- How to change root password in Ubuntu Linux
- How to change root password in Ubuntu
- How to disable your root account on Ubuntu
- Understanding passwd command option
- A note about root password on an Ubuntu server/desktop
- Пароль root в Ubuntu
- Суперпользователь в Ubuntu
- Пароль root Ubuntu
- Выводы
- How to Reset or Change the Root Password in Linux
- Changing Your Root Password in Ubuntu
- Step 1: Open a Terminal Window
- Step 2: Change Your Root Password
- Resetting a Root Password in Ubuntu
- Step 1: Boot to Recovery Mode
- Step 2: Drop Out to Root Shell
- Step 3: Remount the File System with Write-Permissions
- Step 4: Change the Password
- Changing the Root Password in CentOS
- Step 1: Access the Command Line (Terminal)
- Step 2: Change the Password
- Reset Root Password in CentOS
- Step 1: Access Boot Menu
- Step 2: Edit Boot Options
- Step 3: Remount the Drive
- Step 4: Changing the Password
- Step 5: Restart
- How do I change a user password in Ubuntu Linux?
- How to change a user password in Ubuntu
- How to change a root (superuser) password in Ubuntu
- How do I change the user account password on Ubuntu?
- Deleting a user password
- Linux locking an account
- Linux unlocking an account
- Conclusion
How to change root password in Ubuntu Linux
I am a new Ubuntu Linux server admin. How can I change root password in Ubuntu Linux server using the bash shell over ssh based session?
By default, the root user account password is locked in Ubuntu Linux for security reasons. As a result, you can not login using root user or use a command such as ‘su -‘ to become a SuperUser.
| Tutorial details | |
|---|---|
| Difficulty level | Easy |
| Root privileges | Yes |
| Requirements | Ubuntu |
| Est. reading time | 1m |
You need to use the passwd command to change the password for user accounts on Ubuntu Linux. A typical user can only change the password for his/her account only. A SuperUser (root) can change the password for any user account. Your user account info stored in /etc/passswd and an encrypted password stored in /etc/shadow file.
How to change root password in Ubuntu
The procedure to change the root user password on Ubuntu Linux:
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
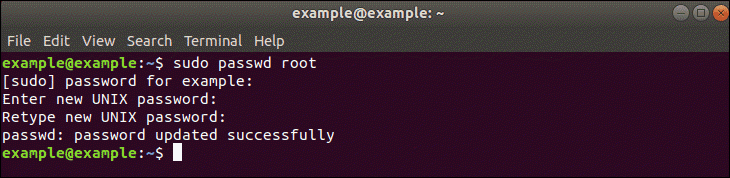
- Type the following command to become root user and issue passwd:
sudo -i
passwd - OR set a password for root user in a single go:
sudo passwd root - Test it your root password by typing the following command:
su —
How to disable your root account on Ubuntu
One can disable the root account by typing the following command:
$ sudo passwd -dl root
OR
$ sudo passwd —delete —lock root
Sample session from the above commands:
Understanding passwd command option
- -d OR —delete : Delete a user’s password (make it empty for root user). This is a quick way to disable a password for an account. It will set the named account passwordless.
- -l OR —lock : Lock the password of the named account such as root. This option disables a password by changing it to a value which matches no possible encrypted value (it adds a ‘!’ at the beginning of the password)
- root : Lock and disble root account i.e. re-disabling your root account
A note about root password on an Ubuntu server/desktop
Enabling the root account by setting the password is not needed. Almost everything you need to do as SuperUser (root) of an Ubuntu server can be done using sudo command. For example, restart apache server:
$ sudo systemctl restart apache2
You can add additional user to sudo by typing the following command:
$ sudo adduser
For example, add a user named tom to sudo:
$ sudo adduser tom sudo
You can in as another user say logging as tom from jerry account:
< jerry@nixcraft >$ sudo -i -u tom
When prompted enter jerry’s password i.e. the password being asked for is your own, not tom’s. For more info see “How to create a new sudo user on Ubuntu Linux server” and RootSudo.
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
Источник
Пароль root в Ubuntu
Как вы знаете, разработчики Ubuntu имеют свой взгляд на безопасность работы с дистрибутивом. Довольно много дистрибутивов, в том числе Debian, на котором основана Ubuntu, предлагают использовать аккаунт суперпользователя для выполнения различных задач по администрированию системы. Но сейчас такой подход считается небезопасным, поскольку вы можете забыть что работаете от имени суперпользователя и удалить какие-либо важные вещи.
Поэтому было решено использовать для административных действий, которые требуют прав суперпользователя команду sudo. Но разработчики Ubuntu пошли еще дальше и вообще отключили аккаунт суперпользователя. Если вы попробуете войти в него, то у вас ничего не выйдет. В этой статье мы разберем как установить пароль суперпользователя Ubuntu и разблокировать его.
Суперпользователь в Ubuntu
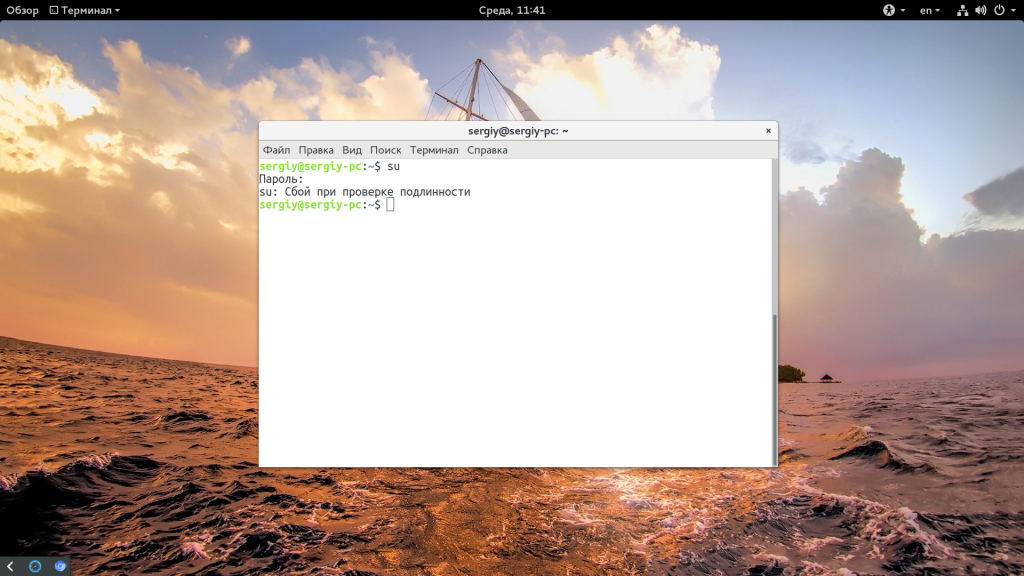
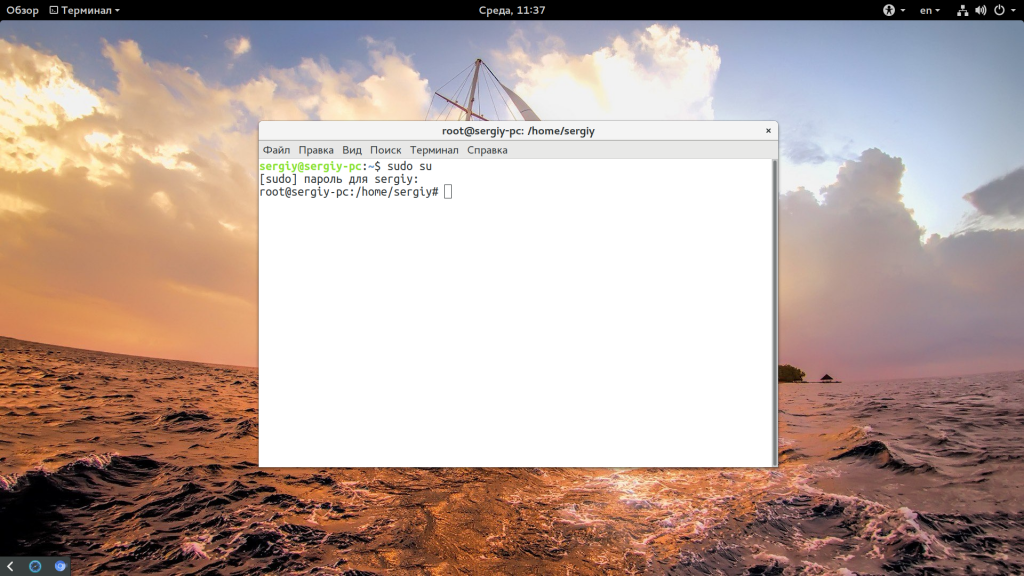
Начнем с того, что суперпользователя в Ubuntu никто не отключал, пользователь root существует и от его имени работают процессы, как в других системах. Просто для этого пользователя не задан пароль. Поэтому вы и не можете войти. Но есть несколько способов авторизоваться от имени root без пароля. Во-первых, это sudo. Команда su запрашивает пароль только в том случае, если вы выполняете ее от имени обычного пользователя. Если команда будет запущена от имени суперпользователя, то пароль спрашиваться не будет, а вы сразу перейдете в терминал root. Первая комбинация, которая приходит на ум:
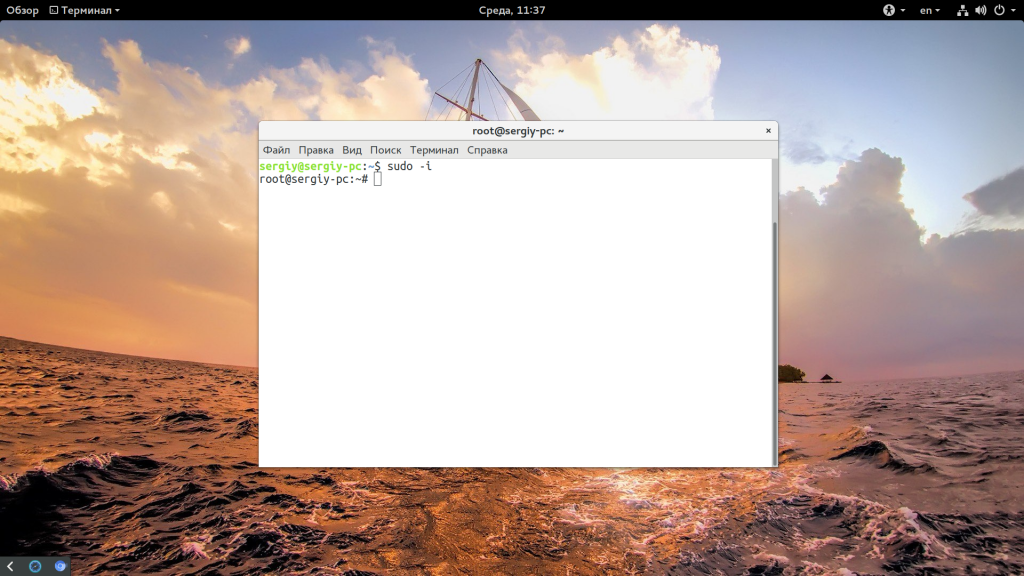
Но есть и более простой и правильный вариант, вы можете использовать опцию -i утилиты sudo чтобы перейти в терминал суперпользователя:
Больше никаких параметров не нужно. Вторая команда предпочтительнее, потому что она позволяет сохранить текущие переменные окружения, что в некоторых случаях будет очень полезно.
Пароль root Ubuntu
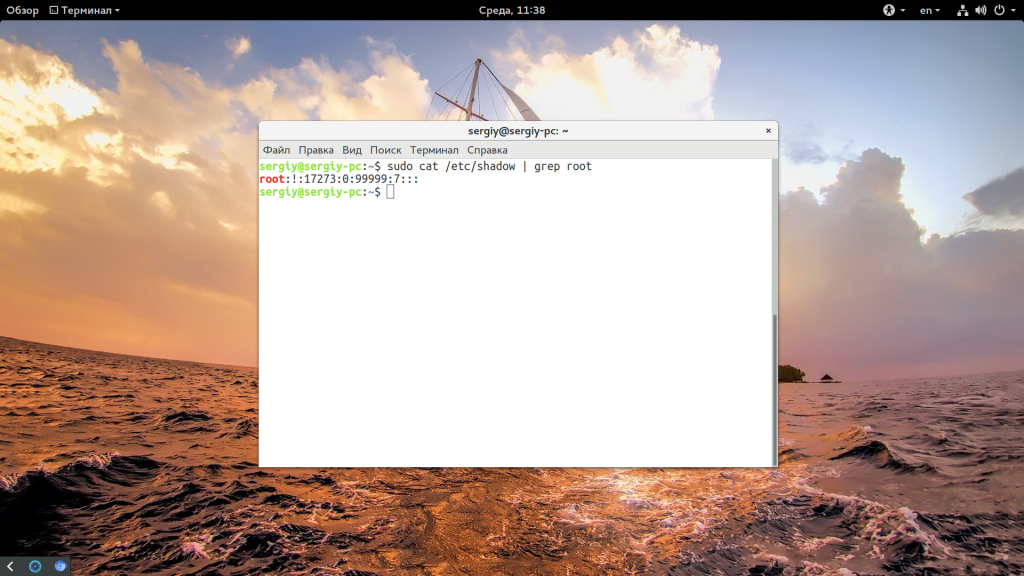
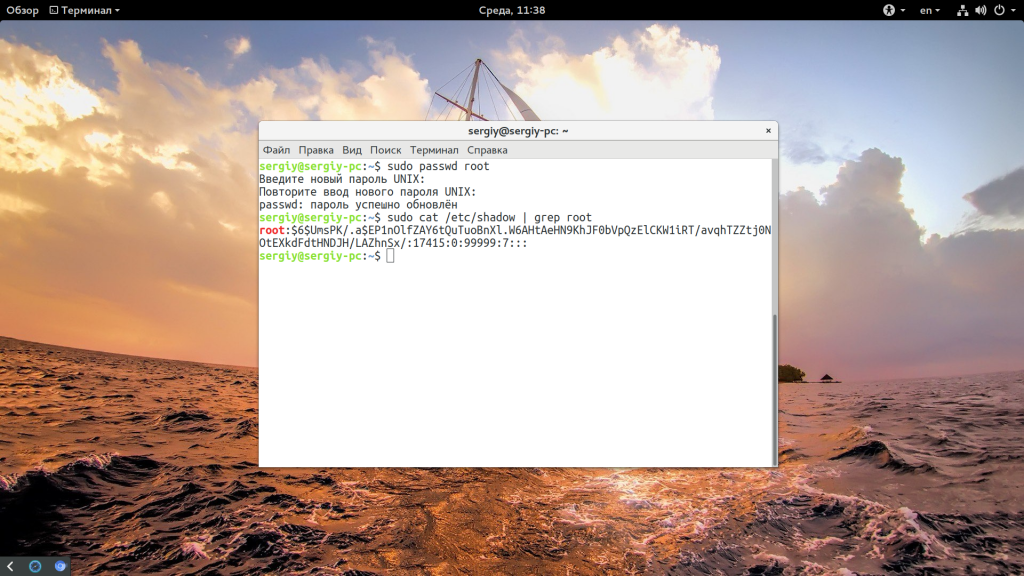
Несмотря на приведенные выше способы решения проблемы, вы все еще не можете авторизоваться от имени суперпользователя в TTY или использовать утилиту su без sudo. Если это для вас важно дальше мы рассмотрим как установить пароль root Ubuntu и вернуть полноценного root пользователя. Только это все нужно делать когда у вас есть обычный пользователь и доступ к нему. Сначала смотрим /etc/shadow и убеждаемся, что пароля действительно нет:
sudo cat /etc/shadow | grep root
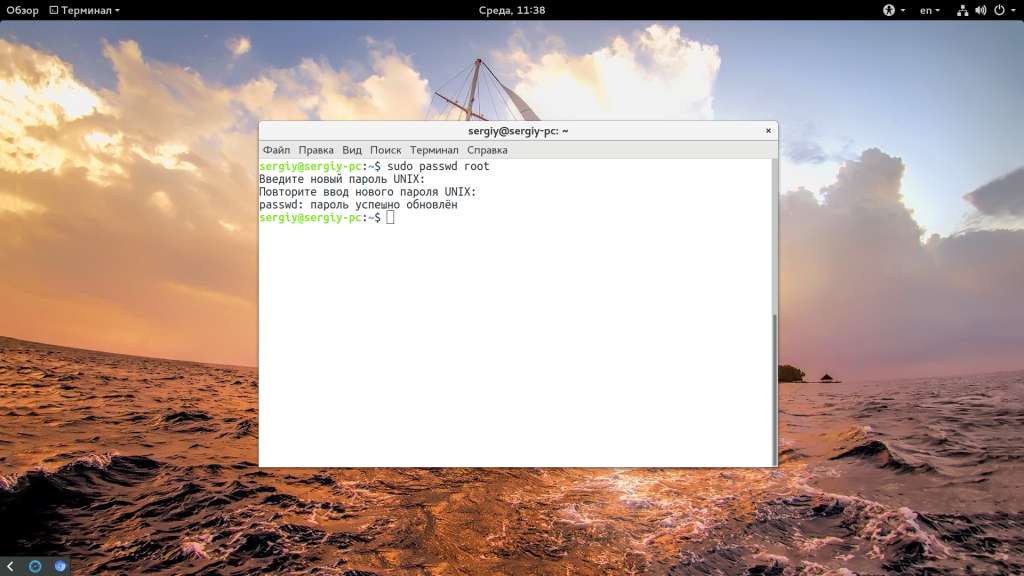
Для установки пароля для root наберите:
sudo passwd root
Теперь нужно ввести два раза пароль и готово. Проверяем снова:
sudo cat /etc/shadow | grep root
Если же вы потеряли пароль своего пользователя и вам нужна смена пароля root ubuntu, то вам понадобиться войти в режим восстановления и выполнять все действия там. Подробнее об этом читайте в статье сброс пароля Gentoo.
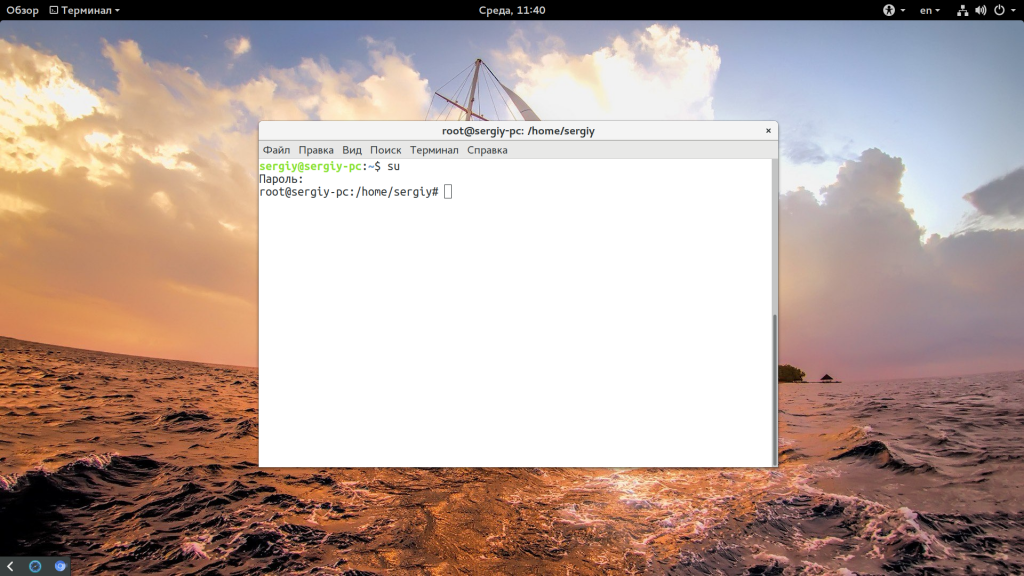
Дальше вы можете использовать команду su для авторизации, авторизоваться от root по ssh и многое другое. Например:
Введите только что полученный пароль и вы попадете в консоль суперпользователя. Только будьте осторожны, поскольку здесь можно случайно что-либо удалить. Используйте аккаунт суперпользователя только для административных задач, не пользуйтесь им постоянно и не запускайте графическое окружение от имени root.
Выводы
Пароль root по умолчанию ubuntu не задан, но вы можете это очень просто исправить чтобы использовать вашу систему так, как вам удобно. Чтобы задать пароль root ubuntu достаточно выполнить только одну команду, но нужно никогда не забывать про осторожность. Если у вас остались вопросы, спрашивайте в комментариях.
Источник
How to Reset or Change the Root Password in Linux
Home » SysAdmin » How to Reset or Change the Root Password in Linux
In Linux, root privileges (or root access) refers to a user account that has full access to all files, applications, and system functions.
Most basic Linux user accounts run with limited privileges. This keeps users from making mistakes or accidentally exposing the system to vulnerabilities.
To use protected operating system features, a Linux user has to temporarily elevate their privileges using a command like sudo . The sudo command tells the system to run a command as a superuser, or root user. When you run a function using sudo , you’ll usually have to enter your password.
Some versions of Linux will elevate your user privileges for a set amount of time around (15 minutes) before reverting. Other versions only perform a single task with elevated privileges.
It’s a good idea to change your passwords regularly and consider using enterprise password management software.
This guide will help you change your Linux root password in Ubuntu or CentOS, or reset the password.
- A computer running Linux
- Command-line interface (terminal)
Changing Your Root Password in Ubuntu
Step 1: Open a Terminal Window
Right-click the desktop, then left-click Open in terminal.
Alternately, you can click Menu > Applications > Accessories > Terminal.
Step 2: Change Your Root Password
In the terminal window, type the following:
The system will prompt you to enter your password – this is the same password you use to log in to the system.
Next, the system will prompt you to enter a new password. Do so, and then re-enter it exactly the same when the system prompts you to retype the password. This double-entry confirms that you have typed the password correctly.
Resetting a Root Password in Ubuntu
In some situations, you may need to access an account for which you’ve lost or forgotten a password.
Step 1: Boot to Recovery Mode
Restart your system. Once you see the splash screen for the computer manufacturer, hold down the shift key. The system should come up with a black and white GRUB, or boot menu, with different Linux kernel versions displayed.
Select the second one from the top – the highest revision, followed by (recovery mode). Press Enter.
Step 2: Drop Out to Root Shell
The system should display a menu with different boot options. Use the arrow keys to navigate to the option labeled root and press Enter.
The system should respond by giving you a command-line interface with a prompt.
Step 3: Remount the File System with Write-Permissions
Right now, your system only has read-only access to your system. That means it can look at the data, but cannot make any changes. But we need write-access to change the password, so we’ll need to remount the drive with the appropriate permissions.
At the prompt, type:
Press Enter. This should allow you to make changes to the data on the hard drive.
Step 4: Change the Password
At the prompt, type:
Substitute the name of the user for username, then press Enter. The system asks you to type a new UNIX password and then to retype it.
Once you’ve entered and confirmed the new password, reboot the system by entering the following:
Hit Enter, and your system should restart. Don’t press any keys, let the system come up to the login screen, and test to make sure the new password works.
Changing the Root Password in CentOS
Changing a password in CentOS is almost identical to changing it in Ubuntu.
Step 1: Access the Command Line (Terminal)
Right-click the desktop, then left-click Open in Terminal. Or, click Menu > Applications > Utilities > Terminal.
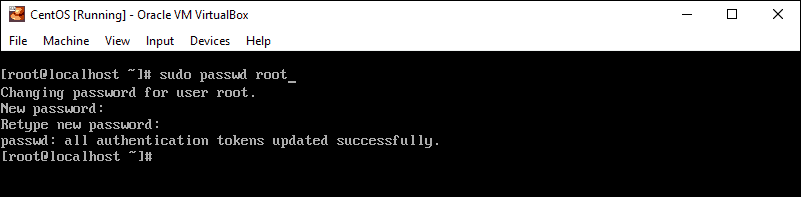
Step 2: Change the Password
At the prompt, type the following, then press Enter:
The system should prompt you to enter your existing password. Do so, then follow the prompts to enter and confirm a new root password.
Reset Root Password in CentOS
This is a similar process as in Ubuntu, with a couple of variations.
Step 1: Access Boot Menu
Restart the system, then tap the Esc key about once per second to launch the GRUB menu.
Step 2: Edit Boot Options
Use the arrows to highlight the version of Linux you boot into, then press e.
Use the arrows to highlight the line that starts with kernel or Linux.
Press E.
At the end of the line, add a space then type single. Press Enter, then boot into single-user mode by pressing Ctrl-X or B. (The system will display the command to use.)
Step 3: Remount the Drive
You should have a command line, and you’ll have root privileges. To enable read/write access on your hard drive, type the following:
Step 4: Changing the Password
Type the following:
Press Enter, and the system should prompt you to enter and confirm a new password.
Step 5: Restart
Type the following, pressing enter after each line:
Your system should restart. Confirm that your new password works by logging in.
If you already have access to your user account, resetting or changing your password in Linux is simple.
It can be more challenging if you’ve lost or forgotten a password, but with a little creative restarting and editing, you shouldn’t find it too hard.
Источник
How do I change a user password in Ubuntu Linux?
W e recently switched from Windows server operating system to Ubuntu Linux operating system at work. I am a developer by profession and do not know much about Linux. I need to change the sftp/ssh user account password on Ubuntu. How do I change a user password in Ubuntu Linux?
Introduction – Your Ubuntu Linux account information stored in a file named /etc/passwd and encrypted password in /etc/shadow . This page explains to you how to change the Ubuntu Linux root and user account password using the passwd command line.
| Tutorial details | |
|---|---|
| Difficulty level | Easy |
| Root privileges | Yes |
| Requirements | Ubuntu Linux |
| Est. reading time | 2 minutes |
How to change a user password in Ubuntu
- Open the terminal application by pressing Ctrl + Alt + T
- To change a password for user named tom in Ubuntu, type:
sudo passwd tom - To change a password for root user on Ubuntu Linux, run:
sudo passwd root - And to change your own password for Ubuntu, execute:
passwd
How to change a root (superuser) password in Ubuntu
Firstly, open a terminal window. If you want to change the password for remote Ubuntu server, log in using the ssh command:
ssh user@ubuntu-server-ip
ssh vivek@ubuntu-webserver-1
Type ‘sudo -i’ at the command prompt, and Enter key:
sudo -i
Type the current user password and press Enter key. Finally type NA command and press Enter to change password for root user:
passwd
Change password for root user on Ubuntu
How do I change the user account password on Ubuntu?
Again open a terminal window. Type the following command to change the password for regular Ubuntu user account named jerry:
sudo passwd < userNameHere >
sudo passwd jerry ## ##
sudo passwd vivek ## ##
How to change the user Password in Ubuntu Linux
Deleting a user password
Users will not be able to log in when the password is deleted or expired on Ubuntu Linux.
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
The syntax is as follow to remove the password for the account called tom:
sudo passwd -d tom
## OR ##
sudo passwd —delete jerry
You will see confirmation on screen as follows:
To set up a new password when deleted, run:
sudo passwd -d tom
We can also force expire the password for the named account jerry. Open the terminal and then type the following command:
sudo passwd -e jerry
sudo passwd —expire jerry
When user login they will be forced to reset their credentials when you use the -e / —expire option:
Linux locking an account
sudo passwd -l
sudo passwd -l tom
Linux unlocking an account
sudo passwd -u
sudo passwd -u tom
Conclusion
This quick tutorial taught you how to change the Ubuntu Linux root user and other user account password using the passwd command. You must root user to change the password for all other users, however users can change their password without sudo access. For more info see the passwd command help page using the man command man passwd
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
| Category | List of Unix and Linux commands |
|---|---|
| Documentation | help • mandb • man • pinfo |
| Disk space analyzers | df • duf • ncdu • pydf |
| File Management | cat • cp • less • mkdir • more • tree |
| Firewall | Alpine Awall • CentOS 8 • OpenSUSE • RHEL 8 • Ubuntu 16.04 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Linux Desktop Apps | Skype • Spotify • VLC 3 |
| Modern utilities | bat • exa |
| Network Utilities | NetHogs • dig • host • ip • nmap |
| OpenVPN | CentOS 7 • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Debian 8/9 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Package Manager | apk • apt |
| Processes Management | bg • chroot • cron • disown • fg • glances • gtop • jobs • killall • kill • pidof • pstree • pwdx • time • vtop |
| Searching | ag • grep • whereis • which |
| Shell builtins | compgen • echo • printf |
| Text processing | cut • rev |
| User Information | groups • id • lastcomm • last • lid/libuser-lid • logname • members • users • whoami • who • w |
| WireGuard VPN | Alpine • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Firewall • Ubuntu 20.04 |
Comments on this entry are closed.
For your own password:
passwd
For root password:
sudo passwd root
FYI, we don’t set root password on Ubuntu for security reasons. One user will be added to the ‘sudo’ group and that will act as admin user. This ensures safety as root account without password is locked and cannot be used for ssh.
Источник