- Как просмотреть статус службы в Linux с помощью systemctl
- Просмотр статуса сервиса:
- Как просмотреть статус службы под названием nginx
- Понимание состояний службы / модулей systemd
- В настоящее время systemd поддерживает следующие модули
- Чтобы показать все установленные файлы модулей, используйте:
- Linux просмотр статуса службы
- Как вывести список модулей, которые systemd в настоящее время имеет в памяти
- Список systemd/systemctl всех отказавших модулей units/services в Linux
- Что делать, если такой сервис, как nginx, не запущен?
- Как просмотреть источник файла службы / модуля systemd
- Вывод
- How to view status of a service on Linux using systemctl
- Viewing the Status of a Service
- How to view status of a service called nginx
- Understanding systemd service/unit states
- Currently following units are supported by systemd
- To show all installed unit files use:
- Linux view status of a service
- How to list units that systemd currently has in memory
- List systemd/systemctl all failed units/services on Linux
Как просмотреть статус службы в Linux с помощью systemctl
Мы используем systemctl status команду под systemd для просмотра статуса данной службы в операционных системах Linux..
Просмотр статуса сервиса:
Синтаксис команды systemctl следующий
systemctl status
systemctl status
Как просмотреть статус службы под названием nginx
Тип:
$ systemctl status nginx.service
ssh server status
$ systemctl status sshd.service
Lighttpd web server status
$ systemctl status lighttpd.service
Точка (« ● ») использует цвет на поддерживаемых терминалах, чтобы быстро обозначить состояние устройства. Белый цвет указывает на «неактивное» или «деактивированное» состояние. Красный цве т указывает на состояние «сбой» или «ошибка». Зеленый цвет указывает на состояние «активное», «перезагрузка» или «активация».
Понимание состояний службы / модулей systemd
Статус службы Linux зависит от различных состояний, таких как:
| Service status | Описание |
|---|---|
| active (running) | Служба или демон работает в фоновом режиме. Например, веб-сервер sshd или nginx / apache и список для входящего трафика. |
| active (exited) | Служба успешно запущена из файла конфигурации. Обычно однократная конфигурация сервисов считывается до выхода из сервиса. Например, сервис AppArmor или Firewall. |
| active (waiting) | Наша служба работает, но ожидает события, такого как событие CPUS / печати. |
| inactive | Сервис не работает. |
| enabled | Служба включается во время загрузки. |
| disabled | Служба отключена и не будет запущена при загрузке сервера Linux. |
| static | Служба не может быть включена в Linux, но обычно запускается другим модулем systemd автоматически. Другими словами, файл модуля не включен и не имеет условий для разрешения в разделе [Установить] файл модуля. |
| masked | Служба полностью отключена, и любая операция запуска на ней всегда заканчивается неудачей. |
| alias | Имя службы — это псевдоним. Это означает, что служба является символической ссылкой на другой файл модуля. |
| linked | Доступен через одну или несколько символических ссылок на файл модуля (постоянно в /etc/systemd/system/ или временно в /run/systemd/system/), даже если файл модуля может находиться за пределами пути поиска файла модуля |
В настоящее время systemd поддерживает следующие модули
- service : Конфигурация служебного модуля о процессе, который контролируется и контролируется systemd.
- mount : Точка монтирования файловой системы контролируется и контролируется systemd.
- swap : Конфигурация файла подкачки / диска контролируется systemd.
- socket : IPC, сетевой сокет или FIFO файловой системы, управляемый и контролируемый systemd, для активации на основе сокетов.
- target : Он содержит информацию о целевом модуле systemd. Он используется для группирования блоков и как известные точки синхронизации при запуске. Например, graphical.target используется для входа на рабочий стол на основе графического интерфейса пользователя. Точно так же multi-user.target используется серверами, на которых пользователи могут входить в систему с помощью ssh / console.
- device : Устройство, представленное в дереве устройств sysfs / udev. Он включает в себя сетевые и другие устройства.
- automount : Автоматическое монтирование файловых систем
- timer : Cron как модуль systemd для запуска команд и служб в заданном формате даты / времени. Например, обновить прошивку или очистить сеанс, созданный веб-приложениями Python или PHP
- path : Специальный целевой модуль systemd, который устанавливает все модули пути. Например, systemd может выполнять определенные действия в зависимости от пути к файловой системе. Если / etc / foo / modifed предприняли какие-то действия..
- slice : Мы используем срез systemd для изоляции рабочих нагрузок. Они определяют иерархию, в которой размещаются области и услуги. Фактические процессы содержатся в объемах или услугах. Считайте это легким докером. Для каждого слайса могут быть установлены определенные ограничения ресурсов, такие как ограничение ЦП или дискового ввода-вывода, которые применяются ко всем процессам.
- scope : Единицы области видимости не конфигурируются через файлы конфигурации юнитов, а создаются только программно с использованием шинных интерфейсов systemd. Они названы аналогично именам файлов. Единица, имя которой заканчивается на «.scope», относится к единице области видимости. Подразделения областей видимости управляют набором системных процессов. В отличие от единиц обслуживания, единицы области видимости управляют процессами, созданными извне, и не разделяют процессы сами по себе. Основное назначение единиц области видимости — это группировка рабочих процессов системного сервиса для организации и управления ресурсами.
Мы можем перечислить все сервисные единицы следующим образом:
$ sudo systemctl —type=service
Хотите увидеть единицы типа монтирования? Попробуйте:
$ sudo systemctl —type=mount
Отобразить все блоки таймера systemd в вашем Linux:
$ sudo systemctl -t timer
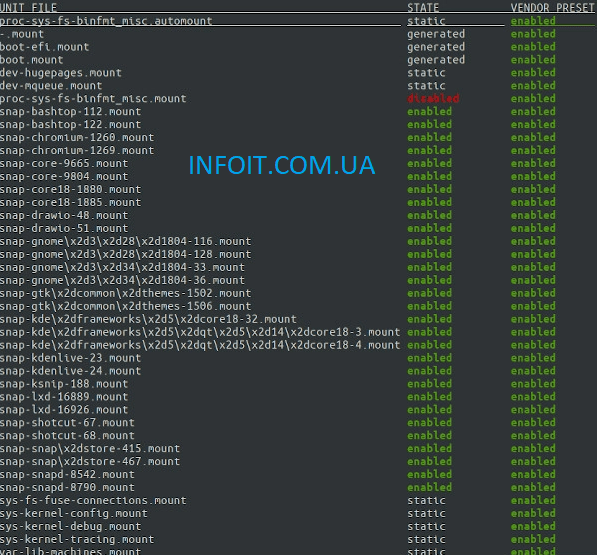
Чтобы показать все установленные файлы модулей, используйте:
$ sudo systemctl list-unit-files
Linux просмотр статуса службы
Введите следующую команду, чтобы просмотреть все службы и состояние модулей в вашей системе Linux с момента загрузки:
$ sudo systemctl
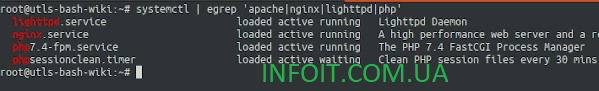
Используйте команду grep command/egrep command чтобы отфильтровать требуемые единицы / службы
$ sudo systemctl | grep ssh
$ sudo systemctl | egrep ‘apache|nginx|lighttpd|php’
Как вывести список модулей, которые systemd в настоящее время имеет в памяти
Выполните следующую команду:
$ sudo systemctl list-units
$ sudo systemctl list-units | more
$ sudo systemctl list-units | grep sshd
$ sudo systemctl list-units —type service
$ sudo systemctl list-units —type timer
Список systemd/systemctl всех отказавших модулей units/services в Linux
$ sudo systemctl list-units —failed
$ sudo systemctl list-units —state failed
$ sudo systemctl list-units —state failed —type service
$ sudo systemctl list-units —state failed —type timer
Что делать, если такой сервис, как nginx, не запущен?
Включите службу systemd:
$ sudo systemctl enable nginx.service
Запустите службу nginx:
$ sudo systemctl start nginx.service
Мы можем остановить или перезапустить службу следующим образом:
$ sudo systemctl stop nginx.service
$ sudo systemctl restart nginx.service
Проверить, включена ли служба или нет, запустить:
$ sudo is-enabled nginx.service
Снова просмотреть статус:
$ sudo status nginx.service
Чтобы увидеть полные выходные данные для проблемы службы -full или -l :
$ sudo status nginx.service -l
$ sudo status openvpn.service —full
Мы может отлаживать и просматривать все сообщения журнала, относящиеся к службе, с помощью команды journalctl:
$ sudo journalctl UNIT=nginx.service
Как просмотреть источник файла службы / модуля systemd
Передайте параметр cat следующим образом:
$ sudo systemctl cat
$ sudo systemctl cat nginx.service
/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service
# Stop dance for nginx
# =======================
#
# ExecStop sends SIGSTOP (graceful stop) to the nginx process.
# If, after 5s (—retry QUIT/5) nginx is still running, systemd takes control
# and sends SIGTERM (fast shutdown) to the main process.
# After another 5s (TimeoutStopSec=5), and if nginx is alive, systemd sends
# SIGKILL to all the remaining processes in the process group (KillMode=mixed).
#
# nginx signals reference doc:
# http://nginx.org/en/docs/control.html
#
[Unit]
Description=A high performance web server and a reverse proxy server
Documentation=man:nginx(8)
After=network.target [Service]
Type=forking
PIDFile=/run/nginx.pid
ExecStartPre=/usr/sbin/nginx -t -q -g ‘daemon on; master_process on;’
ExecStart=/usr/sbin/nginx -g ‘daemon on; master_process on;’
ExecReload=/usr/sbin/nginx -g ‘daemon on; master_process on;’ -s reload
ExecStop=-/sbin/start-stop-daemon —quiet —stop —retry QUIT/5 —pidfile /run/nginx.pid
TimeoutStopSec=5
KillMode=mixed [Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Вывод
Вы узнали о перечислении модулей systemd, включая службы Linux, с помощью команды systemctl. См. Документацию по systemctl или введите следующую команду man:
Источник
How to view status of a service on Linux using systemctl
H ow do I use the systemctl command to view status of a systemd service on Linux operating systems?
We use systemctl status command under systemd to view the status of the given service on Linux operating systems.
| Tutorial details | |
|---|---|
| Difficulty level | Easy |
| Root privileges | Yes |
| Requirements | Linux & systemd |
| Est. reading time | 8 minutes |
Viewing the Status of a Service
The syntax is as follows for the systemctl command systemctl status
systemctl status
How to view status of a service called nginx
Type:
$ systemctl status nginx.service
## ssh server status ##
$ systemctl status sshd.service
## Lighttpd web server status ##
$ systemctl status lighttpd.service
The dot (“ ● “) uses color on supported terminals to summarize the unit state at a glance. White color indicates an “inactive” or “deactivating” state. Red color indicates a “failed” or “error” state. Green indicates an “active”, “reloading” or “activating” state.
Understanding systemd service/unit states
The status of Linux service depends upon various states such as follows:
| Service status | Description |
|---|---|
| active (running) | Service or daemon is running in the background. For example, sshd or nginx/apache web server and listing for incoming traffic. |
| active (exited) | Service successfully started from the config file. Typically one time services configuration read before Service was exited. For example, AppArmor or Firewall service. |
| active (waiting) | Our service is running but waiting for an event such as CPUS/printing event. |
| inactive | Service is not running. |
| enabled | Service is enabled at boot time. |
| disabled | Service is disbled and will not be started at Linux server boot time. |
| static | Service cannot be enabled on Linux, but mostly started by another systemd unit automatically. In other words, the unit file is not enabled and has no provisions for allowing in the [Install] unit file section. |
| masked | Service is completely disabled and any start operation on it always fails. |
| alias | Service name is an alias. It means service is symlink to another unit file. |
| linked | Made available through one or more symlinks to the unit file (permanently in /etc/systemd/system/ or transiently in /run/systemd/system/), even though the unit file might reside outside of the unit file search path. |
Currently following units are supported by systemd
- service : Service unit configuration about a process controlled and supervised by systemd.
- mount : File system mount point controlled and supervised by systemd.
- swap : Swap file/disk configuration controlled by systemd.
- socket : An IPC or network socket or a file system FIFO controlled and supervised by systemd, for socket-based activation.
- target : It contains information about a target unit of systemd. It is used for grouping units and as well-known synchronization points during start-up. For example, graphical.target is used for GUI based desktop login. Similarly, multi-user.target is used by servers where users can log in using ssh/console.
- device : A device unit as exposed in the sysfs/udev device tree. It includes networking and other devices.
- automount : Automount file systems
- timer : Cron like systemd unit to run commands and services at a given date/time format. For example, refresh firmware or clean session created by Python or PHP webapps.
- path : A systemd special target unit that sets up all path units. For example, systemd can take certian action depend upon file system path. If /etc/foo/ modifed take some action.
- slice : We use a systemd slice for isolating workloads. They define a hierarchy in which scopes and service is placed. The actual processes are contained in scopes or in services. Think it as lightweight Docker. For each slice, certain resource limits such as CPU or disk I/O limit may be set that apply to all processes.
- scope : Scope units are not configured via unit configuration files, but are only created programmatically using the bus interfaces of systemd. They are named similar to filenames. A unit whose name ends in “.scope” refers to a scope unit. Scopes units manage a set of system processes. Unlike service units, scope units manage externally created processes, and do not fork off processes on its own. The main purpose of scope units is grouping worker processes of a system service for organization and for managing resources.
We can list all services unit as follows:
$ sudo systemctl —type=service
Want to see mount type units? Try:
$ sudo systemctl —type=mount
Display all systemd timer units on your Linux box:
$ sudo systemctl -t timer
To show all installed unit files use:
$ sudo systemctl list-unit-files
Linux view status of a service
Type the following command to view all services and unit status on your Linux system since boot time:
$ sudo systemctl
Click to enlarge
How to list units that systemd currently has in memory
Execute the following command:
$ sudo systemctl list-units
$ sudo systemctl list-units | more
$ sudo systemctl list-units | grep sshd
## filter by unit types ##
$ sudo systemctl list-units —type service
$ sudo systemctl list-units —type timer
List systemd/systemctl all failed units/services on Linux
$ sudo systemctl list-units —failed
$ sudo systemctl list-units —state failed
## filtering by unit type ##
$ sudo systemctl list-units —state failed —type service
$ sudo systemctl list-units —state failed —type timer
The systemctl command options to list all failed units/services
Источник