- Смотрим информацию о системе в Linux (Ubuntu, CentOS, Fedora)
- 16 Commands to Check Hardware Information on Linux
- Hardware information
- 1. lscpu
- 2. lshw — List Hardware
- 3. hwinfo — Hardware Information
- 4. lspci — List PCI
- 5. lsscsi — List scsi devices
- 6. lsusb — List usb buses and device details
- 7. Inxi
- 8. lsblk — List block devices
- 9. df — disk space of file systems
- 10. Pydf — Python df
- 11. fdisk
- 12. mount
- 13. free — Check RAM
- 14. dmidecode
- 15. /proc files
- 16. hdparm
- Summary
- 48 thoughts on “ 16 Commands to Check Hardware Information on Linux ”
- 10 Commands to Collect System and Hardware Info in Linux
- 1. How to View Linux System Information
- 2. How to View Linux System Hardware Information
- 3. How to View Linux CPU Information
- 4. How to Collect Linux Block Device Information
- 5. How to Print USB Controllers Information
- 6. How to Print PCI Devices Information
- 7. How to Print SCSI Devices Information
- 8. How to Print Information about SATA Devices
- 9. How to Check Linux File System Information
- 10. How to Check Linux Hardware Components Info
- Summary
- If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
Смотрим информацию о системе в Linux (Ubuntu, CentOS, Fedora)
Тем кто только-только пересел с операционной системы Windows на более сложный Linux, порой бывает сложно выполнить те операции, которые на знакомой ОС делались за пару секунд.
Одна из подобных задач — посмотреть основную информацию о системе: какой стоит процессор, материнская плата, версия операционной системы, разрядность, ядро и т.п. В старой доброй Windows достаточно было вывести свойства системы или открыть диспетчер задач. А тут всё сложнее. Но вся сила Линукс — в консоли и есть ряд специальных команд командой строки, которые помогут узнать всю необходимую информацию о Вашей ОС Linux, будь то Ubuntu, CentOS, Fedora или иной дистрибутив. Сейчас я Вам их покажу!
hwinfo — эта утилита выдаёт массу информации о комплектующих: процессоре, материнской плате, оперативной памяти, видеокарте, жесткому диску и т.п. К сожалению, не во всех дистрибутивах она присутствует, но установить ещё случай чего — проще простого:
— в Debian, Ubuntu: sudo apt-get install hwinfo
— в Fedora и Red Hat: yum install hwinfo
Чтобы вывести основную информацию, воспользуйтесь ключом —short.
lshw — эта команда выдаёт полную информацию о аппаратной части компьютера или ноутбука.
Конечно, до уровная утилиты hwinfo ещё далеко, но основную информацию получить вполне реально. Команда lshw выполняется с правами рута — sudo lshw.
cat /proc/cpuinfo — вывод полной информации о процессоре, установленном на ПК.
cat /proc/meminfo — подробные данные о полном объёме оперативной памяти, сколько её занято и сколько свободно.
free -m — команда похожа по результату на предыдущую, за тем лишь результатом, что вывод будет в виде небольшой таблицы.
lspci | grep VGA — эта директива отобразит информацию по установленной видеокарте.
lspci | grep Audio — смотрим какая на компьютере установлена звуковая карта.
df -H — подробная информация по разделам жесткого диска, их объём и текущая загрузка.
lspci | grep Ethernet — модель и производитель сетевого адаптера ПК.
uname -a — эта команда отобразит в консоли основные данные по операционной системе Linux — версию ядра, дистрибутива, а так же используемую архитектуру — 32 или 64 бита).
uname -r — выводится информация о версии ядра ОС.
cat /proc/version — вывод команды полностью аналогичен предыдущей.
lsb_release -a — здесь в качестве результата выполнения команды будет название установленного дистибутива Линукс и его версия:
cat /etc/*release* — результат выполнения команды будет во много аналогичным предшествующей директиве. То есть будет показана инфа о дистрибутиве и его версии.
Важное отличие — если Вы используете ОС построенную на каком либо дистрибутиве, то команда отобразить и информацию о базовом дистрибутиве Линукс.
ls -clt / | tail -n 1 | awk ‘< print $7, $6, $8 >’ — эта команда отобразит Вам дату и время установки системы.
ls -dl /var/log/installer/ — эта команда Linux так же позволяет узнать дату и время установки системы.
cat /etc/issue — результат выполнения команды аналогичен предыдущей. Вам будет показана версия дистрибутива ОС.
С помощью этого списка основных команд Вы сможете без проблем посмотреть и узнать основную информацию о ПК и операционной системе.
Источник
16 Commands to Check Hardware Information on Linux
Hardware information
Like for every thing, there are plenty of commands to check information about the hardware of your linux system.
Some commands report only specific hardware components like cpu or memory while the rest cover multiple hardware units.
This post takes a quick look at some of the most commonly used commands to check information and configuration details about various hardware peripherals and devices.
The list includes lscpu, hwinfo, lshw, dmidecode, lspci etc.
1. lscpu
The lscpu command reports information about the cpu and processing units. It does not have any further options or functionality.
2. lshw — List Hardware
A general purpose utility, that reports detailed and brief information about multiple different hardware units such as cpu, memory, disk, usb controllers, network adapters etc. Lshw extracts the information from different /proc files.
Check out the following post to learn more about lshw
3. hwinfo — Hardware Information
Hwinfo is another general purpose hardware probing utility that can report detailed and brief information about multiple different hardware components, and more than what lshw can report.
4. lspci — List PCI
The lspci command lists out all the pci buses and details about the devices connected to them.
The vga adapter, graphics card, network adapter, usb ports, sata controllers, etc all fall under this category.
Filter out specific device information with grep.
5. lsscsi — List scsi devices
Lists out the scsi/sata devices like hard drives and optical drives.
6. lsusb — List usb buses and device details
This command shows the USB controllers and details about devices connected to them. By default brief information is printed. Use the verbose option «-v» to print detailed information about each usb port
On the above system, 1 usb port is being used by the mouse.
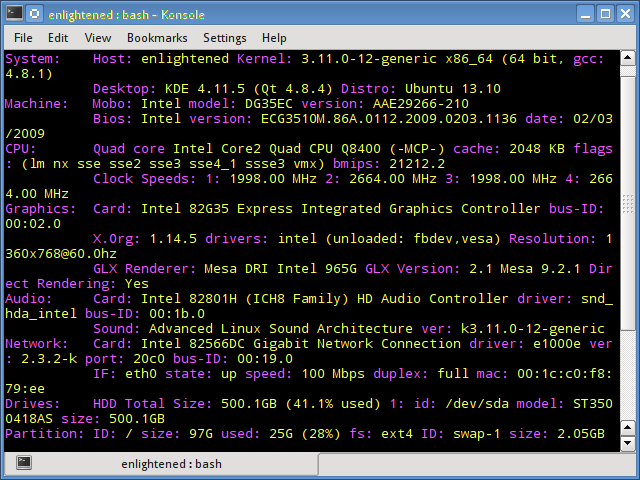
7. Inxi
Inxi is a 10K line mega bash script that fetches hardware details from multiple different sources and commands on the system, and generates a beautiful looking report that non technical users can read easily.
8. lsblk — List block devices
List out information all block devices, which are the hard drive partitions and other storage devices like optical drives and flash drives
9. df — disk space of file systems
Reports various partitions, their mount points and the used and available space on each.
10. Pydf — Python df
An improved df version written in python, that displays colored output that looks better than df
11. fdisk
Fdisk is a utility to modify partitions on hard drives, and can be used to list out the partition information as well.
12. mount
The mount is used to mount/unmount and view mounted file systems.
Again, use grep to filter out only those file systems that you want to see
13. free — Check RAM
Check the amount of used, free and total amount of RAM on system with the free command.
14. dmidecode
The dmidecode command is different from all other commands. It extracts hardware information by reading data from the SMBOIS data structures (also called DMI tables).
Check out the man page for more details.
15. /proc files
Many of the virtual files in the /proc directory contain information about hardware and configurations. Here are some of them
16. hdparm
The hdparm command gets information about sata devices like hard disks.
Summary
Each of the command has a slightly different method of extracting information, and you may need to try more than one of them, while looking for specific hardware details. However they are available across most linux distros, and can be easily installed from the default repositories.
On the desktop there are gui tools, for those who do not want to memorise and type commands. Hardinfo, I-nex are some of the popular ones that provide detailed information about multiple different hardware components.
A Tech Enthusiast, Blogger, Linux Fan and a Software Developer. Writes about Computer hardware, Linux and Open Source software and coding in Python, Php and Javascript. He can be reached at [email protected] .
48 thoughts on “ 16 Commands to Check Hardware Information on Linux ”
How i can check memory in CPU. Example OPT, Efuse
Thanks for this. I’m just getting going on a VPS and this helped me discover they’d not given me the extra 1Gb I ordered. Very well explained.
Super happy with
inxi -Fx
more accurate than some of the other utilities.. for instance hwinfo was inaccurate for my Lenovo
Thanks for the great post!
Thank you! Your descriptions were useful and well explained!
Источник
10 Commands to Collect System and Hardware Info in Linux
It is always a good practice to know the hardware components of your Linux system is running on, this helps you to deal with compatibility issues when it comes to installing packages, drivers on your system using yum, dnf, or apt.

Therefore in these tips and tricks series, we shall look at some useful commands that can help you to extract information about your Linux system and hardware components.
1. How to View Linux System Information
To know only the system name, you can use the uname command without any switch that will print system information or the uname -s command will print the kernel name of your system.
To view your network hostname, use the ‘-n’ switch with the uname command as shown.
To get information about kernel-version, use the ‘-v’ switch.
To get the information about your kernel release, use the ‘-r’ switch.
To print your machine hardware name, use the ‘-m’ switch:
All this information can be printed at once by running the ‘uname -a’ command as shown below.
2. How to View Linux System Hardware Information
Here you can use the lshw tool to gather vast information about your hardware components such as cpu, disks, memory, usb controllers, etc.
lshw is a relatively small tool and there are few options that you can use with it while extracting information. The information provided by lshw was gathered from different /proc files.
Note: Do remember that the lshw command is executed by the superuser (root) or sudo user.
To print information about your Linux system hardware, run this command.
You can print a summary of your hardware information by using the -short option.
If you wish to generate output as an html file, you can use the option -html.

3. How to View Linux CPU Information
To view information about your CPU, use the lscpu command as it shows information about your CPU architecture such as a number of CPUs, cores, CPU family model, CPU caches, threads, etc from sysfs and /proc/cpuinfo.
4. How to Collect Linux Block Device Information
Block devices are storage devices such as hard disks, flash drives, etc. lsblk command is used to report information about block devices as follows.
If you want to view all block devices on your system then include the -a option.
5. How to Print USB Controllers Information
The lsusb command is used to report information about USB controllers and all the devices that are connected to them.
You can use the -v option to generate detailed information about each USB device.
6. How to Print PCI Devices Information
PCI devices may include usb ports, graphics cards, network adapters, etc. The lspci tool is used to generate information concerning all PCI controllers on your system plus the devices that are connected to them.
To print information about PCI devices run the following command.
Use the -t option to produce output in a tree format.
Use the -v option to produce detailed information about each connected device.
7. How to Print SCSI Devices Information
To view all your scsi/sata devices, use the lsscsi command as follows. If you do not have the lsscsi tool installed, run the following command to install it.
After installation, run the lsscsi command as shown:
Use the -s option to show device sizes.
8. How to Print Information about SATA Devices
You can find some information about sata devices on your system as follows using the hdparm utility. In the example below, I used the block device /dev/sda1 which is the hard disk on my system.
To print information about device geometry in terms of cylinders, heads, sectors, size, and the starting offset of the device, use the -g option.
9. How to Check Linux File System Information
To gather information about file system partitions, you can use the fdisk command. Although the main functionality of the fdisk command is to modify file system partitions, it can also be used to view information about the different partitions on your file system.
You can print partition information as follows. Remember to run the command as a superuser or else you may not see any output.
10. How to Check Linux Hardware Components Info
You can also use the dmidecode utility to extract hardware information by reading data from the DMI tables.
To print information about memory, run this command as a superuser.
To print information about the system, run this command.
To print information about BIOS, run this command.
To print information about the processor, run this command.
Summary
There are many other ways you can use to obtain information about your system hardware components. Most of these commands use files in the /proc directory to extract system information.
Hope you find these tips and tricks useful and remember to post a comment in case you want to add more information to this or if you face any difficulties in using any of the commands. Remember to always stay connected to Tecmint.
If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
TecMint is the fastest growing and most trusted community site for any kind of Linux Articles, Guides and Books on the web. Millions of people visit TecMint! to search or browse the thousands of published articles available FREELY to all.
If you like what you are reading, please consider buying us a coffee ( or 2 ) as a token of appreciation.
We are thankful for your never ending support.
Источник