- Find Linux / UNIX Kernel Version Command
- uname command to display the Linux or Unix kernel version
- Outputs from my OS X Unix desktop
- Outputs from OpenBSD Unix server
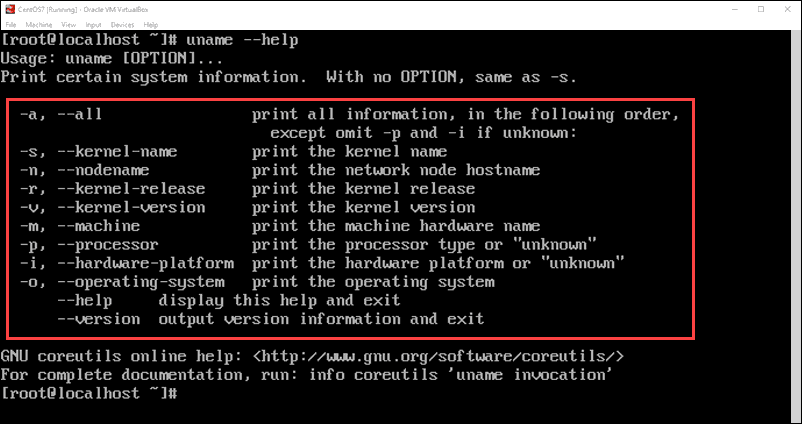
- Common uname options
- How to find the kernel version with /proc/version file ( Linux only command )
- Related media
- Package management tools ( Linux only command )
- Conclusion
- The Linux Kernel Archives
- Distribution kernels
- How to Check Kernel Version in Linux in Command Line
- 4 Commands to Find Linux Kernel Version
- uname Command
- hostnamectl Command
- Display the /proc/version File
- dmesg Command
Find Linux / UNIX Kernel Version Command
H ow do I find out what kernel version I am currently running under Debian Linux or any other Linux distribution using a shell prompt? How do I find out Unix kernel version? How can I find out my Linux / UNIX kernel version using the ssh command?
| Tutorial details | |
|---|---|
| Difficulty level | Easy |
| Root privileges | Yes |
| Requirements | Linux or Unix |
| Est. reading time | 3 mintues |
- Linux Kernel version and name.
- Print the Unix machine hardware name.
- Find out about server processor type.
- Display the operating system and more.
uname command to display the Linux or Unix kernel version
This command works under all Linux distributions and other UNIX-like operating systems such as FreeBSD, OpenBSD, Solaris, HP UX, OS X and friends. Type the following command to see running kernel version:
$ uname -r
Output taken from Linux based system:
- 2 : Kernel version
- 6 : The major revision of the kernel
- 22 : The minor revision of the kernel
- 14 : Immediate fixing / bug fixing for critical error
- generic : Distribution specific sting. For example, Redhat appends string such as EL5 to indicate RHEL 5 kernel.
Another common usage is as follows:
$ uname -mrsn
Output taken from Linux:
Here is another output from RHEL 8:
My RHEL 8 kernel version
Outputs from my OS X Unix desktop
Outputs from OpenBSD Unix server
For example, at the prompt, I type the following on AIX unix to print OS name:
uname
Sample outputs:
Common uname options
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| -a | Behave as though the options -m, -n, -r, -s, and -v were specified. |
| -i | Write the kernel ident to standard output. |
| -K | Write the FreeBSD version of the kernel. |
| -m | Displays the machine ID number of the hardware running the system. |
| -n | Write the name of the system/node to standard output. |
| -o | This is a synonym for the -s option, for compatibility with other systems. |
| -p | Displays the architecture of the system processor. |
| -r | Displays the release number of the operating system. |
| -s | Write the name of the operating system implementation to standard output. |
| -v | Write the version level of this release of the operating system to standard output. |
How to find the kernel version with /proc/version file ( Linux only command )
You can also obtain kernel version from /proc/version file by using cat command as follows:
$ less /proc/version
$ more /proc/version
$ cat /proc/version
Sample outputs:
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
Related media
See how to use uname and other commands to find the kernel version on Linux or Unix-like oses:
Package management tools ( Linux only command )
You can list all installed kernel and its version with the following command under RHEL / CentOS / Suse / Fedora Linux :
$ rpm -q kernel
Output:
If you are using Debian / Ubuntu , try:
$ dpkg —list | grep linux-image
Output:
Conclusion
We have shown you how to find the version of the Unix and Linux kernel running on your server/desktop/laptop/workstion from the command line. See uname man page here and here for more info.
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
| Category | List of Unix and Linux commands |
|---|---|
| Documentation | help • mandb • man • pinfo |
| Disk space analyzers | df • duf • ncdu • pydf |
| File Management | cat • cp • less • mkdir • more • tree |
| Firewall | Alpine Awall • CentOS 8 • OpenSUSE • RHEL 8 • Ubuntu 16.04 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Linux Desktop Apps | Skype • Spotify • VLC 3 |
| Modern utilities | bat • exa |
| Network Utilities | NetHogs • dig • host • ip • nmap |
| OpenVPN | CentOS 7 • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Debian 8/9 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Package Manager | apk • apt |
| Processes Management | bg • chroot • cron • disown • fg • glances • gtop • jobs • killall • kill • pidof • pstree • pwdx • time • vtop |
| Searching | ag • grep • whereis • which |
| Shell builtins | compgen • echo • printf |
| Text processing | cut • rev |
| User Information | groups • id • lastcomm • last • lid/libuser-lid • logname • members • users • whoami • who • w |
| WireGuard VPN | Alpine • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Firewall • Ubuntu 20.04 |
Comments on this entry are closed.
In Solaris uname -r will give you the solaris release level.
some other usefull options with uname are
uname -s [Operating system]
SunOS
uname -r [Release version]
5.8
uname -v
Generic_117350-27[OS version]
uname -a
SunOS hostname 5.8 Generic_117350-27 sun4u sparc
the last two words describes h/w name and processor respctl[equivalent to -m and -p),
I log on to different RedHat based servers, Can you please update on how to differentiate between Centos, RedHat, Oracle Linux (i.e. RedHat based distributions) sitting remotely.
# uname -a (doesn’t help)
# cat /etc/redhat-relaese (its changed to RedHat as some softwares don’t get installed otherwise.
Quite useful for beginners and mediocre persons.
i need linux fonts
cat /etc/redhat-release
this will give you redh hat version or centos version
this command return the Centos version
Newbie here….kind of got thrown in Linux admin for Centos at work due to staff reduction. Confused about something (well lots of things, but can’t seem to find the answer to this particular question).
]# rpm -qa kernel
kernel-2.6.9-89.0.15.EL
kernel-2.6.9-89.0.19.EL
kernel-2.6.9-89.0.28.EL
kernel-2.6.9-89.0.29.EL
kernel-2.6.9-78.0.22.EL
kernel-2.6.9-89.0.11.EL
kernel-2.6.9-89.0.16.EL
kernel-2.6.9-89.0.23.EL
kernel-2.6.9-89.0.25.EL
kernel-2.6.9-89.29.1.EL
kernel-2.6.9-78.0.5.EL
kernel-2.6.9-78.0.8.EL
kernel-2.6.9-78.0.13.EL
kernel-2.6.9-89.0.18.EL
]# uname -a
Linux xxx 2.6.9-78.0.22.EL #1 Thu Apr 30 19:03:25 EDT 2009 i686 athlon i386 GNU/Linux
Why does rpm -qa show kernel-2.6.9-89.0.xxxxx installed but uname -a shows 2.6.9-78.00.22.EL?
I know this probably really stupid question – sorry 🙁
Send me all shell and kernel cammond of linux or unix
Life is so easy huh? 🙂
Send me all the words in the english language and their uses ( I dont claim that this line is original 😉 )
hahaha…lol…AMukh…ur reply is perfect….life is not that easy
Thank you very much all friend
Utility uname don’t have any info about OS version, only OS platform. uname -p gives
GNU/Linux… No info there are in environment variables. But I need the info like that
openSUSE 12.1 (x86_64)… How to solve this problem? I don’t want to set some environment variable manually…
can you install linux on a computer that has another operating system already installed
Yes, this is possible.
use any VM to install multiple os on same machine
I have installed “Linux mint” I want to know the complete info of my Linux version installed like Linux version kernel version
Thank U Very Much senior and all
xcuse me bro..
i wanna install fedora on VMWARE for running shell and c programming but my vmware is not listing out fedora OS .. what i should do …
It listing out “Linux Kernel 2.6.10” Is it similar to fedora ? Can i run shell scripts and c programz .
how to get the OS manufacturer,OS version,OS serial number and number of registered users on linux machine
sudo cat /etc/passwd | grep /bin/bash
UID’s 1000 and above are valid users plus UID 0 for root
dpkg –list | grep linux-image
ii linux-image-2.6.38-11-generic 2.6.38-11.50 Linux kernel image for version 2.6.38 on x86/x86_64
rc linux-image-2.6.38-8-generic 2.6.38-8.42 Linux kernel image for version 2.6.38 on x86/x86_64
ii linux-image-3.0.0-12-generic 3.0.0-12.20 Linux kernel image for version 3.0.0 on x86/x86_64
ii linux-image-3.0.0-16-generic 3.0.0-16.29 Linux kernel image for version 3.0.0 on x86/x86_64
ii linux-image-3.0.0-17-generic 3.0.0-17.30 Linux kernel image for version 3.0.0 on x86/x86_64
ii linux-image-generic 3.0.0.17.20 Generic Linux kernel image
what does it mean 32 or 64 bit ?
when give uname -a o/p is
Linux xxxxx 3.0.0-17-generic #30-Ubuntu SMP Thu Mar 2 17:34:21 UTC 2012 i686 i686 i386 GNU/Linux
when i do file on some executable it tells it 32 bit.
ELF 32-bit LSB executable, Intel 80386, version 1 (SYSV), statically linked, stripped
Источник
The Linux Kernel Archives
There are several main categories into which kernel releases may fall:
Prepatch Prepatch or «RC» kernels are mainline kernel pre-releases that are mostly aimed at other kernel developers and Linux enthusiasts. They must be compiled from source and usually contain new features that must be tested before they can be put into a stable release. Prepatch kernels are maintained and released by Linus Torvalds. Mainline Mainline tree is maintained by Linus Torvalds. It’s the tree where all new features are introduced and where all the exciting new development happens. New mainline kernels are released every 2-3 months. Stable After each mainline kernel is released, it is considered «stable.» Any bug fixes for a stable kernel are backported from the mainline tree and applied by a designated stable kernel maintainer. There are usually only a few bugfix kernel releases until next mainline kernel becomes available — unless it is designated a «longterm maintenance kernel.» Stable kernel updates are released on as-needed basis, usually once a week. Longterm There are usually several «longterm maintenance» kernel releases provided for the purposes of backporting bugfixes for older kernel trees. Only important bugfixes are applied to such kernels and they don’t usually see very frequent releases, especially for older trees.
| Version | Maintainer | Released | Projected EOL |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5.10 | Greg Kroah-Hartman & Sasha Levin | 2020-12-13 | Dec, 2026 |
| 5.4 | Greg Kroah-Hartman & Sasha Levin | 2019-11-24 | Dec, 2025 |
| 4.19 | Greg Kroah-Hartman & Sasha Levin | 2018-10-22 | Dec, 2024 |
| 4.14 | Greg Kroah-Hartman & Sasha Levin | 2017-11-12 | Jan, 2024 |
| 4.9 | Greg Kroah-Hartman & Sasha Levin | 2016-12-11 | Jan, 2023 |
| 4.4 | Greg Kroah-Hartman & Sasha Levin | 2016-01-10 | Feb, 2022 |
Distribution kernels
Many Linux distributions provide their own «longterm maintenance» kernels that may or may not be based on those maintained by kernel developers. These kernel releases are not hosted at kernel.org and kernel developers can provide no support for them.
It is easy to tell if you are running a distribution kernel. Unless you downloaded, compiled and installed your own version of kernel from kernel.org, you are running a distribution kernel. To find out the version of your kernel, run uname -r :
If you see anything at all after the dash, you are running a distribution kernel. Please use the support channels offered by your distribution vendor to obtain kernel support.
Источник
How to Check Kernel Version in Linux in Command Line
Home » SysAdmin » How to Check Kernel Version in Linux in Command Line
Want to find out which kernel version you are running?
The Linux kernel is much like the central brain of the operating system. Although it is open-source – meaning anyone can view and modify the code – the Linux kernel is built with multiple protocols to ensure stability and security.
This guide will walk you through how to check the Linux kernel version of your distribution.
- A system running Linux (Ubuntu, Debian, RHEL, CentOS, or another version)
- A terminal window / command line (Ctrl–Alt–T, Ctrl–Alt–F2)
4 Commands to Find Linux Kernel Version
uname Command
Launch a terminal window, then enter the following:
The system will return a numeric code, for example:
Each number, separated by a dot or hyphen, is part of a code:
- 3 – This is the main kernelversion
- .10 – This is the major releaseversion
- .0 – This is the minor revisionlevel
- -957 – This is the level of patches and bug fixes
The uname command includes additional options that you can use to get more information about your kernel. Simply add an option after the command:
- -a – Display all information
- -o – Display the operating system (usually GNU/Linux)
- -r – Display kernel release
- -v – Display kernel version (usually includes the base OS and time the kernel was compiled)
For a full list of uname commands, enter
Note: Your kernel version will likely be different than this example. At the time of writing this article, the latest version is Linux kernel 5.0.
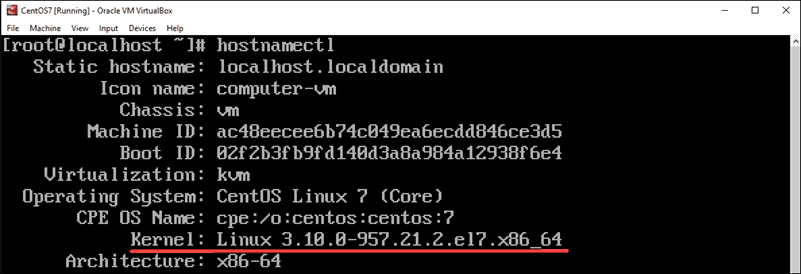
hostnamectl Command
The hostnamectl command is typically used to display information about the system’s network configuration. It also displays the kernel version.
To check the kernel version, enter the following:
The second-to-last line should read:
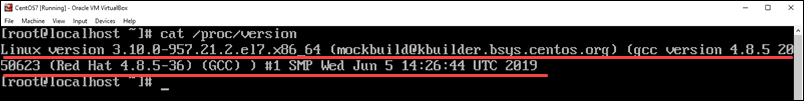
Display the /proc/version File
To display the proc/version file, enter the command:
The cat command displays the contents of the /proc/version file. This will output the Linux kernel version first, along with additional data about your operating system.
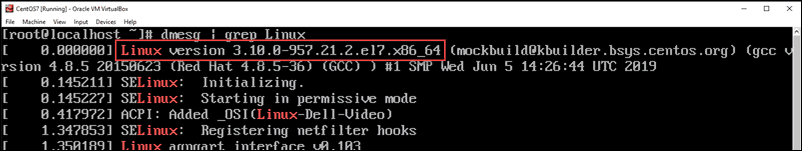
dmesg Command
The dmesg command is used to print the message buffer of the kernel. This is usually used to read messages from device drivers, but it can also be used to find the kernel version.
Enter the command:
The | (pipe) symbol is usually on the same key as the symbol, just above the enter key.
The commands work as follows:
- dmesg – read the contents of the kernel buffer
- | – pipe the command into the next command
- grep – search for a particular string of characters, and display lines that contain them
- Linux – the exact string of characters that grep should search for (capitalization matters)
The first line of output displays the Linux kernel version.
Note: When updating your kernel, it is recommended that you choose a release version that’s compatible with your version of Linux. Your package manager will typically give you kernel versions that are tested and verified.
This guide showed you several different ways to check the Linux kernel version. Since you’re only reading the output of a file, you shouldn’t need sudo privileges.
The Linux kernel has a modular design. Functionality is extendible with modules or drivers. Learn how to use the modprobe command to add or remove modules on Linux.
Источник