- Linux Command: Show Mounted Hard Drives Partition
- Examples
- Как посмотреть точки монтирования Linux
- Что такое точки монтирования в Linux?
- Как посмотреть точки монтирования?
- Выводы
- How do I show unmounted drives in Linux
- How do I show unmounted drives in Linux
- How to show Unmounted drives using the “lsblk” command:
- How to show Unmounted drives using the “fdisk” command:
- How to show Unmounted drives using the “parted” command:
- How to show Unmounted drives using the “blkid” command:
- Conclusion:
- About the author
- Wardah Batool
- How to List Mounted Drives on Linux
- 1) Listing from /proc using cat command
- 2) Using Mount Command
- 3) Using df command
- 4 ) Using findmnt
- Conclusion
Linux Command: Show Mounted Hard Drives Partition
[a] df command – Shoe file system disk space usage.
| Tutorial details | |
|---|---|
| Difficulty level | Easy |
| Root privileges | No |
| Requirements | Linux |
| Est. reading time | N/A |
[b] mount command – Show all mounted file systems. [c] /proc/mounts or /proc/self/mounts file – Show all mounted file systems.
Examples
Open a terminal or login using ssh into the remote server and type the following command:
$ cat /proc/mounts
OR
$ cat /proc/self/mounts
Sample outputs:
Type the mount command as follows to get same information:
Type the df command shows more human readable output:
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
Fig.01: df command in action
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
| Category | List of Unix and Linux commands |
|---|---|
| Documentation | help • mandb • man • pinfo |
| Disk space analyzers | df • duf • ncdu • pydf |
| File Management | cat • cp • less • mkdir • more • tree |
| Firewall | Alpine Awall • CentOS 8 • OpenSUSE • RHEL 8 • Ubuntu 16.04 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Linux Desktop Apps | Skype • Spotify • VLC 3 |
| Modern utilities | bat • exa |
| Network Utilities | NetHogs • dig • host • ip • nmap |
| OpenVPN | CentOS 7 • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Debian 8/9 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Package Manager | apk • apt |
| Processes Management | bg • chroot • cron • disown • fg • glances • gtop • jobs • killall • kill • pidof • pstree • pwdx • time • vtop |
| Searching | ag • grep • whereis • which |
| Shell builtins | compgen • echo • printf |
| Text processing | cut • rev |
| User Information | groups • id • lastcomm • last • lid/libuser-lid • logname • members • users • whoami • who • w |
| WireGuard VPN | Alpine • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Firewall • Ubuntu 20.04 |
Comments on this entry are closed.
command not found…
Which command will display the number of devices in my system (routers/switches/AP)
I purchased the Hp 15-n018 model laptop, when i checking with vendor they said will not support for Linux operating and i didn’t found the driver in internet….. i able found in win 8 and 8.1….
But am very interested in Linux operating system…. any one can please help me where i can the driver.
Sudinhar: it really depends on what driver you’re talking about for which specific device and for which specific Linux distribution.
The laptop itself may require any number of drivers, including HD, CD/DVD, sound, display, network, etc.
Many Linux distributions come with drivers for a wide variety of systems & devices, and you can generally get Linux up & running on just about anything these days with enough patience.
You can generally repartition your hard drive without losing any data using tools provided in distribution ISOs/DVDs & install Linux as a dual boot without fear of not being able to also use Windows if necessary as a backup.
I first installed Linux on a laptop back in the 90s, and it was difficult to get all the drivers but I did eventually & it worked ok.
These days it’s usually much simpler and any up to date Linux distribution should run just fine on your laptop with a little setup & TLC.
As a side note, I’d like to thank the author of this article, the commands worked as advertised & provided the information I required.
Linux has a long history of not “playing well” with laptops, and unless you get a laptop that is “certified” to run with Linux, you’re bound to have headaches. Something else you might try is keeping the laptop as is, and installing Virtual Box, by Sun (Oracle?) I believe it’s available on-line at no charge. This is a VM system, which will allow you to load a real copy of Linux, as it emulates a real computer. Personally, I use VMware Workstation (I’ve had it for years, but it’s a commercial product) which does the same thing, but I’ve heard nothing but good things about Virtual Box. You can then launch Linux in a window, and it’s a “real” linux version, which you will install from the distribution ISO.
Let’s say I want to display on the i3status bar whether a device/share is mounted.
How would that be accomplished?
I’m kind of new to i3, but as of what I’ve found online about the wm, it is a matter of finding the right parameter on i3status or i3blocks (whichever you use).
Источник
Как посмотреть точки монтирования Linux
Одно из самых заметных отличий Linux от Windows, это то, что операционная система позволяет пользователям прозрачно управлять монтированием разделов диска. Это позволяет гибким образом настроить структуру каталогов, использовать несколько файловых систем, где каждая будет выполнять свое предназначение.
Благодаря такой возможности, вы можете переустановить операционную систему и не потерять пользовательские файлы, обращаться к параметрам ядра с помощью каталогов /proc и /sys, а к блочным устройствам с помощью каталога /dev. В этой статье мы разберемся что такое точки монтирования, а также как посмотреть точки монтирования в Linux.
Что такое точки монтирования в Linux?
Чтобы понять как тут всё происходит, давайте проведём аналогию. Допустим, у вас есть большое поле и вы на нём хотите посадить картошку. Но выращивать вы хотите несколько сортов. Поэтому вы делите поле на несколько участков и на каждом из них садите нужный сорт. Когда приходит время собирать урожай, независимо от сорта картошку надо выкопать и вывезти, а к полю идёт только одна дорога и вся полученная картошка будет вывезена именно по ней не зависимо от того, с какого участка она была собрана.
Допустим, у вас есть один большой жесткий диск, на который надо записать данные. Это наше поле. Но вам надо файловая система без журналирования для каталога /boot, отдельная файловая система для корня и для /home. Поэтому жесткий диск разбивается на разделы. Дальше эти разделы надо отформатировать в нужную файловую систему. Это аналогия сорта картошки. А монтирование — это аналогия дороги, по которой картошку вывозят с поля. На каком бы разделе диска или части оперативной памяти не располагались данные, получить к ним доступ вы сможете только с помощью корневого каталога /. Все разделы монтируются сюда, если не к самому корню, то в одну из папок. Такая папка и называется точкой монтирования и её содержимое во время монтирования заменяется на содержимое раздела.
Как посмотреть точки монтирования?
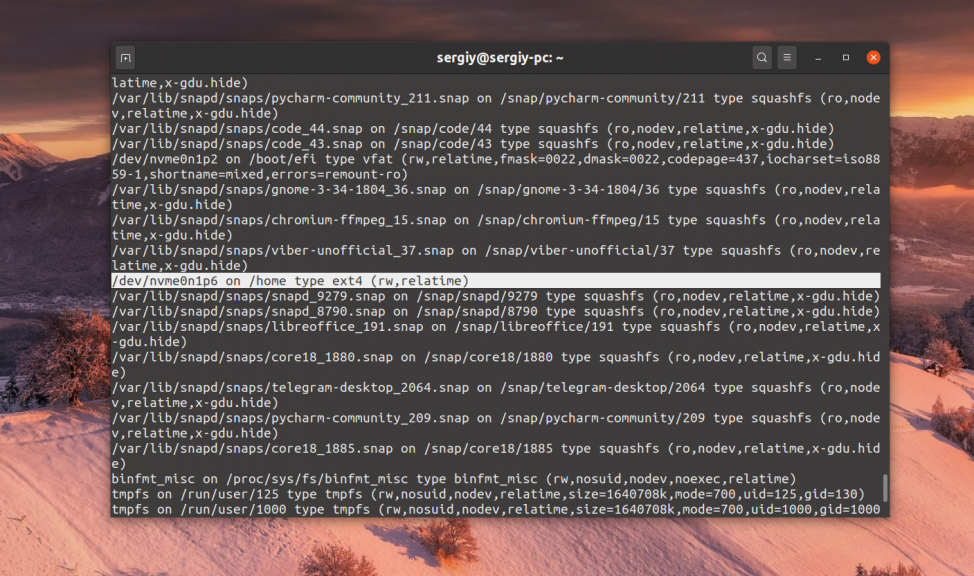
Для просмотра точек монтирования можно использовать команду mount. Её надо запустить без параметров:
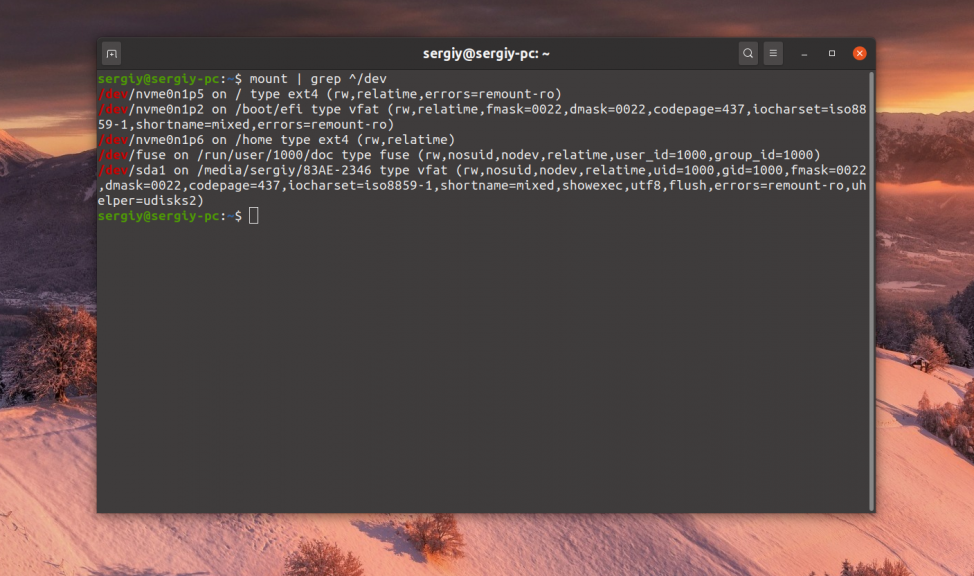
С появлением технологии snap и flatpack, точки монтирования Linux слегка засорены монтированием различных snap пакетов и их содержимого к файловой системе, но всё же здесь можно разобрать и смонтированные жесткие диски. Чтобы отфильтровать только жесткие диски используйте утилиту grep:
mount | grep ^/dev
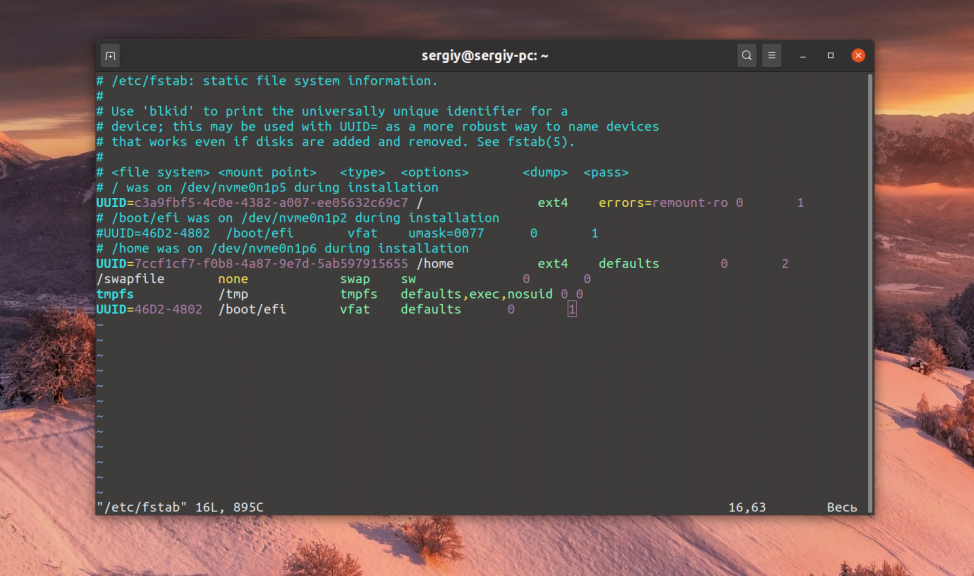
Не только посмотреть, но и настроить точки монтирования можно с помощью файла /etc/fstab. Здесь перечислены все разделы диска, которые монтируются к системе.
Более подробно о его настройке я писал в этой статье.
Выводы
Из этой статьи вы узнали что такое точки монтирования Linux, а также как их посмотреть и настроить. А что вы думаете по поводу них? Удобнее ли это чем в Windows? Напишите в комментариях!
Источник
How do I show unmounted drives in Linux
Multiple types of disks can be mounted, such as USB, flash memory disk, external hard drives, etc. When a disk or drive is unmounted, it prevents the data from the device.
In the Linux system, there are several mounted and unmounted devices. The mount command helps to mount while the umount command unmount the storage drives or filesystem.
How do I show unmounted drives in Linux
There are several ways to address the list of unmounted drives.
Let’s check how we can do it:
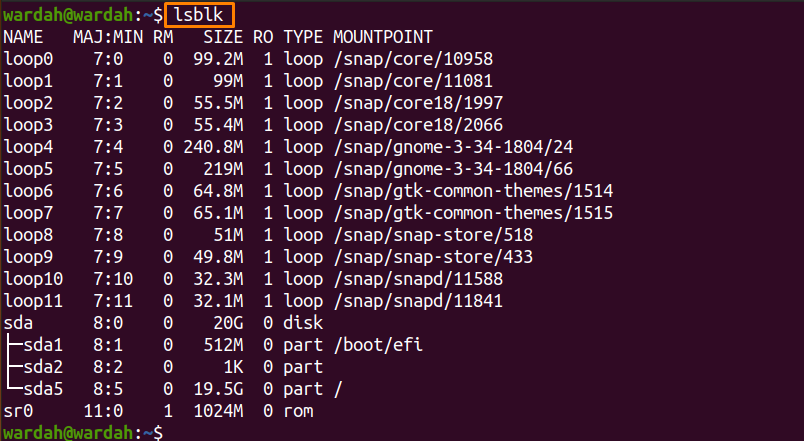
How to show Unmounted drives using the “lsblk” command:
The “lsblk” command-line tool is used to list down information about all the present or defined block devices.
To show unmounted drives, open the terminal and type:
How to show Unmounted drives using the “fdisk” command:
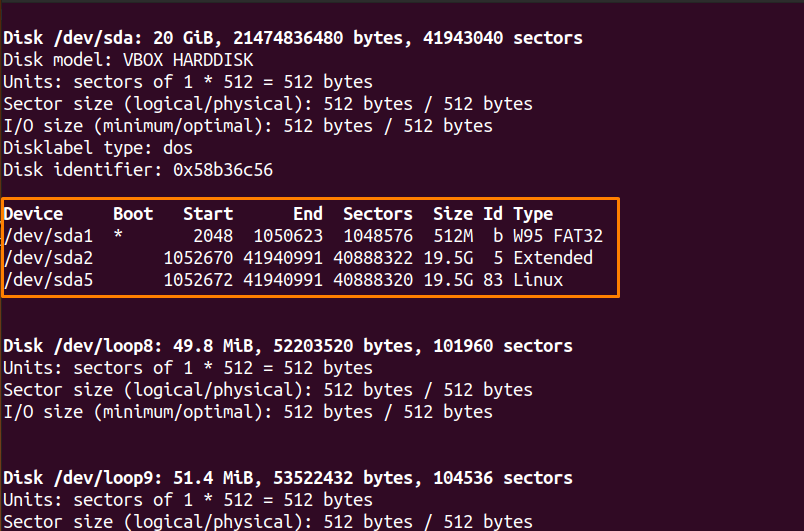
The format disk or fdisk is a Linux menu-driven command-line tool to create and utilize the disk partition table. Use the “-l” option to read data from the /proc/partitions file and display it.
You can also specify the disk name with the fdisk command.
To show the partition table of all the devices, use the following command:
How to show Unmounted drives using the “parted” command:
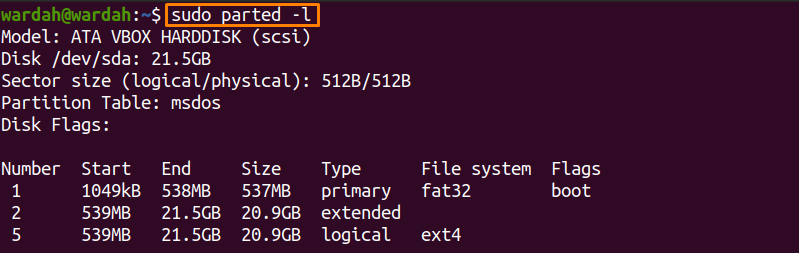
The “parted” command-line utility is popular for managing the partitions of a hard disk. It helps the user to shrink, extend, add or delete the partition according to the requirement.
Use the “parted” command to show unmounted drives as well:
How to show Unmounted drives using the “blkid” command:
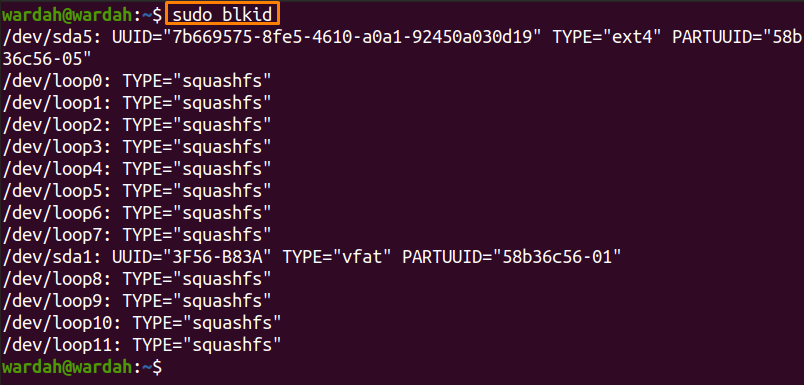
The “blkid” command-line utility works with the libblkid library that contains block type information.
To display block device information using the “blkid” command tool, use:
Conclusion:
Your device may contain mounted and unmounted devices, which means some files or drives are accessible, and some are not. The unmount drives are not accessible for the system even if they cannot transfer the files or connect with other system files.
To show the unmounted devices, we have multiple command-line tools. The guide has mentioned the most straightforward approaches to get them.
About the author
Wardah Batool
I am a Software Engineer Graduate and Self Motivated Linux writer. I also love to read latest Linux books. Moreover, in my free time, i love to read books on Personal development.
Источник
How to List Mounted Drives on Linux
In this tutorial, I will show you the different ways to list mounted drives on Linux. We can use mount, findmnt, and df commands to list mounted device any Linux distribution like Ubuntu or Centos.
In Linux, mount command mounts a storage device or filesystem, and let’s go through commands that can display all those mounts.
1) Listing from /proc using cat command
To list mount points you can read contents of the file /proc/mounts.
In the following example, I have used cat command to read the /proc/mounts file:
2) Using Mount Command
You can use mount command to list mount points. When you run mount command without any options it will list mount points.
3) Using df command
You can use df command to list mount points.
The following command shows the output of df with -aTh option:
You can use -t followed by filesystem type (say ext3, ext4, nfs) to display respective mount points. For examples below df command display all NFS mount points.
4 ) Using findmnt
Findmnt is a powerful tool to find mounted filesystems. This command comes with lots of options to list mount filesystems.
The following command print all mounted filesystems:
Print mount point by specific filesystem type:
Search and list fstab contents:
Display all /etc/fstab file and converts LABEL= and UUID= tags to the real device names:
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we learned commands to list mounted drives or filesystems on Linux. I hope you enjoyed reading and please leave your suggestion in the comment section.
Источник