- How to Skip the First Line of a File Using `awk`
- Create a text file
- Example 1: Skip the first line of a file using NR and the ‘>’ operator
- Example 2: Skip the first line by using NR and the ‘!=’ operator
- Example 3: Skip the first line of a file by using a conditional statement
- Example 4: Print the book names from the file but skip the first line
- Example 5: Format the file content after skipping the first line
- Example 6: Print the book names after skipping the first line using NR and NF
- Example 7: Print the formatted author names after skipping the first line
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Fahmida Yesmin
- awk / cut: Skip First Two Fields and Print the Rest of Line
- Old solution
- How to create HTML table using awk
- Linux / Unix: Display First Line of a File
- Syntax
- Example: Displaying the first line
- A note about sed command
How to Skip the First Line of a File Using `awk`
There are various uses of the `awk` command in Linux. For example, it can be used to print the content of a text file. The first line of many text files contains the heading of the file, and sometimes, the first line must be skipped when printing the content of the file. In this tutorial, we will show you how to accomplish this task by using the `awk` command.
Create a text file
To follow along with this tutorial, create a tab-delimited text file named booklist.txt with the following content. This file contains a list of books with their corresponding authors. In this tutorial, we will show you how to print different parts of this file after skipping the first line.
Cybersecurity with bash Paul Troncone, Carl Albing
Command Line Kung Fu Jason Cannon
Linux Command Line Travis Booth
Bash in easy steps Mike McGrath
Unix in easy steps Mike McGrath
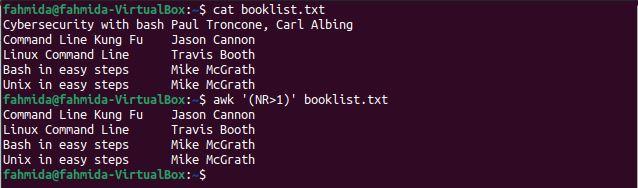
Example 1: Skip the first line of a file using NR and the ‘>’ operator
The NR variable indicates the number of records in a file. The following `awk` command uses the NR variable to skip the first line of a file. The value of NR is 1 for the first line. The following command will print lines for which the NR value is greater than 1.
$ awk ‘(NR>1)’ booklist.txt
The following output will be produced after running the above commands. The output includes all lines other than the first line of the file.
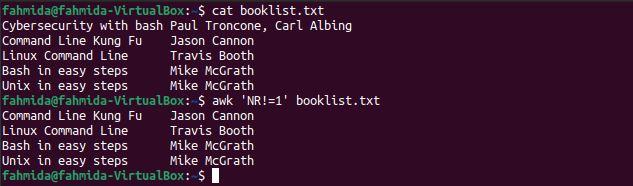
Example 2: Skip the first line by using NR and the ‘!=’ operator
The following `awk` command is similar to that in the previous example. However, the ‘!=’ comparison operator is used here instead of ‘>’.
$ awk ‘NR!=1’ booklist.txt
The following output will be produced after running the above commands. The output shows all lines other than the first line of the file.
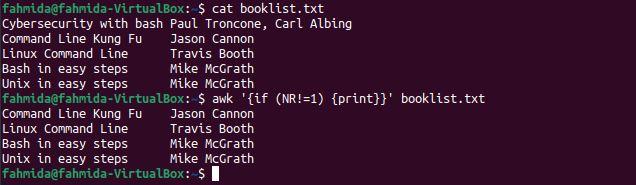
Example 3: Skip the first line of a file by using a conditional statement
The following `awk` command will print the lines of the file if the if statement is true. Here, the if statement will be true only when the NR value does not equal 1.
The following output will be produced after running the above commands. The output includes all lines except the first line of the file.
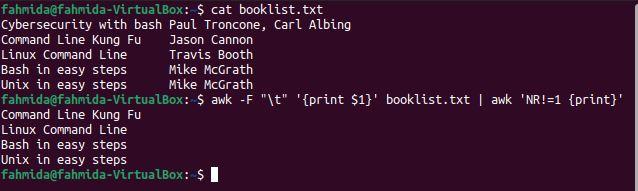
Example 4: Print the book names from the file but skip the first line
Two `awk` commands are used in this example to print all book names except the first. The `awk` command will read the first column from the file based on the field separator (\t) and send the output to the second `awk` command. The second `awk` command will print the desired output.
$ awk -F » \t » ‘
The following output will be produced after running the above commands. The output shows all the book names except for that of the first book.
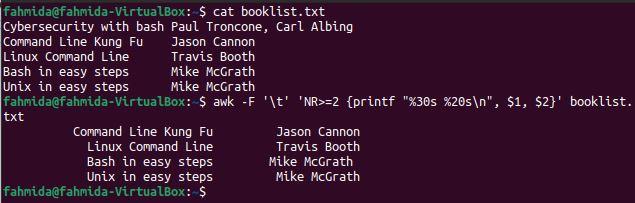
Example 5: Format the file content after skipping the first line
The ‘-F’ option, NR variable, and printf function are used in the following `awk` command to generate formatted output after skipping the first line. The command will divide the file content into columns based on \t, and printf will print the first and second columns when the NR value is at least 2.
The following output will be produced after running the above commands. The output shows the formatted content of the file, excluding the first line of the file.
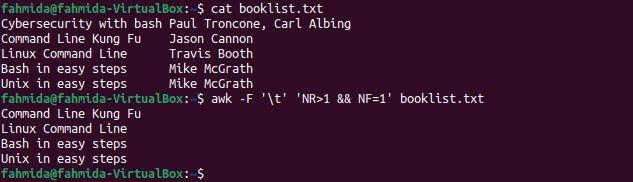
Example 6: Print the book names after skipping the first line using NR and NF
The following `awk` command uses the ‘-F’ option and NR and NF to print the book names after skipping the first book. The ‘-F’ option is used to separate the content of the file base on \t. NR is used to skip the first line, and NF is used to print the first column only.
$ awk -F ‘\t’ ‘NR>1 && NF=1’ booklist.txt
The following output will be produced after running the above commands. The output includes all the book names in the file except for that of the first book.
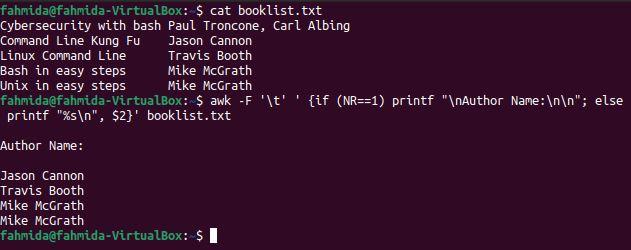
Example 7: Print the formatted author names after skipping the first line
The following `awk` command uses the ‘-F’ option and a conditional statement to print the author names after skipping the first line. Here, the NR value is used in the if condition. Here, “Author Name:\n\n” will be printed as the first line instead of the content from the first line. The author’s names from the file will be printed for the other values of NR.
The following output will be produced after running the above commands. The output shows the text, “Author Name:” with a newline, and all author names are printed except the first one.
Conclusion
The first line of a file can be skipped by using various Linux commands. As shown in this tutorial, there are different ways to skip the first line of a file by using the `awk` command. Noteably, the NR variable of the `awk` command can be used to skip the first line of any file.
About the author
Fahmida Yesmin
I am a trainer of web programming courses. I like to write article or tutorial on various IT topics. I have a YouTube channel where many types of tutorials based on Ubuntu, Windows, Word, Excel, WordPress, Magento, Laravel etc. are published: Tutorials4u Help.
Источник
awk / cut: Skip First Two Fields and Print the Rest of Line
Old solution
My old solution to skip first two fileds and print the rest of line:
echo ‘This is a test’ | awk ‘
You can also use substr:
substr(s, i [, n])
It return the at most n-character substring of s starting at i. If n is omitted, use the rest of s. So:
awk ‘
You can also use the cut command:
echo ‘This is a test’ | cut -d ‘ ‘ -f3-
cut -d ‘ ‘ -f3-
Finally, process the file using bash while loop:
How to create HTML table using awk
Say you have data as follows in a text file called data.txt:
To create html table code run:
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
| Category | List of Unix and Linux commands |
|---|---|
| Documentation | help • mandb • man • pinfo |
| Disk space analyzers | df • duf • ncdu • pydf |
| File Management | cat • cp • less • mkdir • more • tree |
| Firewall | Alpine Awall • CentOS 8 • OpenSUSE • RHEL 8 • Ubuntu 16.04 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Linux Desktop Apps | Skype • Spotify • VLC 3 |
| Modern utilities | bat • exa |
| Network Utilities | NetHogs • dig • host • ip • nmap |
| OpenVPN | CentOS 7 • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Debian 8/9 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Package Manager | apk • apt |
| Processes Management | bg • chroot • cron • disown • fg • glances • gtop • jobs • killall • kill • pidof • pstree • pwdx • time • vtop |
| Searching | ag • grep • whereis • which |
| Shell builtins | compgen • echo • printf |
| Text processing | cut • rev |
| User Information | groups • id • lastcomm • last • lid/libuser-lid • logname • members • users • whoami • who • w |
| WireGuard VPN | Alpine • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Firewall • Ubuntu 20.04 |
Comments on this entry are closed.
thanks.. this is the most elegant, simplest and my preferred way of doing this. The other way of doing this is with awk’s NF variable in a for-loop. This non-trivial situation is best explained in http://awk.freeshell.org/RangeOfFields.
Very useful, thanks. I went for the first Awk option to trim the permissions and filesize off the output of ls -l
Didn’t know about cut. Time to read the man page! 🙂
The awk method works perfectly well if the first three fields are unique. However, if your string was as follows:
“This This This will break the awk method”
…. the output will be unchanged since when it indexes the third field, it finds the first.
The cut method works perfectly well as long as your fields are not separated by more than a single space. It treats multiple spaces as separate fields.
Awk… how I love thee.
If in 9th field($9) there is sth like: A/B/C and one needs C. how can we extract C and put it in output?
I see this thread is a few years old, but I could not resist adding for the sake of searching the internet for a simple (but less elegant) answer.
awk ‘< $1=""; $2=""; print>‘ filename
The above simply uses the default field separator, replaces the content of the first two fields with “nothing”, and prints the modified line. No need to use redirection, awk expects a file as input.
Note1: The field separators are left in tact, so your output lines begin with two blank spaces. This can be compensated for using substr($0,3) behind the print command.
Note2: The advantage to this syntax, is “any” field(s) may be ommitted, not just the first X number of fields.
Excellent Mr. danliston , this was easy and powerful.
Appreciate your comments.
Thanks. The faq has been updated.
The with this approach is that it prints leading spaces – the substr() way doesn’t.
Источник
Linux / Unix: Display First Line of a File
Syntax
| Tutorial details | |
|---|---|
| Difficulty level | Easy |
| Root privileges | No |
| Requirements | None |
| Est. reading time | 1m |
head -1 filename
Example: Displaying the first line
Open the Terminal application and type the following command:
$ head -1 foo.txt
The following example will show first 3 lines from /etc/passwd file:
$ head -3 /etc/passwd
Sample outputs:
To print first 3 lines and number lines of files use nl command as follows:
$ head -3 /etc/passwd | nl
Sample outputs:
A note about sed command
You can use sed command as follows:
$ sed -n 1p foo.txt
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
For more information see man pages: nl(1).
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
Источник