- 15+ examples for listing users in Linux
- What file contains the list of the users on Linux?
- List all users
- List & sort users by name
- Linux list users without password
- List users by disk usage
- List the currently logged users
- Linux list of users who recently logged into the system
- List users’ logins on a specific date or time
- List all users in a group
- List users with UID
- List root users
- Get the total number of users
- List sudo users
- List users who have SSH access
- List users who have permissions to a file or directory
- List locked (disabled) users
- Listing remote users (LDAP)
- Conclusion
- Linux users be like.
- 10 Best Linux Distros For A Beginner User In 2021
- Best Linux Distros For Beginners Or New Users
- 1. Linux Mint
- Why Choose Linux Mint?
- 2. Ubuntu
- Why Choose Ubuntu?
- 3. Pop!_OS
- Why Choose Pop!_OS?
- 4. Zorin OS
- Why Choose Zorin OS?
- 5. elementary OS
- Why Choose elementary OS?
- 6. MX Linux
- Why Choose MX Linux?
- 7. Solus
- Why Choose Solus?
- 8. Deepin Linux
- Why Choose Deepin Linux?
- 9. Manjaro Linux
- Why Choose Manjaro Linux OS?
- 10. Linux Lite
- Why Choose Linux Lite?
15+ examples for listing users in Linux
In this post, you will learn about listing users in Linux. Besides this, you will know other tricks about Linux users’ characteristics.
There are two types of users in Linux, system users who are created by default with the system. On the other hand, there are regular users who are created by system administrators and can log in to the system and use it.
Table of Contents
What file contains the list of the users on Linux?
Before we start listing users, we need to know where these users saved on Linux?
The users are stored in a text file on the system called the passwd file. This file is located in the /etc directory.
The file is located on the following path:
In this file, you can find all the information about the users in the system.
List all users
Listing users is the first step to manage them. This way, we will know how many they are and who they are. In Linux, almost everything can be done in various ways, and this is no exception.
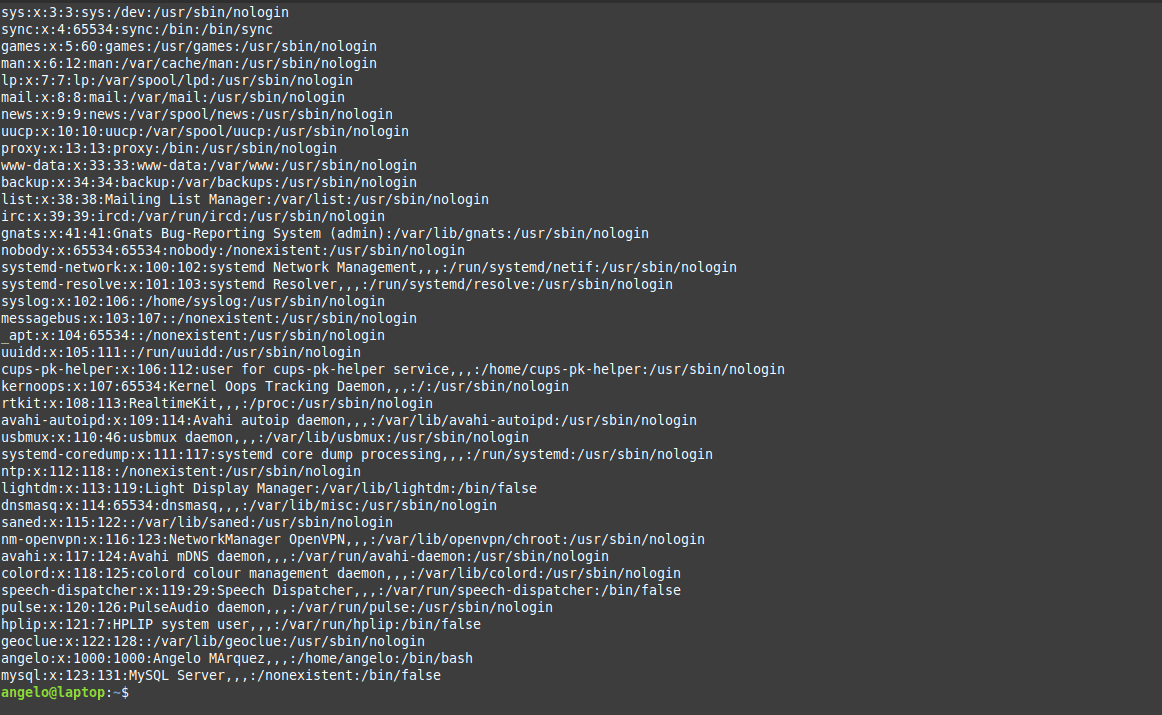
To list all users, you can use the cat command:
As you can see in the image, there is all the information about the users.
1- In the first field, you will see the user name.
2- The second field (The x character) is a representation of the encrypted password. The encrypted password is stored in /etc/shadow file.
3- The UID or the user ID.
4- The next field refers to the primary group of the user.
5- Then, it shows user ID info such as the address, email, etc.
6- After this, you will see the home directory of the user.
7- The last field is the shell used by that user.
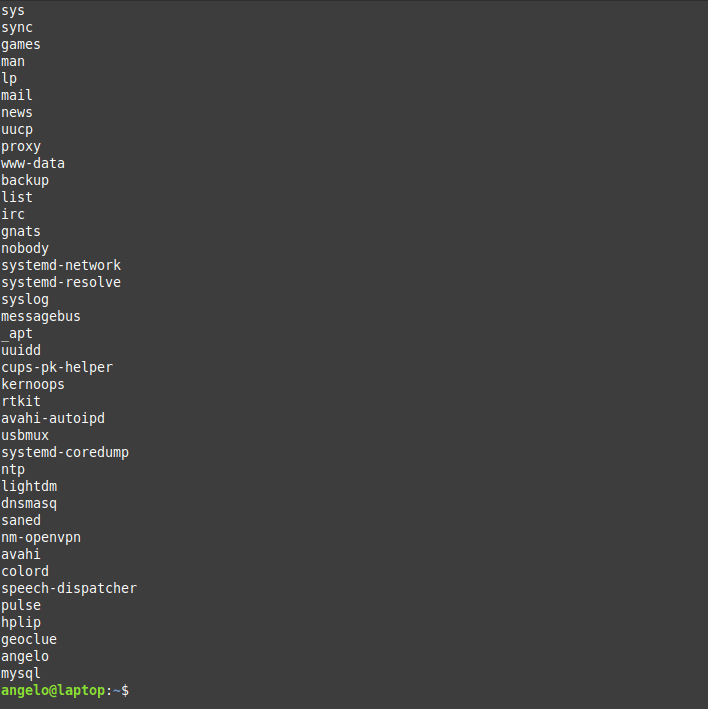
However, although the information is quite useful, if you only want to list users’ names in a basic way, you can use this command:
Now we have the names only by printing the first field of the file only.
List & sort users by name
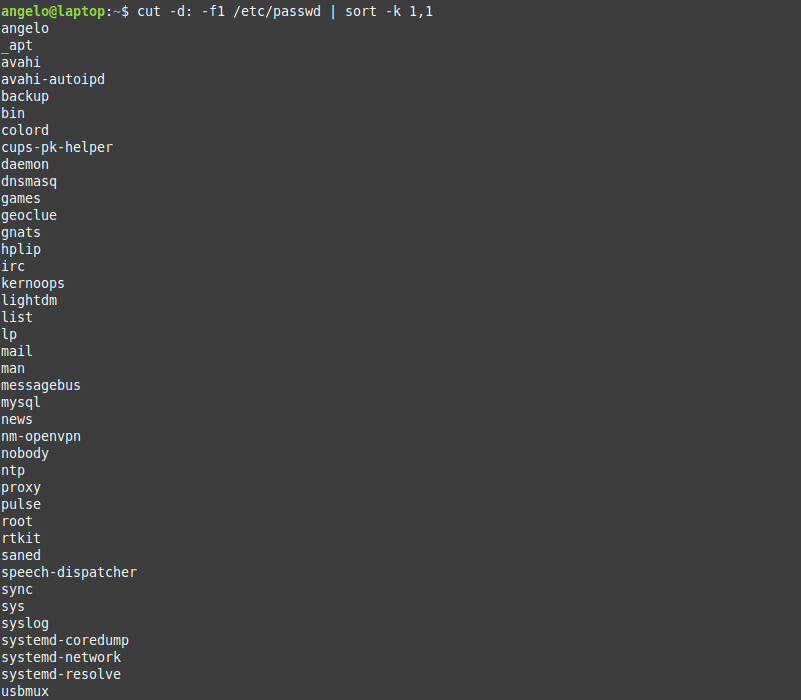
The above command serves the purpose of listing users on Linux. But what about listing the users in alphabetical order?
To do this, we will use the previous command, but we will add the sort command.
So, the command will be like this:
As you can see in the image, the users are shown sorted.
Linux list users without password
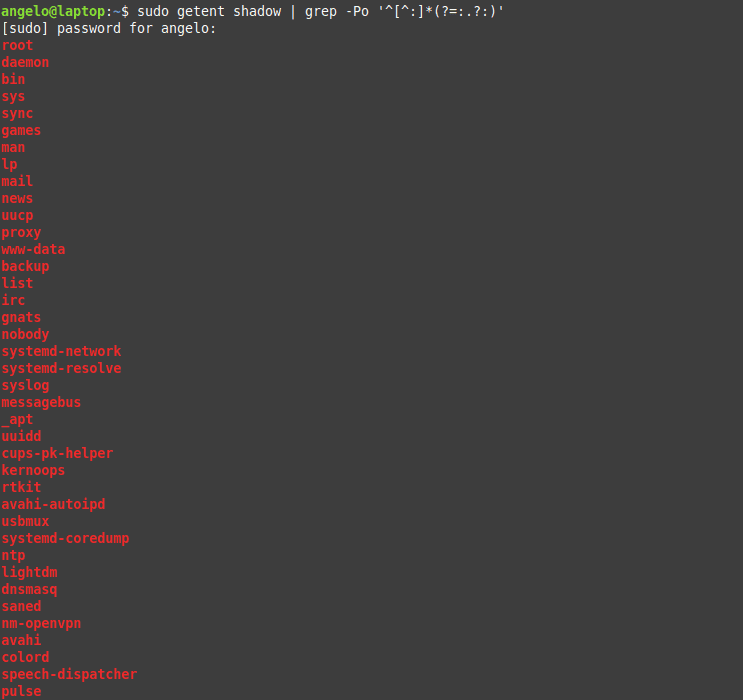
It is important to know users who have no password and to take appropriate action. To list users who do not have a password, just use the following command:
The used regex will list all users with no password.
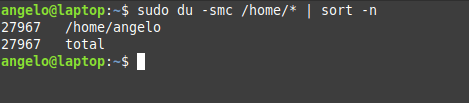
List users by disk usage
If you have a big directory and you want to know which user is flooding it, you can use the du command to get the disk usage.
With this, you can detect which of these users are misusing the disk space.
For it, it is enough to use the following command:
In this way, you will have the users ordered by the disk usage for the /home directory.
We used the -n for the sort command to sort the output by numbers.
List the currently logged users
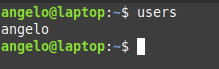
To list the currently logged in users, we have several ways to do it. The first method we can use the users command:
It will list the users with open sessions in the system.
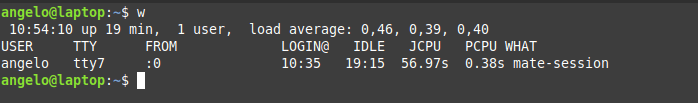
But this information is a little basic; however, we have another command that gives more details. The command is simply w.
With this command, we can have more information, such as the exact time when the session was started and the terminal session he has available.
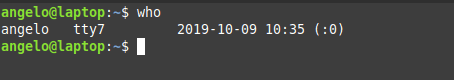
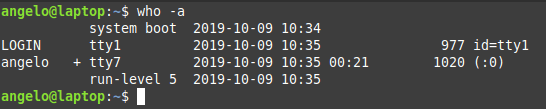
Finally, there is a command called who. It is available to the entire Unix family. So you can use it on other systems like FreeBSD.
With who command, we also have some information about currently logged in users. Of course, we can add the option -a and show all the details.
This way, you know everything about the logged in users.
Linux list of users who recently logged into the system
We saw how to get the currently logged in users, what about listing the login history of users?
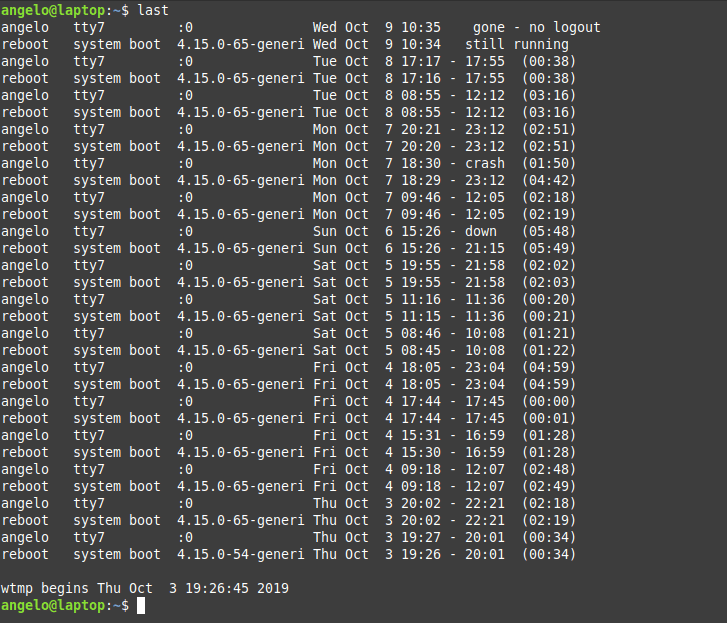
You can use the last command to get more info about the logins that took place:
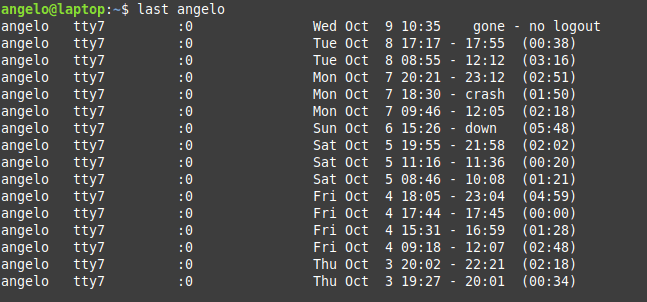
Or the logins of a particular user
These are the user login activity and when it was started and how long it took.
List users’ logins on a specific date or time
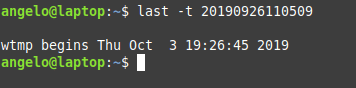
What about listing users’ logins on a specific date or time? To achieve this, we use the last command but with the -t parameter:
And now, all you have to do is choose an exact date & time to list who logged at that time.
List all users in a group
There are two ways to list the members of a group in Linux, the easiest and most direct way is to get the users from the /etc/group file like this:
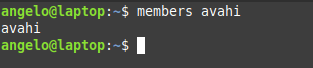
This command will list users in the likegeeks group.
The other way is by using commands like the members command in Debian based distros. However, it is not installed by default in Linux distributions.
To install it in Ubuntu / Linux Mint 19, just use APT:
Or in the case of CentOS:
Once it’s installed, you can run the command then the name of the group you want to list the users to:
This way, you can list users for a group in a Debian based distro. What about a RedHat based distro like CentOS?
You can use the following command:
List users with UID
In Unix systems, each user has a user identifier or ID. It serves to manage and administer accounts internally in the operating system.
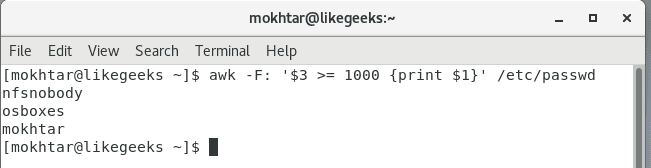
Generally, UIDs from 0 to 1000 are for system users. And thereafter for regular users. Always on Unix systems, UID zero belongs to the root users (You can have more than one user with UID of zero).
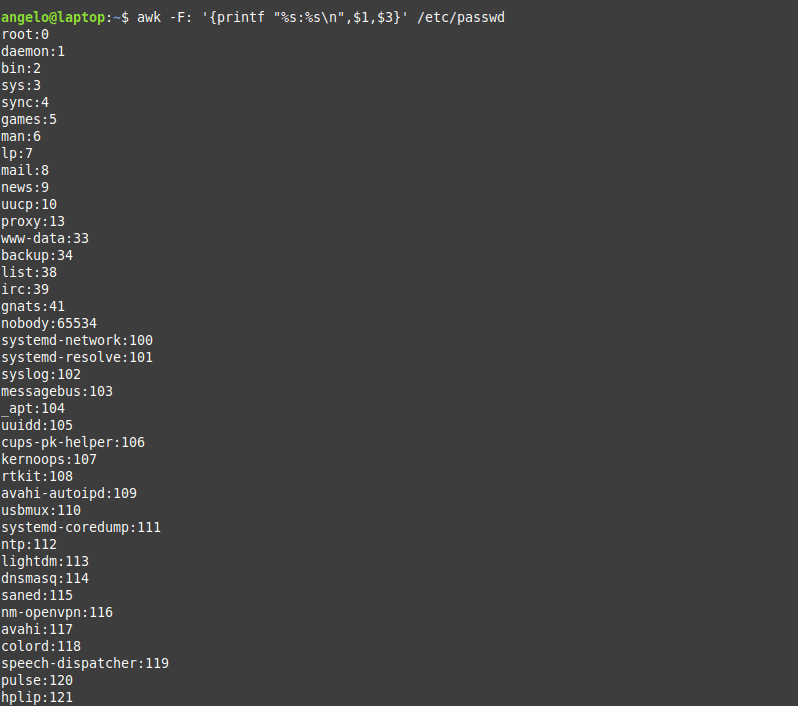
So now, we will list the users with their respective UID using Awk.
The command that performs the task is the following:
As you can see, each user with his UID.
List root users
In a Unix-like system like Linux, there is usually only one root user. If there are many, how to list them?
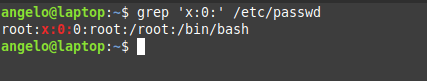
To do this, we can use this command:
Here we are filtering the file to get users with UID of zero (root users).
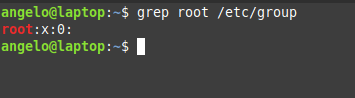
Another way by checking the /etc/group file:
Here we are getting users in the group root from the /etc/group file.
Also, you can check if any user can execute commands as root by checking the /etc/sudoers file:
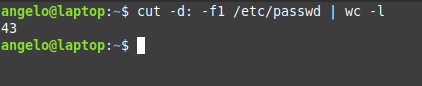
Get the total number of users
To get the total number of users in Linux, you can count lines in /etc/passwd file using the wc command like this:
Great! 43 users. But this includes system and regular users. What about getting the number of regular users only?
Easy! Since we know from above that regular users have UID of 1000 or greater, we can use Awk to get them:
List sudo users
Linux systems have a utility called sudo that allows you to execute commands as if you were another user who is usually the root user.
This should be handled with care in a professional environment.
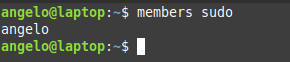
Also, it is very important to know which users can run the sudo command. For this, it is enough to list the users that belong to the sudo group.
Users in this group can execute commands as super users.
List users who have SSH access
SSH allows users to access remote computers over a network. It is quite secure and was born as a replacement for Telnet.
By default, all regular users can log in and use SSH. If you want to limit this, you can use the SSH configuration file (/etc/ssh/ssh_config) and add the following directive:
Also, you can allow groups instead of allowing users only using the AllowGroups directive:
These directives define who can access the service. Don’t forget to restart the SSH service.
List users who have permissions to a file or directory
We can give more than one user permission to access or modify files & directories in two ways.
The first method is by adding users to the group of the file or the directory.
This way, we can list the group members using the members utility as shown above.
Okay, but what if we just want this user to have access to this specific file only (Not all the group permissions)?
Here we can set the ACL for this file using setfacl command like this:
Here we give the user called newser the permission for the file called myfile the permissions of read & write & execute.
Now the file can be accessed or modified by the owner, and the user called newuser. So how to list them?
We can list them using the getfacl command like this:
This command will list all users who have permissions for the file with their corresponding permissions.
List locked (disabled) users
In Linux, as a security measure, we can lock users. This as a precaution if it is suspected that the user is doing things wrong, and you don’t want to completely remove the user and just lock him for investigation.
To lock a user, you can use the following command:
Now the user named myuser will no longer be able to login or use the system.
To list all locked users of the system, just use the following command:
This will print all locked users, including system users. What about listing regular users only?
As we saw above, using Awk, we can get locked regular users like this:
Listing remote users (LDAP)
Okay, now can list all system users (local users), but what about remote users or LDAP users? Well, we can use a tool like ldapsearch, but is there any other way?
Luckily yes! You can list local & remote users with one command called getent
This command lists both local system users and LDAP or NIS users or any other network users.
You can pipe the results of this command to any of the above-mentioned commands the same way.
Also, the getent command can list group accounts like this:
You can check the man page of the command to know the other databases the command can search in.
Conclusion
Listing users in the Linux system was fun! Besides this, we have learned some tips about users and how to manage them in different ways.
Finally, this knowledge will allow a better administration of the users of the system.
I hope you find the tutorial useful. Keep coming back.
Источник
Linux users be like.
Linux users Installing a web browser be likeПодробнее
linux users be likeПодробнее
Linux users be likeПодробнее
Linux users explaining thingsПодробнее
Linux users be likeПодробнее
Reacting to «The REAL Reason Linux Users Love The Command Line»Подробнее
linux users be likeПодробнее
Linux users be like 11Подробнее
Linux users putting on clothes be likeПодробнее
linux users be like | cyberpunk memeПодробнее
linux users opening an internet browser be likeПодробнее
Why I use Linux | Linux like users | Fuck off MicrosoftПодробнее
linux users be likeПодробнее
Linux users installing a web browsers be like 100% legitПодробнее
linux user be like part 1Подробнее
Linux users Be LikeПодробнее
How actually Linux Users update their System ? #kali #kalilinux2021 #linux #hacker #hackingПодробнее
shitpost status linux users be likeПодробнее
Источник
10 Best Linux Distros For A Beginner User In 2021
It’s time to switch from Windows 10.
These days, Linux Mint is giving a tough competition to Ubuntu as it’s very beginner-friendly. But what about other options for new Linux users?
The beauty of Linux lies in the plethora of options available to the users. While some call it Linux distro fragmentation, I love to call it Linux’s strength. It allows the users to choose a Linux distro suitable for their needs and learn new things. The same choice allows one to find a beginner-friendly Linux distro, lightweight distro, gaming distro, etc.
Best Linux Distros For Beginners Or New Users
1. Linux Mint
Linux Mint is one of the most popular Linux distributions around. Over the years, it has grown to become one of the chief competitors of Ubuntu Linux, its parent operating system. It’s known to provide one of the most polished and complete desktop experiences to a beginner. If someone asks me to recommend the best Linux distro for beginners, I’d promptly recommend Linux Mint.
So, what makes Linux Mint a great distro for beginners? How can a typical Windows user adapt to Mint? The answer lies in the fact that Linux Mint was created to provide an out-of-the-box experience to the newbies. Mint’s large set of pre-bundled tools ensure that Windows users transition to Linux Mint without regrets. It turns out to be equally good on laptops and powerful desktops.
There are three major editions of Linux Mint: Cinnamon, MATE, Xfce
Why Choose Linux Mint?
- Near-perfect desktop experience
- Cinnamon desktop is a great option
- Full access to Ubuntu software repo
- Great community
2. Ubuntu
We’re pretty sure that Ubuntu needs no introduction if you’re a regular reader of Fossbytes. But why is Ubuntu such a tempting distro for beginners while other “Easy-to-use” distros are struggling to get user’s attention? That’s because Ubuntu has been in the Linux market for a long time and has become a lot popular. This Debian-based Linux distribution also enjoys the status of the most popular open-source operating system in the world.
Every new release is more polished and comes loaded with new features and improvements—many PC makers like Dell and Lenovo design specific machines with preinstalled Ubuntu Linux. After conquering the desktop world, Ubuntu has also managed to gain big in the cloud. Another major reason to use Ubuntu for a new Linux user is its vast community of users and online forums.
On top of the already popular vanilla Ubuntu, it comes in various flavors like Ubuntu Kylin, Edubuntu, Lubuntu, Xubuntu, Ubuntu MATE, Ubuntu Studio, Ubuntu Budgie, and Kubuntu.
Why Choose Ubuntu?
- Tons of free software in the Software Center
- Vast Ubuntu community
- Lots of flavors to suit your needs
- Compatible with most hardware
- Some more reasons
3. Pop!_OS
Pop!_OS needs no introduction. In the past few years, it has managed to gain an incredible amount of traction thanks to some of its unique features like Pop Shell and a separate version of the distro that comes with pre-installed NVIDIA drivers, which makes it one of the best distros for gaming.
And that’s not it. Being an Ubuntu-based distro means it is pretty stable. Pop!_OS’s default desktop was GNOME until recently, System76 decided to make its own environment called COSMIC, which is based on GNOME. Overall, it is definitely one of the best Linux distros for beginners.
If you’re confused between Pop!_OS and Ubuntu, make sure to read our Ubuntu Vs. Pop!OS comparison. Want to know what else Pop!OS can do? Here’s our Pop!_OS 20.04 review.
Why Choose Pop!_OS?
- Flatpack support
- Stable Ubuntu-base
- A great number of nifty features like Window tiling, etc
- Separate ISO for laptops/PCs with NVIDIA GPUs
4. Zorin OS
While one can argue that Canonical has worked hard to develop Ubuntu and make it popular, many other operating system developers have dedicated themselves to creating one of the finest Linux distros for beginners. Apart from Linux Mint, Zorin OS is another major player focusing on user-friendliness and usability.
Zorin OS calls itself a replacement for Windows and macOS. It comes loaded with everything that one needs to complete daily tasks. With a Windows-like interface built with beginners in mind, Zorin OS is easily the best Linux distro for Windows users. Its Windows 10-styled desktop is great at making things easier for a Windows lover. It also ships with a skinned version of Ubuntu Software that answers a beginner’s most software needs.
Why Choose Zorin OS?
- Focus on user-friendliness
- Windows-like interface
- Great out-of-the-box experience
- Appealing desktop effects
- Feature-packed media software
5. elementary OS
This visually stunning desktop is often listed as one of the most beautiful Linux distributions around, but it’s a lot more than that. The creators of elementary OS call their OS a fast and open replacement for Windows and macOS. Well, is their claim credible? Is elementary OS the best Linux distro for new users? Here’s what we think.
Unlike other distros, there are many interesting things about elementary. It’s intuitive, clean, and endearing. The makers of elementary are experts in design, and their operating system makes sure that the user doesn’t get confused.
The OS looks are very pleasing, with a simple dock at the bottom and a panel at the top. The applications that come loaded with this beginner-friendly Linux distribution follow the same clean theme and are fairly basic in nature. Overall, it’s a very nice Linux distribution for a new user who doesn’t want to indulge in terminal sorcery. Elementary OS comes with the Pantheon desktop environment.
Why Choose elementary OS?
- Visually appealing
- Stable and lightweight
- Clean looking desktop
- A lot of useful, pre-installed software
6. MX Linux
MX Linux, a joint venture of antiX Linux distro and MEPIC community, places itself a bit differently when it comes to its highlights. Unlike other distros that either call them lightweight or performance-focused, MX Linux labels itself as a midweight operating system.
Thanks to its easy installation process and familiar looks, the new users find themselves at home while using MX Linux. With a pretty good hardware recognition and automatic configuration for an out-of-the-box experience, this Debian GNU/Linux-based is also stable for dependable performance. The default desktop environment used by this beginner-friendly distro is Xfce.
Why Choose MX Linux?
- A unique midweight approach
- Familiar Xfce desktop environment
- Easy installation and configuration
7. Solus
Solus is an independent Linux distribution that is built from scratch. It follows the “Install Today. Updates Forever” model that promises to deliver updates regularly with a rolling release model. Apart from offering installation media with various desktop environments, the Solus team has also created its own Budgie desktop environment.
Linux beginners will surely like the look and feel of the Solus as it’s elegant and clean. Even though the dedicated software selection of Solus is smaller as compared to other distros, the applications are really refined to make the default software actually useful. The distro is also known for a smooth and hiccup-free experience when it comes to hardware issues. Also, as expected, the installation is smooth, and you can get a working system up and running in no time.
It also comes with pre-bundled development tools, which makes it one of the best distros for programming. It is also one of the best non-Ubuntu-based distros out there.
Why Choose Solus?
- Beautiful user interface
- Easy installation
- Regular updates and excellent hardware support
8. Deepin Linux
Just Like elementary OS, Deepin Linux is another visually appealing Linux distro for beginners. Developed by the Chinese Linux community, Deeping is created to provide a functional Linux desktop experience. One thing that sets Deepin apart is its installation process, which is one of the simplest.
Deepin Linux offers a newbie a clean and simple user interface. The icons and color theme look modern and are eye candy. To access the system settings, you need to access a right panel that lets you manage all settings, users, themes, wallpapers, etc.
On the applications front, Deeping Linux manages to woo first-time Linux users. It comes loaded with many useful pre-installed programs like Chrome, Nautilus file manager, Deepin media player, USB Creator, PDF viewer, LibreOffice, etc. Even for experienced users, Deepin feels like a breath of fresh air. So, go ahead and give it a try. Deepin Linux uses the Deepin Desktop Environment (DDE).
Why Choose Deepin Linux?
- Deepin’s own desktop environment is visually pleasing
- Beautiful and pleasant experience
- Custom installer and system settings
9. Manjaro Linux
After Linux Mint and elementary OS, Manjaro is my third personal favorite Linux distro on this list of best Linux distros for beginners. Manjaro is one of the best non-Ubuntu Linux distributions for users tired of Ubuntu or Ubuntu-based distros. It’s often called Arch Linux for human beings, and there are plenty of great reasons to support this argument. However, it’s worth noting that its learning curve is steeper as compared to other solutions.
Manjaro is based on Arch Linux, and it’s one of the fastest-growing Linux distributions around. It’s an attractive and simple-to-use Linux distro that seems like a perfect Windows replacement. Manjaro maintains its own package repositories and aims to add its user-friendliness to the power of Arch Linux.
It comes with its own installer for easy installation. It should be noted that Manjaro is a Rolling Linux distribution, which means that it is continuously updated. Another great feature of Manjaro is that a beginner would love its ability to switch between different Linux kernels without a hassle. Major editions of Manjaro Linux are Xfce and KDE. There are other community editions as well.
Why Choose Manjaro Linux OS?
- Power of Arch Linux without hassle
- Easy to use
- Rolling Linux distro
- Great distro for Gaming
- Fast growing community
10. Linux Lite
Wishing to use a Linux distro that’s suitable for new users and loves your old PC? Well, in that case, you should try out Linux Lite. As the name suggests, it doesn’t demand much from you. Based on the Ubuntu LTS releases, it’s fully functional out of the box. What does that mean? It means that a new Linux user doesn’t need to install extra software for performing daily chores. It includes Firefox, GIMP, LibreOffice, Thunderbird, VLC media player, etc.
Linux Lite has a menu similar to Windows, making things easier for Windows users who are planning to dive into the world of Linux. It also provides automatic upgrades for smooth operating. So, if you wish to try out Linux on your outdated laptop/PC, Linux Lite is the right choice. Linux Lite runs the Xfce desktop environment by default
Why Choose Linux Lite?
- Very lightweight Linux distro
- A great choice for Windows users
- Easy to use
- Optimized for old hardware
- Pre-installed software
Editor’s recommendation:
If you’re looking for a Linux distro that’s overall best, you can go ahead with Linux Mint Cinnamon Edition or Pop!_OS. Apart from being beginner-friendly Linux distros, they’re also powerful. If you have an old PC, we’d recommend settling with Linux Lite. Users who want to switch from Windows, Zorin OS, Deepin, and Linux Lite are popular choices.
Источник