- Set Time/Date/Timezone in Ubuntu Linux
- Check Current Time
- Using the date command
- Using timedatectl command
- Changing Time
- using date command
- Change Date
- Create custom date format
- List/Change time zone
- Set the Local-rtc
- Check/Change CMOS Time
- Conclusion
- Как изменить часовой пояс Linux
- Как работает время в Linux?
- Настройка часового пояса в linux
- 1. Ссылка /etc/localtime
- 2. Настройка с помощью tzdata
- 3. Настройка с помощью systemd
- 4. Настройка часового пояса в GUI
- Выводы
- How To Set/Change Time, Date And Timezone In Linux?
- 1) How To Check Current Date, Time And Timezone Information In Linux?
- 2) How To Set/Change Date And Time In SysVinit Systems?
- 3) How To Set/Change Date And Time In systemd Systems?
- 4) How To Change The TimeZone In systemd Systems?
- 5) How To Change The TimeZone In RHEL 6/CentOS 6 Systems?
- 6) How To Automatically Adjust Your Linux System Clock?
Set Time/Date/Timezone in Ubuntu Linux
Time is an important aspect in Linux systems especially in critical services such as cron jobs. Having the correct time on the server ensures that the server operates in a healthy environment that consists of distributed systems and maintains accuracy in the workplace.
In this tutorial, we will focus on how to set time/date/time zone and to synchronize the server clock with your Ubuntu Linux machine.
Check Current Time
You can verify the current time and date using the date and the timedatectl commands. These linux commands can be executed straight from the terminal as a regular user or as a superuser. The commands are handy usefulness of the two commands is seen when you want to correct a wrong time from the command line.
Using the date command
Log in as a root user and use the command as follows
Output
You can also use the same command to check a date 2 days ago
Output
Using timedatectl command
Checking on the status of the time on your system as well as the present time settings, use the command timedatectl as shown
Changing Time
We use the timedatectl to change system time using the format HH:MM: SS. HH stands for the hour in 24-hour format, MM stands for minutes and SS for seconds.
Setting the time to 09:08:07 use the command as follows (using the timedatectl)
using date command
Changing time means all the system processes are running on the same clock putting the desktop and server at the same time. From the command line, use date command as follows
Where,
• 10: Hour (hh)
• 13: Minute (mm)
• 13: Second (ss)
To change the locale to either AM or PM use the %p in the following format.
Change Date
Generally, you want your system date and time is set automatically. If for some reason you have to change it manually using date command, we can use this command :
It will set your current date and time of your system into ‘January 25, 2014′ and ’09:17:00 AM’. Please note, that you must have root privilege to do this.
You can use timedatectl to set the time and the date respectively. The accepted format is ‘YYYY-MM-DD’, ‘YYYY’ represents the year, ‘MM’ the month in two digits and ‘DD’ for the day in two digits.
Changing the date to ’15 January 2019′, you should use the following command:
Create custom date format
To create custom date format, use a plus sign (+)
%D format follows Year/Month/Day format.
You can also put the day name if you want. Here are some examples :
List/Change time zone
Changing the time zone is crucial when you want to ensure that everything synchronizes with the Network Time Protocol. The first thing to do is to list all the region’s time zones using the list-time zones option or grep to make the command easy to understand
The above command will present a scrollable format.
Recommended timezone for servers is UTC as it doesn’t have daylight savings. If you know, the specific time zones set it using the name using the following command
To display timezone execute
Set the Local-rtc
The Real-time clock (RTC) which is also referred to as the hardware clock is independent of the operating system and continues to run even when the server is shut down.
Use the following command
In addition, the following command for the local time
Check/Change CMOS Time
The computer CMOS battery will automatically synchronize time with system clock as long as the CMOS is working correctly.
Use the hwclock command to check the CMOS date as follows
To synchronize the CMOS date with system date use the following format
Conclusion
To have the correct time for your Linux environment is critical because many operations depend on it. Such operations include logging events and cron jobs as well.
If you have any questions or feedback, feel free to leave a comment.
Источник
Как изменить часовой пояс Linux
Мы очень часто пользуемся временем в Linux, начиная от простой задачи узнать сколько сейчас времени, до более сложной — посмотреть логи или узнать когда произошло то или иное событие в системе. Все завязано на времени, поэтому очень важно, чтобы часы шли правильно.
Наша планета разделена на часовые пояса, это было сделано с одной простой целью, чтобы время в любой точке планеты соответствовало солнечному времени. Время между этими зонами отличается на час и всего таких поясов — 24, за эталон взято время по нулевому, Гринвичскому меридиану.
Поэтому в определенный момент время в разных участках планеты будет отличаться на час. В этой небольшой статье мы рассмотрим как изменить часовой пояс Linux, чтобы операционная система правильно работала со временем и могла правильно его синхронизировать через интернет.
Как работает время в Linux?
Операционная система Linux хранит и обрабатывает системное время в специальном Unix формате — количество секунд прошедших с полуночи первого января 1970 года. Эта дата считается началом эпохи Unix. И используется не ваше локальное время, а время по гринвичскому меридиану.
Для преобразования времени по Гринвичу в региональное время используется часовой пояс. Это преобразование выполняется для каждого пользователя. Это необходимо, чтобы каждый пользователь мог настроить для себя правильное по его временной зоне время. Такое поведение просто необходимо на серверах, когда на одной машине могут работать люди из разных частей мира.
По умолчанию в системе может быть установлен неправильный часовой пояс, это приведет к путанице в логах событий, да и другим трудностям. Но все это легко исправить. Дальше мы рассмотрим несколько способов изменить часовой пояс Linux.
Настройка часового пояса в linux
1. Ссылка /etc/localtime
Наиболее популярный и поддерживаемый в большинстве дистрибутивов способ установки часового пояса для всех пользователей — с помощью символической ссылки /etc/localtime на файл нужного часового пояса. Список доступных часовых поясов можно посмотреть командой:
Сначала создайте резервную копию текущего часового пояса:
cp /etc/localtime /etc/localtime.bak
Для создания символической ссылки используйте команду ln -sf. Файл зоны нужно выбрать из доступных в системе. Например, мой часовой пояс — Украина, Киев, для установки будет использоваться следующая команда:
ln -sf /usr/share/zoneinfo/Europe/Kiev /etc/locatime
Теперь можете проверить текущее системное время с помощью утилиты date:
Если у вас установлена утилита rdate можно синхронизировать время с сетью:
sudo rdate -s time-a.nist.gov
Осталось только синхронизировать ваши аппаратные часы с новыми настройками, для этого выполните команду:
Если нужно изменить часовой пояс только для определенной программы или скрипта, просто измените для нее переменную окружения TZ, например:
Эта настройка сохраняется только для текущего сеанса командной оболочки. Чтобы сменить часовой пояс linux для определенного пользователя тоже нужно использовать переменную среды TZ. Только ее нужно добавить в файл
/.environment. Этот файл читается по умолчанию при входе в систему, а значит переменная будет доступна всем программам:
Готово, теперь вы знаете как выполняется настройка часового пояса linux для определенного пользователя.
2. Настройка с помощью tzdata
Если вы не хотите использовать описанный выше способ, можно воспользоваться специальными утилитами. Вот только в разных дистрибутивах используются свои утилиты. Рассмотрим варианты для самых популярных дистрибутивов.
В Red Hat Linux:
В CentOS и Fedora:
В Slackware или FreeBSD:
В большинстве случаев вы увидите подобное диалоговое окно:
Здесь просто нужно выбрать нужный часовой пояс и нажать кнопку Enter. После этого для окончательного применения настроек нужно будет перезагрузить систему.
3. Настройка с помощью systemd
В systemd есть своя утилита для настройки даты и часового пояса. Чтобы узнать текущее состояние выполните:
Для просмотра всех доступных временных зон выполните такую команду:
А для установки нужного часового пояса используйте команду set-timezone, например, тот же Europe/Kiev:
sudo timedatectl set-timezone Europe/Kiev
4. Настройка часового пояса в GUI
В дистрибутиве Ubuntu и других, использующих Gnome, настройка часового пояса Linux может быть выполнена прямо в параметрах системы. Для этого выберите пункт Сведения о системе, затем Дата и время, выберите свое местоположение на карте, или наберите название для поиска в поле ввода:
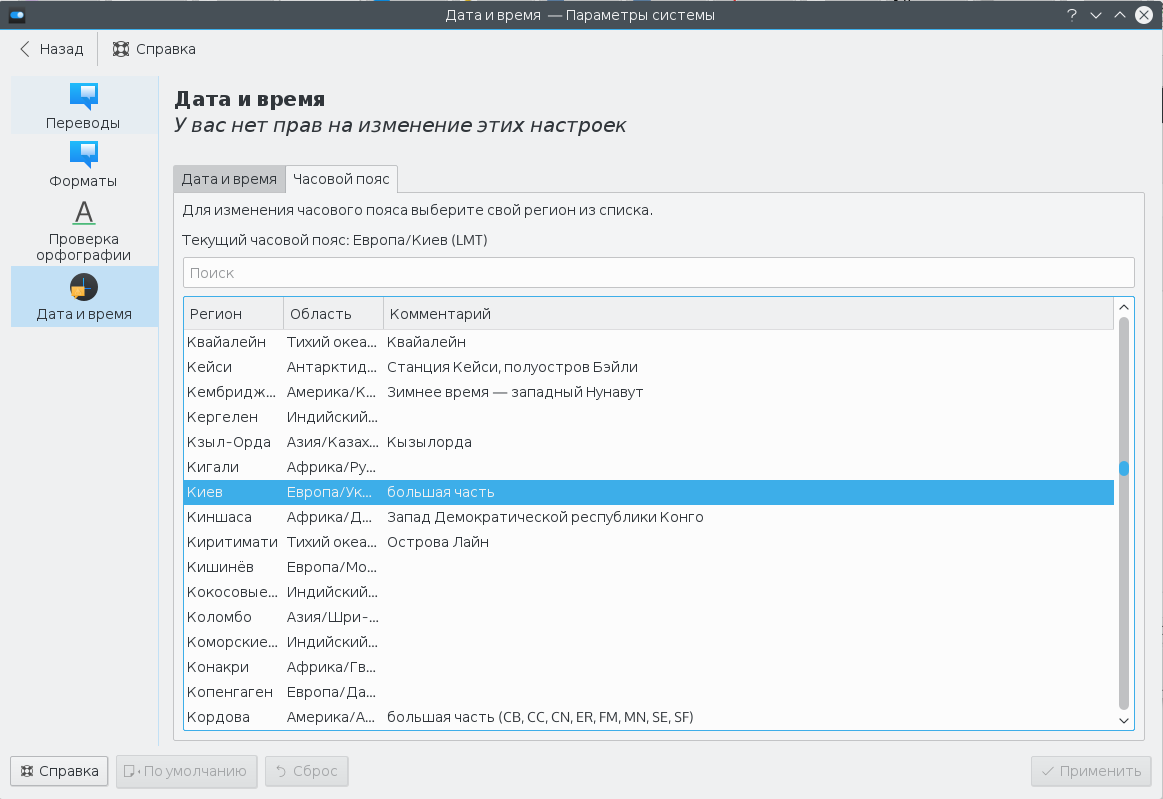
В KDE аналогично можно установить часовой пояс в настройках системы. Запустите утилиту настроек, откройте пункт Локализация, перейдите в раздел Дата и время, а затем откройте вкладку Часовой пояс:
Остается выбрать часовой пояс в списке и нажать кнопку Применить. Здесь уже изменения должны проявиться моментально.
Выводы
Теперь вы знаете как выполняется установка часового пояса в linux и сможете настроить не только свой домашний компьютер но и сервер с множеством пользователей, которым нужен отдельный часовой пояс для правильного местного времени. Если у вас остались вопросы, спрашивайте в комментариях!
На завершение видео, в котором подробно рассказано, что такое часовые пояса и зачем они нужны:
Источник
How To Set/Change Time, Date And Timezone In Linux?
If you missed to set the proper timezone, date and time while installing the OS. Don’t worry it can be changed at any point of time.
If we bought the server from some providers and they might have set the timezone based on their location.
Say for example, if you buy a server from USA then they will build a system based on their GEO location.
If so, don’t worry you can simply change the timezone and date formats as per your requirement using the below commands on your Linux Box.
In this article, i have covered all the possible methods with all Major Linux Distribution such as CentOS, Redhat (RHEL), Fedora, Ubuntu, Debian, Mint & openSUSE systems.
Also, we have updated the information based on the system manager such as SysVinit and systemd. Timezone is controlled by /etc/localtime file.
The below files are belongs to timezone on Linux.
- /usr/share/zoneinfo: This directory contains timezone files.
- /etc/localtime: This file is symlink with timezone file.
- /etc/timezone: This file is holding timezone name on debian based systems.
- /etc/sysconfig/clock: This file is holding timezone name on RHEL based systems.
1) How To Check Current Date, Time And Timezone Information In Linux?
Use the following commands to check the current date, time and timezone information in Linux systems.
To check current system date and time.
To display current system date and time with UTC format.
Run the following command to display Hardware Clock (RTC).
To check the timezone on SysVinit systems.
We can sell all the details together in the single command for systemd systems. See the details below.
2) How To Set/Change Date And Time In SysVinit Systems?
Use the following commands to set or change the time and date as you wish in Linux SysVinit systems. If you requires locale’s then you can set accordingly.
Common Syntax:
To set new date and time in one shot, use the following format.
You can double confirm this by running date command once again.
To set only time, use the following format.
To set only date, use the following format.
To Set time with locale’s.
To set the hardware clock to local time.
To set the hardware clock to UTC time.
3) How To Set/Change Date And Time In systemd Systems?
Use the following commands to set or change the time and date as you wish in Linux systemd systems.
Common Syntax:
To change the new date and time in one shot, use the following format.
To set only time, use the following format.
To set only date, use the following format.
Use the following format to set RTC time.
4) How To Change The TimeZone In systemd Systems?
For systemd system, use the timedatectl command to change the timezone. Navigate to the following url to change the timezone in Linux.
If you would like to restart the timedatectl service, use the following command.
Run the following command to verify the new timezone.
5) How To Change The TimeZone In RHEL 6/CentOS 6 Systems?
For RHEL/CentOS systems, use the following command to change the timezone.
Run the following command to check the new timezone in RHEL/CentOS systems.
6) How To Automatically Adjust Your Linux System Clock?
If you would like to sync your Linux system clock to remote NTP server then you have configure it.
To do so, navigate the following urls because we had written an detailed articles about these in the past.
Источник