- Как создать Ubuntu Live USB в Windows
- Как создать загрузочный USB Ubuntu в Windows:
- Шаг 1. Загрузите установочный образ Ubuntu
- Шаг 2. Загрузите Universal USB Installer
- Шаг 3: Создайте загрузочный USB
- Ubuntu Documentation
- Outline
- Introduction
- Prerequisites
- Dummy headlines
- Notes about speed
- Notes about size
- Notes about bootability
- The flash hardware
- Creating a bootable Ubuntu USB flash drive from Windows
- Rufus
- balenaEtcher
- Pendrivelinux’s Universal USB Installer
- UNetbootin
- Win32 Disk Imager
- Creating a bootable Ubuntu USB flash drive from Ubuntu
- Install and run Startup Disk Creator alias usb-creator
- UNetbootin
- mkusb — dd image of iso file to USB device safely
- Creating a bootable Ubuntu USB flash drive from Mac OSX
- Test if running in UEFI mode
- Linux ubuntu usb installer
- 2. Requirements
- 3. Launch Startup Disk Creator
- 4. ISO and USB selection
- 5. Confirm USB device
- 6. Installation complete
Как создать Ubuntu Live USB в Windows
Краткое описание: туториал, который покажет вам, как создать загрузочную флешку Ubuntu в Windows. Инструкции действительны для всех версий Ubuntu и Windows.
Одним из первых этапов установки Ubuntu является создание загрузочной USB-флешки. Если вы используете Windows 7 или 10, вы можете использовать такой инструмент, как Universal USB Installer, чтобы легко создать лайв USB. Это мой любимый и невероятно легкий в использовании инструмент.
Как создать загрузочный USB Ubuntu в Windows:
Шаг 1. Загрузите установочный образ Ubuntu
Перейдите на страницу Ubuntu и загрузите ISO-образ предпочитаемой версии Ubuntu. В настоящее время доступны две версии: Ubuntu 20.04 LTS и Ubuntu 20.10. Вы можете скачать ту, которая вам больше нравится.
И будет совершенно не лишним проверить контрольную сумму файла ISO, загруженного из Интернета.
Шаг 2. Загрузите Universal USB Installer
После того, как вы загрузили ISO-образ Ubuntu, перейдите на эту страницу и загрузите последнюю версию универсального установщика USB.
Шаг 3: Создайте загрузочный USB
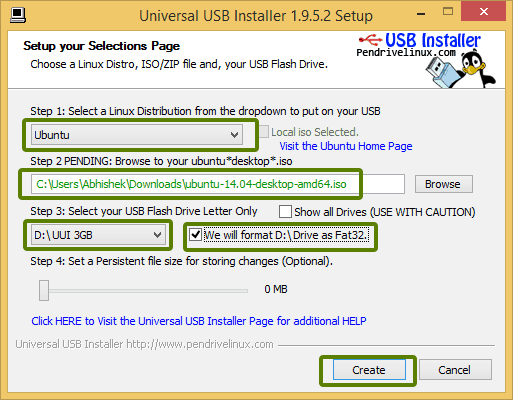
Вставьте флешку в ваш компьютер и запустите универсальный установщик USB. Теперь вам нужно сделать следующее:
· Выберите Ubuntu – шаг 1 на картинке ниже;
· Укажите путь к загруженному ISO-образу Ubuntu – Шаг 2;
· И наконец, выберите USB-накопитель, а также поставьте галочку в чекбоксе «Форматирование»;
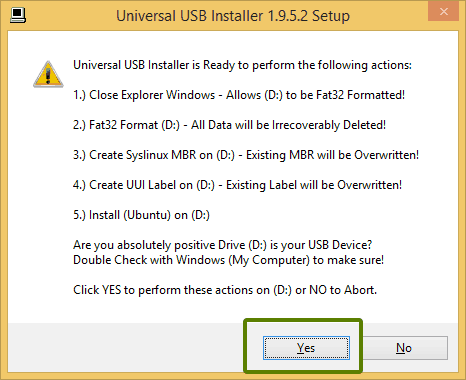
Далее появятся очевидные предупреждения, некогда объяснять, жамкайте «Да».
Подождите, пока процесс завершится. Вы можете переместить его в фоновый режим, если хотите.
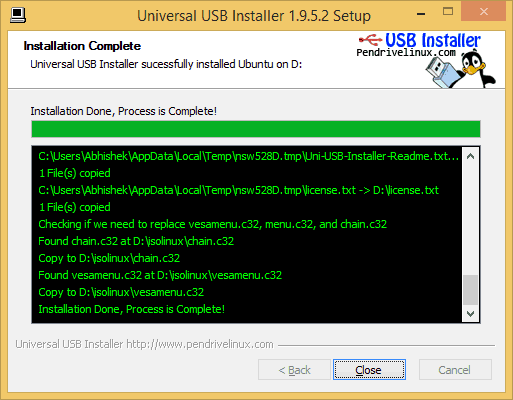
Тем не менее, ваша загрузочная USB Ubuntu должна быть создана за несколько минут.
После создания лайв USB-накопителя вы можете продолжить тестирование Ubuntu в живом режиме. Все, что вам нужно сделать, это перезагрузить компьютер. Во время загрузки нажмите F2, F10 или F12 (в зависимости от вашей системы), чтобы получить доступ к меню загрузки.
В этом меню выберите загрузку с USB или съемного носителя. Вот оно! Вы можете использовать Ubuntu без установки в лайв режиме или продолжить установку, если хотите.
В этом видео я показал процесс создания загрузочного USB-накопителя Ubuntu Linux с помощью инструмента Rufus:
Я очень надеюсь, что это руководство помогло вам легко создать Ubuntu Live USB в Windows.
Учитывая, что вы только начинаете, я советую следовать этому руководству по Ubuntu для начинающих и узнать, как использовать Ubuntu.
Дайте мне знать, если вам понадобится помощь.
Источник
Ubuntu Documentation
Outline
The general procedure to install Ubuntu (or Ubuntu flavour, Kubuntu, Lubuntu, Xubuntu, . ) from a USB flash drive is:
Get the correct Ubuntu installation file, ‘the iso file’, via this link or Ubuntu flavour via this link. Download the iso file into your running computer (for example into the directory Downloads in the internal drive, not into the USB flash drive that you want to make into a USB boot drive).
Check with md5sum (or another checksum tool) that the download was good.
Try Ubuntu (Kubuntu, Lubuntu, Xubuntu, . ) before installing it.
See also: Installation/FromUSBStickQuick for beginners starting from Windows.
Introduction
Ubuntu can be installed from a USB flash drive. This may be necessary for most new portable computers without DVD drives and is handy for others because a USB flash drive is so convenient. Also, you can configure Ubuntu on the USB flash drive to save changes you make, unlike a read-only CD/DVD disk.
Booting from a USB flash drive created with usb-creator alias Startup Disk Creator and mkusb will behave just as if you had booted from the install CD. It will show the language selection and then the install menu, from which you can install Ubuntu onto the computer’s hard drive or launch the LiveCD environment. Other utilities, e.g. UNetbootin, may create slightly different boot drives or if on UEFI might not work at all with Debian iso files due to a bug
Note: This article uses the term «USB flash drive» alongside USB stick, USB drive, USB device, USB pendrive and thumb drive.
Prerequisites
To create a USB installation device, you will need:
a 4 GB USB flash device/drive/stick. If the iso file is smaller than 2 GB, it is possible to use a 2 GB USB device, at least with some of the methods. Files on this USB device will be erased, so backup the files you want to keep before making the device bootable. Some of the tools require that this USB device is properly formatted and mounted while other tools will overwrite whatever is on the target device. Please follow the instructions for each tool.
an Ubuntu flavour ISO file downloaded from an official web page, ubuntu.com/download or http://releases.ubuntu.com, stored in your running computer (for example in the directory Downloads in the internal drive, not in the USB flash drive that you want to make into a USB boot drive).
Check with md5sum (or another checksum tool) that the download was good. In Linux there is the tool ‘md5sum’. In Windows you can do it with Rufus: click on the circle with a tick mark (more about Rufus here.)
Dummy headlines
After a major remake of this help page the following headlines are kept here because they may be linked to from other web sites. Several other headlines further down in the page are also kept for this reason.
Notes about speed
Notes about size
Notes about bootability
The flash hardware
There is a detailed description at the sub-page /pre
Creating a bootable Ubuntu USB flash drive from Windows
There are various methods available for Windows to create a bootable Ubuntu USB flash drive.
NEVER try to use one of your hard disk drives or partitions in this process unless you really know what you are doing, as data will get erased.
Rufus
Rufus is the tool in Windows that is recommended officially by Ubuntu. A tutorial is available from here.
balenaEtcher
Pendrivelinux’s Universal USB Installer
UNetbootin
Win32 Disk Imager
There is a detailed description at /fromWindows including Rufus, balena Etcher, Universal USB Installer, Unetbootin and Win32 Disk Imager.
Creating a bootable Ubuntu USB flash drive from Ubuntu
Install and run Startup Disk Creator alias usb-creator
The Ubuntu Startup Disk Creator is dedicated to creating USB boot drives for Ubuntu and Ubuntu family flavours (Kubuntu, Lubuntu . Xubuntu).
You can find usb-creator-gtk by typing «Startup Disk Creator» (Ubuntu Desktop) or usb-creator-kde in K-Menu—>Applications—>System—>Startup Disk Creator (Kubuntu). If it is not there, then you can install it using the Ubuntu Software Center.
- Insert and mount the USB drive. Inserting the USB drive should auto-mount it.
- Start the Startup Disk Creator
- In the top pane of the Startup Disk Creator, pick the .iso file that you downloaded.
- If the .iso file isn’t listed, click «Other» to locate and select the .iso file that you downloaded.
- In the bottom pane of the Startup Disk Creator, pick the target device, the USB flash drive. If more than one choice, please check carefully, until you are sure that you will be writing to the correct device.
- After checking that you are pointing to the correct target device, the USB flash drive, you can start the action.
You must enter a password because this is a risky operation. Use the password of the current user ID (the same as for login and running tasks with 'sudo'. Password is not required when installing from a ‘live’ system (booted from a DVD disk or another USB flash drive).
The Startup Disk Creator clones the iso file, which means that you need neither erase nor format the target drive. It will be completely overwritten anyway by the cloning process. The Startup Disk Creator looks like this in Ubuntu 18.04 LTS:
Notes
NEVER try to use one of your hard disk drives or SSDs or partitions in this process unless you really know what you are doing, as data will get erased.
There are bugs that affect the Ubuntu Startup Disk Creator, when you run it in old Ubuntu versions in BIOS mode and try to create USB boot drives with other versions. In the Ubuntu Startup Disk Creator version 0.3.2 in Ubuntu 16.04 LTS, these bugs are no longer a problem, so you can install any version of the Ubuntu flavours from 16.04 LTS and newer versions.
UNetbootin
Download UNetbootin
mkusb — dd image of iso file to USB device safely
If you want to clone from a general image file to a drive, you can use mkusb. It lets you clone to any drive that is not busy, also an internal drive, and there are very obvious warnings to prevent mistakes.
- run in Debian and many linux distros that are similar to Ubuntu and Debian,
- clone from iso files of most Linux distros to create USB boot drives,
- create persistent live drives of the Ubuntu family and Debian, using all available drive space for persistence and/or data storage,
- restore a USB boot drive to a standard storage device.
There is a detailed description at /fromUbuntu including the Startup Disk Creator, UNetbootin and mkusb.
Creating a bootable Ubuntu USB flash drive from Mac OSX
There is a good wiki page about booting with UEFI, and a good tutorial thread, UEFI Installing — Tips.
Test if running in UEFI mode
You may want to test if your Ubuntu flavour is running in [U]EFI mode. An installed system and a live system too is using the directory /sys/firmware/efi, so you can run the following command line,
The following command line is more robust and also easier to understand, so you may prefer it (if you copy & paste and are not bothered by typing a long command line),
Источник
Linux ubuntu usb installer
With a bootable Ubuntu USB stick, you can:
- Install or upgrade Ubuntu
- Test out the Ubuntu desktop experience without touching your PC configuration
- Boot into Ubuntu on a borrowed machine or from an internet cafe
- Use tools installed by default on the USB stick to repair or fix a broken configuration
Creating a bootable Ubuntu USB stick is very simple, especially from Ubuntu itself, and we’re going to cover the process in the next few steps.
Alternatively, we also have tutorials to help you create a bootable USB stick from both Microsoft Windows and Apple macOS.
2. Requirements
- A 4GB or larger USB stick/flash drive
- Ubuntu Desktop 14.04 or later installed
- An Ubuntu ISO file. See Get Ubuntu for download links
3. Launch Startup Disk Creator
We’re going to use an application called ‘Startup Disk Creator’ to write the ISO image to your USB stick. This is installed by default on Ubuntu, and can be launched as follows:
- Insert your USB stick (select ‘Do nothing’ if prompted by Ubuntu)
- On Ubuntu 18.04 and later, use the bottom left icon to open ‘Show Applications’
- In older versions of Ubuntu, use the top left icon to open the dash
- Use the search field to look for Startup Disk Creator
- Select Startup Disk Creator from the results to launch the application
4. ISO and USB selection
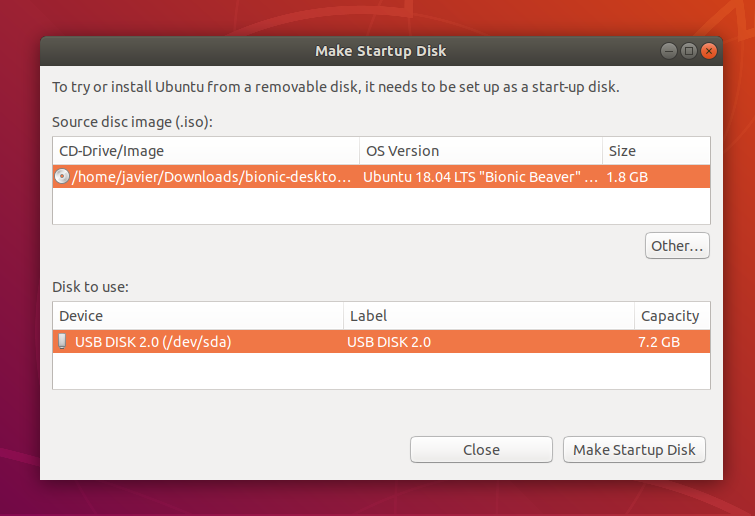
When launched, Startup Disk Creator will look for the ISO files in your Downloads folder, as well as any attached USB storage it can write to.
It’s likely that both your Ubuntu ISO and the correct USB device will have been detected and set as ‘Source disc image’ and ‘Disk to use’ in the application window. If not, use the ‘Other’ button to locate your ISO file and select the exact USB device you want to use from the list of devices.
Click Make Startup Disk to start the process.
5. Confirm USB device
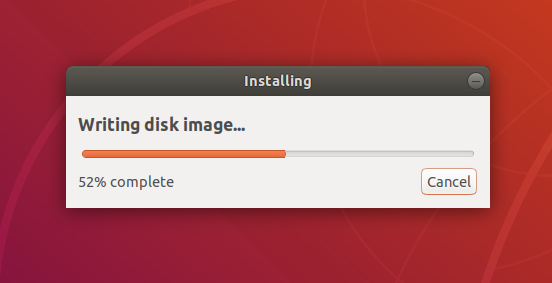
Before making any permanent changes, you will be asked to confirm the USB device you’ve chosen is correct. This is important because any data currently stored on this device will be destroyed.
After confirming, the write process will start and a progress bar appears.
6. Installation complete
That’s it! You now have Ubuntu on a USB stick, bootable and ready to go.
If you want to install Ubuntu, take a look at our install Ubuntu desktop tutorial.
Источник