердите решение нажатием y. Для выхода из менеджера окон нажмите Ctrl + a и d.
Команда screen обладает большим набором горячих клавиш. Полный их список можно посмотреть с помощью Ctrl + a и ?.
При создании новой сессии screen можно задать ей имя. Таким образом можно создать несколько сессий. Чтобы сделать это, используйте параметр -S, после которого укажите название.
screen -S name-of-screen
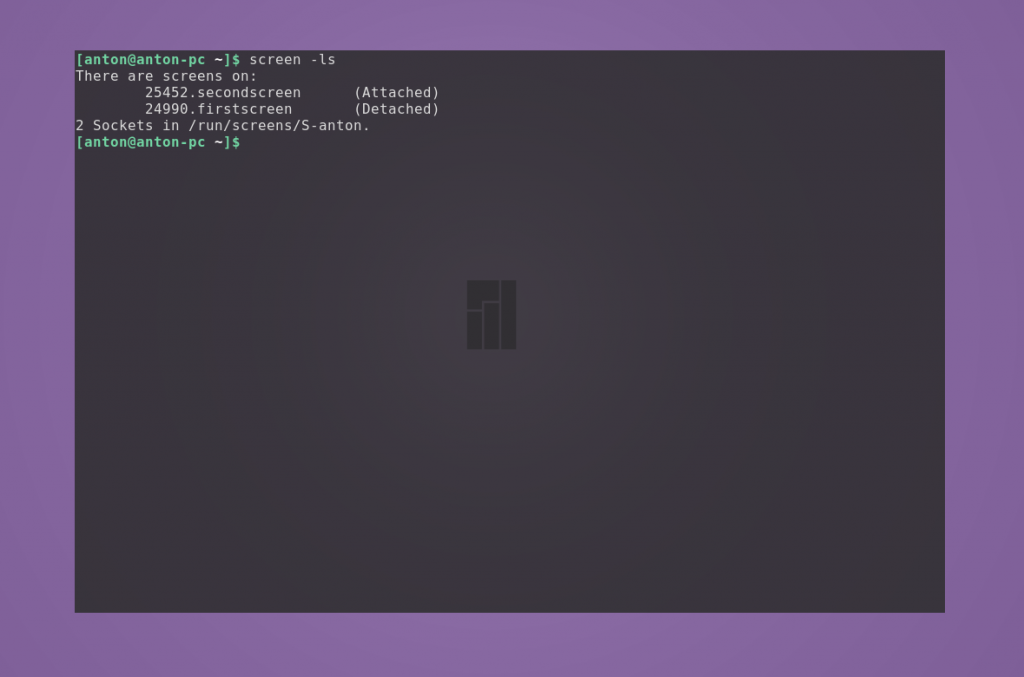
Посмотреть список запущенных сессий можно командой
Строка, идентифицирующая сессию, состоит из нескольких полей: id, название и статус.
Значение id отображается в списке всех запущенных процессов. Это означает, что его можно завершить с помощью команды kill. Завершить работу текущего окна можно с помощью комбинации Ctrl+a и k; подтвердите решение нажатием y.
Статус может иметь два состояния: Attached (задействован) и Detached (незадействован). Второе состояние у сессий, в которых ещё не происходили никакие процессы.
Чтобы перейти в нужную сессию, следует указать параметру -r её id или название.
Это всё основные команды screen Linux.
Как пользоваться screen Linux
Теперь давайте рассмотрим, как пользоваться screen Linux более подробно.
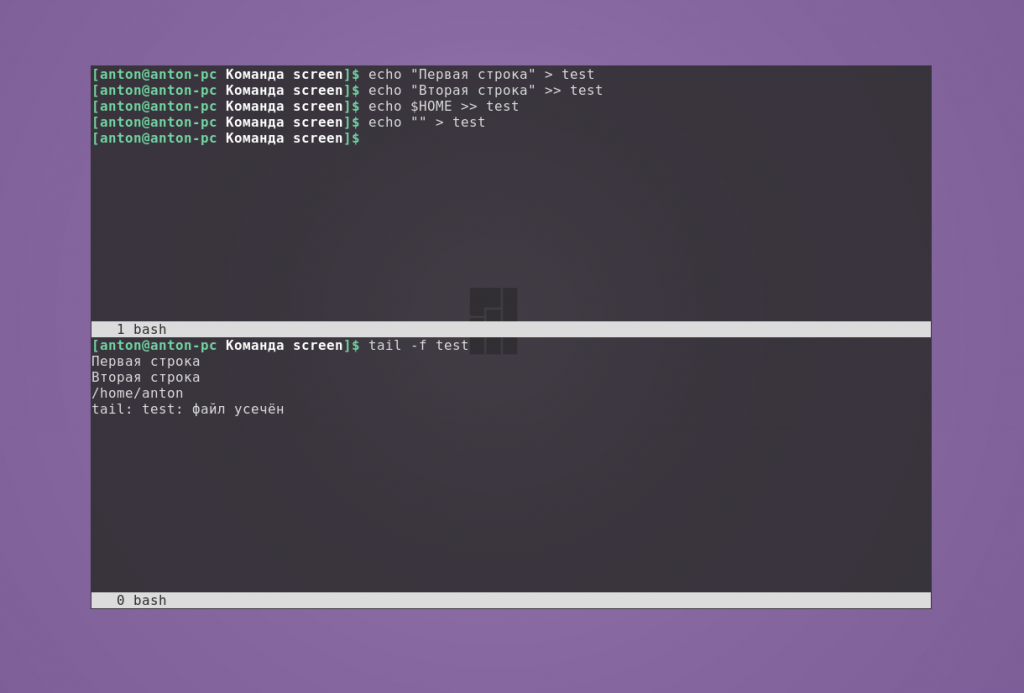
Пример 1. Необходимо отслеживать изменения файла в реальном времени. Для этого в одном окне будем вносить изменения в новый файл, а в другом — отображать файл командой tail с опцией -f:
При стирании содержимого показывается сообщение, что файл усечён, при этом этот текст в него, конечно, не записывается.
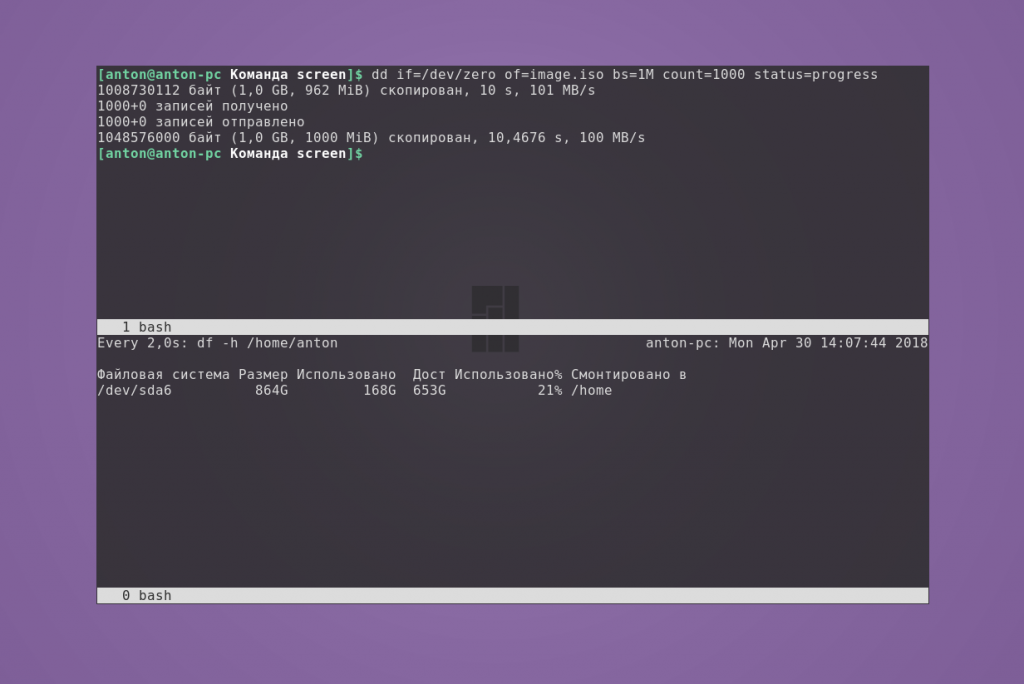
Пример 2. Необходимо отслеживать размер каталога в реальном времени. В одном окне записываем данные, в другом — отображаем, как изменяется размер домашнего каталога командой watch с задержкой в две секунды.
Выводы
Команда screen является эффективным инструментом для системного администрирования, особенно при работе с системой без среды рабочего стола. Имея один терминал, вы можете создавать несколько окон для обработки параллельных процессов без конфликтов между ними.
Источник
Screen Command Examples: Get Control of Linux / Unix Terminal

When the session is detached, the process that was originally started from the screen is still running and managed by the screen. You can then re-attach the session at a later time, and your terminals are still there, the way you left them.
In this article, let us review the how to manage the virtual terminal sessions using screen command with examples.
Screen Command Example 1: Execute a command (or shell-script), and detach the screen
Typically you’ll execute a command or shell-script as shown below from the command.
Instead, use the screen command as shown below.
Once you’ve used the screen command, you can detach it from the terminal using any one of the following method.
Screen Detach Method 1: Detach the screen using CTRL+A d
When the command is executing, press CTRL+A followed by d to detach the screen.
Screen Detach Method 2: Detach the screen using -d option
When the command is running in another terminal, type the command as following.
Screen Command Example 2: List all the running screen processes
You can list all the running screen processes using screen -ls command.
On terminal 1 you did the following:
From terminal 2 you can view the list of all screen processes. You can also detach it from terminal 2 as shown below.
Screen Command Example 3: Attach the Screen when required
You can attach the screen at anytime by specifying the screen id as shown below. You can get the screen id from the “screen -ls” command output.
Screen Command Usage Scenario 1
When you have access to only one terminal, you can use screen command to multiplex the single terminal into multiple, and execute several commands. You might also find it very useful to combine the usage of screen command along with the usage of SSH ControlMaster.
Screen Command Usage Scenario 2
When you are working in a team environment, you might walk over to your colleagues desk and get few things clarified. At that time, if needed, you can even start some process from their machine using screen command and detach it when you are done. Later when you get back to your desk, you can login and attach the screen back to your terminal.
If you enjoyed this article, you might also like..
|
|
 |  |  |  |
Why not tmux instead?
It might seem a clone at first, but definitely better after some time…
A really huge advantage with using screen (or VNC as I more commonly do), is that when doing work that must not be interrupted, such as an installation or complex update, and your connection may be erratic, you can work from a screen session on a more reliable server, such as inside a corporate data center. That way, if your PC loses its connection, your work is not lost, and you do not face the tedious process of a backout/restart – instead, you just re-connect to your still-running screen session. That approach has saved me a lot of grief over the years in supporting important business applications.
Hi,
There is another important usage of screen command, which is sharing a session between multiple users.
Here is the step to achieve that:
* The screen executable has to setuid
chmod u+s /usr/bin/screen
* Launch a screen session
screen
Type ctrl + a and : ( You will get a prompt at the bottom of the screen to type screen commands)
Type “multiuser on” ( We enabled multiuser session ).
Press ctrl + a and : again.
Type aclchg user5 -w “#” ( username is the name of the user to whom we have to share with. -w is to disable write permission to the user )
Now login as user5 and type
screen -x lakshmanan/
Now the user5 will be able to see what the user lakshmanan is doing in the screen.
So, is this isolated to a per user instance? If I log in as bob, then log into the same machine as sam, does sam get bob’s screen activity when doing screen -ls?
Also if I sudo to root, does root own the screen instance. If bob sudos to root, then sam logs in and sudos to root, could sam see the items that bob started after sudo’ing, or is it on a per sudo basis?
you can also name the screen so when you’re doing screen -ls or screen -r you can use a simple name
screen -S jimtest
screen -r jimtest
In general I recommend against starting screen like “screen ./unix-command”. When the unix-command exits, the controlling screen will also exit. This will prevent you from seeing any errors, warnings, or output messages. Instead, run “screen” by itself which will cause it to spawn a subshell prompt, then run “unix-command” in the subshell. I do this as my default behaviour so I don’t have to think about whether I need the screen to persist or not.
My logic is that since most things you want to run in screen are long-running tasks that you don’t want interrupted, it’s usually true that you want to see what messages it left on the terminal, especially if it crashed or was killed.
The downside of this approach is that you can’t start screen sessions programmatically (say, at boot). That hasn’t been a problem for me, but as a work around I suppose you could write a shell script that runs your command then blocks on input (“read X”), then run that script as the article originally describes.
Thank you for a great blog. I have a question.
How can we see exactly the command (name, arguments, etc) which is being handled by screen instead of screen ID? If so, I don’t have to attempt to attach into all ID to find expected handled command.
I want to group 10 unix commands in one shell script which while invoked can run these 10 jobs in parallel, as one job serves the input to the other.
So can I use “screen” command to open a new window each time running a job? and if yes then how should i handle the authentication as it need username and password at every login.
thanks in advance.
thanks for this great article actually it helped me a lot to understand this easy and powerful unix command
Источник