- Посоветуйте Serial port terminal
- minicom, GtkTerm.
- Working with the serial console
- Contents
- Configure console access on the target machine
- Boot loader
- GRUB Legacy
- rEFInd
- Syslinux
- Kernel
- getty
- Making Connections
- Connect using a terminal emulator program
- Command line
- And, for Windows
- Graphical front-ends
- Installing Arch Linux using the serial console
- Debugging an unresponsive machine using a serial console
- Troubleshooting
- Ctrl+c and Minicom
- Resizing a terminal
- Missing ports on multi-port expansion cards
- Serial Terminal Emulator
- Contents
- Introduction
- Prerequisites
- CLI options
- Picocom
- Screen
- Minicom
- GUI options
- GTKterm
- Putty
- TeraTerm
- Заметки о Linux, электронике, радиолюбительстве
- воскресенье, 27 июля 2014 г.
- Работа с последовательным портом из консоли Linux
Посоветуйте Serial port terminal
Сабж, в данный момент пользую это, но хотелось бы что-то более удобное.
minicom ищете? И что подразумевается под «более удобное»?
телепаты в отпуске, так что требования предъявляйте самостоятельно
Нет, не оно. Под более удобное, что бы меньше зависимостей, без GUI.
по ссылке не ходи @ сразу посылай
миником и так без гуи, из зависимостей
screen /dev/ttyUSB0 9600
если надо еще меньше зависимостей, то это только из /dev/tty0 читать-писать
minicom, GtkTerm.
GtkTerm не развивается, имеет ряд неисправленных ошибок. Так что рекомендую осилить minicom.
Есть очень минималистичный picocom.
> миником и так без гуи
Уродский «псевдооконный» интерфейс в консоли ничем не лучше гуя. И вообще миником корявый и не unix-style.
Можно без ncurses, например kermit. Много лет пользуюсь именно им и доволен как слон.
Еще можно клепать перлоскрипты под конкретную задачу на Device::SerialPort + Term::Readline. В них легко делать дополнение по табу, цветной вывод и кучу других полезных фич. История и редактирование в стиле vim/emacs прилагается.
Источник
Working with the serial console
An Arch Linux machine can be configured for connections via the serial console port, which enables administration of a machine even if it has no keyboard, mouse, monitor, or network attached to it.
Installation of Arch Linux is possible via the serial console as well.
A basic environment for this scenario is two machines connected using a serial cable (9-pin connector cable). The administering machine can be any Unix/Linux or Windows machine with a terminal emulator program (PuTTY or Minicom, for example).
The configuration instructions below will enable boot loader menu selection, boot messages, and terminal forwarding to the serial console.
Contents
Configure console access on the target machine
Boot loader
When using GRUB with a generated grub.cfg , edit /etc/default/grub and enable serial input and output support:
Next add the GRUB_SERIAL_COMMAND variable and set the options for the serial connection. For COM1 ( /dev/ttyS0 ) with baud rate of 115200 bit/s:
Read GRUB’s manual on Using GRUB via a serial line and the serial command for detailed explanation of the available options.
GRUB Legacy
Edit the GRUB Legacy configuration file /boot/grub/menu.lst and add these lines to the general area of the configuration:
rEFInd
rEFInd supports serial console only in text mode. Edit refind.conf and uncomment textonly .
Syslinux
To enable serial console in Syslinux, edit syslinux.cfg and add SERIAL as the first directive in the configuration file.
For COM1 ( /dev/ttyS0 ) with baud rate of 115200 bit/s:
The serial parameters are hardcoded to 8 bits, no parity and 1 stop bit.[1]. Read Syslinux Wiki:Config#SERIAL for the directive’s options.
Kernel
Kernel’s output can be sent to serial console by setting the console= kernel parameter. The last specified console= will be set as /dev/console .
getty
At boot, systemd-getty-generator(8) will start a getty instance for each console specified in the kernel command line.
If you have not configured console= in kernel command line start serial-getty@device.service . For /dev/ttyS0 (COM1) that would be serial-getty@ttyS0.service . Enable the service to start it at boot.
Unless specified otherwise in the kernel command line, getty will be expecting 38400 bit/s baud rate, 8 data bits, no parity and one stop bit-times.
Making Connections
Connect using a terminal emulator program
Perform these steps on the machine used to connect the remote console.
Command line
dterm
dterm AUR is a tiny serial communication program. If you invoke it without parameters, it will connect to /dev/ttyS0 at 9600 baud by default. The following example connect to /dev/ttyS0 at 115200 baud, with 8 data bits, no parity bit and 1 stop bit-times:
See its homepage[2] for more examples.
Minicom
minicom can be obtained from the official repositories. Start Minicom in setup mode:
Using the textual navigation menu, change the serial port settings to the following:
Press Enter to exit the menus (pressing Esc will not save changes). Remove the modem Init and Reset strings, as we are not connecting to a modem. To do this, under the Modem and Dialing menu, delete the Init and Reset strings. Optionally save the configuration by choosing save setup as dfl from the main menu. Restart minicom with the serial cable connected to the target machine. To end the session, press Ctrl+A followed by Ctrl+X .
picocom
picocom is a tiny dumb-terminal emulation program that is very like minicom, but instead of mini, it is pico. The following example connect to ttyS0 at 9600 bps:
See its manual for detailed usage.
Screen
GNU Screen is able to connect to a serial port. It will connect at 9600 baud by default:
A different baud rate (e.g. 115200) may be specified on the command line.
To end the session, press Ctrl+a followed by K . Alternatively, press Ctrl+a , type :quit and confirm it by pressing Enter .
Serialclient
Serialclient[3] is a CLI client for serial connection written in ruby. Install ruby package, then install it with the following:
Then, you can use like this:
And, for Windows
On Windows machines, connect to the serial port using programs like PuTTY[4] or Terminalbpp[5].
Graphical front-ends
cutecom AUR is another gui enabled serial monitor.
putty is also available for Linux.
moserial is a gtk-based serial terminal, primarily intended for technical users and hardware hackers who need to communicate with embedded systems, test equipment, and serial consoles.
Installing Arch Linux using the serial console
- Connect to the target machine using the method described above.
- Boot the target machine using the Arch Linux installation CD.
- When the bootloader appears, select Boot Arch Linux () and press Tab to edit
- Append console=ttyS0,115200 and press Enter .
- Now systemd should detect ttyS0 and spawn a serial getty on it. Login as root and start the installation as usual.
Debugging an unresponsive machine using a serial console
Even though [7] has only raw and terse instructions, it presents the full scene. It is important to note that here, the machine under test got unresponsive in a reproducible manner. And that it happened during normal operation. So it could be accessed normally before it needed debugging. However, in general, the serial console is also useful for debugging boot issues. Perhaps by configuring the boot loader by hand at machine startup time. Also note the mentioned netconsole within the P.S paragraph of the external link from this section.
Troubleshooting
Ctrl+c and Minicom
If you are having trouble sending a Ctrl+c command through minicom you need to switch off hardware flow control in the device settings ( minicom -s ), which then enables the break.
Resizing a terminal
Unlike ssh, serial connections do not have a mechanism to transfer something like SIGWINCH when a terminal is resized. This can cause weird problems with some full-screen programs (e.g. less ) when you resize your terminal emulator’s window.
Resizing the terminal via stty is a workaround:
However, this requires you to manually input the proper geometry. The following methods should be simpler.
1. There is a lesser-known utility called resize , shipped with xterm , that can solve this problem. Invoke it without parameters after you resize the terminal emulator’s window:
2. If you do not want to install xterm, it is possible to do the same work via a shell function. Put the following function into your zshrc and invoke it without parameters after resizing the terminal emulator’s window:
Missing ports on multi-port expansion cards

The number of serial ports using the generic 8250 driver on the default kernel configuration is set to 4 at runtime with a maximum of 32. This will prevent the creation of /dev/ttyS4 and above. Counting the typical built in serial port on the motherboard this prevents the use of the 4th serial port on a 4 port expansion card.
Источник
Serial Terminal Emulator
Contents
Introduction
There are several Terminal Emulators available to connect to the board from the debug UART. This article lists two different types:
Prerequisites
CLI options
This section lists command-line applications to communicate with the serial port.
Picocom
Picocom is a simple and effective solution for those who like command-line:
Screen
Screen is a good alternative for the picocom:
Note: By default, if no option is specified, screen uses the standard 9600 baud rate.
Minicom
Minicom is also a good choice to access the serial port on Linux. You can visualize the setup above by running the following command:
Note: In case you run Minicom without any additional arguments, it will use the default settings saved on /etc/minicom/minirc.dfl .
GUI options
This section lists Graphical User Interface applications to communicate with the serial port.
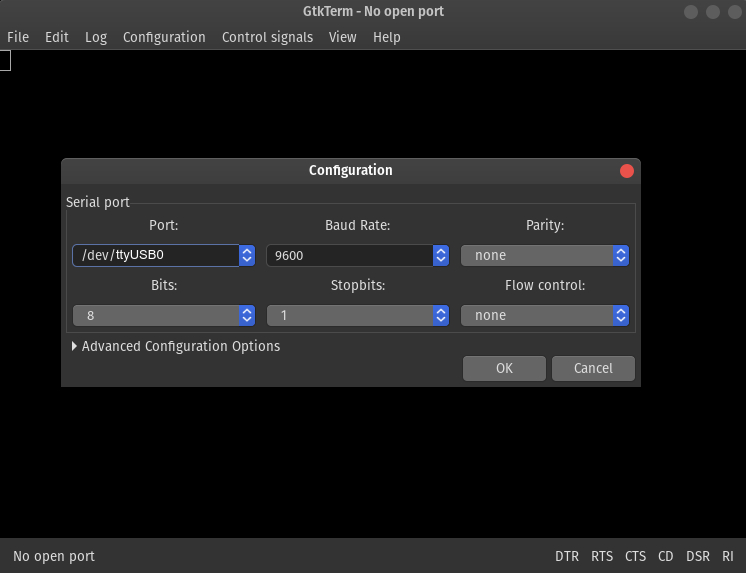
GTKterm
GTKterm is a simple GTK+ terminal that can be used on Linux to communicate with the serial port:
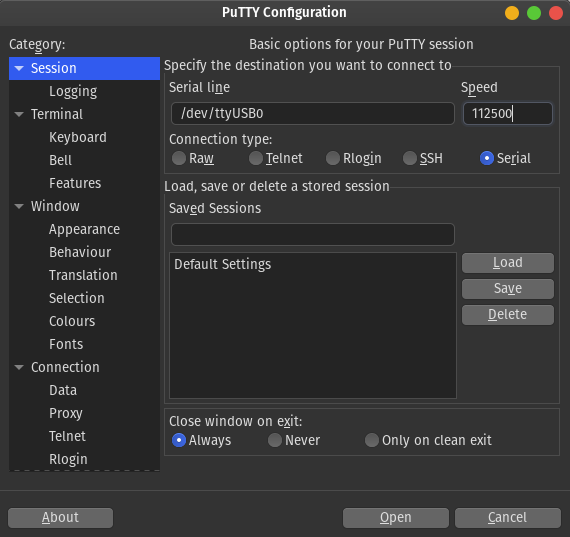
Putty
Putty is an SSH client that can also be used to communicate with the serial port on Windows and Linux:
TeraTerm
TeraTerm is a terminal emulator that can be used on Windows with the purpose to connect via SSH and also to access serial ports:
Источник
Заметки о Linux, электронике, радиолюбительстве
Личный блог Вадима Кузнецова, RA3XDH
воскресенье, 27 июля 2014 г.
Работа с последовательным портом из консоли Linux
В предыдущем посте было показано как запустить UART на отладочной плате Launchpad для MSP430. Теперь рассмотрим как общаться с платой при помощи средств командной строки Linux. Используется плата с прошивкой из предыдущего поста. Для подробностей — см. под кат
Как известно, все устройства последовательных портов представлены файлами устройств в каталоге /dev.Через эти файлы и происходит общение ОС Linux с внешним устройством на последовательном порту. Чтобы передать что-то на внешнее устройство нужно записать данные в файл устройства, а чтобы считать информацию из устройства — прочитать данные из файла устройства. Это можно делать при помощи команд cat и echo так же как для обычных файлов на диске. Или внутри программы на С при помощи вызовов ioctl(), read() и write() или библиотеки termios.
Физическим последовательным портам RS232, к которым подключались диалапные модемы на старых компьютерах, соответствуют файлы устройств /dev/ttyS*, начиная с /dev/ttyS0. Виртуальным последовательным портам, которые создаются различными конвертерами USB UART соответствуют файлы устройств /dev/ttyUSB* и /dev/ttyACM*. Ядро Linux автоматически разпознаёт подключенное устройство, загружает для него драйвер и создаёт файл устройства. Вручную устанавливать драйвер, как в ОС Windows не требуется. Например, если подключить к USB преобразователь USB UART FT232, то создаётся файл устройства /dev/ttyUSB0, с которым можно работать также как и с обычным последовательным портом. На плате Launcpad находится микросхема TUSB3410, которая тоже представляет собой конвертер USB UART. Если подключить её к USB, то создаётся файл устройства /dev/ttyACM0. Чтобы общаться с платой нужно что-либо писать/читать с этого файла.
Чтобы пользователь мог читать или писать в файл устройства последовательного порта, его нужно добавить в группу dialout. Иначе работать с последовательным портом сможет только администратор root.
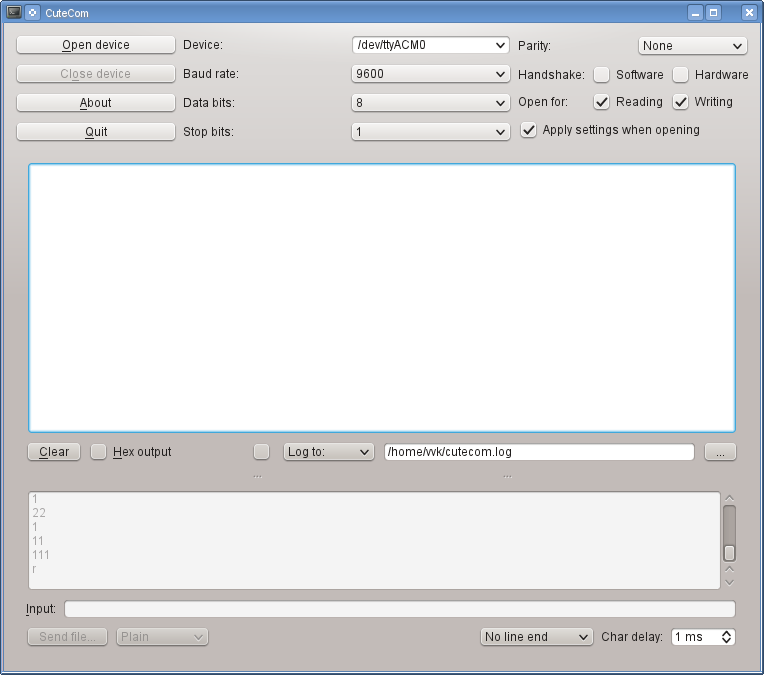
Простейшим приложением с графическим интерфейсом, которое работает с последовательным портом, является CuteCOM. Он обычно уже есть в вашем дистрибутиве Linux. Его можно установить из репозиториев. При помощи CuteCOM мы работали с платой в предыдущем посте. Выглядит CuteCOM вот так:
Работать с ним крайне просто. Указываем нужное устройство, если его нет в списке, то его можно впечатать вручную. Затем указываем скорость и параметры и нажимаем OpenDevice. В окне видим данные, которые пришли от устройства. В поле ввода в нижней части можем печать строку символов, которые предаются на устройство. Чтобы передать данный нажимаем Enter и смотрим ответ устройства в окне.
Теперь рассмотрим как работать с COM-портом из командной строки. Для этого служат три команды: stty, cat и echo.
Команда stty устанавливает параметры и скорость COM-порта. Её формат:
stty -F
Чтобы установить параметры для платы Launchpad для соединения на скорости 9600 нужно выполнить:
$ stty 9600 -F /dev/ttyACM0 raw -echo
Параметр raw устанавливает, что данные в компьютер передаются байт за байтом так же как приходят в порт без преобразований. Аппаратное управление потоком отключено. Подробнее о том, что включает и выключает raw — см. man stty. Если не включить raw, то скорее всего ничего работать не будет.
Теперь в той же консоли нужно набрать
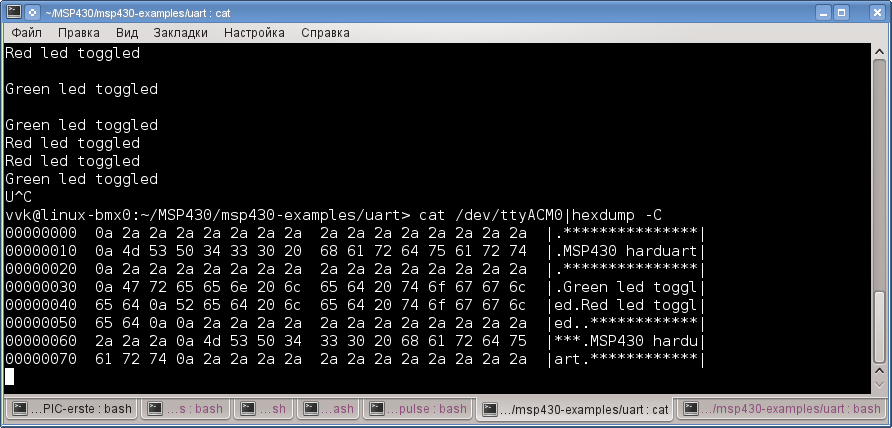
$ cat /dev/ttyACM0
И можно смотреть данные, которые приходят от платы. Выход — нажать Ctrl+C.
Теперь нажимаем на плате RESET и видим, что в консоди напечатался текст.
Чтобы передать в плату данные, в другой консоли нужно использовать команду echo и перенаправление вывода в файл устройства. Наберём в другой консоли:
$ echo "1">/dev/ttyACM0
Видим, что на плате загорелся красный светодиод и в первой консоли было выдано сообщение об этом. Чтобы убрать конец строки в передаваемых данных, то нужно использовать запуск echo -n, а чтобы интерпретировать 16-ричные коды — нужно echo -e. Ключи можно комбинировать.
В итоге должно получиться так:
Чтобы увидеть 16-ричные коды данных, приходящих от устройства, нужно использовать команду hexdump:
$ cat /dev/ttyACM0|hexdump -C
Получится вот так:
Чтобы иметь вывод данных от устройство на экран и в текстовый файл нужно использовать tee:
Источник