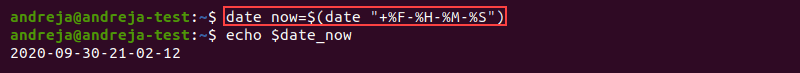- ⏱️ Как создать каталоги или файлы с именами на текущую дату/время/месяц/год на Linux
- Создание каталогов или файлов с именами текущей даты / времени / месяца / года на Linux
- Создание каталогов или файлов с произвольным именем с текущей датой
- Создание каталогов файлов в формате ISO
- Больше примеров
- Добавить комментарий Отменить ответ
- • Свежие записи
- • Категории
- • itsecforu.ru
- • Страны посетителей
- IT is good
- Linux Set Date and Time From a Command Prompt
- Linux Display Current Date and Time
- Linux Display The Hardware Clock (RTC)
- Linux Set Date Command Example
- Linux Set Time Examples
- How do I set the Hardware Clock to the current System Time?
- A note about systemd based Linux system
- timedatectl: Display the current date and time
- How do I change the current date using the timedatectl command?
- How do I set the current time only?
- How do I set the time zone using timedatectl command?
- How do I synchronizing the system clock with a remote server using NTP?
- Date Command in Linux: How to Set, Change, Format and Display Date
- Linux date Command Syntax
- How to Use date Command in Linux
- Linux date Command Format Options
- Set or Change Date in Linux
- Display Past Dates
- Display Future Dates
- Display the Date String at Line of File
- Display Last Modified Timestamp of a Date File
- Override a Time Zone
- Use date with Other Commands
- Use Unix Epoch Time (Epoch Converter)
⏱️ Как создать каталоги или файлы с именами на текущую дату/время/месяц/год на Linux
Показанные далее команды создадут каталоги или файлы с именами с текущей датой или временем на основе часов вашего компьютера.
Создание каталогов или файлов с именами текущей даты / времени / месяца / года на Linux
Чтобы создать каталог и назвать его текущей датой, просто запустите:
Эта команда создаст каталог и назовет его сегодняшней датой в формате dd: mm: yyyy.
Создание каталогов или файлов с произвольным именем с текущей датой
Как насчет пользовательского имени для каталога или файла с датой / временем / месяцем / годом?
Это также возможно.
Создание каталогов файлов в формате ISO
Если вы хотите использовать формат даты ISO (например, 2020-06-06), запустите:
Все вышеперечисленные три команды дают одинаковый результат.
Для создания файлов просто замените mkdir командой «touch».
Больше примеров
Если вы хотите только день текущей даты, используйте:
Эта команда создаст каталог только с текущим днем в имени. т.е. 06.
Точно так же вы можете создавать каталоги с именем текущего месяца только в имени:
Обратите внимение что S – заглавная
Чтобы назвать каталог с текущими минутами, используйте заглавную M:
Во всех приведенных выше примерах мы создали каталоги с номерами на их именах.
Что если вы хотите назвать каталоги с фактическим названием текущего дня / месяца, например, Saturday, October и т. д.?
Добавить комментарий Отменить ответ
• Свежие записи
• Категории
• itsecforu.ru
• Страны посетителей
 IT is good
IT is good
Источник
Linux Set Date and Time From a Command Prompt
H ow can I set the system date and time from the command prompt (bash shell)? I don’t have GUI installed and I am login over ssh session. How can I set date under Linux operating systems?
Use the date command to display the current date and time or set the system date / time over ssh session. You can also run the date command from X terminal as root user.
| Tutorial details | |
|---|---|
| Difficulty level | Easy |
| Root privileges | Yes |
| Requirements | None |
| Est. reading time | 2m |
This is useful if the Linux server time and/or date is wrong, and you need to set it to new values from the shell prompt.
You must login as root user to use date command.
Linux Display Current Date and Time
Just type the date command:
$ date
Sample outputs:
Linux Display The Hardware Clock (RTC)
Type the following hwclock command to read the Hardware Clock and display the time on screen:
# hwclock -r
OR
# hwclock —show
$ sudo hwclock —show —verbose
OR show it in Coordinated Universal time (UTC):
# hwclock —show —utc
Sample outputs:
Linux Set Date Command Example
Use the following syntax to set new data and time:
date —set=»STRING»
For example, set new data to 2 Oct 2006 18:00:00, type the following command as root user:
# date -s «2 OCT 2006 18:00:00»
OR
# date —set=»2 OCT 2006 18:00:00″
You can also simplify format using following syntax:
# date +%Y%m%d -s «20081128»
Linux Set Time Examples
To set time use the following syntax:
# date +%T -s «10:13:13»
Where,
Use %p locale’s equivalent of either AM or PM, enter:
# date +%T%p -s «6:10:30AM»
# date +%T%p -s «12:10:30PM»
How do I set the Hardware Clock to the current System Time?
Use the following syntax:
# hwclock —systohc
OR
# hwclock -w
A note about systemd based Linux system
With systemd based system you need to use the timedatectl command to set or view the current date and time. Most modern distro such as RHEL/CentOS v.7.x+, Fedora Linux, Debian, Ubuntu, Arch Linux and other systemd based system need to the timedatectl utility. Please note that the above command should work on modern system too.
timedatectl: Display the current date and time
Type the following command:
$ timedatectl
Fig.01: Systemd Linux timedatecetl command to display the current date and time
How do I change the current date using the timedatectl command?
To change the current date, type the following command as root user:
# timedatectl set-time YYYY-MM-DD
OR
$ sudo timedatectl set-time YYYY-MM-DD
For example set the current date to 2015-12-01 (1st, Dec, 2015):
# timedatectl set-time ‘2015-12-01’
# timedatectl
Sample outputs:
To change both the date and time, use the following syntax:
# timedatectl set-time YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS
Where,
- HH : An hour.
- MM : A minute.
- SS : A second, all typed in two-digit form.
- YYYY: A four-digit year.
- MM : A two-digit month.
- DD: A two-digit day of the month.
For example, set the date ’23rd Nov 2015′ and time to ‘8:10:40 am’, enter:
# timedatectl set-time ‘2015-11-23 08:10:40’
# date
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
How do I set the current time only?
The syntax is:
# timedatectl set-time HH:MM:SS
# timedatectl set-time ’10:42:43′
# date
Sample outputs:
How do I set the time zone using timedatectl command?
To see list all available time zones, enter:
$ timedatectl list-timezones
$ timedatectl list-timezones | more
$ timedatectl list-timezones | grep -i asia
$ timedatectl list-timezones | grep America/New
To set the time zone to ‘Asia/Kolkata’, enter:
# timedatectl set-timezone ‘Asia/Kolkata’
Verify it:
# timedatectl
How do I synchronizing the system clock with a remote server using NTP?
Simply type the following command:
# timedatectl set-ntp yes
Verify it:
$ timedatectl
Sample outputs:
Conclusion
Linux users can use date command to print or set the system date and time. Systemd based Linux users can use timedatectl to control the system time and date.
- You can also set new timzone using this mini-howto.
- Man pages – timedatectl(8)
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
Источник
Date Command in Linux: How to Set, Change, Format and Display Date
Home » SysAdmin » Date Command in Linux: How to Set, Change, Format and Display Date
Linux date command displays and sets the system date and time. This command also allows users to print the time in different formats and calculate future and past dates.
Read on to learn how to use the date command in Linux.
- A system running Linux
- A user account with root privileges
- Access to a terminal window/command line
Linux date Command Syntax
The syntax for the date command is:
How to Use date Command in Linux
To show the current system time and date, type in the date command:
The output displays the day of the week, day of the month, month, year, current time, and time zone. By default, the date command is set to the time zone of the operating system.
The -d option allows users to operate on a specific date. For example, we can type in the following command:
You can use the —date command to display the given date string in the format of a date. This command does not affect the system’s actual date and time values, and it only prints the requested date. For example:
Linux date Command Format Options
To format the date command’s output, you can use control characters preceded by a + sign. Format controls begin with the % symbol and are substituted by their current values.
Here, the %Y character is replaced with the current year, %m with month, and %d with the day of the month:
Here are another two formatting examples:
These are the most common formatting characters for the date command:
-
- %D – Display date as mm/dd/yy
- %Y – Year (e.g., 2020)
- %m – Month (01-12)
- %B – Long month name (e.g., November)
- %b – Short month name (e.g., Nov)
- %d – Day of month (e.g., 01)
- %j – Day of year (001-366)
- %u – Day of week (1-7)
- %A – Full weekday name (e.g., Friday)
- %a – Short weekday name (e.g., Fri)
- %H – Hour (00-23)
- %I – Hour (01-12)
- %M – Minute (00-59)
- %S – Second (00-60)
To see all formatting options, run date —help or the man command man date in your terminal.
Set or Change Date in Linux
To change the system clock manually, use the —set command. For example, to set the date and time to 5:30 PM, May 13, 2010, type:
Most Linux distributions have the system clock synchronized using the ntp or the systemd-timesyncd services, so be careful when the setting the clock manually.
Display Past Dates
Use the —date option to display past dates in Linux. The date command accepts values such as «tomorrow» , «Friday» , «last Friday» , «next Friday» , «next week» , and similar. So, use the following strings to print past dates::
Display Future Dates
The —date option can also display future dates. Like with past dates, you can type in strings to print upcoming dates:
Display the Date String at Line of File
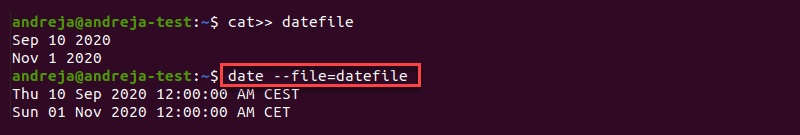
The —file option prints the date string present at each line of the file. Unlike the —date option, —file can present multiple date strings at each line.
This is the syntax for the —file command:
Here we use the cat command to add dates to a file and then print them with the date command:
Display Last Modified Timestamp of a Date File
When you use the -r option, the date command prints the last modification time of a file. For example, the following command prints the last time the hosts file was changed:
Override a Time Zone
By default, the date command uses the time zone defined in /etc/localtime . To use a different time zone in the environment, set the TZ variable to the desired time zone.
For example, to switch to New York time, enter:
Type in the date command to return the system to its default time zone. To see all available time zones, use the timedatectl list-timezones command.
The date command can also show the local time for a different time zone. For example, to display the local time for 4:30 PM next Monday on the Australian east coast, type:
Use date with Other Commands
You can use the date command to create file names that contain the current time and date. The input below creates a backup MySQL file in the format of the current date:
Another common use of the date command is in shell scripts. Below we assign the output of date to the date_now variable:
Use Unix Epoch Time (Epoch Converter)
You can use the date command as an Epoch converter. Epoch, or Unix timestamps, is the number of seconds that have passed since January 1, 1970, at 00:00:00 UTC.
To show the number of seconds from the epoch to the current day, use the %s format control:
To see how many seconds passed from epoch to a specific date, enter:
You now have a good understanding of how to use the date command in Linux. If you are interested in more date/time configuration options for Linux, read How to Set or Change Timezone/Date/Time on Ubuntu.
Источник


 IT is good
IT is good