- Команда source в Bash
- Синтаксис команды source
- Примеры команды source
- Функции поиска
- Файл конфигурации Bash
- Выводы
- Команда Source в Bash
- Bash Source Command
- Команда source читает и выполняет команды из файла, указанного в качестве аргумента в текущей среде оболочки. Полезно загружать функции, переменные и файлы конфигурации в сценарии оболочки.
- Синтаксис исходной команды
- Примеры исходных команд
- Функции поиска
- Конфигурационный файл Bash
- Вывод
- source command in Linux with Examples
- What is Source Command in Linux and How Does it Work?
- How does source command work?
- Overview of Variables
- Environment variables vs shell Variables
- Source vs Bash
- Refresh environment variables with source command
- Source Command in Linux
- Syntax for source command
- How to use source command
- 1. Refresh your current shell environment
- 2. Execute a shell script in the context of the current shell environment
- 3. Import a shell function
- 4. Read variables from a shell script
- 5. Read and execute commands
- 6. Pass arguments to functions
- Conclusion
Команда source в Bash
source команда считывает и выполняет команды из файла, указанного в качестве аргумента в текущей среде оболочки. Полезно загружать функции, переменные и файлы конфигурации в сценарии оболочки.
source — это оболочка, встроенная в Bash и другие популярные оболочки, используемые в операционных системах Linux и UNIX. Его поведение может немного отличаться от оболочки к оболочке.
Синтаксис команды source
Синтаксис source команды следующий:
- source и . (точка) — это та же команда.
- Если FILENAME не является полным путем к файлу, команда будет искать файл в каталогах, указанных в $PATH среды $PATH . Если файл не найден в $PATH , команда будет искать файл в текущем каталоге.
- Если заданы какие-либо ARGUMENTS , они станут позиционными параметрами для FILENAME .
- Если FILENAME существует, source выхода source команды равен 0 , в противном случае, если файл не найден, он вернет 1 .
Примеры команды source
В этом разделе мы рассмотрим несколько основных примеров использования source команды.
Функции поиска
Если у вас есть сценарии оболочки, использующие те же функции, вы можете извлечь их в отдельный файл, а затем указать этот файл в своих сценариях.
В этом примере мы создадим файл, который включает функцию bash, которая проверяет, является ли пользователь, запускающий скрипт, корневым, и если нет, он показывает сообщение и завершает скрипт.
Теперь в каждом скрипте, который должен запускаться только пользователем root, просто укажите файл functions.sh и вызовите функцию:
Если вы запустите приведенный выше сценарий как пользователь без полномочий root, он напечатает «Этот сценарий должен быть запущен от имени пользователя root» и завершится.
Преимущество этого подхода заключается в том, что ваши сценарии будут меньше и более читабельны, вы можете повторно использовать один и тот же файл функции, когда это необходимо, а в случае, если вам нужно изменить функцию, вы отредактируете только один файл.
Файл конфигурации Bash
С помощью source команды вы также можете читать переменные из файла. Переменные должны быть установлены с использованием синтаксиса Bash, VARIABLE=VALUE .
Создадим тестовый файл конфигурации:
В вашем сценарии bash используйте команду source для чтения файла конфигурации:
Если вы запустите сценарий, результат будет выглядеть так:
Выводы
В этом руководстве вы узнали, как использовать встроенную команду source в сценариях оболочки.
Если у вас есть какие-либо вопросы или отзывы, не стесняйтесь оставлять комментарии.
Источник
Команда Source в Bash
Bash Source Command
Команда source читает и выполняет команды из файла, указанного в качестве аргумента в текущей среде оболочки. Полезно загружать функции, переменные и файлы конфигурации в сценарии оболочки.
source это оболочка, встроенная в Bash и другие популярные оболочки, используемые в операционных системах Linux и UNIX. Его поведение может немного отличаться от оболочки к оболочке.
Синтаксис исходной команды
Синтаксис source команды следующий:
- source и . (точка) — это одна и та же команда.
- Если FILENAME путь к файлу не полный, команда выполнит поиск файла в каталогах, указанных в $PATH переменной среды . Если файл не найден в $PATH команде, будет выполнен поиск файла в текущем каталоге.
- Если ARGUMENTS они заданы, они станут позиционными параметрами для FILENAME .
- Если FILENAME существует source код завершения команды 0 , в противном случае, если файл не найден, он вернется 1 .
Примеры исходных команд
В этом разделе мы рассмотрим некоторые основные примеры использования source команды.
Функции поиска
Если у вас есть сценарии оболочки, использующие те же функции, вы можете извлечь их в отдельный файл, а затем получить этот файл в своих файлах.
В этом примере мы создадим файл, который включает в себя функцию bash, которая проверяет, является ли пользователь, выполняющий сценарий, пользователем root, и, если нет, показывает сообщение и завершает работу сценария.
Преимущество этого подхода состоит в том, что ваши скрипты будут меньше и более читабельными, вы можете повторно использовать один и тот же файл функций при необходимости, и в случае, если вам нужно изменить функцию, вы отредактируете только один файл.
Конфигурационный файл Bash
С помощью source команды вы также можете читать переменные из файла. Переменные должны быть установлены с использованием синтаксиса Bash VARIABLE=VALUE .
Давайте создадим тестовый файл конфигурации:
В вашем bash-скрипте используйте source команду для чтения файла конфигурации:
Если вы запустите скрипт, результат будет выглядеть так:
Вывод
Из этого руководства вы узнали, как использовать source встроенную команду в сценариях оболочки.
Источник
source command in Linux with Examples
source is a shell built-in command which is used to read and execute the content of a file(generally set of commands), passed as an argument in the current shell script. The command after taking the content of the specified files passes it to the TCL interpreter as a text script which then gets executed. If any arguments are supplied, they become the positional parameters when filename is executed. Otherwise, the positional parameters remain unchanged. The entries in $PATH are used to find the directory containing FILENAME, however if the file is not present in $PATH it will search the file in the current directory. The source command has no option and the argument is the file only.
Syntax:
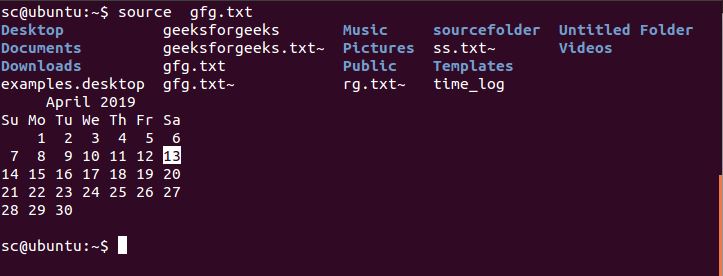
Example 1: To pass gfg.txt as an argument which is stored in the home directory and contain list of command i.e. ls, date and time. Each command enlisted in the file will be executed line by line.
Example 2: To pass a path_name of a file as an argument where, /home/sc/sourcefolder/ is the file directory here. The content of the file is written below:
echo ” Hello, Welcome to Geeksforgeeks”
echo “current directory is:”
pwd
echo “Date is:”
date
Источник
What is Source Command in Linux and How Does it Work?
The source command executes commands from a file in the current shell. It can also be used to refresh environment variables and to be honest, the primary use of source command is to refresh environment variables.
You can also use . (dot) instead of source command like this:
How does source command work?
The syntax of this command is simple, but understanding it requires a slightly deeper look at some Linux concepts. If you’re brand new to Linux or programming, you might only have a vague idea about what a variable is.
If you’ve heard this term, but don’t know exactly what it means, that is okay! Remember, all of us start from exactly the same place. No one suddenly wakes up in the morning being a system administrator or programmer.
I will give a brief explanation before moving on.
You may skip to the next header if you’re already familiar with how to create variables in bash.
Overview of Variables
You can open any bash terminal and create new variables. A variable can be thought of as a placeholder that can be used to point your system to a piece of information (letters, numbers or symbols).
Let’s look at an example. I am going to make a new variable called name and I’m going to assign the value Christopher.
In bash, this is done using the formula: variable_name=your_variable. Do not add any spaces between = symbol and your text.
What happens if I just type the variable name?
If you forget this symbol, bash will return the text that you’ve entered. Here, I tell it to echo, or print, “name”. Without the $ symbol, bash does not recognize that you want to use the variable you’ve created.
Your variable will be inserted where it is called. So I can also include it in a sentence like this:
There are many things you can do with variables, but I’m hoping that primer will be enough to allow anyone reading this to understand how they work.
Environment variables vs shell Variables
For the next key to understanding source command, let’s talk about persistence. This is an easy way to think about the difference between shell and environmental content. You might also think of it in terms of “portability” depending on the context.
Simply put, if you create a variable in a terminal shell, it will be lost once you exit that shell.
In contrast, an environmental variable has persistence in your operating system. These variables typically use all caps to distinguish themselves.
An example of this is your username which is known by the OS as $USER.
Okay, so you spent quite a bit of time going over the differences between environment and shell variables. What does that have to do with source? Everything, really.
Otherwise there would be no difference in running source and bash. In order to illustrate this point, I have one more demonstration lined up.
Source vs Bash
If you’ve been around Linux for a little while, you may have encountered these commands and thought they did the same thing. After all, both commands can be used to execute a script.
Source works in the current shell, unlike running bash which creates a new shell. This isn’t obvious since no new windows are displayed.
If you’re following along, this one will require you to write a very simple script (let’s call it echo.sh) that looks like this:
Before you do anything else in your terminal, assign your name to the variable name.
Next, I am going to show you what happens when you try all 3 commands in the same terminal that you assigned your variable in.
As you can see, your local variable was not recognized when you executed your script via bash.
Refresh environment variables with source command
Source can also be used to update environmental variables in the current shell. A common application for this task is updating your bash profile in the current shell.
A user may want to modify their bash profile to, say, create an alias. Normally, once you save the configuration you will need to open a new terminal window for the changes to take place.
Running this will refresh the settings in your current shell without forcing you to open a new terminal.
Conclusion
We hope that you enjoyed this tutorial on the source command. As always, please let us know your thoughts in the comment section. If you enjoyed this post please share it on social media using the buttons below.
Источник
Source Command in Linux
The source command is a built-in shell command used to read and execute commands from a file inside the current shell session. The source command is commonly used to retain/change the environment variable in the current shell. In short, sourcing a script will run execute commands in the current shell.
The source command is useful for:
- Refreshing your current shell environment
- To execute a shell script in the context of the current environment
- To import a shell function in your script
- Read variables from a shell script
Syntax for source command
The syntax for this builtin shell command is human readable. It takes a file and if arguments are provided they serve as positional parameters for the script being passed.
The . (dot) can also be used as an alternative for source command.
How to use source command
Here I explain some practical examples where you can apply source command.
1. Refresh your current shell environment
As a user you can define an alias in your current shell environment. To define one for ls -l type:
Although the above list the files in the current directory in the long format, it works only for the current shell session. To make the changes permanently, open the
/.bashrc file and add:
To refresh the current shell environment type:
2. Execute a shell script in the context of the current shell environment
A shell script is not aware of the variables you define as a user in your current shell environment. The source command can be used to execute your shell script in the context of the current session.
To define a temporary variable type:
To create a custom script type:
Save the file. To execute it in the context of the current shell session type:
The output is shown below.
3. Import a shell function
To define a custom shell script type:
Save the above as script.sh.
To import the function of the above script in your current shell session, type:
To use the foo function type:
The output is shown below.
4. Read variables from a shell script
To create a shell script with some variables, type:
To read the variables within another shell script type:
The output should be:
5. Read and execute commands
Source command can read and execute commands from a file. Lets have a text file with a set of commands.
For example file commands.txt has the following content:
The output of source :
6. Pass arguments to functions
This section describes how to pass the parameter to the function and same function we can re-use via source command.
Conclusion
Source command evaluvated script in the current shell whereas exec command runs in a new shell.
Through this article, you learned four practical examples of the source command. Although all of them are useful, the most important one for you as a user is the first one.
Источник