- 15 simple TOP command examples on Linux to monitor processes
- Linux TOP command
- Note your «top» command variant
- 1. Display processes
- 2. Sort by Memory/Cpu/Process ID/Running Time
- 3. Reverse the sorting order — ‘R’
- 4. Highlight the sorted column with bold text — ‘x’
- 5. Highlight sorted column background color ‘b’
- 6. Change the update delay — ‘d’
- 7. Filter or Search processes — ‘o’/’O’
- 8. Display full command path and arguments of process — ‘c’
- 9. View processes of a user — ‘u’/’U’
- 10. Toggle the display of idle processes — ‘i’
- 11. Hide/Show the information on top — ‘l’, ‘t’, ‘m’
- 12. Forest mode — ‘V’
- 13. Change the number of processes to display — ‘n’
- 14. Display all CPU cores — ‘1’
- 15. Show/Hide columns ‘f’
- 16. Batch mode
- 17. Split output in multiple panels — ‘A’
- Conclusion
- 10 thoughts on “ 15 simple TOP command examples on Linux to monitor processes ”
- Linux Top Source Code
- linux/builtin-top.c at master · torvalds/linux · GitHub
- The Top 3 Linux Lines Of Code Open Source Projects …
- Linux source code (v5.14.9) — Bootlin
- GitHub — soarpenguin/procps-3.0.5: linux command …
- The Best Linux Tutorials — Learn to Code — For Free
- top utility source code — LinuxQuestions.org
- How can I find the source code for linux commands? — …
- process monitor — Need the source code for top and …
- Linux Top Source Code Images — imageslink.org
- ‘top’ command source code. — LinuxQuestions.org
- Get Source Code for any Linux Command — The Geek …
- Source code for Linux utilities and daemons — Server …
- 5 Best Free Code Editors for Ubuntu, Linux — Top List of …
- How to Install Software from Source Code in Linux .
- Best Linux Source Code Management Software | GetApp
- Linux Foundation «31 Billion Lines» Of Open Source …
- Best Command Line Games for Linux — Linux Hint
- Running Visual Studio Code on Linux
- How to edit Linux source code? — Stack Overflow
- Best Free and Open Source Software — LinuxLinks
15 simple TOP command examples on Linux to monitor processes
Linux TOP command
One of the most basic command to monitor processes on Linux is the top command. As the name suggests, it shows the top processes based on certain criterias like cpu usage or memory usage.
The processes are listed out in a list with multiple columns for details like process name, pid, user, cpu usage, memory usage.
Apart from the list of processes, the top command also shows brief stats about average system load, cpu usage and ram usage on the top.
This post shows you some very simple examples of how to use the top command to monitor processes on your linux machine or server.
Note your «top» command variant
Be aware that the top command comes in various variants and each has a slightly different set of options and method of usage.
To check your top command version and variant use the -v option
This post focuses on the top command coming from the procps-ng project. This is the version available on most modern distros like Ubunut, Fedora, CentOS etc.
1. Display processes
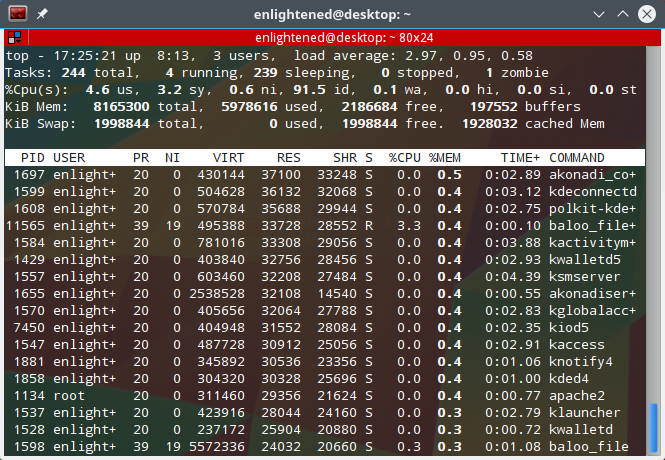
To get a glimpse of the running processes, just run the top command as is without any options like this.
And immediately the output would be something like this —
The screen contains a lot of information about the system. The header areas include uptime, load average, cpu usage, memory usage data.
The process list shows all the processes with various process specific details in separate columns.
Some of the column names are pretty self explanatory.
PID — Process ID
USER — The system user account running the process.
%CPU — CPU usage by the process.
%MEM — Memory usage by the process
COMMAND — The command (executable file) of the process
2. Sort by Memory/Cpu/Process ID/Running Time
To find the process consuming the most cpu or memory, simply sort the list.
Press M key ( yes, in capital, not small ) to sort the process list by memory usage. Processes using the most memory are shown first and rest in order.
Here are other options to sort by CPU usage, Process ID and Running Time —
Press ‘P’ — to sort the process list by cpu usage.
Press ‘N’ — to sort the list by process id
Press ‘T’ — to sort by the running time.
3. Reverse the sorting order — ‘R’
By default the sorting is done in descending order. Pressing ‘R’ shall reverse the sorting order of the currently sorted column
Here is the output sorted in ascending order of cpu usage. Processes consuming the least amount of cpu are shown first.
4. Highlight the sorted column with bold text — ‘x’
Press x, to highlight the values in the sort column with bold text. Here is a screenshot, with the memory column in bold text —
top command highlight column
5. Highlight sorted column background color ‘b’
After highlighting the sorted column with bold font, its further possible to highlight with a different background color as well. This is how it looks
Top command highlight column background
6. Change the update delay — ‘d’
The top command updates the information on the screen every 3.0 seconds by default. This refresh interval can be changed.
Press the ‘d’ key, and top will ask you to enter the time interval between each refresh. You can enter numbers smaller than 1 second as well, like 0.5. Enter the desired interval and hit Enter.
7. Filter or Search processes — ‘o’/’O’
You can filter the process list based on various criterias like process name, memory usage, cpu usage etc. Multiple filter criterias can be applied.
Press the ‘o’ or ‘O’ to activate filter prompt. It will show a line indicating the filter format like this —
Then enter a filter like this and hit Enter.
COMMAND=apache
Now top will show only those processes whose COMMAND field contains the value apache.
Here is another filter example that shows processes consuming CPU actively —
%CPU>0.0
See active filters — Press Ctrl+o to see currently active filters
Clear filter — Press ‘=’ key to clear any active filters
8. Display full command path and arguments of process — ‘c’
Press ‘c’ to display the full command path along with the commandline arguments in the COMMAND column.
9. View processes of a user — ‘u’/’U’
To view the processes of a specific user only, press ‘u’ and then top will ask you to enter the username.
Which user (blank for all)
Enter the desired username and hit Enter.
10. Toggle the display of idle processes — ‘i’
Press ‘i’ to toggle the display of idle/sleeping processes. By default all processes are display.
11. Hide/Show the information on top — ‘l’, ‘t’, ‘m’
The ‘l’ key would hide the load average information.
The ‘m’ key will hide the memory information.
The ‘t’ key would hide the task and cpu information.
Hiding the header information area, makes more processes visible in the list.
12. Forest mode — ‘V’
Pressing ‘V’ will display the processes in a parent child hierarchy. It looks something like this —
13. Change the number of processes to display — ‘n’
Lets say you want to monitor only few processes based on a certain filter criteria. Press ‘n’ and enter the number of processes you wish to display.
It will display a line saying —
Maximum tasks = 0, change to (0 is unlimited)
14. Display all CPU cores — ‘1’
Pressing ‘1’ will display the load information about individual cpu cores. Here is how it looks —
15. Show/Hide columns ‘f’
By default top displays only few columns out of many more that it can display. If you want to add or remove a particular column or change the order of columns, then press f
The fields marked * or bold are the fields that are displayed, in the order in which they appear in this list.
Navigate the list using up/down arrow keys and press ‘d’ to toggle the display of that field. Once done, press q to go back to the process list
The following output displays only PID, USER, CPU, MEMORY and COMMAND columns.
16. Batch mode
Top also supports batch mode output, where it would keep printing information sequentially instead of a single screen. This is useful when you need to log the top output for later analysis of some kind.
Here is a simple example that shows the Cpu usage at intervals of 1 second.
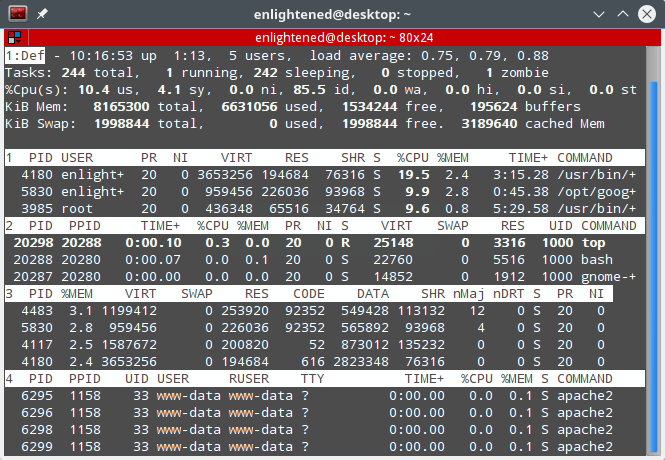
17. Split output in multiple panels — ‘A’
Each panel can be sorted on a different column. Press ‘a’ to move through the panels. Each panel can have a different set of fields displayed and different sort columns.
top command multiple panels
Conclusion
Top is a great commandline tool to check system resource usage and process details. Its often used on servers for monitoring and quick diagnosis.
If you are looking for something easier with a better user interface then try htop. Htop has a intuitive user interface, where you need not memorize keyboard shortcuts. Htop has onscreen instructions that guide you on how to use it.
A Tech Enthusiast, Blogger, Linux Fan and a Software Developer. Writes about Computer hardware, Linux and Open Source software and coding in Python, Php and Javascript. He can be reached at [email protected] .
10 thoughts on “ 15 simple TOP command examples on Linux to monitor processes ”
Nice article and great explanation.
if same user id is running multiple times how to delete all others except one.Please any one reply me fast.
exp
PID USER PR %cpu
QPD02201
QPD02201
QPD02201
QPD02201
A really top article!
Hi, thanks for the great article but I’m still looking for an answer for my case: It looks like that all the time. CPU load is around 45-50% all the time but if I add up the CPU usage of the services it never gets close… Why’s that?
Tasks: 251 total, 1 running, 250 sleeping, 0 stopped, 0 zombie
%Cpu0 : 50,1 us, 10,1 sy, 0,0 ni, 39,8 id, 0,0 wa, 0,0 hi, 0,0 si, 0,0 st
%Cpu1 : 55,7 us, 7,2 sy, 0,0 ni, 36,8 id, 0,0 wa, 0,0 hi, 0,2 si, 0,0 st
%Cpu2 : 35,6 us, 4,4 sy, 0,0 ni, 58,8 id, 0,0 wa, 0,0 hi, 1,2 si, 0,0 st
%Cpu3 : 36,7 us, 5,8 sy, 0,0 ni, 56,9 id, 0,0 wa, 0,0 hi, 0,6 si, 0,0 st
KiB Mem : 16242248 total, 12711832 free, 2071424 used, 1458992 buff/cache
KiB Swap: 3809276 total, 3809276 free, 0 used. 13807884 avail Mem
PID USER PR NI VIRT RES SHR S %CPU %MEM TIME+ COMMAND
9066 root 20 0 830468 35332 25632 S 2,2 0,2 2:19.18 metricbeat
5428 www-data 20 0 72168 27716 2520 S 1,2 0,2 3:28.49 kix.Daemon.pl
590 kopano 20 0 291488 41016 24640 S 0,6 0,3 1:27.52 kopano-search
581 kopano 20 0 355280 38644 18984 S 0,4 0,2 1:27.69 kopano-presence
7 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 0,2 0,0 0:31.24 rcu_sched
580 root 20 0 250116 4332 2508 S 0,2 0,0 0:01.37 rsyslogd
821 postgres 20 0 268376 6448 4688 S 0,2 0,0 0:00.07 postgres
1569 mysql 20 0 739704 114760 17024 S 0,2 0,7 0:38.78 mysqld
1802 root 20 0 392128 12028 6828 S 0,2 0,1 0:08.35 docker-containe
1875 root 20 0 3125288 23428 9428 S 0,2 0,1 0:40.27 slapd
2043 root 20 0 818760 70340 28176 S 0,2 0,4 0:37.41 named
2686 kdm 20 0 392288 59108 33904 S 0,2 0,4 0:29.23 kdm_greet
2871 root 20 0 4822492 437276 23464 S 0,2 2,7 2:01.74 java
9560 root 20 0 588668 69552 22952 S 0,2 0,4 0:40.12 packetbeat
10650 root 20 0 38144 3588 3012 R 0,2 0,0 0:04.37 top
Maybe it looks better like this
%Cpu0 : 50,1 us, 10,1 sy,
%Cpu1 : 55,7 us, 7,2 sy,
%Cpu2 : 35,6 us, 4,4 sy,
%Cpu3 : 36,7 us, 5,8 sy,
Источник
Linux Top Source Code
linux/builtin-top.c at master · torvalds/linux · GitHub
top-> hide_kernel_symbols = !top-> hide_kernel_symbols; break; case ‘ q ‘: case ‘ Q ‘: printf (» exiting. \n «); if (top-> dump_symtab) perf_session__fprintf_dsos (top-> session, stderr); ret = false; break; …
The Top 3 Linux Lines Of Code Open Source Projects …
The Top 3 Linux Lines Of Code Open Source Projects on Github. . Linux Code Cloc Projects (3) Counter Lines Of Code Projects (2) Cpp Cmake Lines Of Code Projects (2) Cmake Lines Of Code Projects (2) Java Lines Of Code Projects (2) Java Lines Of Code Sloc Projects (2)
Linux source code (v5.14.9) — Bootlin
Elixir Cross Referencer — Explore source code in your browser — Particularly useful for the Linux kernel and other low-level projects in C/C++ (bootloaders, C libraries. )
GitHub — soarpenguin/procps-3.0.5: linux command …
8/3/2013 · In the path of the program exist, use the command like: $chown root ping $chmod u+s ping (XXX: may be have security problem when the program is a virus or have some malicious code) …
The Best Linux Tutorials — Learn to Code — For Free
27/11/2019 · Linux is a name which broadly denotes a family of free and open-source software operating system distributions built around the Linux kernel. The Linux kernel, an operating system kernel which all Linux distributions use, was first released on September 17, 1991 by Linux Torvalds. Many Linux distributions use the word “Linux” in their name.
top utility source code — LinuxQuestions.org
9/10/2015 · ‘Top‘ utility floating point error: Ealric: Linux — Software: 4: 07-24-2003 06:18 AM: where can i get the source for the convert utility? o_helman: Programming: 2: 07-25-2002 08:09 AM: Where i can get the source code of the command ‘top‘ hustning: Programming: 2: 03-31-2002 12:06 AM: Where can I get source code of Linux shell utility? John Wu: Linux — General: 0: 04-17-2001 10:20 AM
How can I find the source code for linux commands? — …
There is an apt-get paramater that you can use to get packages source code: apt-get source. To get coreutils’ source code, use sudo apt-get source coreutils. It’s important to know that commands are nothing more than binaries placed in the paths of the PATH environment variable. These binaries are usually written in C.
process monitor — Need the source code for top and …
30/7/2010 · Need the source code for top and find the connection between top and /proc/ directory in linux. Ask Question Asked 11 years, 1 month ago. . I wanted the source code for top which I could not find anywhere also, i wanted a little more information on what exactly does the /proc directory contain.y I have seen it have a series .
Linux Top Source Code Images — imageslink.org
Linux Top Source Code Images! simple art pictures Download free images, photos, pictures, wallpaper and use it.
‘top’ command source code. — LinuxQuestions.org
19/1/2010 · top utility source code: puishor: Programming: 5: 10-09-2015 01:55 AM: source code for fg, bg command: mohit_parihar: Linux — General: 4: 12-10-2009 04:00 AM: Where can i get the source code of rm command: jaikris: Linux — Software: 6: 09-19-2009 12:04 AM: source code of ps command: sudeepghiya: Linux — General: 1: 09-21-2006 10:35 AM: Where i .
Get Source Code for any Linux Command — The Geek …
19/2/2010 · Example: Download the source code of the vim editor. Step 1: Go to the listing page of Lenny in packages.debian.org. Step 2: Click on the link that says ‘editors’. Step 3: Search and go to the vim editor page. Step 4: In the right side bar, select and download: vim_7.1.314.orig.tar.gz. Tweet. > …
Source code for Linux utilities and daemons — Server …
There is no single repository containing all of the source code for every distribution of Linux. The official releases of the kernel are available from http://www.kernel.org/
5 Best Free Code Editors for Ubuntu, Linux — Top List of …
30/12/2018 · Here’s 5 free code editors for Linux systems which you should try. Atom. Atom is a free and open-source code editor developed by GitHub. This Electron-based code editor comes with plugin support for Node.JS, embedded Git control. Atom supports more than 30+ languages.
How to Install Software from Source Code in Linux .
17/8/2020 · But, for the vast majority of Linux users, compiling and installing software from the source code for the first time might look like an initiation ceremony: somewhat frightening; but with the promise of entering a new world of possibilities and a place of prestige in a privileged community. A. Installing software from source code in Linux
Best Linux Source Code Management Software | GetApp
Visual Studio Code is a source code editor, which helps businesses build and debug web applications running on Windows, Linux, and macOS. Features include syntax highlighting, code refactoring and navigation, snippets, Emmet abbreviations, command-line interface (CLI), and text wrap. Read more about Visual Studio Code.
Linux Foundation «31 Billion Lines» Of Open Source …
Linux Command Line – Linux Foundation “31 Billion Lines” Of Open Source Code. Linux is primarily command line based, naturally, you can get a graphical user interface or GUI on top of a Linux operating system, setup, but actually the stamina of Linux is that it’s, I do not want to say a bare bone os, yet it does not require a GUI.
Best Command Line Games for Linux — Linux Hint
Nudoku, as the name suggests, is a sudoku implementation that can be run in a terminal. The ncurses based game can be navigated in a terminal through arrow keys and various other keyboard shortcuts. To install Nudoku in Ubuntu, execute the following command: $ sudo apt install nudoku.
Running Visual Studio Code on Linux
14/4/2016 · Another option for Linux development with VS Code is to use a Windows machine with the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL). Windows Subsystem for Linux. With WSL, you can install and run Linux distributions on Windows. This enables you to develop and test your source code on Linux while still working locally on a Windows machine.
How to edit Linux source code? — Stack Overflow
Directly Trying to Edit the source code may be Tough a.It depends on your proficiency of C and Operating System knowledge.I would say that you should first look about how functionalities like cat ,grep ,etc are implemented in C.Then comes the modules concepts .Different types of kernel module and basic linux operations with the modules .Then choose a specific functionality like networking or .
Best Free and Open Source Software — LinuxLinks
4/9/2020 · Best Free and Open Source Software. September 4, 2020 Steve Emms Software. Open source software is any program where the developer releases the source code for free. Whenever software has an open source license, it means anyone in the world can download, modify and distribute it without paying fees to its original creator.
Источник