- Linux show hidden files and folders with simple commands
- Create hidden Files
- Create hidden folder or directory
- Linux show hidden files and folders with ‘ls’ command
- Linux show hidden files and folders with ‘find’ command
- Check size of hidden files and folders
- Related Posts
- ИТ База знаний
- Полезно
- Навигация
- Серверные решения
- Телефония
- Корпоративные сети
- Как показать скрытые файлы в Linux
- Показать скрытые файлы в Linux с помощью ls
- Показать исключительно скрытые файлы с помощью ls
- Показать скрытые файлы в Linux, используя find
- Показать скрытые каталоги используя find
- Показать скрытые файлы в Linux, используя dir
- Отображение скрытых файлов в среде рабочего стола GNOME
- Вывод
- how to show or display hidden files in linux
- ls command
- dir command
- KDE File Manager (dolphin)
- Gnome File Manager (files or nautilus)
- Xfce File Manager (thunar)
- Midnight Commander
Linux show hidden files and folders with simple commands
Table of Contents
In this article we will cover below topics
- Create hidden files and folders/directories
- Linux show hidden files and folders/directories
- Linux find hidden files and folder/directories
- Check size of hidden files and folder/directories
The commands from this article to view hidden files and folders can be used across any Linux platform such as Ubuntu, Debian, Linux Mint, RHEL, CentOS, SuSE etc or any Unix node such as HP-UX, Solaris, etc.
I am using RHEL/CentOS 8 node installed on Oracle VirtualBox . Please do let me know via comment section if you face any issues following the commands from this article to view hidden files or folders in Linux or Unix.
Create hidden Files
To create hidden files you just need to make sure the filename starts with dot character ( . ). In Linux any filename which starts with dot ( . ) character is considered as hidden file. For example here I create a normal file using touch command
To list the file, as you see since the filename does not starts with dot ( . ) character, it is not hidden
Next we rename the file and make it .hidden_file starting with (.)
Next if you try to list the available files, we don’t see hidden_file anymore.
Check alias on this node
As you see there is an alias for ls command so by default it is configured to hidden files and folders. To remove this temporarily execute » unlias ls «
Next show hidden files and folders using ls , now this works as expected as we don’t see hidden folders or files.
This is temporary fix only for the current session, you need to check where this setting is configured for alias , it may be /etc/profile or /etc/bashrc some other system file based on your distribution.
Similarly to create hidden files you can just put a ( . ) infront of the filename, for example to create hidden files with filename » my_file «:
Create hidden folder or directory
The steps to create hidden folder or directory in Linux or Unix is similar to create hidden files. We just need to make sure the folder name starts with dot ( . ) character.
Now list the available files in current directory, as expected we don’t see any directory/folder since the folder is hidden. So we were able to create hidden folder here.
Linux show hidden files and folders with ‘ls’ command
- In this example we will use ls command in Linux show hidden files and folders.
- We can use ls command with » -a » to show all files including hidden files and folder.
- With -a «we do not ignore entries starting with . » that means also Linux show hidden files and folders.
- For example to show hidden files and folders which we created in above steps, navigate to your directory and execute ls -a
- We have also used -l to give us a long list so we use ls -al to show all files under test directory in long list format
As you see we were able to show hidden folders and files with » ls -a » which we had created earlier in this article.
Linux show hidden files and folders with ‘find’ command
Now with ls command we were able to show hidden files in one directory or may be multiple directories in Linux and Unix. But with ls it is little tricky to show hidden folders and files across all partitions. Here we can find hidden files using find command in Linux or Unix.
Now from our chapter » create hidden files » and » create hidden directory «, we know that hidden files start with dot ( . ) character. So we can use this trick with find command to find hidden files.
For example to find hidden files use -type f under /etc/ directory we can use below command
Here we are only search of files using » -type f » and any filename starting with dot ( . )
With Linux show hidden files and folders we can use the same command with -type d to find hidden folders under /usr
Here we could not have used » ls -a » to show hidden files in all these directories without using extra commands, so find is a better alternative to find hidden folder and files in Linux or Unix.
Check size of hidden files and folders
Now once you find hidden files or folders, you may also wish to check size of hidden files or folders.
For example we will find hidden files under our
So we have two hidden files, we can use ls with -Sh to check size of hidden files but it again has it’s own challenges.
- -S means sort by file size
- -h means print sizes in human readable format (e.g., 1K 234M 2G)
We use ls -lSha to show and check size of hidden file but as you see ls could only identify .hidden_file in the current folder but missed .hidden_file_2 available inside .hidden_directory
We will use du command to check size of hidden files in Linux or Unix. du command is used to estimate file space usage. We must combine du with find commands to first we find hidden files and folders and then we check size of hidden files using du command
For example to check size of hidden files under /test folder
Similarly to check size of hidden files under /tmp folder
Lastly I hope the steps from this article to Linux show hidden files and folders, create hidden files, create hidden folder and find hidden files and folders in Linux and Unix was helpful. So, let me know your suggestions and feedback using the comment section.
Related Posts
Didn’t find what you were looking for? Perform a quick search across GoLinuxCloud
If my articles on GoLinuxCloud has helped you, kindly consider buying me a coffee as a token of appreciation.

For any other feedbacks or questions you can either use the comments section or contact me form.
Thank You for your support!!
Источник
ИТ База знаний
Курс по Asterisk
Полезно
— Узнать IP — адрес компьютера в интернете
— Онлайн генератор устойчивых паролей
— Онлайн калькулятор подсетей
— Калькулятор инсталляции IP — АТС Asterisk
— Руководство администратора FreePBX на русском языке
— Руководство администратора Cisco UCM/CME на русском языке
— Руководство администратора по Linux/Unix
Навигация
Серверные решения
Телефония
FreePBX и Asterisk
Настройка программных телефонов
Корпоративные сети
Протоколы и стандарты
Как показать скрытые файлы в Linux
показать все что скрыто
В Linux скрытые файлы — это файлы, которые не отображаются напрямую при выполнении стандартного списка каталогов ls.
Мини — курс по виртуализации
Знакомство с VMware vSphere 7 и технологией виртуализации в авторском мини — курсе от Михаила Якобсена
Скрытые файлы, также называемые dotfiles в операционных системах Unix, — это файлы, используемые для выполнения некоторых сценариев или для хранения конфигурации некоторых служб на вашем хосте.Некоторым популярным примером скрытых файлов являются файлы, содержащиеся в домашнем каталоге пользователя: .bashrc , в котором хранятся сценарии инициализации пользователя, или .bash_logout , который выполняется всякий раз, когда вы выходите из сеанса bash.
В некоторых случаях вам необходимо иметь возможность легко находить скрытые файлы для настройки параметров конфигурации по умолчанию. Мы рассмотрим все методы, используемые для отображения скрытых файлов в Linux.
Показать скрытые файлы в Linux с помощью ls
Самый простой способ показать скрытые файлы в Linux — это использовать команду ls с опцией -a , что значит all.
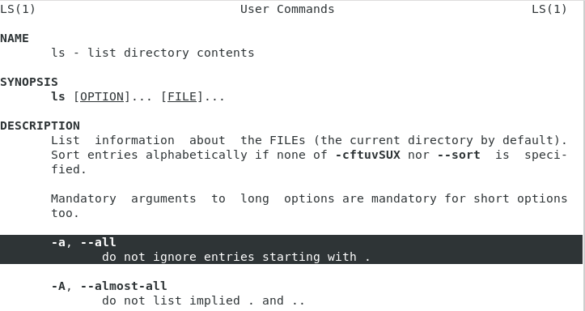
Например, чтобы показать скрытые файлы в домашнем каталоге пользователя, вы должны выполнить эту команду. Кроме того, вы можете использовать флаг -A для отображения скрытых файлов в Linux. При использовании A подразумеваемые файлы не будут отображаться (например, предыдущая папка также называется . )
В этом случае скрытыми файлами являются файлы bash_history, bash_logout , bashrc и файлы кэша.
Показать исключительно скрытые файлы с помощью ls
В некоторых случаях вас могут не интересовать другие файлы, кроме тех которые скрыты. Чтобы показать исключительно скрытые файлы в Linux, используйте команду ls со специальным регулярным выражением.
Например, используя пример, который мы описали ранее, мы получили бы следующий результат.
Показать скрытые файлы в Linux, используя find
Еще один эффективный способ найти скрытые файлы во всей вашей системе — использовать команду find.
Чтобы показать все скрытые файлы в вашей системе, запустите find с опцией name .
Обратите внимание, что выходные данные команды перенаправляются в /dev/null , чтобы не отображаться в каталогах, к которым у вас нет доступа.
/dev/null — специальный файл в системах UNIX, представляющий собой так называемое «пустое устройство», в которое всегда успешно происходит запись. Обычно используется для того чтобы туда отправлять ненужный вывод программы.
Чтобы показать скрытые файлы в текущем рабочем каталоге, запустите find с параметром maxdepth .
Показать скрытые каталоги используя find
Чтобы показать скрытые каталоги в текущем рабочем каталоге, без рекурсивного поиска, используйте команду find и укажите тип d .
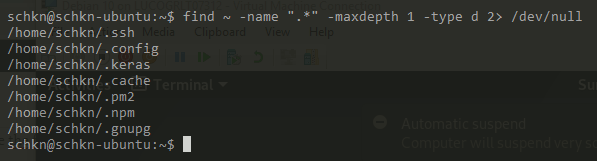
Показать скрытые файлы в Linux, используя dir
Команда dir — это команда, близкая к команде ls в Linux: она отображает содержимое каталога в вашей системе.
Подобно команде ls , ее можно использовать для отображения скрытых файлов в каталоге.
Чтобы показать скрытые файлы, выполните команду dir с опцией -a или -A .
Например, чтобы показать скрытые файлы в вашем домашнем каталоге, вы должны выполнить:
Обратите внимание, что команда dir также показывает скрытые каталоги, которые могут находиться в пути, который вы ищете.
Подобно команде ls , вы можете выбрать отображение скрытых файлов исключительно в папке, чтобы не беспокоиться обо всех остальных файлах.
Например, в домашнем каталоге это даст такой вывод:
Отображение скрытых файлов в среде рабочего стола GNOME
Наконец, для тех, кто работает в среде рабочего стола GNOME, вы также можете показывать скрытые файлы, когда просматриваете систему с помощью проводника.
Чтобы отобразить скрытые файлы через интерфейс GNOME, нажмите небольшую стрелку вниз, расположенную в верхнем правом углу экрана.
При появлении небольшого выпадающего меню обязательно установите флажок «Показать скрытые файлы» (Show Hidden Files).
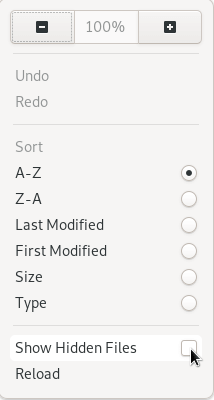
Как следствие, скрытые файлы и папки будут видны в проводнике.

Вывод
В этом руководстве вы увидели все способы отображения скрытых файлов в Linux: с помощью команды ls, но у вас также есть команда find и dir. Если вы используете среду рабочего стола GNOME, есть возможность легко их отобразить с помощью небольшой опции.
Онлайн курс по Linux
Мы собрали концентрат самых востребованных знаний, которые позволят тебе начать карьеру администратора Linux, расширить текущие знания и сделать уверенный шаг к DevOps
Источник
This post and this website contains affiliate links. See my disclosure about affiliate links.
how to show or display hidden files in linux
In Linux, as you should already know, there is the concept of hidden files and hidden folders. It is not exactly hidden in the literal sense, but all that means is that the file managers and file system utilities will not display these types of files (or folders) by default.
The hidden file concept is not a security feature and it does not provide any extra protection compared to other files. However, there are a couple of reasons (or benefits) for these kind of files.
- These files are usually a mechanism to store user preference or system files that are not modified by user regularly.
- They are also used by different utilities to store configuration and state of the programs. As these files are not actively used by user on a normal day-to-day basis, it makes sense to hide them in most cases.
- It also allows the file manager utilities to prevent cluttering up the user interface and provide a soft division between user files and user specific configuration files.
Any file or folder whose name start with a dot (.) is a hidden file, also known as dot file. These files will not be displayed by default when listing the contents of a folder. These files can be referenced just as any file, by using the name of the file (including the dot).
We will see how you can view these files using the most popular directory listing commands and file managers.
ls command
The ls command is probably the most used command line utility and it lists the contents of the specified directory. In order to display all files, including the hidden files in the folder, use the -a or –all option with ls.
This will display all the files, including the two implied folders: . (current directory) and .. (parent folder). If you want to omit the display of these two folders, then use the -A or –almost-all option.
This is quite useful, if you are using the output of the command as input to some other script. You probably do not the script to loop in the current folder (depending on the script).
If you want to display only the hidden files, then you will need to specify a regular expression with the ls command., the following will display just the hidden file and folders.
The -d option is to ensure that the directory contents are not printed out for each directory in the list.
dir command
Another popular command used to display directory contents is dir. Almost all options for dir is the same as ls, which means everything that was shown for ls in the previous section will work for dir as well.
will display all files, hidden files and the implied folders (. and ..).
will display all files, folders including the hidden folders but excluding both . and ..
will display just the hidden files and hidden folders.
KDE File Manager (dolphin)
The default file manager in KDE is Dolphin. The default setting in Dolphin is not to display hidden or dot files. There are couple of different ways you can enable the option here.
The easiest is probably the keyboard shortcut Alt+. (Alt and dot). You can easily enable the display and disable it again using the same shortcut.
The other option is using the menu option. Click on the Hamburger icon on the menu bar (for Settings/Configuration). In the drop down menu, you will see the option named Show Hidden Files. Click and select it on it to enable the display of hidden files.
You can leave that option selected, if you want to always display the hidden files. The other commonly used file manager is Konqueror, which uses embedded dolphin to display the file system, as well.
Gnome File Manager (files or nautilus)
The default file manager in Gnome on most distros is Gnome Files. It was formerly known as Nautilus. The keyboard shortcut to display hidden files in Nautilus is Ctrl+H. This shortcut can be used to toggle the display of dot files.
The other option is to change it in the configuration. Open Edit -> Preferences and navigate to the Views tab. Select the option Shown hidden and backup files. In modern or latest versions, this option is in Files -> Preferences menu.
Xfce File Manager (thunar)
Xfce is a popular light weight desktop environment, and the default file manager is thunar. The keyboard shortcut is display hidden files is again Ctrl+H just as with Gnome File Manager.
You can find the option with in the menu as well, as with other file managers. Click on View in the menu bar, and select Show Hidden Files option.
Midnight Commander
Midnight Commander is a command line based file manager which has a loyal following. The keyboard shortcut to display dot files here is Alt + . (Alt-Period).
There is also a configuration setting with in Panel Options. Open Options from the menu and then Panel Options. Select the option Show Hidden Files.
No matter which file manager you are using, there should be an option to display hidden files. Most times, it is disabled by default and as it should be. You can try first by right clicking and checking the context menu. The next place to check is either the Settings or Preferences dialog which is often in the Edit or View menu.
Источник










