- Системные скрипты на php для linux, пишем скриншотер
- Установка скрипта
- Выводы
- Как запустить PHP скрипт в командной строке (без веб-сервера)
- Как запустить PHP скрипт в командной строке Windows
- Как запустить .php скрипт в командной строке Windows и Linux
- Как передать аргументы PHP скрипту в командной строке
- Как в PHP скрипте обратиться к аргументам
- Как в PHP получить данные от пользователя в консоли
- Выполнение команд PHP в интерактивном режиме
- Запуск отдельных команд PHP
- Использование PHP в командной строке
- Содержание
- User Contributed Notes 35 notes
Системные скрипты на php для linux, пишем скриншотер
Многие люди считают что php подходит только для разработки сайтиков, и никак не может быть использован, в других областях применения языков программирования, для создания программ… В этой статье я бы хотел осветить, применение php скриптов «не целевым» образом, а именно мы напишем скрипт который будет делать скрин, выгружать его на yandex диск и выводить адрес скриншота в консоль…
Рассмотрим структуру проекта, она очень проста и состоит из 3-х файлов:
1. screen.php — точка входа в приложение.
2. classes/autoload.php — автолоадер проекта.
3. classes/Request.php — класс реализующий запросы к api яндекса.
Далее расмотрим код screen.php:
Как видите это точка входа в приложение, логика проста:
1. Формирование имени скриншота
2. Вызов системной программы scrot
3. Запрос api yandex.disk и выгрузка скриншота
Файл autoload.php тоже очень прост и состоит всего из трёх строк кода, я приведу его лишь для ознакомления, и мы не будем его рассматривать подробно.
Работа с yandex api довольно проста я написал небольшой класс Request.php, с набором неких методов, которые помогают мне в работе с ним…
Рассмотрим ключевые методы данного класса для запроса методов api в основном я использовал file_get_contents, и так как мне приходилось использовать, его при запросе многих методов я написал метод генерации контекста:
Он тоже довольно прост мы создаём контекст с определённом методом запроса и информации об аутентификации…
Далее нам необходимо «создать файл на yandex.disk» это действие мы производим следующим методом:
Как я говорил ранее мы запрашиваем api с помощью функции file_get_contents. После того как этот метод отработает, и вся информация будет запрошена, запускаеться метод upload:
В данно случае можно было бы использовать для отправки файла одну из функций `file_get_contents` или `file_put_contents` но это не целесообразно, по причине того что пришлось бы, в контексте данных функций, в ручную имитировать заголовки и другие вытекающие из этого проблемы, так что проще просто использовать для этих целей curl.
И так файл загружен, остаёться только опубликовать его и получить прямую ссылку для просмотра, это выполняет функция publicateFile():
В этом методе тоже всё довольно просто, мы запрашиваем публикацию файла методом PUT у api, яндекс возвращает ссылку, на которую мы должны выполнить запрос для подтвержедения публикации, и метод запроса в диску. И в конце концов, после второго запроса мы получаем массив который соддержит ссылку на публичный файл.
Установка скрипта
Чтож мы закончили, теперь нам предстоит придумать а как же этот скрипт будет работать из консоли? как его запустить там в «глобальной области»? ответом на эти вопросы будет phar — архив содержащий файлы php и способный выполняться как отдельное приложение, похож на тот же jar.
phar мы будем собирать с помощью утилиты box.phar для этого мы пишем простой конфигурационный файл box.json:
Для сборки запускаем:
И наш проект готов теперь осталось только установить права на исполнение файла, и скопировать в директорию /usr/bin/srcphp:
Не забываем о конфигурации файла /home/myname/.config/srcphp/config.php:
в token необходимо вписать полученный oAuth токен от яндекса, при переходе сгенерированной по средством запуска скрипта с ключом —getToken:
Выводы
Главная мысль статьи — рассмотреть как создать консольное приложение с помощью php, на примере программы скриншотера, в следующих я буду поднимать тему использования php в различных сферах применения, и следующая статью будет посвящена разработки простого драйвера usb устройства для linux. Спасибо за внимание и доброго дня.
Источник
Как запустить PHP скрипт в командной строке (без веб-сервера)
Как запустить PHP скрипт в командной строке Windows
Для запуска PHP в командной строке необязательно устанавливать веб-сервер, достаточно скачать и распаковать архив с PHP интерпретатором. О том, где скачать PHP с официального сайта и как разобраться с версиями, смотрите эту статью.
Если вы часто будете запускать PHP скрипты из командной строки Windows, то настоятельно рекомендуется Добавить путь до PHP в переменную окружения PATH в Windows. Благодаря этому не придётся каждый раз указывать полный путь до файла php.exe.
Теперь, когда PHP установлен и путь до php.exe добавлен в переменную окружения Windows, открываем командную строку, для этого нажмите сочетание клавиш Win+x и выберите Windows PowerShell.
Для проверки, что нормально установилось, посмотрим справку по PHP:
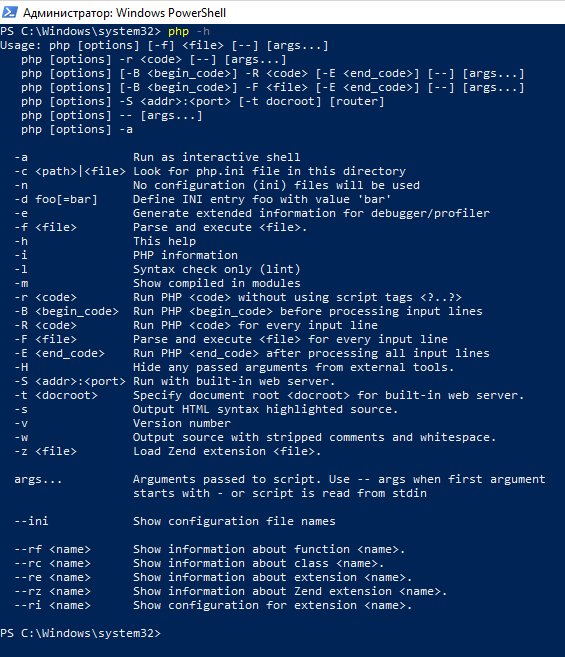
На самом деле, мы запускаем файл php.exe, но расширение можно отбросить. То есть предыдущая запись эквивалентна
Как запустить .php скрипт в командной строке Windows и Linux
Для запуска .php файла в консоли Windows используется следующая команда:
Опцию -f можно отбросить, то есть предыдущая и следующая команды равнозначны:
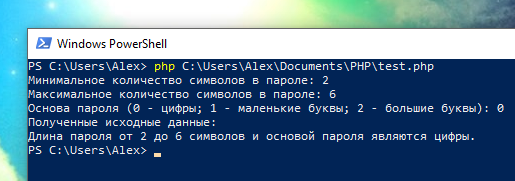
Я создал тестовый файл, который расположен по пути C:\Users\Alex\Documents\PHP\test.php тогда я могу запустить его в PHP так:
Как передать аргументы PHP скрипту в командной строке
Для передачи скрипту аргументов, перечислите их после имени файла, разделяя пробелом. Если сами аргументы содержат пробелы или другие символы, которые имеют особое значение для оболочки командной строки, то поместите эти аргументы и одинарные или двойные кавычки.
Пример запуска PHP скрипта с тремя аргументами:
Как в PHP скрипте обратиться к аргументам
Переданные аргументы содержаться в массиве $argv. Причём, порядковый номер аргумента соответствует номеру в массиве. То есть первый аргумент будет помещён в $argv[1], второй в $argv[2] и так далее.
Самый первый элемент массива $argv[0] содержит полный путь до запускаемого скрипта.
Содержимое файла test.php:
Запустим его и передадим в скрипт три аргумента:

Как в PHP получить данные от пользователя в консоли
Благодаря передаваемым аргументам, скрипт может выполнять действия не только с прописанными в нём данными, но и с другими значениями, указанными при запуске скрипта.
Кстати, при работе в окружении веб-сервера, то есть когда PHP скрипт выполняет задачи для веб-сайта, возможность передать ему аргументы реализована с помощью HTTP методов GET и POST. Эти аргументы передаются перед запуском скрипта, и уже после запуска PHP скрипта новые данные отправить нельзя — нужно ждать завершения работы программы, и при необходимости запустить её ещё раз с новыми данными.
Во время работы скрипта может потребоваться ввод новых данных, в консоли это достигается с помощью строки запроса, в которую пользователь может ввести значение и нажать Enter для передачи его скрипту. В контексте веб-сайта такой возможности — передать данные уже во время выполнения скрипта — нет. То есть консольный запуск PHP скриптов с аргументами не только проще (не нужно возиться с HTML формой), но и даже более гибкий.
В PHP для запроса пользователю используется функция readline.
Эта функция одинаково работает и на Windows и на Linux. Причём на Linux она имеет интерактивные возможности Bash, например, сохраняет историю ввода, к которой можно вернуться с помощью стрелок. На Windows эта возможность появилась начиная с PHP 7.1.
Если сильно надо, можно настроить автозавершение вводимых данных. Все функции GNU Readline рассмотрены здесь. Я же коснусь только readline, которая считывает введённую пользователем строку. С этой функцией можно указать один опциональный аргумент — строку, которая будет показана пользователю в приглашении.
Пример консольного PHP скрипта, которые запрашивает у пользователя данные в приглашении командной строки:
Выполнение команд PHP в интерактивном режиме
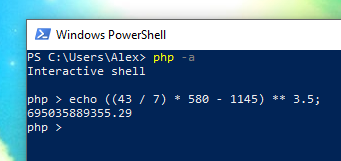
Если вам это нужно, то можно работать с интерпретатором PHP в интерактивном режиме, вводя код построчно. При этом код выполняется после нажатия кнопки Enter, но значения переменных сохраняются в рамках одной сессии. То есть вы можете присвоить значение какой-либо переменной, а затем использовать его в других строках.
Для запуска интерактивного шелла:
Запуск отдельных команд PHP
Для выполнения отдельных команд используйте опцию -r:
Источник
Использование PHP в командной строке
Содержание
User Contributed Notes 35 notes
You can easily parse command line arguments into the $_GET variable by using the parse_str() function.
?>
It behaves exactly like you’d expect with cgi-php.
$ php -f somefile.php a=1 b[]=2 b[]=3
This will set $_GET[‘a’] to ‘1’ and $_GET[‘b’] to array(‘2’, ‘3’).
Even better, instead of putting that line in every file, take advantage of PHP’s auto_prepend_file directive. Put that line in its own file and set the auto_prepend_file directive in your cli-specific php.ini like so:
It will be automatically prepended to any PHP file run from the command line.
use » instead of ‘ on windows when using the cli version with -r
php -r «echo 1»
— correct
php -r ‘echo 1’
PHP Parse error: syntax error, unexpected »echo’ (T_ENCAPSED_AND_WHITESPACE), expecting end of file in Command line code on line 1
When you’re writing one line php scripts remember that ‘php://stdin’ is your friend. Here’s a simple program I use to format PHP code for inclusion on my blog:
UNIX:
cat test.php | php -r «print htmlentities(file_get_contents(‘php://stdin’));»
DOS/Windows:
type test.php | php -r «print htmlentities(file_get_contents(‘php://stdin’));»
Just a note for people trying to use interactive mode from the commandline.
The purpose of interactive mode is to parse code snippits without actually leaving php, and it works like this:
[root@localhost php-4.3.4]# php -a
Interactive mode enabled
I noticed this somehow got ommited from the docs, hope it helps someone!
If your php script doesn’t run with shebang (#!/usr/bin/php),
and it issues the beautifull and informative error message:
«Command not found.» just dos2unix yourscript.php
et voila.
If you still get the «Command not found.»
Just try to run it as ./myscript.php , with the «./»
if it works — it means your current directory is not in the executable search path.
If your php script doesn’t run with shebang (#/usr/bin/php),
and it issues the beautifull and informative message:
«Invalid null command.» it’s probably because the «!» is missing in the the shebang line (like what’s above) or something else in that area.
Parsing commandline argument GET String without changing the PHP script (linux shell):
URL: index.php?a=1&b=2
Result: output.html
echo «» | php -R ‘include(«index.php»);’ -B ‘parse_str($argv[1], $_GET);’ ‘a=1&b=2’ >output.html
(no need to change php.ini)
You can put this
echo «» | php -R ‘include(«‘$1′»);’ -B ‘parse_str($argv[1], $_GET);’ «$2»
in a bash script «php_get» to use it like this:
php_get index.php ‘a=1&b=2’ >output.html
or directed to text browser.
php_get index.php ‘a=1&b=2’ |w3m -T text/html
Ok, I’ve had a heck of a time with PHP > 4.3.x and whether to use CLI vs CGI. The CGI version of 4.3.2 would return (in browser):
—
No input file specified.
—
And the CLI version would return:
—
500 Internal Server Error
—
It appears that in CGI mode, PHP looks at the environment variable PATH_TRANSLATED to determine the script to execute and ignores command line. That is why in the absensce of this environment variable, you get «No input file specified.» However, in CLI mode the HTTP headers are not printed. I believe this is intended behavior for both situations but creates a problem when you have a CGI wrapper that sends environment variables but passes the actual script name on the command line.
By modifying my CGI wrapper to create this PATH_TRANSLATED environment variable, it solved my problem, and I was able to run the CGI build of 4.3.2
If you want to be interactive with the user and accept user input, all you need to do is read from stdin.
echo «Are you sure you want to do this? Type ‘yes’ to continue: » ;
$handle = fopen ( «php://stdin» , «r» );
$line = fgets ( $handle );
if( trim ( $line ) != ‘yes’ ) <
echo «ABORTING!\n» ;
exit;
>
echo «\n» ;
echo «Thank you, continuing. \n» ;
?>
Parsing command line: optimization is evil!
One thing all contributors on this page forgotten is that you can suround an argv with single or double quotes. So the join coupled together with the preg_match_all will always break that 🙂
Here is a proposal:
#!/usr/bin/php
( arguments ( $argv ));
function arguments ( $args )
<
array_shift ( $args );
$endofoptions = false ;
$ret = array
(
‘commands’ => array(),
‘options’ => array(),
‘flags’ => array(),
‘arguments’ => array(),
);
while ( $arg = array_shift ( $args ) )
<
// if we have reached end of options,
//we cast all remaining argvs as arguments
if ( $endofoptions )
<
$ret [ ‘arguments’ ][] = $arg ;
continue;
>
// Is it a command? (prefixed with —)
if ( substr ( $arg , 0 , 2 ) === ‘—‘ )
<
// is it the end of options flag?
if (!isset ( $arg [ 3 ]))
<
$endofoptions = true ;; // end of options;
continue;
>
$value = «» ;
$com = substr ( $arg , 2 );
// is it the syntax ‘—option=argument’?
if ( strpos ( $com , ‘=’ ))
list( $com , $value ) = split ( «=» , $com , 2 );
// is the option not followed by another option but by arguments
elseif ( strpos ( $args [ 0 ], ‘-‘ ) !== 0 )
<
while ( strpos ( $args [ 0 ], ‘-‘ ) !== 0 )
$value .= array_shift ( $args ). ‘ ‘ ;
$value = rtrim ( $value , ‘ ‘ );
>
$ret [ ‘options’ ][ $com ] = !empty( $value ) ? $value : true ;
continue;
// Is it a flag or a serial of flags? (prefixed with -)
if ( substr ( $arg , 0 , 1 ) === ‘-‘ )
<
for ( $i = 1 ; isset( $arg [ $i ]) ; $i ++)
$ret [ ‘flags’ ][] = $arg [ $i ];
continue;
>
// finally, it is not option, nor flag, nor argument
$ret [ ‘commands’ ][] = $arg ;
continue;
>
/* vim: set expandtab tabstop=2 shiftwidth=2: */
?>
I had a problem with the $argv values getting split up when they contained plus (+) signs. Be sure to use the CLI version, not CGI to get around it.
i use emacs in c-mode for editing. in 4.3, starting a cli script like so:
#!/usr/bin/php -q /* -*- c -*- */
— mode automatically when i loaded the file for editing . the ‘-q’ flag didn ‘t actually do anything (in the older cgi versions, it suppressed html output when the script was run) but it caused the commented mode line to be ignored by php.
in 5.2, ‘ — q ‘ has apparently been deprecated. replace it with ‘ — ‘ to achieve the 4.3 invocation-with-emacs-mode-line behavior:
#!/usr/bin/php — /* -*- c -*- */
t go back to your 4.3 system and replace ‘-q’ with ‘—‘ ; it seems to cause php to hang waiting on STDIN .
Just another variant of previous script that group arguments doesn’t starts with ‘-‘ or ‘—‘
function arguments ( $argv ) <
$_ARG = array();
foreach ( $argv as $arg ) <
if ( ereg ( ‘—([^=]+)=(.*)’ , $arg , $reg )) <
$_ARG [ $reg [ 1 ]] = $reg [ 2 ];
> elseif( ereg ( ‘^-([a-zA-Z0-9])’ , $arg , $reg )) <
$_ARG [ $reg [ 1 ]] = ‘true’ ;
> else <
$_ARG [ ‘input’ ][]= $arg ;
>
>
return $_ARG ;
>
print_r ( arguments ( $argv ));
?>
$ php myscript.php —user=nobody /etc/apache2/*
Array
(
[input] => Array
(
[0] => myscript.php
[1] => /etc/apache2/apache2.conf
[2] => /etc/apache2/conf.d
[3] => /etc/apache2/envvars
[4] => /etc/apache2/httpd.conf
[5] => /etc/apache2/mods-available
[6] => /etc/apache2/mods-enabled
[7] => /etc/apache2/ports.conf
[8] => /etc/apache2/sites-available
[9] => /etc/apache2/sites-enabled
)
Just a variant of previous script to accept arguments with ‘=’ also
function arguments ( $argv ) <
$_ARG = array();
foreach ( $argv as $arg ) <
if ( ereg ( ‘—([^=]+)=(.*)’ , $arg , $reg )) <
$_ARG [ $reg [ 1 ]] = $reg [ 2 ];
> elseif( ereg ( ‘-([a-zA-Z0-9])’ , $arg , $reg )) <
$_ARG [ $reg [ 1 ]] = ‘true’ ;
>
>
return $_ARG ;
>
?>
$ php myscript.php —user=nobody —password=secret -p —access=»host=127.0.0.1 port=456″
Array
(
[user] => nobody
[password] => secret
[p] => true
[access] => host=127.0.0.1 port=456
)
We can pass many arguments directly into the hashbang line.
As example many ini setting via the -d parameter of php.
—
#!/usr/bin/php -d memory_limit=2048M -d post_max_size=0
phpinfo();
exit;
—
./script | grep memory
memory_limit => 2048M => 2048M
—
But we can also use this behaviour into a second script, so it call the first as an interpreter, via the hashbang:
—
#!./script arg1 arg2 arg3
—
However the parameters are dispatched in a different way into $argv
All the parameters are in $argv[1], $argv[0] is the interpreter script name, and $argv[1] is the caller script name.
To get back the parameters into $argv, we can simply test if $argv[1] contains spaces, and then dispatch again as normal:
#!/usr/bin/php -d memory_limit=2048M -d post_max_size=0
( $argv );
if ( strpos ( $argv [ 1 ], ‘ ‘ ) !== false ) <
$argw = explode ( » » , $argv [ 1 ]);
array_unshift ( $argw , $argv [ 2 ]);
$argv = $argw ;
>
var_dump ( $argv ); ?>
—
array(3) <
[0]=>
string(8) «./script»
[1]=>
string(15) «arg1 arg2 arg3 »
[2]=>
string(14) «./other_script»
>
array(4) <
[0]=>
string(8) «./other_script»
[1]=>
string(4) «arg1»
[2]=>
string(4) «arg2»
[3]=>
string(4) «arg3»
>
—
This will maintain the same behaviour in all cases and allow to even double click a script to call both parameters of another script, and even make a full interpreter language layer. The other script doesn’t has to be php. Take care of paths.
If you edit a php file in windows, upload and run it on linux with command line method. You may encounter a running problem probably like that:
[root@ItsCloud02 wsdl]# ./lnxcli.php
Extension ‘./lnxcli.php’ not present.
Or you may encounter some other strange problem.
Care the enter key. In windows environment, enter key generate two binary characters ‘0D0A’. But in Linux, enter key generate just only a ‘OA’.
I wish it can help someone if you are using windows to code php and run it as a command line program on linux.
How to change current directory in PHP script to script’s directory when running it from command line using PHP 4.3.0?
(you’ll probably need to add this to older scripts when running them under PHP 4.3.0 for backwards compatibility)
Here’s what I am using:
chdir(preg_replace(‘/\\/[^\\/]+$/’,»»,$PHP_SELF));
Note: documentation says that «PHP_SELF» is not available in command-line PHP scripts. Though, it IS available. Probably this will be changed in future version, so don’t rely on this line of code.
Use $_SERVER[‘PHP_SELF’] instead of just $PHP_SELF if you have register_globals=Off
an another «another variant» :
function arguments ( $argv )
<
$_ARG = array();
foreach ( $argv as $arg )
<
if ( preg_match ( ‘#^-<1,2>([a-zA-Z0-9]*)=?(.*)$#’ , $arg , $matches ))
<
$key = $matches [ 1 ];
switch ( $matches [ 2 ])
<
case » :
case ‘true’ :
$arg = true ;
break;
case ‘false’ :
$arg = false ;
break;
default:
$arg = $matches [ 2 ];
>
$_ARG [ $key ] = $arg ;
>
else
<
$_ARG [ ‘input’ ][] = $arg ;
>
>
return $_ARG ;
>
?>
$php myscript.php arg1 -arg2=val2 —arg3=arg3 -arg4 —arg5 -arg6=false
[arg2] => val2
[arg3] => arg3
[arg4] => true
[arg5] => true
[arg5] => false
)
Spawning php-win.exe as a child process to handle scripting in Windows applications has a few quirks (all having to do with pipes between Windows apps and console apps).
To do this in C++:
// We will run php.exe as a child process after creating
// two pipes and attaching them to stdin and stdout
// of the child process
// Define sa struct such that child inherits our handles
SECURITY_ATTRIBUTES sa = < sizeof(SECURITY_ATTRIBUTES) >;
sa.bInheritHandle = TRUE;
sa.lpSecurityDescriptor = NULL;
// Create the handles for our two pipes (two handles per pipe, one for each end)
// We will have one pipe for stdin, and one for stdout, each with a READ and WRITE end
HANDLE hStdoutRd, hStdoutWr, hStdinRd, hStdinWr;
// Now we have two pipes, we can create the process
// First, fill out the usage structs
STARTUPINFO si = < sizeof(STARTUPINFO) >;
PROCESS_INFORMATION pi;
si.dwFlags = STARTF_USESTDHANDLES;
si.hStdOutput = hStdoutWr;
si.hStdInput = hStdinRd;
// And finally, create the process
CreateProcess (NULL, «c:\\php\\php-win.exe», NULL, NULL, TRUE, NORMAL_PRIORITY_CLASS, NULL, NULL, &si, &pi);
// Close the handles we aren’t using
CloseHandle(hStdoutWr);
CloseHandle(hStdinRd);
// Now that we have the process running, we can start pushing PHP at it
WriteFile(hStdinWr, » echo ‘test’ ; ?> «, 9, &dwWritten, NULL);
// When we’re done writing to stdin, we close that pipe
CloseHandle(hStdinWr);
// Reading from stdout is only slightly more complicated
int i;
std::string processed(«»);
char buf[128];
One of the things I like about perl and vbscripts, is the fact that I can name a file e.g. ‘test.pl’ and just have to type ‘test, without the .pl extension’ on the windows command line and the command processor knows that it is a perl file and executes it using the perl command interpreter.
I did the same with the file extension .php3 (I will use php3 exclusivelly for command line php scripts, I’m doing this because my text editor VIM 6.3 already has the correct syntax highlighting for .php3 files ).
I modified the PATHEXT environment variable in Windows XP, from the » ‘system’ control panel applet->’Advanced’ tab->’Environment Variables’ button-> ‘System variables’ text area».
Then from control panel «Folder Options» applet-> ‘File Types’ tab, I added a new file extention (php3), using the button ‘New’ and typing php3 in the window that pops up.
Then in the ‘Details for php3 extention’ area I used the ‘Change’ button to look for the Php.exe executable so that the php3 file extentions are associated with the php executable.
You have to modify also the ‘PATH’ environment variable, pointing to the folder where the php executable is installed
Hope this is useful to somebody
For those of you who want the old CGI behaviour that changes to the actual directory of the script use:
chdir(dirname($_SERVER[‘argv’][0]));
at the beginning of your scripts.
This posting is not a php-only problem, but hopefully will save someone a few hours of headaches. Running on MacOS (although this could happen on any *nix I suppose), I was unable to get the script to execute without specifically envoking php from the command line:
[macg4:valencia/jobs] tim% test.php
./test.php: Command not found.
However, it worked just fine when php was envoked on the command line:
[macg4:valencia/jobs] tim% php test.php
Well, here we are. Now what?
Was file access mode set for executable? Yup.
[macg4:valencia/jobs] tim% ls -l
total 16
-rwxr-xr-x 1 tim staff 242 Feb 24 17:23 test.php
And you did, of course, remember to add the php command as the first line of your script, yeah? Of course.
#!/usr/bin/php
print «Well, here we are. Now what?\n» ; ?>
So why dudn’t it work? Well, like I said. on a Mac. but I also occasionally edit the files on my Windows portable (i.e. when I’m travelling and don’t have my trusty Mac available). Using, say, WordPad on Windows. and BBEdit on the Mac.
Aaahhh. in BBEdit check how the file is being saved! Mac? Unix? or Dos? Bingo. It had been saved as Dos format. Change it to Unix:
[macg4:valencia/jobs] tim% ./test.php
Well, here we are. Now what?
[macg4:valencia/jobs] tim%
NB: If you’re editing your php files on multiple platforms (i.e. Windows and Linux), make sure you double check the files are saved in a Unix format. those \r’s and \n’s ‘ll bite cha!
You can also call the script from the command line after chmod’ing the file (ie: chmod 755 file.php).
On your first line of the file, enter «#!/usr/bin/php» (or to wherever your php executable is located). If you want to suppress the PHP headers, use the line of «#!/usr/bin/php -q» for your path.
Adding a pause() function to PHP waiting for any user input returning it:
function pause () <
$handle = fopen ( «php://stdin» , «r» );
do < $line = fgets ( $handle ); >while ( $line == » );
fclose ( $handle );
return $line ;
>
?>
To hand over the GET-variables in interactive mode like in HTTP-Mode (e.g. your URI is myprog.html?hugo=bla&bla=hugo), you have to call
php myprog.html ‘&hugo=bla&bla=hugo’
(two & instead of ? and &!)
There just a little difference in the $ARGC, $ARGV values, but I think this is in those cases not relevant.
dunno if this is on linux the same but on windows evertime
you send somthing to the console screen php is waiting for
the console to return. therefor if you send a lot of small
short amounts of text, the console is starting to be using
more cpu-cycles then php and thus slowing the script.
take a look at this sheme:
cpu-cycle:1 ->php: print(«a»);
cpu-cycle:2 ->cmd: output(«a»);
cpu-cycle:3 ->php: print(«b»);
cpu-cycle:4 ->cmd: output(«b»);
cpu-cycle:5 ->php: print(«c»);
cpu-cycle:6 ->cmd: output(«c»);
cpu-cylce:7 ->php: print(«d»);
cpu-cycle:8 ->cmd: output(«d»);
cpu-cylce:9 ->php: print(«e»);
cpu-cycle:0 ->cmd: output(«e»);
on the screen just appears «abcde». but if you write
your script this way it will be far more faster:
cpu-cycle:1 ->php: ob_start();
cpu-cycle:2 ->php: print(«abc»);
cpu-cycle:3 ->php: print(«de»);
cpu-cycle:4 ->php: $data = ob_get_contents();
cpu-cycle:5 ->php: ob_end_clean();
cpu-cycle:6 ->php: print($data);
cpu-cycle:7 ->cmd: output(«abcde»);
now this is just a small example but if you are writing an
app that is outputting a lot to the console, i.e. a text
based screen with frequent updates, then its much better
to first cach all output, and output is as one big chunk of
text instead of one char a the time.
ouput buffering is ideal for this. in my script i outputted
almost 4000chars of info and just by caching it first, it
speeded up by almost 400% and dropped cpu-usage.
because what is being displayed doesn’t matter, be it 2
chars or 40.0000 chars, just the call to output takes a
great deal of time. remeber that.
maybe someone can test if this is the same on unix-based
systems. it seems that the STDOUT stream just waits for
the console to report ready, before continueing execution.
In *nix systems, use the WHICH command to show the location of the php binary executable. This is the path to use as the first line in your php shell script file. (#!/path/to/php -q) And execute php from the command line with the -v switch to see what version you are running.
# which php
/usr/local/bin/php
# php -v
PHP 4.3.1 (cli) (built: Mar 27 2003 14:41:51)
Copyright (c) 1997-2002 The PHP Group
Zend Engine v1.3.0, Copyright (c) 1998-2002 Zend Technologies
In the above example, you would use: #!/usr/local/bin/php
Also note that, if you do not have the current/default directory in your PATH (.), you will have to use ./scriptfilename to execute your script file from the command line (or you will receive a «command not found» error). Use the ENV command to show your PATH environment variable value.
I was looking for a way to interactively get a single character response from user. Using STDIN with fread, fgets and such will only work after pressing enter. So I came up with this instead:
#!/usr/bin/php -q
function inKey ( $vals ) <
$inKey = «» ;
While(! in_array ( $inKey , $vals )) <
$inKey = trim (` read -s -n1 valu;echo \$valu `);
>
return $inKey ;
>
function echoAT ( $Row , $Col , $prompt = «» ) <
// Display prompt at specific screen coords
echo «\033[» . $Row . «;» . $Col . «H» . $prompt ;
>
// Display prompt at position 10,10
echoAT ( 10 , 10 , «Opt : » );
// Define acceptable responses
$options = array( «1» , «2» , «3» , «4» , «X» );
// Get user response
$key = inKey ( $options );
When using the -R flag, the name of the variable containing the content of the current line (not including the LF) is $argn.
For example you can do this code:
cat file.txt | php -R ‘echo $argn . «\n»;’
This will just output each line of the input file without doing anything to it.
Источник



