- Linux / UNIX Find Out What Program / Service is Listening on a Specific TCP Port
- lsof command example
- netstat command example
- /etc/services file
- Further readings:
- Как узнать, какой номер порта используется процессом в Linux?
- Метод-1: Использование команды ss
- Способ-2: Использование команды netstat
- Метод-3: использование команды lsof
- Метод-4: Использование команды fuser
- Метод-5: Использование команды nmap
- Метод-6: Использование команды systemctl
- How to check if port is in use on Linux or Unix
- How to check if port is in use in
- Option #1: lsof command
- Option #2: netstat command
- Linux netstat syntax
- FreeBSD/MacOS X netstat syntax
- OpenBSD netstat syntax
- Option #3: nmap command
- A note about Windows users
- Conclusion
- Linux: Find Out Which Port Number a Process is Listening on
- Method 1: Using the netstat command
- Method 2: Using the lsof command
- Method 3: Using the fuser command
- Karim Buzdar
Linux / UNIX Find Out What Program / Service is Listening on a Specific TCP Port
Q. How do I find out which service is listening on a specific port? How do I find out what program is listening on a specific TCP Port?
A. Under Linux and UNIX you can use any one of the following command to get listing on a specific TCP port:
=> lsof : list open files including ports.
=> netstat : The netstat command symbolically displays the contents of various network-related data and information.
lsof command example
Type the following command to see IPv4 port(s), enter:
# lsof -Pnl +M -i4
Type the following command to see IPv6 listing port(s), enter:
# lsof -Pnl +M -i6
Sample output:
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
First column COMMAND – gives out information about program name. Please see output header for details. For example, gweather* command gets the weather report weather information from the U.S National Weather Service (NWS) servers (140.90.128.70), including the Interactive Weather Information Network (IWIN) and other weather services.
Where,
- -P : This option inhibits the conversion of port numbers to port names for network files. Inhibiting the conver-
sion may make lsof run a little faster. It is also useful when port name lookup is not working properly. - -n : This option inhibits the conversion of network numbers to host names for network files. Inhibiting conversion may make lsof run faster. It is also useful when host name lookup is not working properly.
- -l : This option inhibits the conversion of user ID numbers to login names. It is also useful when login name lookup is working improperly or slowly.
- +M : Enables the reporting of portmapper registrations for local TCP and UDP ports.
- -i4 : IPv4 listing only
- -i6 : IPv6 listing only
netstat command example
Type the command as follows:
# netstat -tulpn
OR
# netstat -npl
Output:
Last column PID/Program name gives out information regarding program name and port.
Where,
- -t : TCP port
- -u : UDP port
- -l : Show only listening sockets.
- -p : Show the PID and name of the program to which each socket / port belongs
- -n : No DNS lookup (speed up operation)
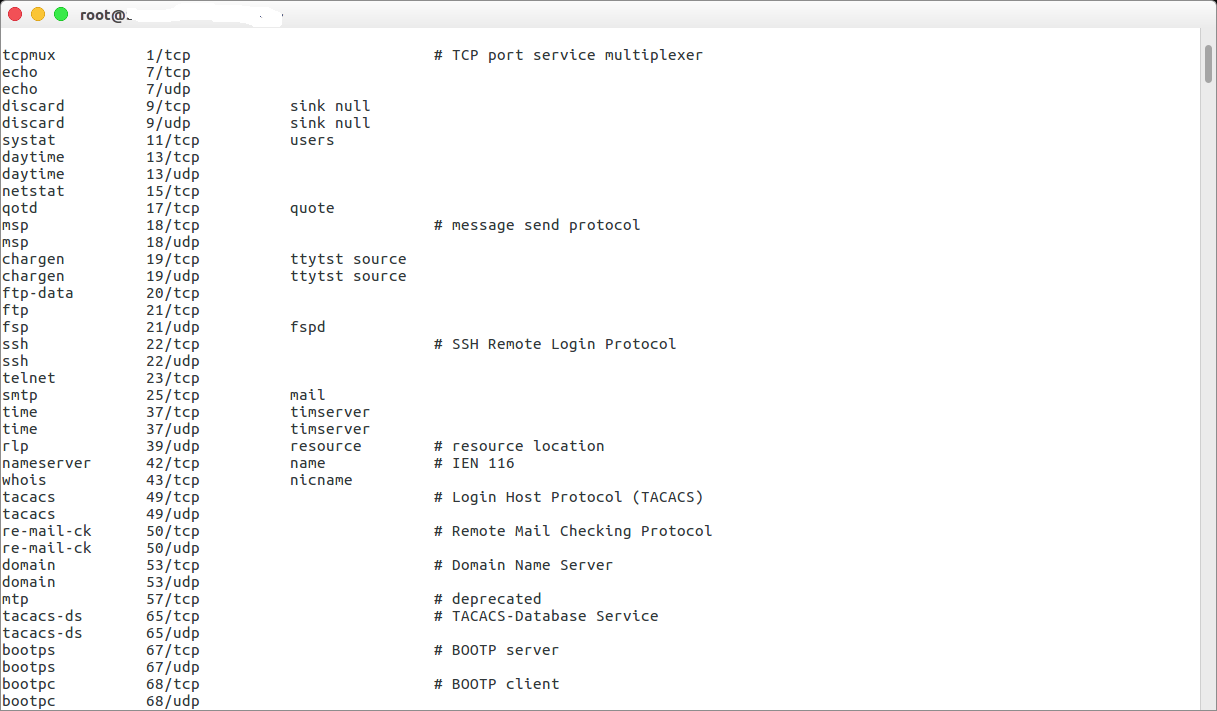
/etc/services file
/etc/services is a plain ASCII file providing a mapping between friendly textual names for internet services, and their underlying assigned port numbers and protocol types. Every networking program should look into this file to get the port number (and protocol) for its service. You can view this file with the help of cat or less command:
$ cat /etc/services
$ grep 110 /etc/services
$ less /etc/services
Further readings:
- man pages – lsof, nmap, services, netstat
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
Источник
Как узнать, какой номер порта используется процессом в Linux?
Как администратор Linux, вы должны знать, является ли соответствующая служба обязательной / прослушивающей с правильным портом или нет.
Это поможет вам легко устранить проблему, когда вы столкнулись с проблемами, связанными с портами.
Порт – это логическое соединение, которое идентифицирует конкретный процесс в Linux.
Доступны два вида порта: физическое и программное обеспечение.
Поскольку операционная система Linux является программным обеспечением, мы собираемся обсудить порт программного обеспечения.
Программный порт всегда связан с IP-адресом хоста и соответствующим типом протокола для связи. Порт используется для распознования приложения.
Большинство служб, связанных с сетью, должны открыть сокет для прослушивания входящих сетевых запросов.
Socket уникален для каждого сервиса.
Сокет – это комбинация IP-адреса, программного порта и протокола.
Область номеров портов доступна для протокола TCP и UDP.
Протокол управления передачей (TCP) и протокол пользовательских дейтаграмм (UDP) используют номера портов для связи.
Это значение от 0 до 65535.
Ниже приведены категории присвоений портов.
- 0-1023: Хорошо известные порты или системные порты
- 1024-49151: Зарегистрированные порты для приложений
- 49152-65535: Динамические порты или частные порты
Вы можете проверить детали зарезервированных портов в файле /etc/services в Linux.
Это может быть достигнуто с использованием шести методов.
- ss: ss используется для вывода статистики сокетов.
- netstat: netstat отображает список открытых сокетов.
- lsof: lsof – список открытых файлов.
- fuser: идентификаторы процессов в списке терминов всех процессов, которые открывают один или несколько файлов
- nmap: nmap – Инструмент сетевого исследования и сканер безопасности / портов
- systemctl: systemctl – Управление системой systemd и менеджером сервисов
Метод-1: Использование команды ss
ss используется для вывода статистики сокетов.
Он позволяет отображать информацию, аналогичную netstat.
Он может отображать больше информации о TCP и его состоянии, чем другие инструменты.
Он может отображать статистику для всех типов сокетов, таких как PACKET, TCP, UDP, DCCP, RAW, домен Unix и т. д.
В качестве альтернативы вы также можете проверить это с помощью номера порта.
Способ-2: Использование команды netstat
netstat – вывод сетевых подключений, таблиц маршрутизации, статистики интерфейсов, соединений маскарада и многоадресной рассылки.
По умолчанию netstat отображает список открытых сокетов.
Если вы не укажете каких-либо семейств адресов, будут выведены активные сокеты всех сконфигурированных семейств адресов.
Эта программа устарела. Замена для netstat – ss.
В качестве альтернативы вы также можете проверить это с помощью номера порта.
Метод-3: использование команды lsof
lsof – список открытых файлов.
Команда lsof Linux выводит информацию о файлах, открытых для процессов, запущенных в системе.
В качестве альтернативы вы также можете проверить это с помощью номера порта.
Метод-4: Использование команды fuser
Утилита fuser должна записывать на стандартный вывод идентификаторы процессов, запущенных в локальной системе, которые открывают один или несколько именованных файлов.
Метод-5: Использование команды nmap
Nmap («Network Mapper») – это инструмент с открытым исходным кодом для проверки сети и проверки безопасности.
Он был разработан для быстрого сканирования больших сетей, хотя он отлично работает с одиночными хостами.
Nmap использует необработанные IP-пакеты в новых способах определения того, какие хосты доступны в сети, какие службы (имя и версия приложения) эти хосты предлагают, какие операционные системы (и версии ОС) они запускают, какие типы фильтров пакетов / брандмауэры используются, и десятки других характеристик
Метод-6: Использование команды systemctl
systemctl – Управление системой systemd и менеджером сервисов.
Это замена старого системного управления SysV, и большинство современных операционных систем Linux были адаптированы под systemd.
Вышеприведенный пример будет показывать фактический порт прослушивания службы SSH при запуске службы SSHD в последнее время.
В большинстве случаев вышеприведенный вывод не показывает фактический номер порта процесса. в этом случае я предлагаю вам проверить детали, используя приведенную ниже команду из файла журнала
Источник
How to check if port is in use on Linux or Unix
H ow do I determine if a port is in use under Linux or Unix-like system? How can I verify which ports are listening on Linux server? How do I check if port is in use on Linux operating system using the CLI?
It is important you verify which ports are listening on the server’s network interfaces. You need to pay attention to open ports to detect an intrusion. Apart from an intrusion, for troubleshooting purposes, it may be necessary to check if a port is already in use by a different application on your servers. For example, you may install Apache and Nginx server on the same system. So it is necessary to know if Apache or Nginx is using TCP port # 80/443. This quick tutorial provides steps to use the netstat, nmap and lsof command to check the ports in use and view the application that is utilizing the port.
| Tutorial details | |
|---|---|
| Difficulty level | Easy |
| Root privileges | Yes |
| Requirements | lsof, ss, and netstat on Linux |
| Est. reading time | 3 minutes |
How to check if port is in use in
To check the listening ports and applications on Linux:
- Open a terminal application i.e. shell prompt.
- Run any one of the following command on Linux to see open ports:
sudo lsof -i -P -n | grep LISTEN
sudo netstat -tulpn | grep LISTEN
sudo ss -tulpn | grep LISTEN
sudo lsof -i:22 ## see a specific port such as 22 ##
sudo nmap -sTU -O IP-address-Here - For the latest version of Linux use the ss command. For example, ss -tulw
Let us see commands and its output in details.
Option #1: lsof command
The syntax is:
$ sudo lsof -i -P -n
$ sudo lsof -i -P -n | grep LISTEN
$ doas lsof -i -P -n | grep LISTEN ### [OpenBSD] ###
Sample outputs:
Fig.01: Check the listening ports and applications with lsof command
Option #2: netstat command
You can check the listening ports and applications with netstat as follows.
Linux netstat syntax
Run netstat command along with grep command to filter out port in LISTEN state:
$ netstat -tulpn | grep LISTEN
The netstat command deprecated for some time on Linux. Therefore, you need to use the ss command as follows:
sudo ss -tulw
sudo ss -tulwn
sudo ss -tulwn | grep LISTEN
Where, ss command options are as follows:
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
- -t : Show only TCP sockets on Linux
- -u : Display only UDP sockets on Linux
- -l : Show listening sockets. For example, TCP port 22 is opened by SSHD server.
- -p : List process name that opened sockets
- -n : Don’t resolve service names i.e. don’t use DNS
FreeBSD/MacOS X netstat syntax
$ netstat -anp tcp | grep LISTEN
$ netstat -anp udp | grep LISTEN
OpenBSD netstat syntax
$ netstat -na -f inet | grep LISTEN
$ netstat -nat | grep LISTEN
Option #3: nmap command
The syntax is:
$ sudo nmap -sT -O localhost
$ sudo nmap -sU -O 192.168.2.13 ##[ list open UDP ports ]##
$ sudo nmap -sT -O 192.168.2.13 ##[ list open TCP ports ]##
Sample outputs:
Fig.02: Determines which ports are listening for TCP connections using nmap
A note about Windows users
You can check port usage from Windows operating system using following command:
netstat -bano | more
netstat -bano | grep LISTENING
netstat -bano | findstr /R /C:»[LISTEING]»
Conclusion
This page explained command to determining if a port is in use on Linux or Unix-like server. For more information see the nmap command and lsof command page online here
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
Источник
Linux: Find Out Which Port Number a Process is Listening on
As Linux users, we sometimes need to know which port number a particular process is listening upon. All ports are associated with a process ID or service in an OS. So how do we find that port? This article presents three different methods for you to find which port number a process is listening on.
We have run the commands and procedures described in this article on an Ubuntu 18.04 LTS system.
Method 1: Using the netstat command
Netstat or the network statistics utility is used to view information related to the network connections. This includes information about interface statistics, routing tables and much more. This utility is available on most Linux systems so let us make use of it to view information about which ports certain processes are using on the system.
For using the netstat command, you need to install the net-tools utility if it is already not installed on your system through the following command:
Then run the following command:
The above command gives netstat information based on the following features:
- l: display only listening sockets
- t: display tcp connection
- n: display addresses in a numerical form
- p: display process ID/ Program name
For example, in the above output of the netstat command, Apache2 program with process ID 950 is running on port number 80.
You can also filter statistics for a specific port by incorporating the grep function into your command.
This command will tell you specifically which process is running on port number 80.

Method 2: Using the lsof command
The lsof or the List of Open Files utility helps in listing all the open files on your Linux system. We can use this utility to view all processes open on a specific port.
For using the lsof command, you need to install the lsof utility if it is already not installed on your system through the following command:
Let us use lsof to view the service listening on a specific port.
This command will list all processes using TCP port number 80.
Method 3: Using the fuser command
The fuser command displays which process IDs are using the named files, sockets or file systems. We can use this command in order to view process IDs running on a specific TCP port.
For using the fuser command, you need to install the psmisc utility if it is already not installed on your system through the following command:
Let us view all the process IDs running on TCP port 3306 through the following command:
You can specify any port number in this command to view its listening processes.
In the above output, you can see that process ID 975 is listening on TCP 3306.
In order to view which program this process ID corresponds to, run the following command:
The output shows that the process ID 975 corresponds to the program names MySDLd. Thus process ID 975 of the program MySQLd is listening on port number 3306.
Through the three methods you have learned in this article, you can easily view which TCP port a specific process on Linux is listening upon.
Karim Buzdar
About the Author: Karim Buzdar holds a degree in telecommunication engineering and holds several sysadmin certifications. As an IT engineer and technical author, he writes for various web sites. You can reach Karim on LinkedIn
Источник