- 12 Useful “df” Commands to Check Disk Space in Linux
- 1. Check File System Disk Space Usage
- 2. Display Information of all File System Disk Space Usage
- 3. Show Disk Space Usage in Human Readable Format
- 4. Display Information of /home File System
- 5. Display Information of File System in Bytes
- 6. Display Information of File System in MB
- 7. Display Information of File System in GB
- 8. Display File System Inodes
- 9. Display File System Type
- 10. Include Certain File System Type
- 11. Exclude Certain File System Type
- 12. Display Information of df Command.
- If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
- Linux / Unix – Checking Free Disk Space
- df command examples to check free disk space
- How to check free disk space in Linux
- du command examples for checking free and used disk space
- Say hello to ncdu command
- GUI program
- Conclusion
- 10 Commands to Check Disk Partitions and Disk Space on Linux
- 1. fdisk
- 2. sfdisk
- 3. cfdisk
- 4. parted
- 6. pydf
- 7. lsblk
- 8. blkid
- 9. hwinfo
- 10. Inxi
- Summary
- 47 thoughts on “ 10 Commands to Check Disk Partitions and Disk Space on Linux ”
- Linux Check Disk Space Command To View System Disk Usage
- Linux commands to check disk space using:
- Linux check disk space with df command
- See information about specific filesystem
- Understanding df command output
- Express df output in human readable form
- Display output using inode usage instead of block usage
- Find out the type of each file system displayed
- Limit listing to file systems of given type
- Exclude given file system type
- Show all file system
- Getting more help about the df command
- Linux check disk space with the du command
- See du output in human readable format
- Finding information about any directory trees or files
- How do I summarize disk usage for given directory name?
- Putting it all together
- Dealing with btrfs file system
- Examples
- Conclusion
12 Useful “df” Commands to Check Disk Space in Linux
On the internet, you will find plenty of tools for checking disk space utilization in Linux. However, Linux has a strong built-in utility called ‘df‘.
The ‘df‘ command stands for “disk filesystem“, it is used to get a full summary of available and used disk space usage of the file system on the Linux system.
Using ‘ -h ‘ parameter with (df -h) will show the file system disk space statistics in “human-readable” format, means it gives the details in bytes, megabytes, and gigabyte.

This article explains a way to get the full information of Linux disk space usage with the help of the ‘df‘ command with their practical examples. So, you could better understand the usage of the df command in Linux.
1. Check File System Disk Space Usage
The “df” command displays the information of device name, total blocks, total disk space, used disk space, available disk space, and mount points on a file system.
2. Display Information of all File System Disk Space Usage
The same as above, but it also displays information of dummy file systems along with all the file system disk usage and their memory utilization.
3. Show Disk Space Usage in Human Readable Format
Have you noticed that the above commands display information in bytes, which is not readable at all because we are in a habit of reading the sizes in megabytes, gigabytes, etc. as it makes it very easy to understand and remember.
The df command provides an option to display sizes in Human Readable formats by using ‘-h’ (prints the results in human-readable format (e.g., 1K 2M 3G)).
4. Display Information of /home File System
To see the information of only device /home file systems in human-readable format use the following command.
5. Display Information of File System in Bytes
To display all file system information and usage in 1024-byte blocks, use the option ‘ -k ‘ (e.g. —block-size=1K ) as follows.
6. Display Information of File System in MB
To display information of all file system usage in MB (MegaByte) use the option ‘ -m ‘.
7. Display Information of File System in GB
To display information of all file system statistics in GB (Gigabyte) use the option as ‘df -h‘.
8. Display File System Inodes
Using ‘ -i ‘ switch will display the information of a number of used inodes and their percentage for the file system.
9. Display File System Type
If you notice all the above commands output, you will see there is no Linux file system type mentioned in the results. To check the file system type of your system use the option ‘ T ‘. It will display file system type along with other information.
10. Include Certain File System Type
If you want to display a certain file system type use the ‘ -t ‘ option. For example, the following command will only display the ext3 file system.
11. Exclude Certain File System Type
If you want to display a file system type that doesn’t belongs to the ext3 type use the option ‘ -x ‘. For example, the following command will only display other file systems types other than ext3.
12. Display Information of df Command.
Using ‘—help ‘ switch will display a list of available option that is used with df command.
Read Also :
If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
TecMint is the fastest growing and most trusted community site for any kind of Linux Articles, Guides and Books on the web. Millions of people visit TecMint! to search or browse the thousands of published articles available FREELY to all.
If you like what you are reading, please consider buying us a coffee ( or 2 ) as a token of appreciation.
We are thankful for your never ending support.
Источник
Linux / Unix – Checking Free Disk Space
| Tutorial details | |
|---|---|
| Difficulty level | Easy |
| Root privileges | No |
| Requirements | None |
| Est. reading time | 1m |
(a) df command : Report file system disk space usage.
(b) du command : Estimate file space usage.
df command examples to check free disk space
Type df -h or df -k to list free disk space:
$ df -h
OR
$ df -k
Sample outputs that show disk space utilization:
The df utility displays statistics about the amount of free disk space on the specified file system or on the file system of which file is a part. Values are displayed in 512-byte per block counts. The -H option is called as “Human-readable” output. It use unit suffixes: Byte, Kilobyte, Megabyte, Gigabyte, Terabyte and Petabyte in order to reduce the number of digits to four or fewer using base 10 for sizes i.e. you see 30G (30 Gigabyte).
How to check free disk space in Linux
To see the file system’s complete disk usage pass the -a option:
df -a
Find out disk usage and filesystem type by passing the -T option:
df -T
Want to get used and free inodes information on Linux? Try:
df -i
du command examples for checking free and used disk space
The du command shows how much space one ore more files or directories is using, enter:
$ du -sh
Sample outputs:
Fig.01: Unix df and du command outputs from my FreeBSD server
Say hello to ncdu command
ncdu (NCurses Disk Usage) is a curses-based version of the well-known ‘du’, and provides a fast way to see what directories are using your disk space. One can install with the following apt command/apt-get command:
sudo apt install ncdu
For RHEL/CentOS, first enable EPEL repo (see CentOS 8 turn on EPEL repo and RHEL 8 enable epel repo) and type the following yum command:
sudo yum install ncdu
Now just type:
ncdu
ncdu [dir] ncdu /etc/
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
GUI program
Above programs are good if GUI is not installed or you are working with remote system over the ssh based session. Linux and UNIX-like oses comes with KDE and Gnome desktop system. You will find Free Disk Space Applet located under GUI menus. Here is a sample from Fedora Linux version 22 system:
Conclusion
You learned how to keep track of disk utilization, and disk space with various Linux and Unix commands.
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
Источник
10 Commands to Check Disk Partitions and Disk Space on Linux
In this post we are taking a look at some commands that can be used to check up the partitions on your system.
The commands would check what partitions there are on each disk and other details like the total size, used up space and file system etc.
Commands like fdisk, sfdisk and cfdisk are general partitioning tools that can not only display the partition information, but also modify them.
1. fdisk
Fdisk is the most commonly used command to check the partitions on a disk. The fdisk command can display the partitions and details like file system type. However it does not report the size of each partitions.
Each device is reported separately with details about size, seconds, id and individual partitions.
2. sfdisk
Sfdisk is another utility with a purpose similar to fdisk, but with more features. It can display the size of each partition in MB.
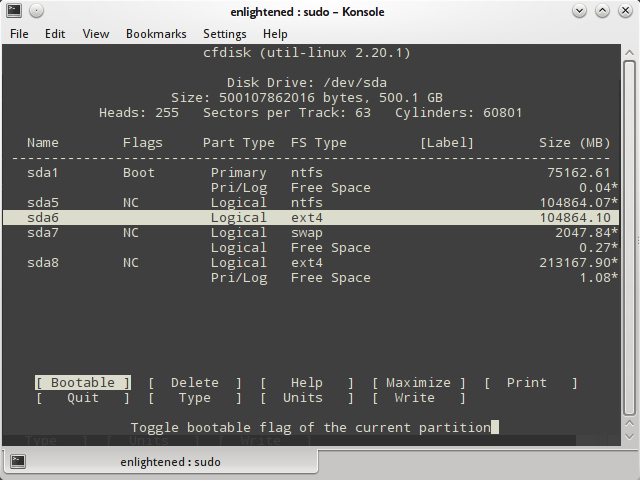
3. cfdisk
Cfdisk is a linux partition editor with an interactive user interface based on ncurses. It can be used to list out the existing partitions as well as create or modify them.
Here is an example of how to use cfdisk to list the partitions.
Cfdisk works with one partition at a time. So if you need to see the details of a particular disk, then pass the device name to cfdisk.
4. parted
Parted is yet another command line utility to list out partitions and modify them if needed.
Here is an example that lists out the partition details.
Df is not a partitioning utility, but prints out details about only mounted file systems. The list generated by df even includes file systems that are not real disk partitions.
Here is a simple example
Only the file systems that start with a /dev are actual devices or partitions.
Use grep to filter out real hard disk partitions/file systems.
To display only real disk partitions along with partition type, use df like this
Note that df shows only the mounted file systems or partitions and not all.
6. pydf
Improved version of df, written in python. Prints out all the hard disk partitions in a easy to read manner.
Again, pydf is limited to showing only the mounted file systems.
7. lsblk
Lists out all the storage blocks, which includes disk partitions and optical drives. Details include the total size of the partition/block and the mount point if any.
Does not report the used/free disk space on the partitions.
If there is no MOUNTPOINT, then it means that the file system is not yet mounted. For cd/dvd this means that there is no disk.
Lsblk is capbale of displaying more information about each device like the label and model. Check out the man page for more information
Display UUID and Model of device
The «-o» option can be used to specify the columns to display. The following example shows the UUID and model name column along with other columns.
The above output has all the necessary information about all the storage devices present on the system or connected via usb. You can see the device name, size, mount point, uuid, model name etc.
This is the best command to see all information about storage devices together in one place.
8. blkid
Prints the block device (partitions and storage media) attributes like uuid and file system type. Does not report the space on the partitions.
9. hwinfo
The hwinfo is a general purpose hardware information tool and can be used to print out the disk and partition list.
The output however does not print details about each partition like the above commands.
To learn more about the Hwinfo command check this post:
Check hardware information on Linux with hwinfo command
10. Inxi
Inxi is a very useful command line program that can display information about various hardware components present on the system. To display information about the disk drives and storage devices use the «-D» option with inxi.
The «-x» option prints extra available information.
The output from inxi does not contains details like UUID and mount directory.
To learn more about the inxi command check out this post:
Inxi is an amazing tool to check hardware information on Linux
Summary
The output of parted is concise and complete to get an overview of different partitions, file system on them and the total space. Pydf and df are limited to showing only mounted file systems and the same on them.
Fdisk and Sfdisk show a whole lot of information that can take sometime to interpret whereas, Cfdisk is an interactive partitioning tool that display a single device at a time.
So try them out, and do not forget to comment below.
A Tech Enthusiast, Blogger, Linux Fan and a Software Developer. Writes about Computer hardware, Linux and Open Source software and coding in Python, Php and Javascript. He can be reached at [email protected] .
47 thoughts on “ 10 Commands to Check Disk Partitions and Disk Space on Linux ”
Thank you for this great summary of relevant commands and also showing whether SU privileges are needed or not.
Good article. Thanks for writing this .
I’d also suggest including “ncdu” (stands for ncurses du) – https://dev.yorhel.nl/ncdu – in this as it’s quite useful in knowing the disk usage on the terminal in a graphical way
pydf hands down the best alternative if you want a quick glance at disk usage!
Very useful, thank you!
very useful,
How about GUI tools?
Hardinfo is a GUI tool that shows hardware information including disk drives and partitions..
On ubuntu it can be installed with the following command
sudo apt-get install hardinfo
Another tool is gparted.
It is a partition management tool, but can also be used to list the disk drives and partitions
Well done — I learned something!
glad to know that.
thanks for the comment.
Very useful. Thank you for your effort.
Detailed and to the point post. Thanks A Ton!
Источник
Linux Check Disk Space Command To View System Disk Usage
Linux commands to check disk space using:
- df command – Shows the amount of disk space used and available on Linux file systems.
- du command – Display the amount of disk space used by the specified files and for each subdirectory.
- btrfs fi df /device/ – Show disk space usage information for a btrfs based mount point/file system.
Linux check disk space with df command
- Open the terminal and type the following command to check disk space.
- The basic syntax for df is:
df [options] [devices]
Type: - df
- df -H
Fig.01: df command in action
See information about specific filesystem
You can give a device or mount point as an argument, and df report data only for the filesystem physically residing on that device. For example, the following command provides information only for the partition /dev/sda:
$ df /dev/sda
$ df -h /dev/sdc1
$ df /data/
Sample outputs:
Understanding df command output
The valid fields are as follows:
| Display name | Valid field name (for —output option) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Filesystem | source | The source of the mount point, usually a device. |
| 1K-blocks | size | Total number of blocks. |
| Used | used | Number of used blocks. |
| Available | avail | Number of available blocks. |
| Use% | pcent | Percentage of USED divided by SIZE. |
| Mounted on | target | The mount point. |
You can pass the output format defined by ‘valid field name’ as follows:
$ df —output=field1,field2.
$ df —output=source,used,avail /data/
Sample outputs:
You can print all available fields, enter:
$ df —o
Sample outputs:
Express df output in human readable form
Pass the -h option to see output in human readable format. You will device size in gigabytes or terabytes or megabytes:
$ df -h ### Human format
$ df -m ### Show output size in one-megabyte
$ df -k ### Show output size in one-kilobyte blocks (default)
Display output using inode usage instead of block usage
An inode is a data structure on a Linux file system that stores all information about file. To list inode information, enter:
$ df -i
$ df -i -h
Sample outputs:
Find out the type of each file system displayed
Pass the -T option to display the type of each filesystems listed such as ext4, btrfs, ext2, nfs4, fuse, cgroup, cputset, and more:
$ df -T
$ df -T -h
$ df -T -h /data/
Sample outputs:
Limit listing to file systems of given type
The syntax is:
$ df -t ext3 #Only see ext3 file system
$ df -t ext4 #Only see ext4 file system
$ df -t btrfs #Only see btrfs file system
Exclude given file system type
To list all but exclude ext2 filesystem pass the -x TYPE option, enter:
$ df -x ext2
Show all file system
Pass the -a or —all option to the df command to include in its output filesystems that have a size of zero blocks, run:
$ df -a
These file systems omitted by default.
Getting more help about the df command
Pass the —help option see a brief help message:
$ df —help
Or read its man page by typing the following command:
$ man df
Linux check disk space with the du command
The NA command is very useful to track down disk space hogs. It is useful to find out the names of directories and files that consume large amounts of space on a disk. The basic syntax is:
du
du /path/do/dir
du [options] [directories and/or files]
To see the names and space consumption of each of the directories including all subdirectories in the directory tree, enter:
$ du
Sample outputs:
The first column is expressed in kilobytes (file size) and the second column is the filename or directory name.
See du output in human readable format
Pass the -h option to display size in K (kilobytes), M (megabytes), G (gigabytes) instead of the default kilobytes:
$ du -h
Sample outputs:
Finding information about any directory trees or files
To find out /etc/ directory space usage, enter:
# du /etc/
# du -h /etc/
The following will report the sizes of the thee files named hdparm, iptunnel and ifconfig that are located in the /sbin directory:
$ du /sbin/hdparm /sbin/iptunnel /sbin/ifconfig
$ du -h /sbin/hdparm /sbin/iptunnel /sbin/ifconfig
Sample outputs:
How do I summarize disk usage for given directory name?
Pass the -s option to the du command. In this example, ask du command to report only the total disk space occupied by a directory tree and to suppress subdirectories:
# du -s /etc/
# du -sh /etc/
Sample outputs:
Pass the -a (all) option to see all files, not just directories:
# du -a /etc/
# du -a -h /etc/
Sample outputs:
You can also use star ( * ) wildcard, which will match any character. For example, to see the size of each png file in the current directory, enter:
$ du -ch *.png
The -c option tells du to display grand total.
Putting it all together
To list top 10 directories eating disk space in /etc/, enter:
# du -a /etc/ | sort -n -r | head -n 10
Sample outputs:
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
For more information on the du command, type:
$ man du
$ du —help
Dealing with btrfs file system
For btrfs filesystem use the btrfs fi df command to see space usage information for a mount point. The syntax is:
Examples
# btrfs fi df /data/
# btrfs fi df -h /data/
Sample outputs:
To see raw numbers in bytes, run:
# btrfs fi df -b /data/
OR
# btrfs fi df -k /data/ ### show sizes in KiB ##
# btrfs fi df -m /data/ ### show sizes in MiB ##
# btrfs fi df -g /data/ ### show sizes in GiB ##
# btrfs fi df -t /data/ ### show sizes in TiB ##
Conclusion
Here is quick summary for Linux check disk space commands. Use the du command when you need to estimate file space usage. To report Linux file system disk space usage use the df command. The btrfs df command must be used when using btrfs file system. Fore more info see GNU coreutils page here.
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
| Category | List of Unix and Linux commands |
|---|---|
| Documentation | help • mandb • man • pinfo |
| Disk space analyzers | df • duf • ncdu • pydf |
| File Management | cat • cp • less • mkdir • more • tree |
| Firewall | Alpine Awall • CentOS 8 • OpenSUSE • RHEL 8 • Ubuntu 16.04 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Linux Desktop Apps | Skype • Spotify • VLC 3 |
| Modern utilities | bat • exa |
| Network Utilities | NetHogs • dig • host • ip • nmap |
| OpenVPN | CentOS 7 • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Debian 8/9 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Package Manager | apk • apt |
| Processes Management | bg • chroot • cron • disown • fg • glances • gtop • jobs • killall • kill • pidof • pstree • pwdx • time • vtop |
| Searching | ag • grep • whereis • which |
| Shell builtins | compgen • echo • printf |
| Text processing | cut • rev |
| User Information | groups • id • lastcomm • last • lid/libuser-lid • logname • members • users • whoami • who • w |
| WireGuard VPN | Alpine • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Firewall • Ubuntu 20.04 |
Comments on this entry are closed.
Nice article. What about “ncdu”
For graphical overview… 🙂
How do i format a 39TB drive with ext4?
web-a1
Источник