- How do you find the uptime of a Linux server?
- Command to find the uptime of a Linux server
- How to check system uptime in Linux
- Want to find out the system is up since what time?
- Check Linux system uptime with w command
- Display server uptime in Linux using top command
- Conclusion
- Linux Server Uptime Command To Find Out How Long The System Has Been Running
- Linux Server Uptime Command
- See uptime in pretty format pass the -p option to the uptime command
- Getting help about uptime command
- Use top command to display Linux system uptime
- Conclusion
- Как узнать время работы процесса в Linux
- 5 ответов
- How To Find Out How Long A Process Has Been Running In Linux
- Find out how long a process has been running in Linux
How do you find the uptime of a Linux server?
I am a new Linux system user. I need to find the uptime of a Linux server located in AWS cloud. How do I check Linux system uptime?
Linux command ship with various command line tools to find out server uptime command. File /proc/uptime has uptime information, and file /var/run/utmp has information about who is currently logged on. However, data from /proc/uptime or /var/run/utmp file is not directly readable by humans, so you need to use the following commands.
| Tutorial details | |
|---|---|
| Difficulty level | Easy |
| Root privileges | No |
| Requirements | Linux terminal |
| Est. reading time | 2 minutes |
Command to find the uptime of a Linux server
To find the uptime of a Linux server use any one of the following command. First, open the terminal window and then type:
- uptime command – Tell how long the Linux system has been running
- w command – Show who is logged on and what they are doing including the uptime of a Linux box
- top command – Display Linux server processes and display system Uptime in Linux too.
Let us see examples.
How to check system uptime in Linux
Open the terminal application on Linux and type the following uptime command:
uptime
My Linux system is running from last 13 days
Show uptime in pretty and human readable format by passing the -p as follows:
uptime -p
Sample outputs:
Want to find out the system is up since what time?
Try passing the -s as follows to see information in yyyy-mm-dd HH:MM:SS format:
uptime -s
Sample outputs:
Check Linux system uptime with w command
Run the w command to show information about the users currently on the Linux machine, and their processes. The header shows, in this order, the current time, how long the system has been running, how many users are currently logged on, and the system load averages for the past 1, 5, and 15 minutes. For example, type the following w command:
w
Display server uptime in Linux using top command
The top command provides a dynamic real-time view of a running system. It can display system summary information as well as a list of processes including system uptime. Open the terminal and run:
top
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
Conclusion
You learned how to use the uptime command that display the current time, the length of time the Linux system has been up, the number of users online, and the load average. For more information, see this page and the following pages using the man command:
man uptime
man w
Also see:
- Linux Server see the historical and statistical uptime of system with tuptime utility
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
Источник
Linux Server Uptime Command To Find Out How Long The System Has Been Running
Linux Server Uptime Command
Open a command-line terminal (select Applications > Accessories > Terminal), and then type the following command:
$ uptime
Sample outputs:
The uptime command gives a one line display of the following information.
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
- The current time (21:54:11)
- How long the system has been running (up 13 days)
- How many users are currently logged on (1 user)
- The system load averages for the past 1, 5, and 15 minutes (0.21, 0.21, 0.12)
See uptime in pretty format pass the -p option to the uptime command
$ uptime -p
Sample outputs:
This is the same information contained in the header line displayed by the w command and top command:
$ w
Sample outputs:
Getting help about uptime command
To check system uptime in Linux and Unix we use the uptime command. However, if you need more information on command option type the following man command:
$ man uptime
OR
$ uptime —help
Sample outputs:
Use top command to display Linux system uptime
Type the following command:
$ top
Sample outputs:
Fig.01: UNIX uptime top command output
Conclusion
In this quick tutorial, you learned how to use uptime, w, and top commands to see system uptime and other information from the command line.
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
| Category | List of Unix and Linux commands |
|---|---|
| Documentation | help • mandb • man • pinfo |
| Disk space analyzers | df • duf • ncdu • pydf |
| File Management | cat • cp • less • mkdir • more • tree |
| Firewall | Alpine Awall • CentOS 8 • OpenSUSE • RHEL 8 • Ubuntu 16.04 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Linux Desktop Apps | Skype • Spotify • VLC 3 |
| Modern utilities | bat • exa |
| Network Utilities | NetHogs • dig • host • ip • nmap |
| OpenVPN | CentOS 7 • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Debian 8/9 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Package Manager | apk • apt |
| Processes Management | bg • chroot • cron • disown • fg • glances • gtop • jobs • killall • kill • pidof • pstree • pwdx • time • vtop |
| Searching | ag • grep • whereis • which |
| Shell builtins | compgen • echo • printf |
| Text processing | cut • rev |
| User Information | groups • id • lastcomm • last • lid/libuser-lid • logname • members • users • whoami • who • w |
| WireGuard VPN | Alpine • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Firewall • Ubuntu 20.04 |
Comments on this entry are closed.
my favorite 🙂 updates every second….
Nice looking site; useful and clear information. Good job!
The only problem with the uptime command is that it isn’t always obvious what units of measure to the time it has been up. Just a bit confusing for those new to it, especially those from the Windoze world trying to come over to Linux. Just fleshing out the units (up 5 hours:54 minutes (days:hours:minutes)) on this would certainly help in bringing more over, especially if we can get into the man&info pages.
$ uptime
07:55:56 up 3 days, 17:37, 6 users, load average: 0.04, 0.06, 0.01
$
by default it will give how many days the OS is up, and how many hours:mins.
if it less than 1 day, it will give only hours:mins.
what is the command for checking how many bites are already downloaded in your server
How do I get only time information excluding other load information
How do I get only time information excluding other load information
# 1. run Command
# 2. strip unneeded leading data
# 3. check if the uptime is greater than 24 hours
# 4. make the output human readable
# 5. trim any leading space
For people who want to get uptime within a C program I would suggest having a look at sysinfo() too…
nice and so useful
thank you
How can i know uptime of a server machine without logging in it ?? Is there any way?
Hello Buddies , plz specify whats the value ‘4:29’ in the above output.
@Kunal It’s 4 hours and 29mins. So from the output the server uptime is 13 days, 4 hours and 31 mins.
thanks for this!
Did you see the output within one hour of startup? Is it, e.g. 0:15, :15 or 15 for the 15 minutes after startup?
On most systems you can do cat /proc/uptime if you’re only interested in the uptime. The first number is how many seconds the system has been up for, and the second number is how many seconds it’s spent idle.
Tuptime is a uptime with steroids, nice tool for getting uptime, downtime and other interesting stuff:
https://github.com/rfrail3/tuptime
How can i see the only up time without any other information is there Any command to know only the Uptime i mean to say the if i issue a command it should print 21:54:11 up 13 days, 4:29
Источник
Как узнать время работы процесса в Linux
Как узнать аптайм данного процесса в Linux.
дает мне много информации, которая включает в себя время, когда процесс был запущен.
Я специально ищу switch, который возвращает время работы процесса в миллисекундах.
5 ответов
как «uptime» имеет несколько значений, вот полезная команда.
эта команда выводит список всех процессов с несколькими различными столбцами, связанными со временем. Он имеет следующие столбцы:
PID = идентификатор процесса
первый COMMAND = только имя команды без параметров и без аргументов
STARTED = абсолютное время начала процесса
ELAPSED = время, прошедшее с момента запуска процесса (времени), формат [[dd-]hh:]mm: ss TIME = накопительное время процессора,» [dd-]hh:mm:ss » формат
second COMMAND = снова команда, на этот раз со всеми предоставленными параметрами и аргументами
если у вас есть ограниченная версия ps таких как находится в busybox , вы можете получить время запуска процесса, глядя на метку /proc/
. Например, если pid, который вы хотите посмотреть, 55.
. а затем сравнить его с текущей датой.
Я думаю, что вы можете просто запустить:
пример с двумя процессами, запущенными в один и тот же час минуты секунды, но не те же миллисекунды:
такая простая вещь не правильно ответил после 5 лет?
Я не думаю, что вы можете точно сделать миллисекунд. напр. если вы видите Man procfs и видите /proc / $$ / stat, который имеет поле 22 как startime, которое находится в «Clock ticks», у вас будет что-то более точное, но тики часов не собираются с совершенно постоянной скоростью (относительно «настенного времени») и будут выключены. сон и некоторые вещи (ntpd, я думаю) компенсируют это. Например, на машине, работающей под управлением ntpd, с 8 днями uptime и никогда не спал, dmesg-T имеет ту же проблему (я думаю. ), и вы можете увидеть его здесь:
Да, слишком старые и слишком сложные вещи. Я попытался с выше предложенным методом «stat», но что, если бы у меня было»прикосновение» -ed PID proc dir вчера? Это означает, что мой летний процесс показан со вчерашней отметкой времени. Нет, не то, что мне нужно: (
в более новых, это просто:
как просто. Время присутствует в секундах. Делайте все, что вам нужно. С некоторыми старыми коробками ситуация сложнее, так как нет времени. Можно рассчитывать on:
которые выглядят «немного» странно, так как он находится в формате dd-hh:mm:ss. Не подходит для дальнейшего расчета. Я бы предпочел его в секундах, поэтому я использовал этот:
Источник
How To Find Out How Long A Process Has Been Running In Linux
Have you ever been in a situation where you wanted to know how long a process has been running on your Linux box? No? No problem! This brief guide helps you to find out the uptime of an active process in Linux.
You don’t need any monitoring applications. In Linux and other Unix-like operating systems, there is a command called ps , which is used to display the information about the active processes. Using ps command, we can easily find out how long a process is running in Linux.
Find out how long a process has been running in Linux
The ps command has different format specifiers (keywords) that can be used to control the output format. We are going to use the following two keywords to find the uptime of an active process.
- etime — elapsed time since the process was started, in the form of [[DD-]hh:]mm:ss .
- etimes — elapsed time since the process was started, in seconds.
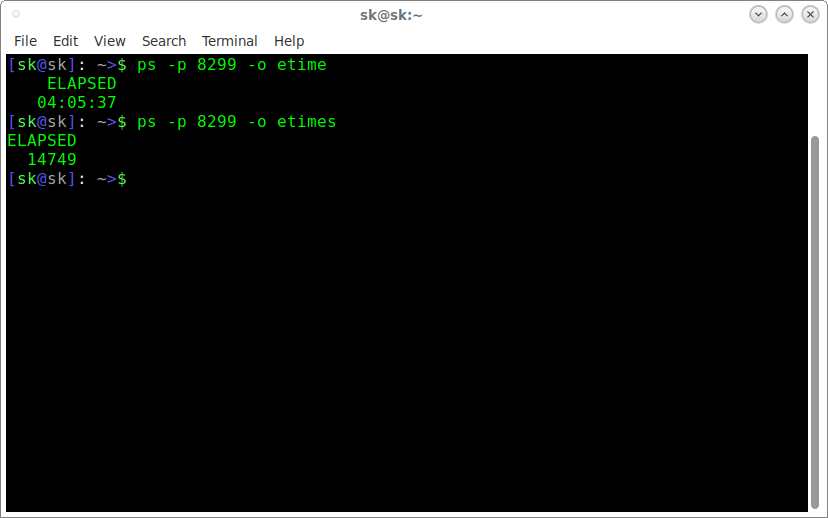
First, you need to find out the PID of a process. The following command displays the PID of dhcpcd process.
As you see in the above output, 8299 is the PID of dhcpcd process.
Now, we can find how long this process has been running using command:
You can also view the elapsed time in seconds using etimes keyword.
Find out how long a process has been running in Linux using ps command
Not only a single process, we can also display the uptime of all processes like below.
The first command displays the uptime of all Linux processes, in [[DD-]hh:]mm:ss format, and the latter displays the uptime in seconds.
Here is the sample output of second command.
Find uptime of all processes using ps command in Linux
As you see in the above output, we have the uptime of all processes with six columns format.
- PID — The Process ID.
- COMMAND (second column) — The command name without options and/or arguments.
- STARTED — The absolute starting time of the process.
- ELAPSED — The elapsed time since the process was started, in the form of [[dd-]hh:]mm:ss.
- TIME — Cumulative CPU time, «[dd-]hh:mm:ss» format.
- COMMAND (last column) — Command name with all its provided options and arguments.
For more details about ps command, check the man pages.
Источник