- Команда Which в Linux
- Linux Which Command
- В этом руководстве мы рассмотрим команду which.
- Что такое PATH
- Как использовать which команду
- Вывод
- Переменная PATH в Linux
- Переменная PATH в Linux
- Выводы
- 12 Linux Which Command, Whatis Command, Whereis Command Examples
- I. Linux whatis Command
- 1. Get information from specific sections of man pages using -s option
- 2. Search information through wild-cards using -w option
- 3. Search information through regular expressions using -r option
- 4. Disable trimmed output using -l option
- 5. Restrict search up to specified path using -M option
- II. Linux whereis Command
- 6. Locate binaries using -b option
- 7. Locate man pages for a command using -m option
- 8. Locate source of a command using -s option
- 9. Locate unusual entries using -u option
- 10. Locate binaries in a specified path using -B option
- 11. Locate man pages with limited scope using -M option
- III. Linux which Command
- 12. Display all the paths using -a option
- Which Command in Linux [Explained with Examples]
- Linux which command examples
- Using which command with multiple executable files
- Display all pathnames with which command
- Exit status of which command
Команда Which в Linux
Linux Which Command
В этом руководстве мы рассмотрим команду which.
which — команда Linux используется для определения местоположения данного исполняемого файла, который выполняется при вводе имени исполняемого файла (команды) в командной строке терминала. Команда выполняет поиск исполняемого файла, указанного в качестве аргумента, в каталогах, перечисленных в переменной среды PATH.
Что такое PATH
В Linux PATH это переменная окружения, которая сообщает оболочке и другим программам, в каких каталогах искать исполняемые файлы. Он состоит из списка разделенных двоеточиями абсолютных путей к каталогам, содержащим исполняемые файлы.
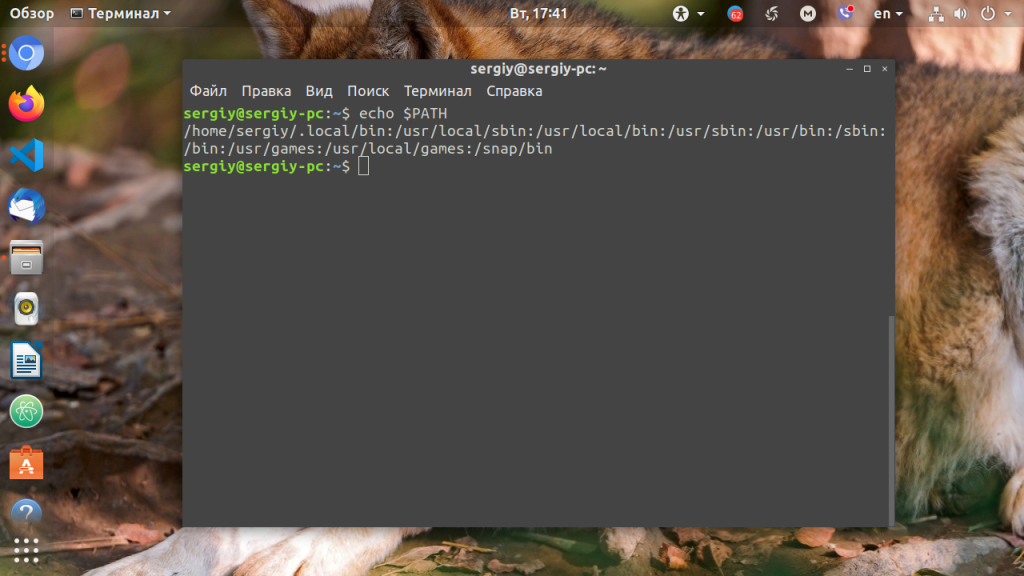
Чтобы просмотреть содержимое вашей переменной PATH, используйте команду echo с $PATH аргументом:
Вывод будет выглядеть примерно так:
Как использовать which команду
Синтаксис which команды следующий:
Например, чтобы найти полный путь команды ping , вы должны набрать следующее:
Результат будет примерно таким:
Вы также можете указать несколько аргументов which команды:
Вывод будет включать полные пути к обоим netcat и uptime исполняемым файлам :
Поиск выполняется слева направо, и если в каталогах, перечисленных в PATH переменной пути, найдено более одного совпадения , which будет напечатано только первое. Чтобы распечатать все совпадения, используйте -a опцию:
Вывод покажет два полных пути к touch команде :
Обычно один из исполняемых файлов предназначен только symlink для другого, но в некоторых случаях в разных местах могут быть установлены две версии одной и той же команды или совершенно разные команды с одним и тем же именем.
Вывод
Команда which используется для поиска команды путем поиска исполняемого файла команды в каталогах, указанных в переменной среды PATH .
Источник
Переменная PATH в Linux
Когда вы запускаете программу из терминала или скрипта, то обычно пишете только имя файла программы. Однако, ОС Linux спроектирована так, что исполняемые и связанные с ними файлы программ распределяются по различным специализированным каталогам. Например, библиотеки устанавливаются в /lib или /usr/lib, конфигурационные файлы в /etc, а исполняемые файлы в /sbin/, /usr/bin или /bin.
Таких местоположений несколько. Откуда операционная система знает где искать требуемую программу или её компонент? Всё просто — для этого используется переменная PATH. Эта переменная позволяет существенно сократить длину набираемых команд в терминале или в скрипте, освобождая от необходимости каждый раз указывать полные пути к требуемым файлам. В этой статье мы разберёмся зачем нужна переменная PATH Linux, а также как добавить к её значению имена своих пользовательских каталогов.
Переменная PATH в Linux
Для того, чтобы посмотреть содержимое переменной PATH в Linux, выполните в терминале команду:
На экране появится перечень папок, разделённых двоеточием. Алгоритм поиска пути к требуемой программе при её запуске довольно прост. Сначала ОС ищет исполняемый файл с заданным именем в текущей папке. Если находит, запускает на выполнение, если нет, проверяет каталоги, перечисленные в переменной PATH, в установленном там порядке. Таким образом, добавив свои папки к содержимому этой переменной, вы добавляете новые места размещения исполняемых и связанных с ними файлов.
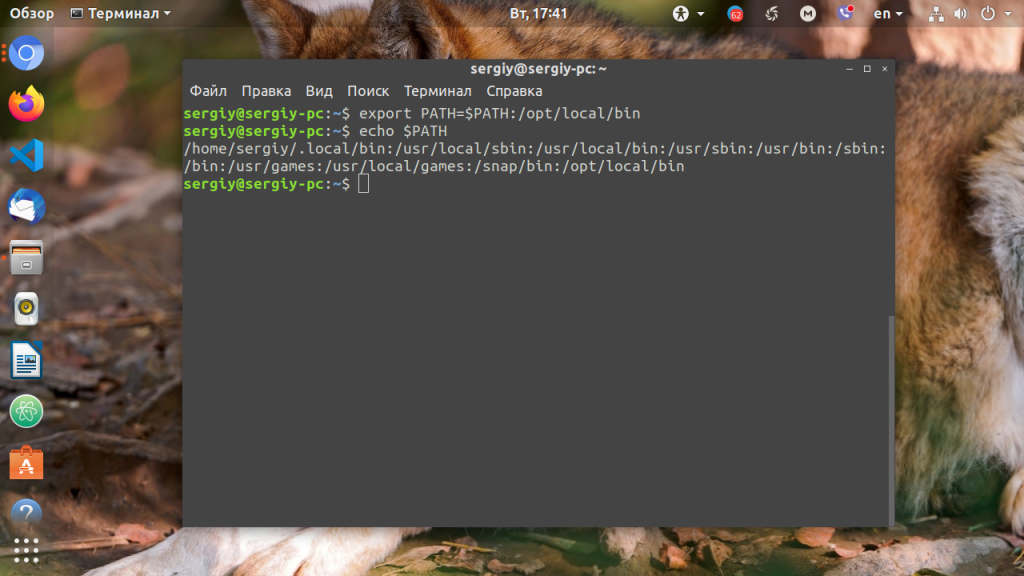
Для того, чтобы добавить новый путь к переменной PATH, можно воспользоваться командой export. Например, давайте добавим к значению переменной PATH папку/opt/local/bin. Для того, чтобы не перезаписать имеющееся значение переменной PATH новым, нужно именно добавить (дописать) это новое значение к уже имеющемуся, не забыв о разделителе-двоеточии:
Теперь мы можем убедиться, что в переменной PATH содержится также и имя этой, добавленной нами, папки:
Вы уже знаете как в Linux добавить имя требуемой папки в переменную PATH, но есть одна проблема — после перезагрузки компьютера или открытия нового сеанса терминала все изменения пропадут, ваша переменная PATH будет иметь то же значение, что и раньше. Для того, чтобы этого не произошло, нужно закрепить новое текущее значение переменной PATH в конфигурационном системном файле.
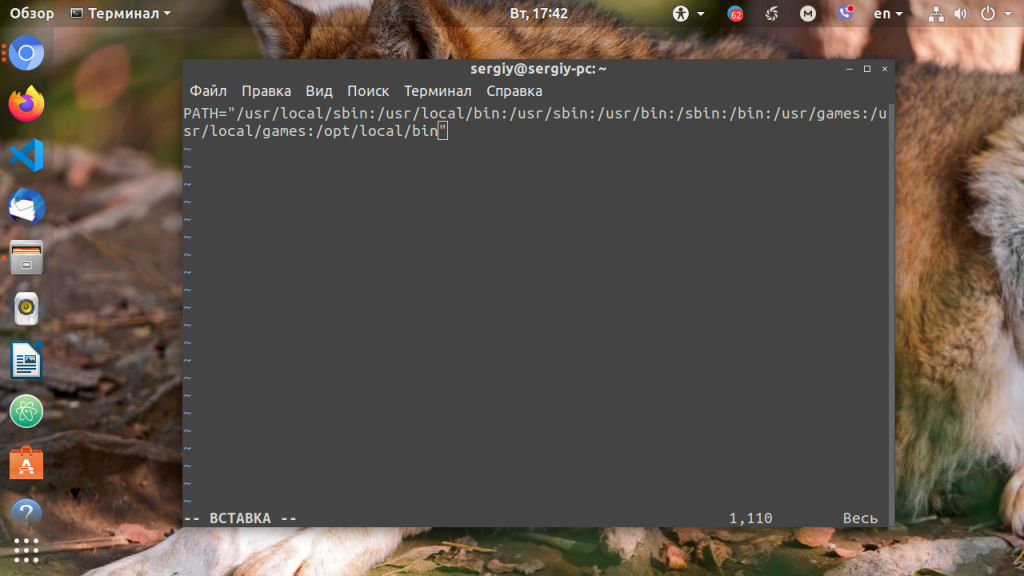
В ОС Ubuntu значение переменной PATH содержится в файле /etc/environment, в некоторых других дистрибутивах её также можно найти и в файле /etc/profile. Вы можете открыть файл /etc/environment и вручную дописать туда нужное значение:
sudo vi /etc/environment
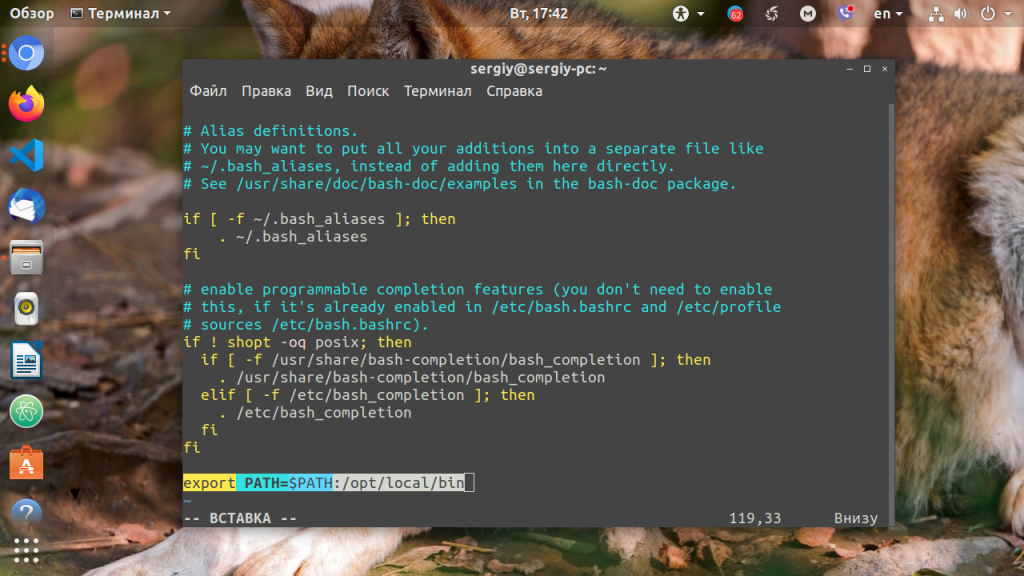
Можно поступить и иначе. Содержимое файла .bashrc выполняется при каждом запуске оболочки Bash. Если добавить в конец файла команду export, то для каждой загружаемой оболочки будет автоматически выполняться добавление имени требуемой папки в переменную PATH, но только для текущего пользователя:
Выводы
В этой статье мы рассмотрели вопрос о том, зачем нужна переменная окружения PATH в Linux и как добавлять к её значению новые пути поиска исполняемых и связанных с ними файлов. Как видите, всё делается достаточно просто. Таким образом вы можете добавить столько папок для поиска и хранения исполняемых файлов, сколько вам требуется.
Источник
12 Linux Which Command, Whatis Command, Whereis Command Examples
This Linux tutorial will explain the three “W” commands. The three “W”s are whatis, whereis and which commands.
You already know how to use find command to efficiently fo find a file.
Now, these three W commands will help you to locate more stuff from Linux command line.
I. Linux whatis Command
Whatis command is helpful to get brief information about Linux commands or functions. Whatis command displays man page single line description for command that matches string passed as a command line argument to whatis command. Whatis command searches for string in its index databases which is maintained by mandb program. Whatis command picks short description of NAME section of man page of command that matches to input given to the whatis command.
Whatis provides several command line options to help user in getting brief information of specific Linux commands as per their need or interest.
For example, here is the output of whatis command, when it is run without any option.
It displays brief information about “write” from man pages.
1. Get information from specific sections of man pages using -s option
If we want to get Linux command information from specific section of man pages, then we can provide sections list using “-s or —sections or –section” option. It will restrict whatis command to display brief information from specified man page section only.
It displays open command and function brief information from man page sections 1 and 2.
It displays open function brief information from man page section 2.
2. Search information through wild-cards using -w option
If we want to search Linux commands or functions information using wild card, then whatis command gives “-w or –wildcard” option. It will make your search specific as per user’s need.
It displays brief information of Linux commands or functions which start from “ab”.
It displays brief information of Linux commands or functions which start from “ab” and followed by any single character.
3. Search information through regular expressions using -r option
If we want to search Linux commands or functions information using regular expressions, then whatis command gives “-r or –regex” option. It will give flexibility to customize your search for Linux commands or functions throughout the Linux system.
It displays brief information of Linux commands or functions which start from “ab”.
It displays brief information of Linux commands or functions which ends with “ab”.
4. Disable trimmed output using -l option
Generally whatis command trims long output of Linux commands or functions information to avoid “Not good” output display on terminal that is going beyond screen. To allow whatis command to show complete output on screen, “-l or –long” option can be used.
It displays trimmed output of brief information of Linux command.
It displays complete output of brief information of Linux command.
5. Restrict search up to specified path using -M option
By default, whatis command uses $MANPATH environment variable. But whatis provides “-M or –manpath” option to restrict search up to specified path of man pages.
It displays brief information of Linux hexdump command from man pages available at path /usr/share/man.
It could not find brief information of Linux hexdump command from specified path /usr/man.
II. Linux whereis Command
Whereis command is helpful to locate binary, source and manual pages of commands in the Linux system. It is very simple utility and provides several options which are given below with examples.
For example, whereis command is run without any option.
It locates binary, source and man pages of “open” command and here it displayed paths where binary, man pages of open command is available in the system.
6. Locate binaries using -b option
If we want to locate binary of Linux command, use “-b” option.
It locates binary of “whereis” command and displays paths where binary of command is available in the system.
7. Locate man pages for a command using -m option
If we want to locate man page of Linux command, use “-m” option.
It locates man page of “whereis” command and displays path where man page of command is available in the system.
8. Locate source of a command using -s option
If we want to locate source of Linux command, use “-s” option.
It locates source of “whereis” command, but source of “whereis” command does not exist in the system, so it did not display path for source of command in the system.
9. Locate unusual entries using -u option
This option is something different that searches for unusual entries. These entries are those command whose source, binary or man page does not exist in the system as per options “[-bms]” specified along with “–u”.
It checks if specified command (i.e. wcgrep) man page does not exist in the system. Whereis command with options “-m and -u” locates for the commands in the system whose man page does not exist.
Here, whereis command with same options is applied on “grep” command whose man page exists in the system, so whereis returned nothing and exits normally.
10. Locate binaries in a specified path using -B option
If user wants to search for binary and wants to limit the scope of search for whereis command up to specified path, then use “-B” option.
It locates binary of “for_loop” user program from path “/bin”.
If open command’s binary is not found at specified path, then it is not shown but whereis command by default searches for other types (i.e. man page and source) of specified command (i.e. open) and displays them if found.
11. Locate man pages with limited scope using -M option
If user wants to search for man pages and wants to limit the scope of search for whereis command up to specified path, then use “-M” option.
Here, it is observed that whereis command is displaying man page of “open” command which is available in specified path only. But, whereis command by default searches for other types (i.e. binary and source) of specified command (i.e. open) and displays them if found.
III. Linux which Command
Which command is very small and simple command to locate executables in the system. It allows user to pass several command names as arguments to get their paths in the system. “which” commands searches the path of executable in system paths set in $PATH environment variable.
It locates command names – “ls”, “gdb”, “open” and “grep” specified as arguments to “which” command and displays paths of each executable where it exists in the system.
12. Display all the paths using -a option
“which” command gives option “-a” that displays all paths of executable matching to argument.
Above will search display the executable “echo” from all paths set in $PATH environment variable and displays the first path where echo executable is found. It may be case that executable is placed at other paths of $PATH environment variable as well. To get all paths where executable is present in the system, “-a” option can be used.
Источник
Which Command in Linux [Explained with Examples]
If you are wondering where exactly is a certain program is located, simply use which on it. The which command locates an executable file in your shell’s search path.
This Linux command has a simple syntax:
Let’s see how to use this simple but useful command.
Linux which command examples
Let’s say you want to know where is the Java executable, use which command:
The output could be like this:
Note that which only works on executable files. So you should use it only with the argument that you can run. For example, you install Java through the JDK package but you don’t run a command called ‘jdk’, you run ‘java’. So you use which command on java, not jdk.
If the which command doesn’t find the executable in the current path, it returns nothing.
Using which command with multiple executable files
You can provide more than one argument to which command:
The output for me was:
Did you notice something here? I gave it four arguments but the result is displayed for three of them only. It’s because ‘nada’ is not an executable. There is no output for that.
Display all pathnames with which command
The which command in Linux has only one option, -a. By default, which command prints only one pathname for its arguments.
If a program has executable in two places, say in /usr/bin/program and in /usr/local/bin/program, you can display both pathnames using the -a option.
Exit status of which command
If you use which command in a bash script, you may need to know its exit status.
Which command has the following exit status:
- 0 – all arguments are found and executable
- 1 – one or more arguments is nonexistent or non-executable
- 2 – if an invalid option is specified
That’s all you need to know about which command in Linux. If you have questions or suggestions, do let me know in the comments below.
Источник