- How to List Only Directories in Linux
- Listing directories using Wildcards
- Using -F option and grep
- Using -l option and grep
- Using echo command
- Using printf
- Using find command
- ls command in Linux/Unix
- ls syntax
- ls command options
- ls command examples
- ls code generator
- Linux / UNIX List Just Directories Or Directory Names
- Display or list all directories in Unix
- Linux list only directories using ls command
- Linux Display or list only files
- Task: Create bash shell aliases to save time
- Use find command to list either files or directories on Linux
- Putting it all together
- The Linux LS Command – How to List Files in a Directory + Option Flags
- Prerequisites
- The Linux ls Command
- How to list Files in a Directory with Options
- List files in the current working directory
- List files in another directory
- List files in the root directory
- List files in the parent directory
- List files in the user’s home directory (/home/user)
- List only directories
- List files with subdirectories
- List files recursively
- List files with their sizes
- List files in long format
- List files in long format with readable file sizes
- List files including hidden files
- List files in long format including hidden files
- List files and sort by date and time
- List files and sort by file size
- List files and output the result to a file
- Conclusion
How to List Only Directories in Linux
The ls command in Linux is used to list the files and directories in a directory. But if you wish to list directories only using ls command, what are the options?
We learn how to use command chaining (using pipes) to see what directories are present in a given directory.
In this tutorial, I will show you a number of ways to list directories only in Linux.
Listing directories using Wildcards
The simplest method is using wildcards. All the directories end in forward slash.
For the long listing, just add -l option.
Using -F option and grep
The -F options appends a trailing forward slash. So we can grep the directories only by ‘grep’ ing lines ending with a forward slash (/).
or for just the directory names, without -l option,
Using -l option and grep
In the long listing of ls i.e. ls -l , we can ‘grep’ the lines starting with d .
We can extract just the file names by printing only the last columns.
Using echo command
We can use echo command to list the entries trailing with forward slash (/).
Using printf
Similarly, printf can be used to highlight strings ending with forward slash (/).
Using find command
We can always find files based on their file types using find command:
The maxdepth option in the above command specifies that the search is to be performed in specified directory only. Otherwise, find command will find the directories recursively, by traversing each directory and their subdirectories. Also, in this command, the hidden directories are also shown. In all above methods that use ls command, the same can be achieved through -a option. For example,
Thanks for reading this article. Let me know your thoughts.
Источник
ls command in Linux/Unix
ls is a Linux shell command that lists directory contents of files and directories.
ls syntax
ls command options
ls command main options:
| option | description |
|---|---|
| ls -a | list all files including hidden file starting with ‘.’ |
| ls —color | colored list [=always/never/auto] |
| ls -d | list directories — with ‘ */’ |
| ls -F | add one char of */=>@| to enteries |
| ls -i | list file’s inode index number |
| ls -l | list with long format — show permissions |
| ls -la | list long format including hidden files |
| ls -lh | list long format with readable file size |
| ls -ls | list with long format with file size |
| ls -r | list in reverse order |
| ls -R | list recursively directory tree |
| ls -s | list file size |
| ls -S | sort by file size |
| ls -t | sort by time & date |
| ls -X | sort by extension name |
ls command examples
You can press the tab button to auto complete the file or folder names.
List directory Documents/Books with relative path:
List directory /home/user/Documents/Books with absolute path.
List root directory:
List parent directory:
List user’s home directory (e.g: /home/user):
List with long format:
Show hidden files:
List with long format and show hidden files:
Sort by date/time:
Sort by file size:
List all subdirectories:
Recursive directory tree list:
List only text files with wildcard:
ls redirection to output file:
List directories only:
List files and directories with full path:
ls code generator
Select ls options and press the Generate Code button:
Источник
Linux / UNIX List Just Directories Or Directory Names
You can use combination of ls command, find command, and grep command to list directory names only. You can use the find command too. In this quick tutorial you will learn how to list only directories in Linux or UNIX.
| Tutorial details | |
|---|---|
| Difficulty level | Easy |
| Root privileges | No |
| Requirements | Linux, macOS, or Unix terminal |
| Est. reading time | 5 minutes |
Display or list all directories in Unix
Type the following command:
$ ls -l | grep `^d’
$ ls -l | egrep `^d’
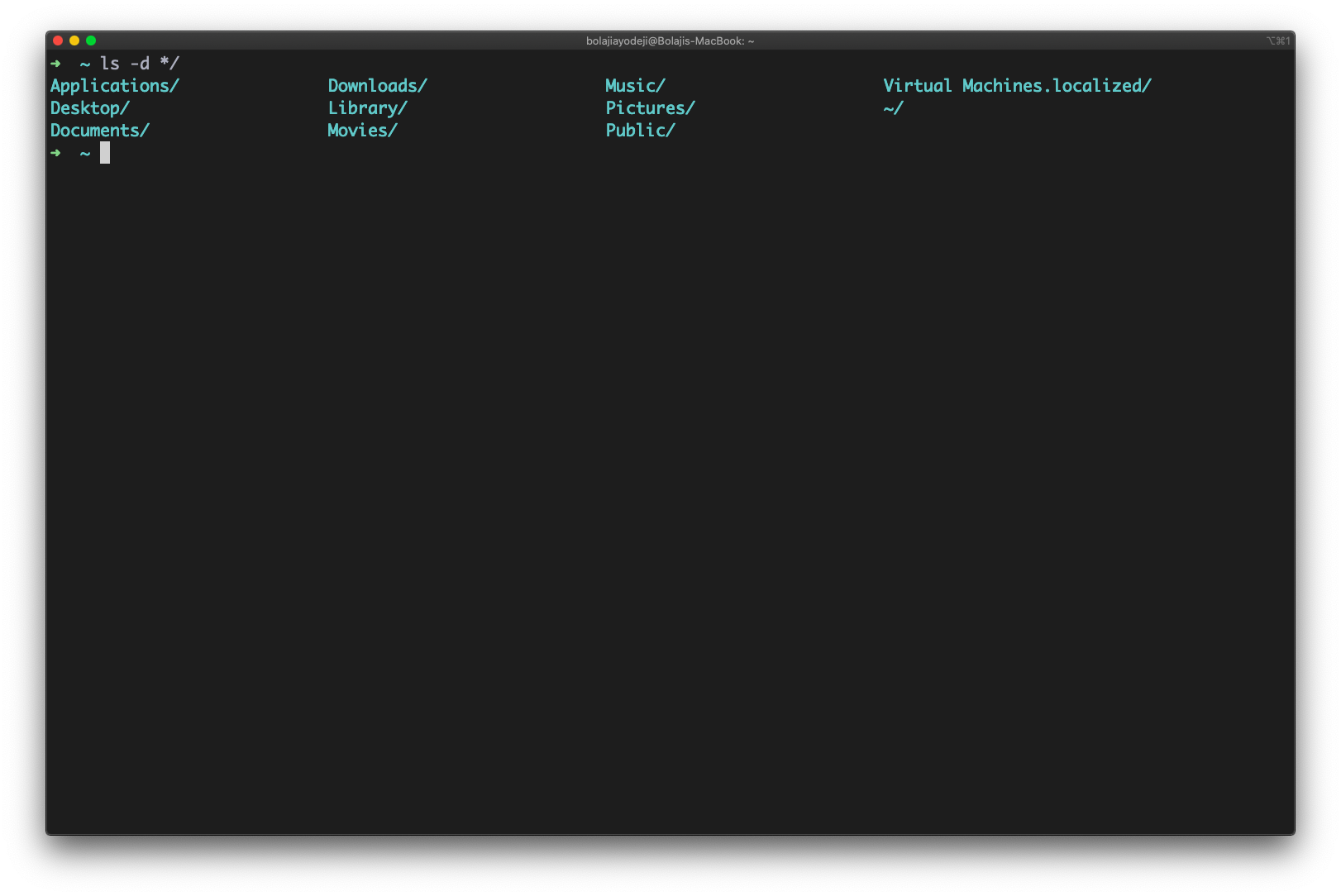
Or better try the following ls command only to list directories for the current directory:
$ ls -d */
Sample outputs:
Fig.01: List Directories in Unix and Linux Systems
Linux list only directories using ls command
Run the following ls command:
ls -d */
Listing only directories using ls command in Linux or Unix-like systems
Linux Display or list only files
Type the following command to display list only files in Linux or Unix:
$ ls -l | egrep -v ‘^d’
$ ls -l | egrep -v ‘^d’
The grep command is used to searches input. It will filter out directories name by matching first character ‘ d ‘. To reverse effect i.e. just to display files you need to pass the -v option. It invert the sense of matching, to select non-matching lines.
Task: Create bash shell aliases to save time
You can create two aliases as follows to list only directories and files.
alias lf=»ls -l | egrep -v ‘^d'»
alias ldir=’ls -d */’
##alias ldir=»ls -l | egrep ‘^d'»
Put above two aliases in your bash shell startup file:
$ cd
$ vi .bash_profile
Append two lines:
alias lf=»ls -l | egrep -v ‘^d'»
alias ldir=’ls -d */’
#alias ldir=»ls -l | egrep ‘^d'»
Save and close the file in vim. Now just type lf – to list files. Again run ldir to list directories only:
$ cd /etc
$ ldir
Sample outputs:
List directory names only:
$ cd /etc
$ ldir
Sample outputs:
Use find command to list either files or directories on Linux
The find command can be used as follows to list all directories in /nas, enter:
Pass the -maxdepth 0 to limit listing to the starting-points i.e. the current working directory only:
find /path/to/dir -maxdepth 1 -type d
find . -maxdepth 1 -type d
find . -maxdepth 1 -type d -ls
Listing only directories using the find command in Linux
Putting it all together
Say you want to find all directories ending with .bak extension and delete it, run the following find command in the current directory:
find . -type d -iname «.bak» -delete
Verify it:
find . -type d -iname «.bak» -ls
The following shell script does two things for Apache/Nginx/Lighttpd Webroot such as /webroot/:
- First, finds all files and directories and set permission to read-only for security reasons.
- Second, it allows our web server to read files regardless of permission so that we don’t get an HTTP/403 error.
In other words, all write permissions are removed from Webroot. The server/web-app can only read files but can not alter any files or upload any files. It helps reduces attack surfaces provided that you configure the rest of the server and web application firewall correctly.
Источник
The Linux LS Command – How to List Files in a Directory + Option Flags
Since the creation of Unix in the 1970s, a lot of operating systems have used it as their foundation. Many of these operating systems failed, while others succeeded.
Linux is one of the most popular Unix based operating systems. It’s open source, and is used all over the world across many industries.
One amazing feature of the Linux operating system is the Command Line Interface (CLI) which allows users to interact with their computer from a shell. The Linux shell is a REPL (Read, Evaluate, Print, Loop) environment where users can enter a command and the shell runs it and returns a result.
The ls command is one of the many Linux commands that allow a user to list files or directories from the CLI.
In this article, we’ll go in depth on the ls command and some of the most important flags you’ll need day-to-day.
Prerequisites
- A computer with directories and files
- Have one of the Linux distros installed
- Basic knowledge of navigating around the CLI
- A smile on your face 🙂
The Linux ls Command
The ls command is used to list files or directories in Linux and other Unix-based operating systems.
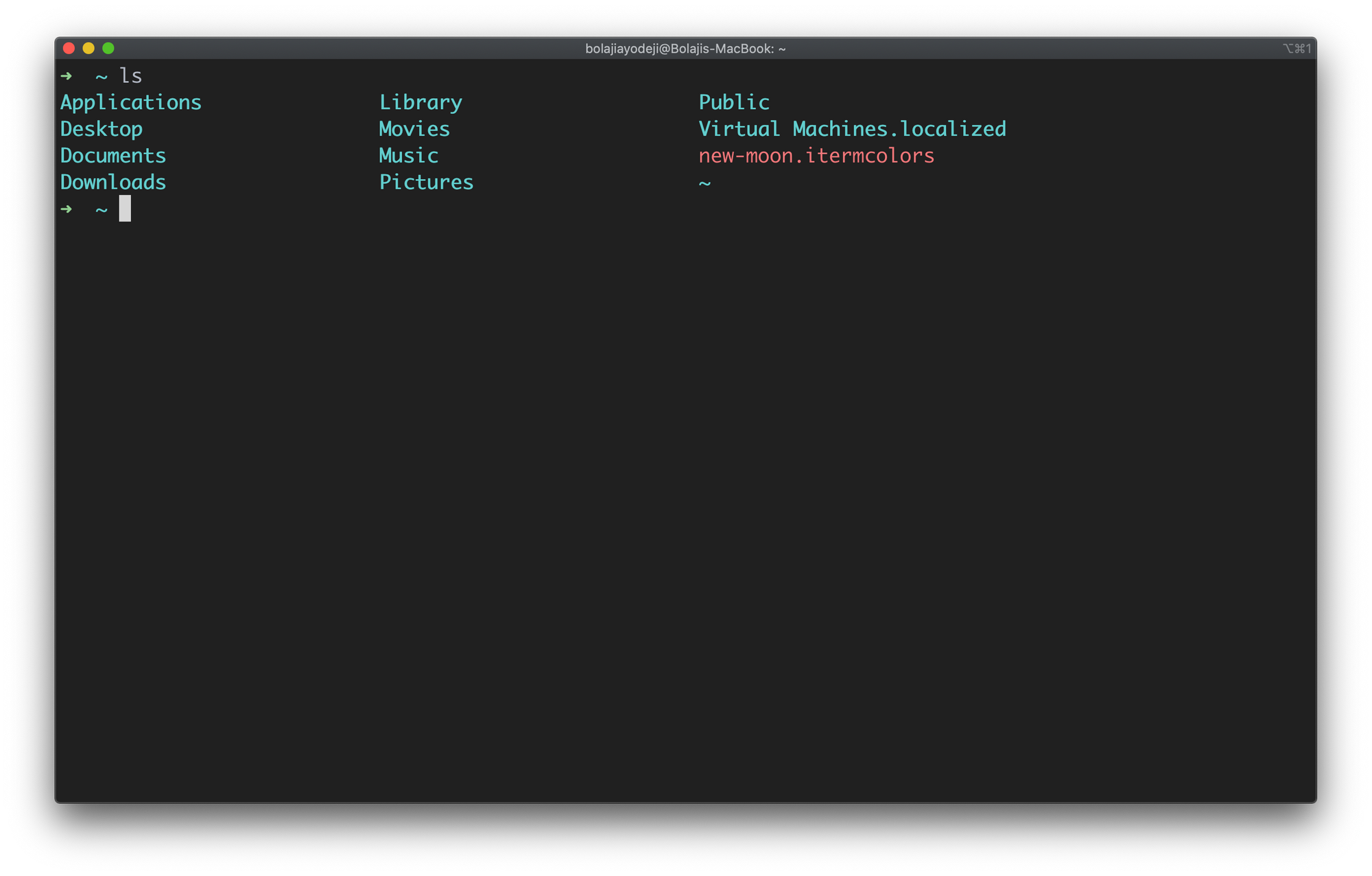
Just like you navigate in your File explorer or Finder with a GUI, the ls command allows you to list all files or directories in the current directory by default, and further interact with them via the command line.
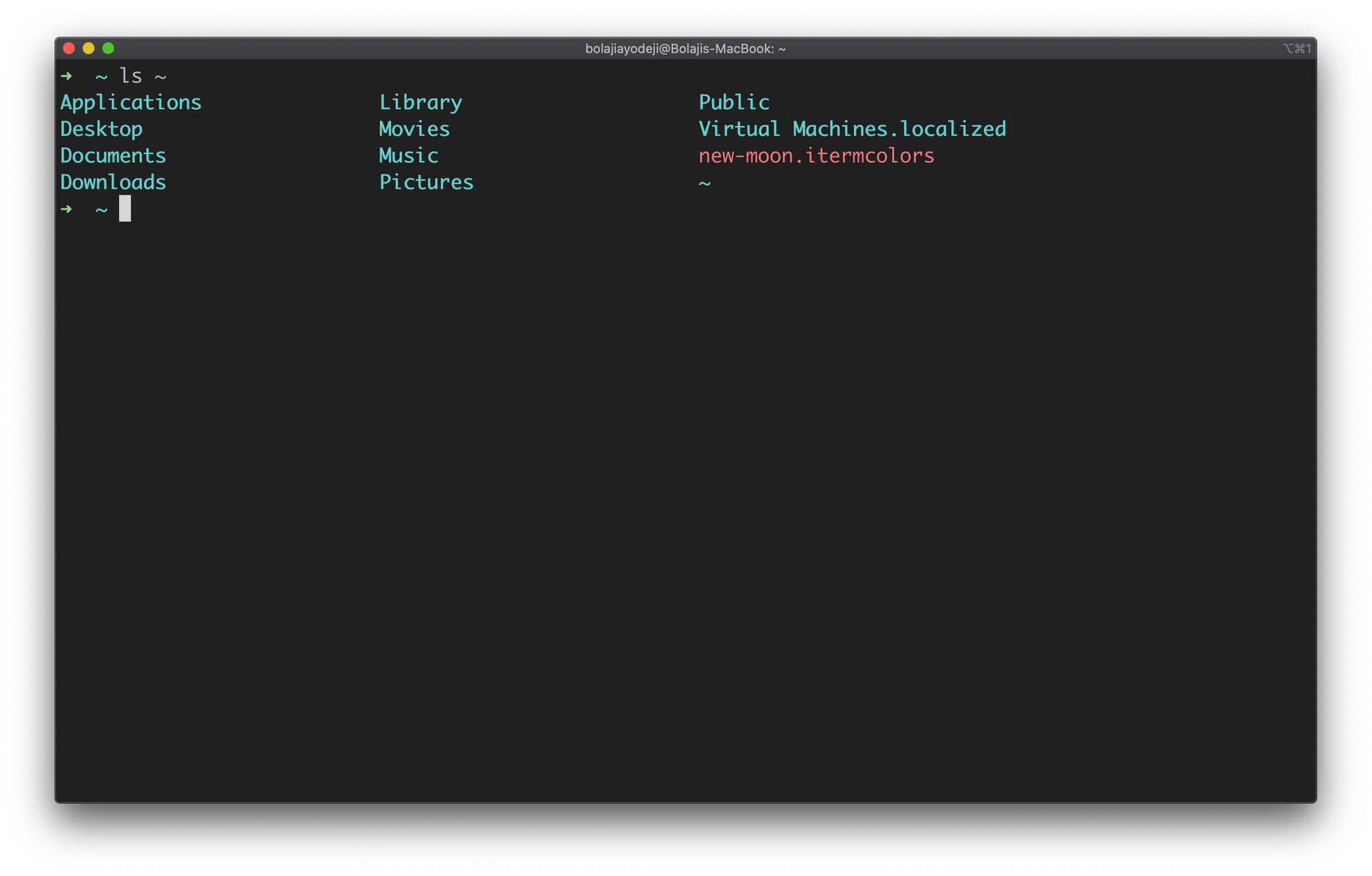
Launch your terminal and type ls to see this in action:
How to list Files in a Directory with Options
The ls command also accepts some flags (also known as options) which are additional information that changes how files or directories are listed in your terminal.
In other words, flags change how the ls command works:
PS: The word contents used in throughout the article refers to the files and directories being listed, not the actual contents of the files/directories ?
List files in the current working directory
Type the ls command to list the contents of the current working directory:
List files in another directory
Type the ls [directory path here] command to list the contents of another directory:
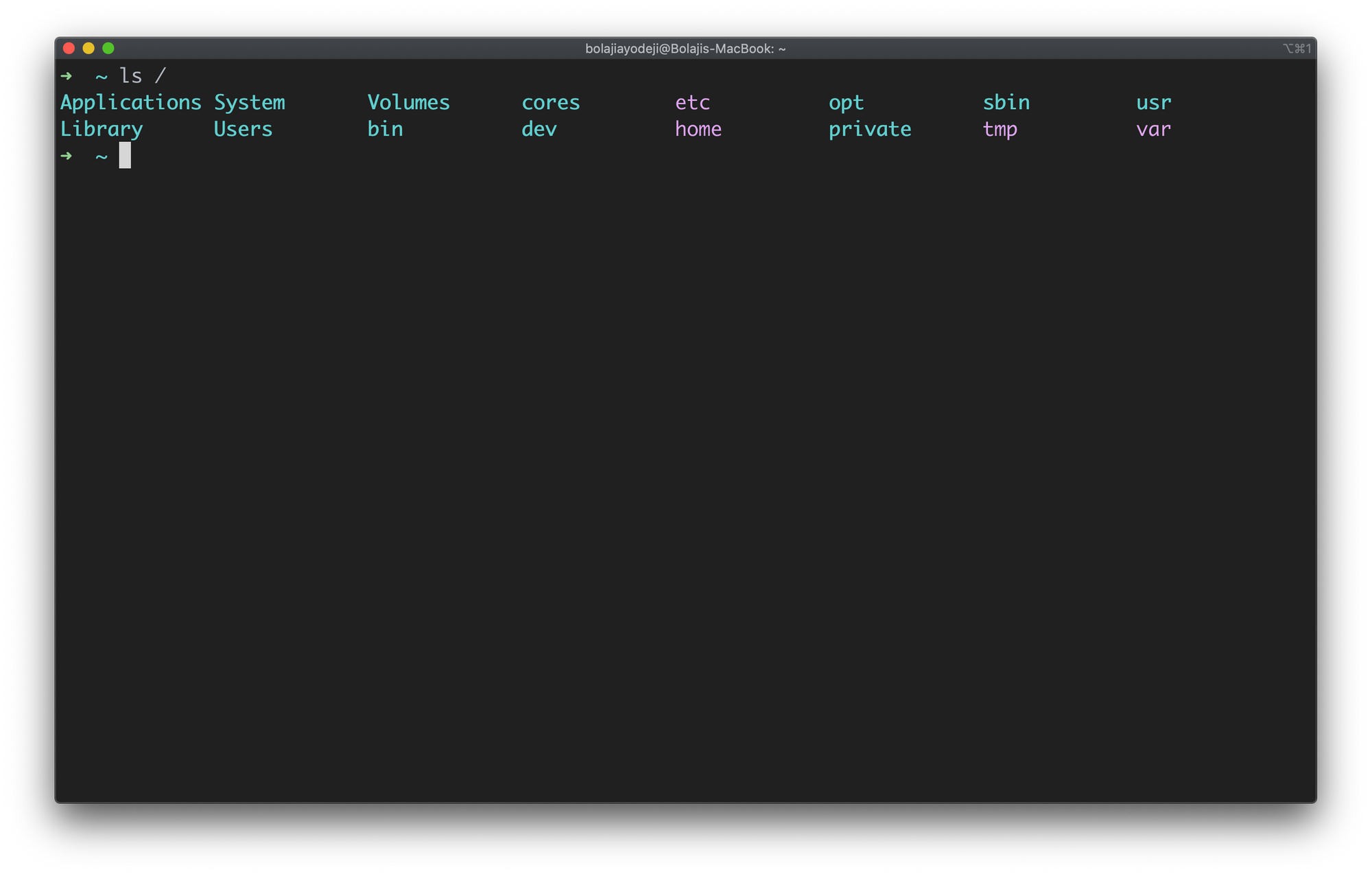
List files in the root directory
Type the ls / command to list the contents of the root directory:
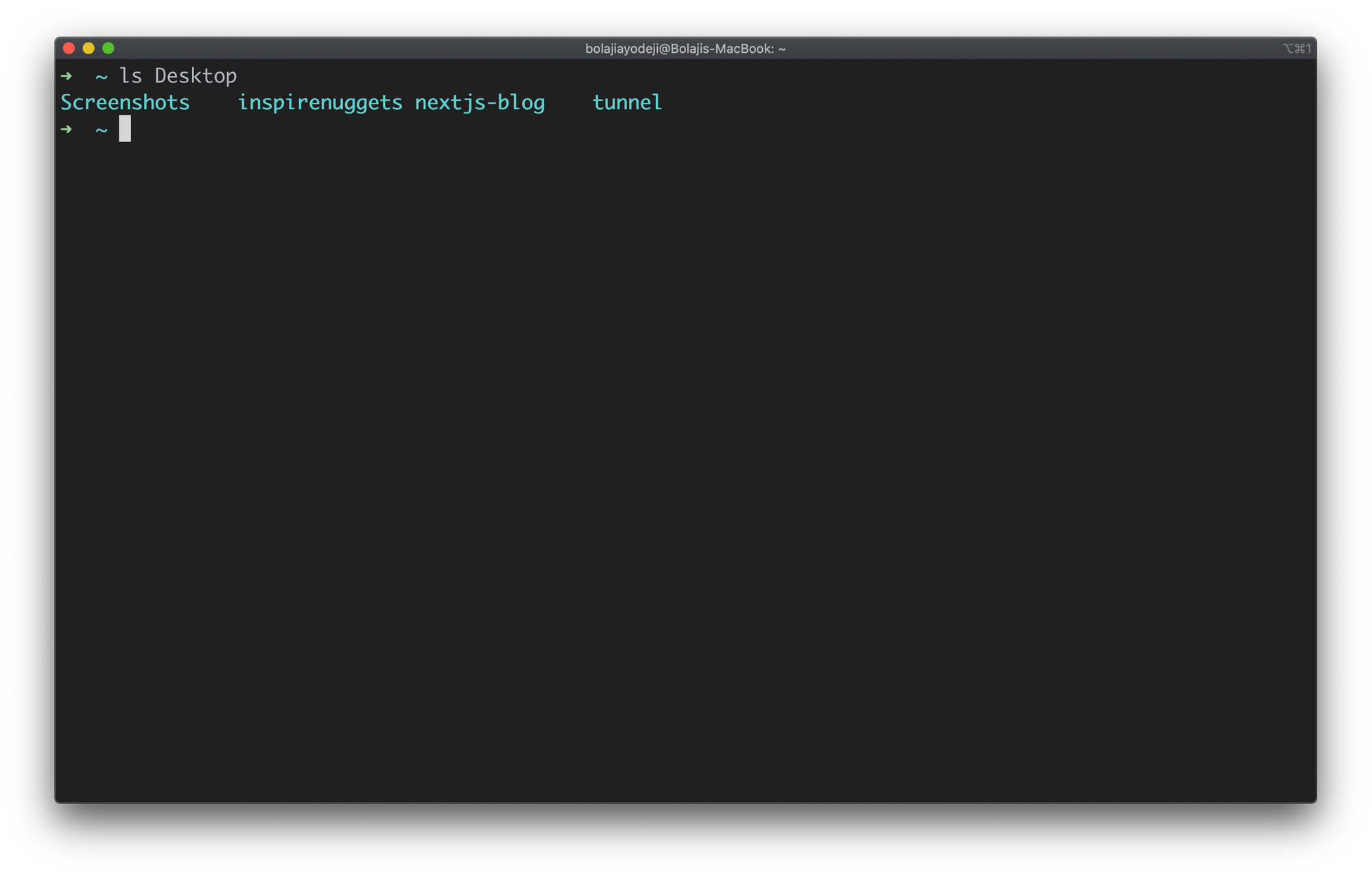
List files in the parent directory
Type the ls .. command to list the contents of the parent directory one level above. Use ls ../.. for contents two levels above:
List files in the user’s home directory (/home/user)
command to list the contents in the users’s home directory:
List only directories
Type the ls -d */ command to list only directories:
List files with subdirectories
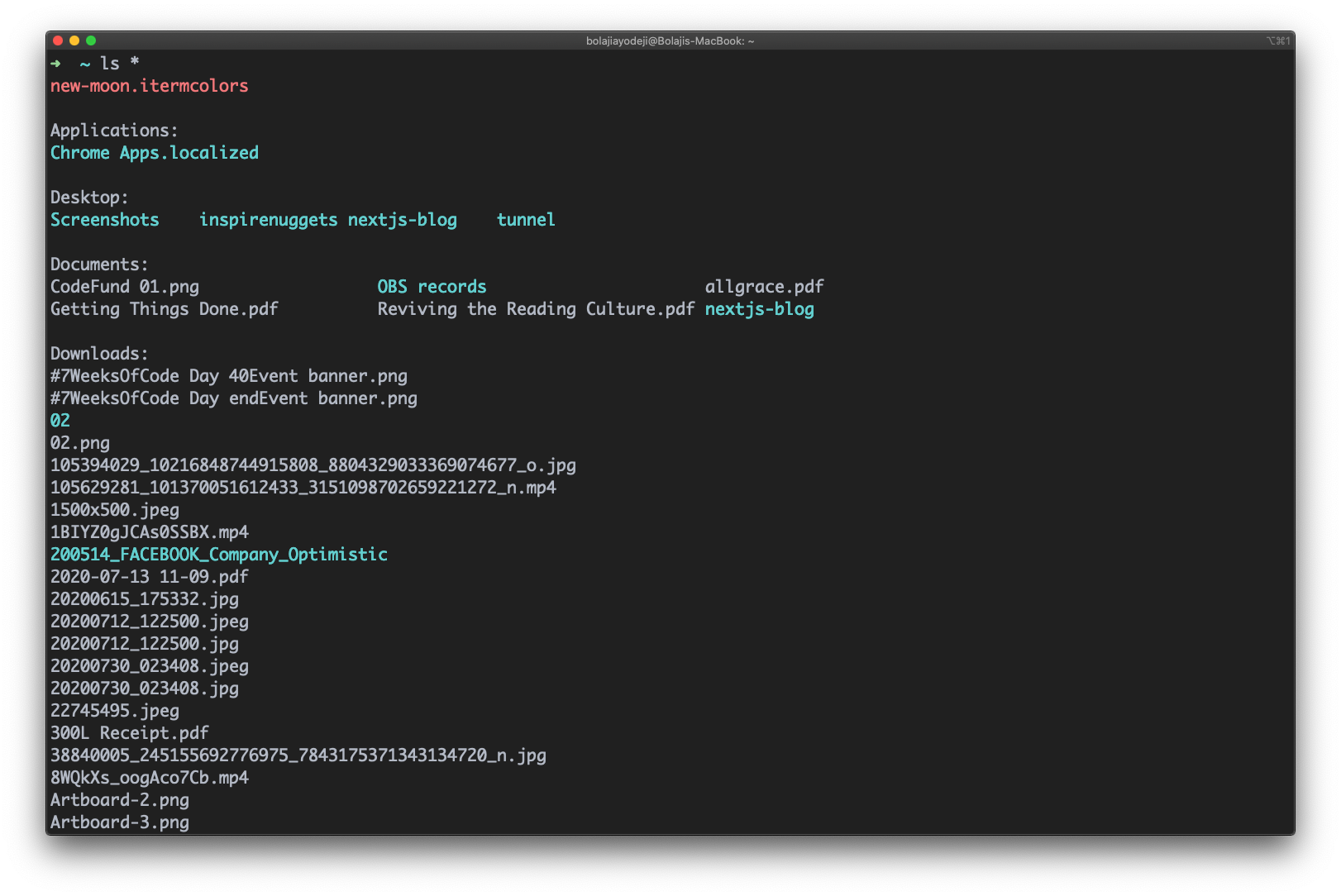
Type the ls * command to list the contents of the directory with it’s subdirectories:
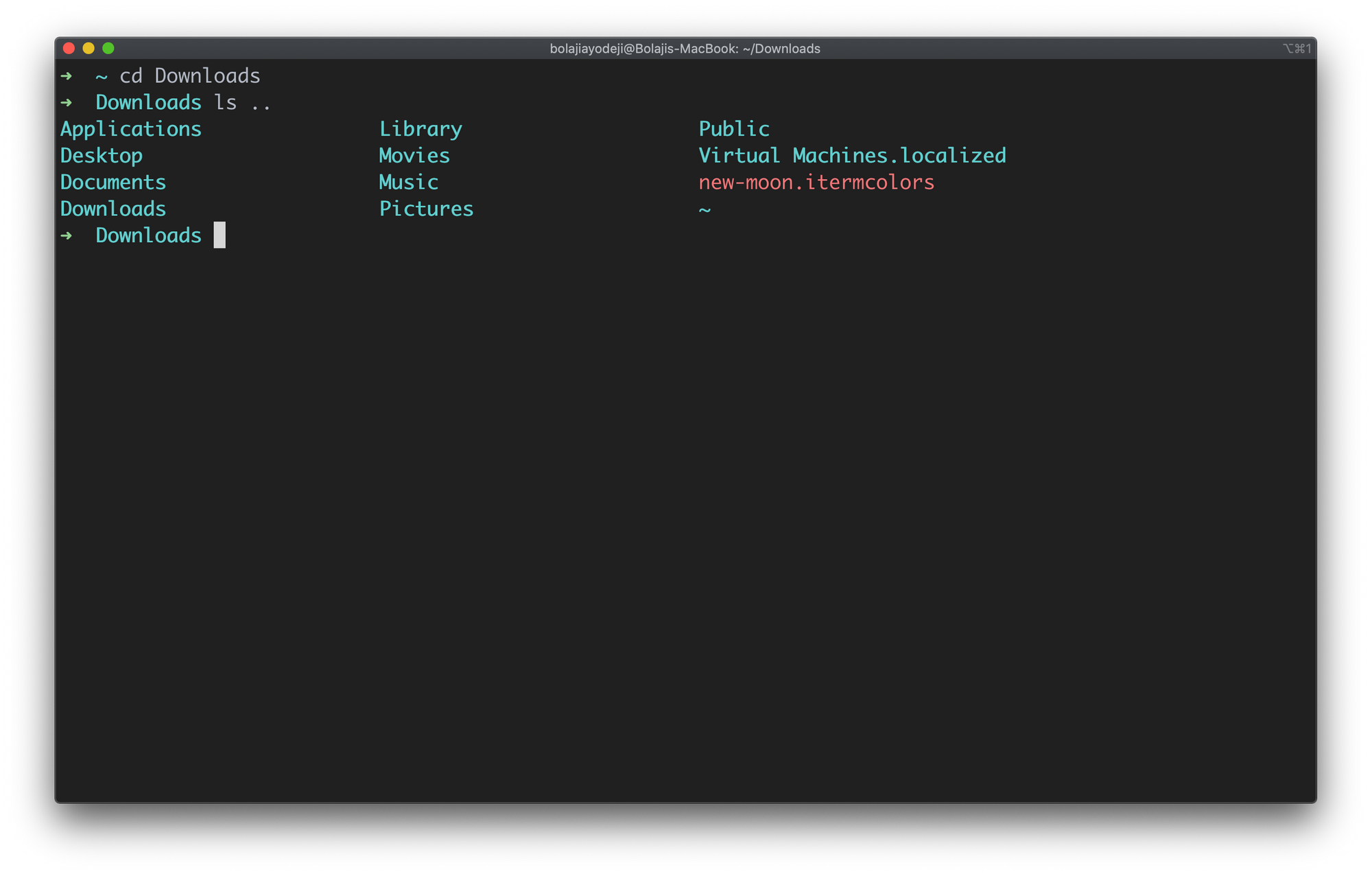
List files recursively
Type the ls -R command to list all files and directories with their corresponding subdirectories down to the last file:
If you have a lot of files, this can take a very long time to complete as every single file in each directory will be printed out. You can instead specify a directory to run this command in, like so: ls Downloads -R
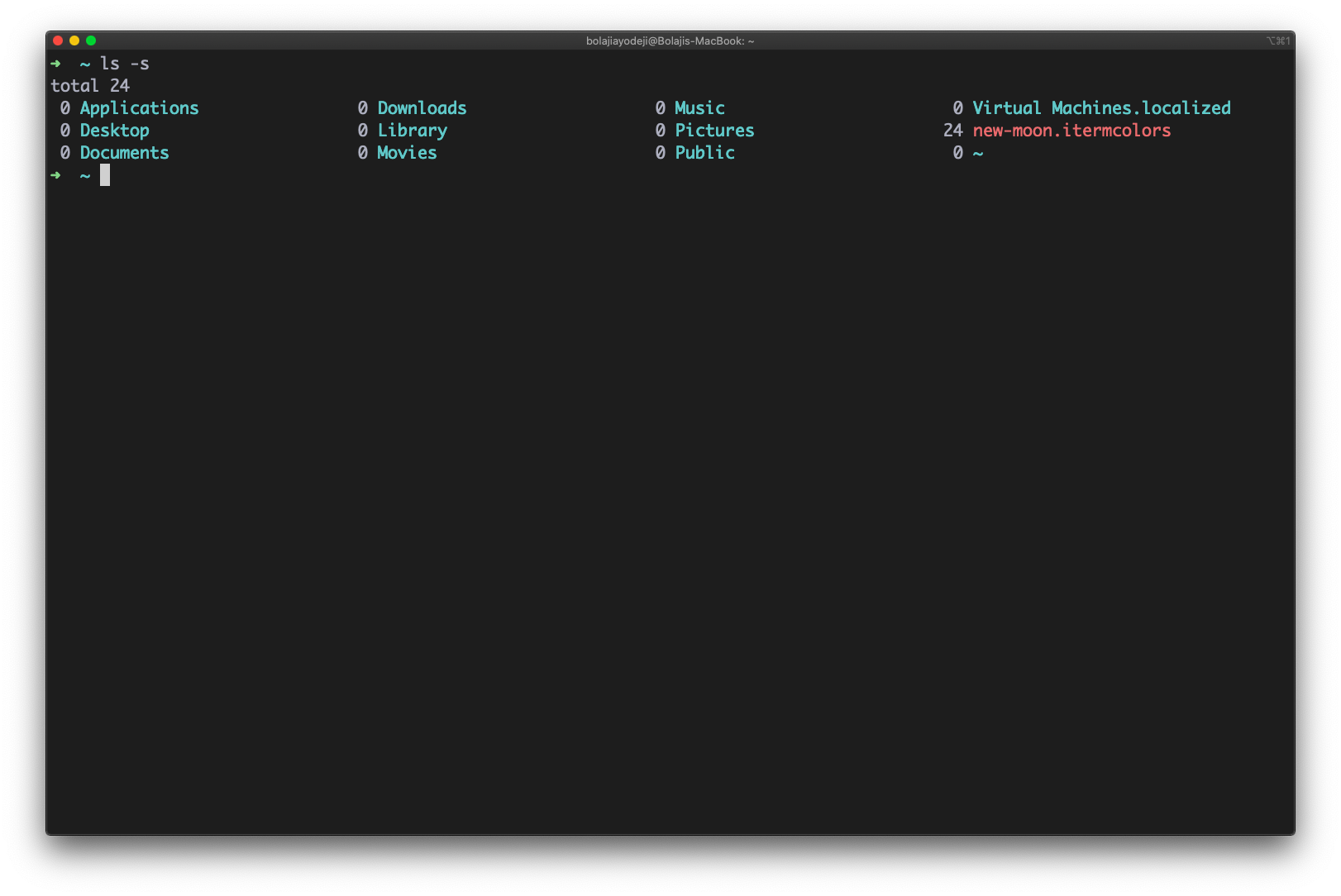
List files with their sizes
Type the ls -s command (the s is lowercase) to list files or directories with their sizes:
List files in long format
Type the ls -l command to list the contents of the directory in a table format with columns including:
- content permissions
- number of links to the content
- owner of the content
- group owner of the content
- size of the content in bytes
- last modified date / time of the content
- file or directory name
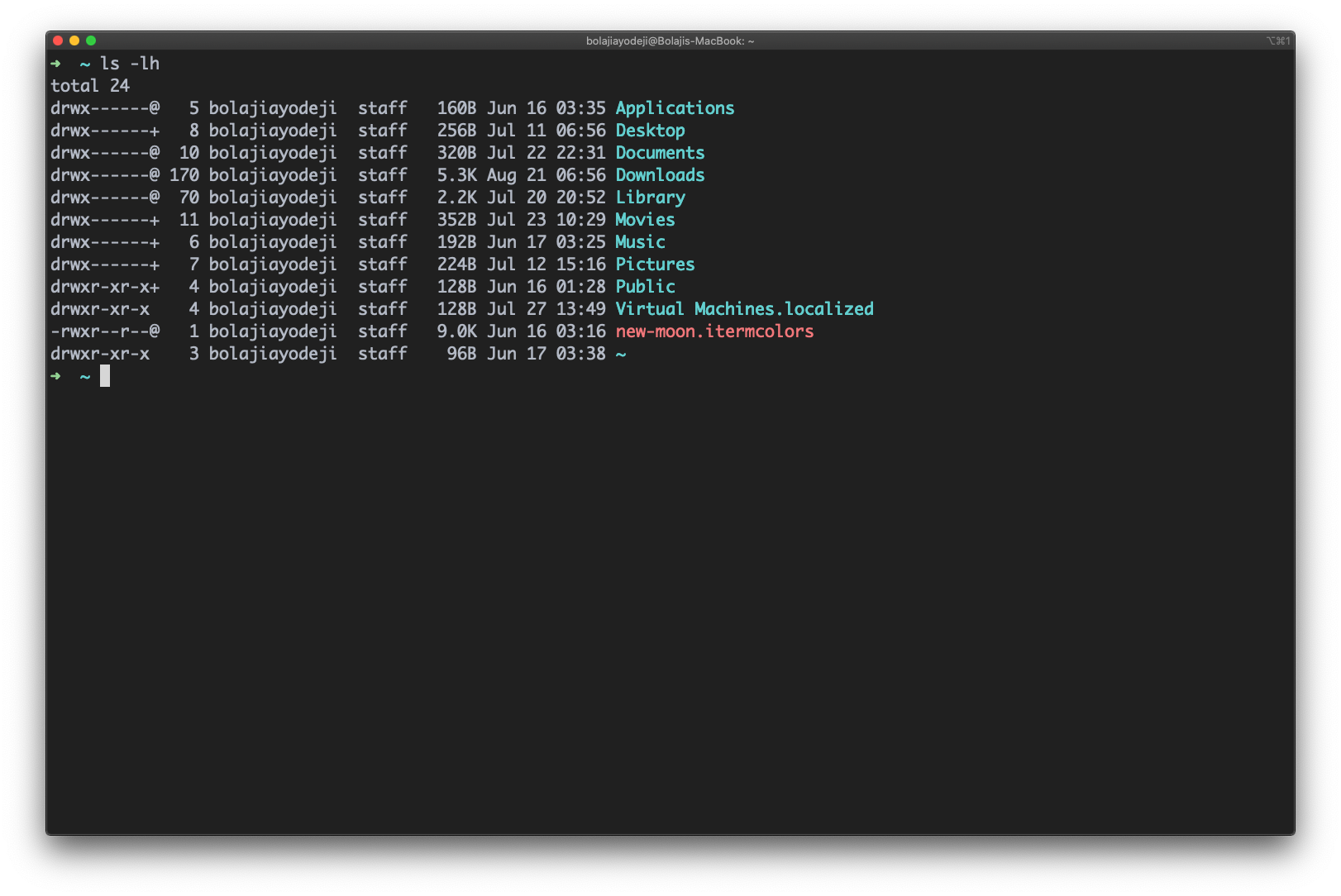
List files in long format with readable file sizes
Type the ls -lh command to list the files or directories in the same table format above, but with another column representing the size of each file/directory:
Note that sizes are listed in bytes (B), megabytes (MB), gigabytes (GB), or terabytes (TB) when the file or directory’s size is larger than 1024 bytes.
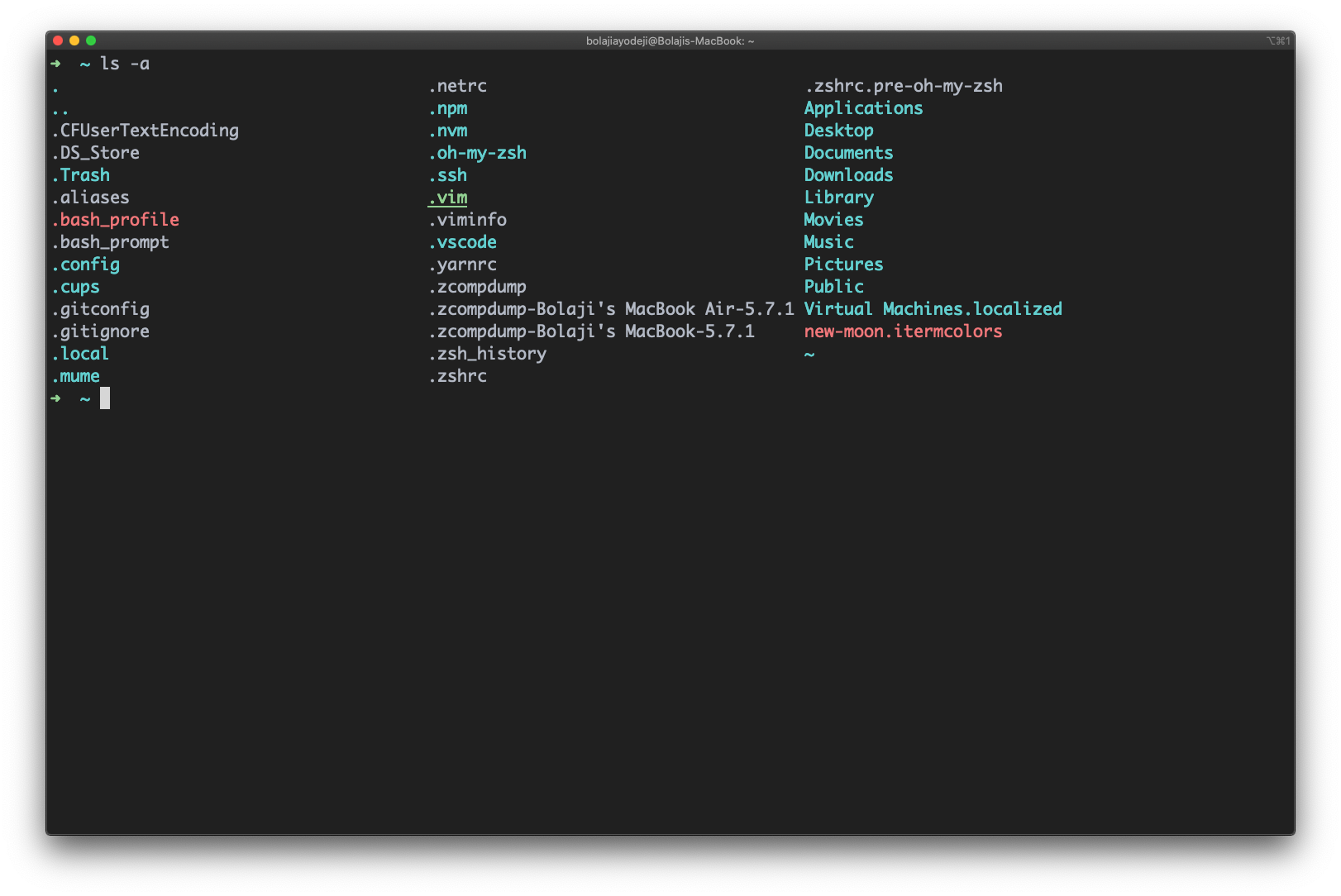
List files including hidden files
Type the ls -a command to list files or directories including hidden files or directories. In Linux, anything that begins with a . is considered a hidden file:
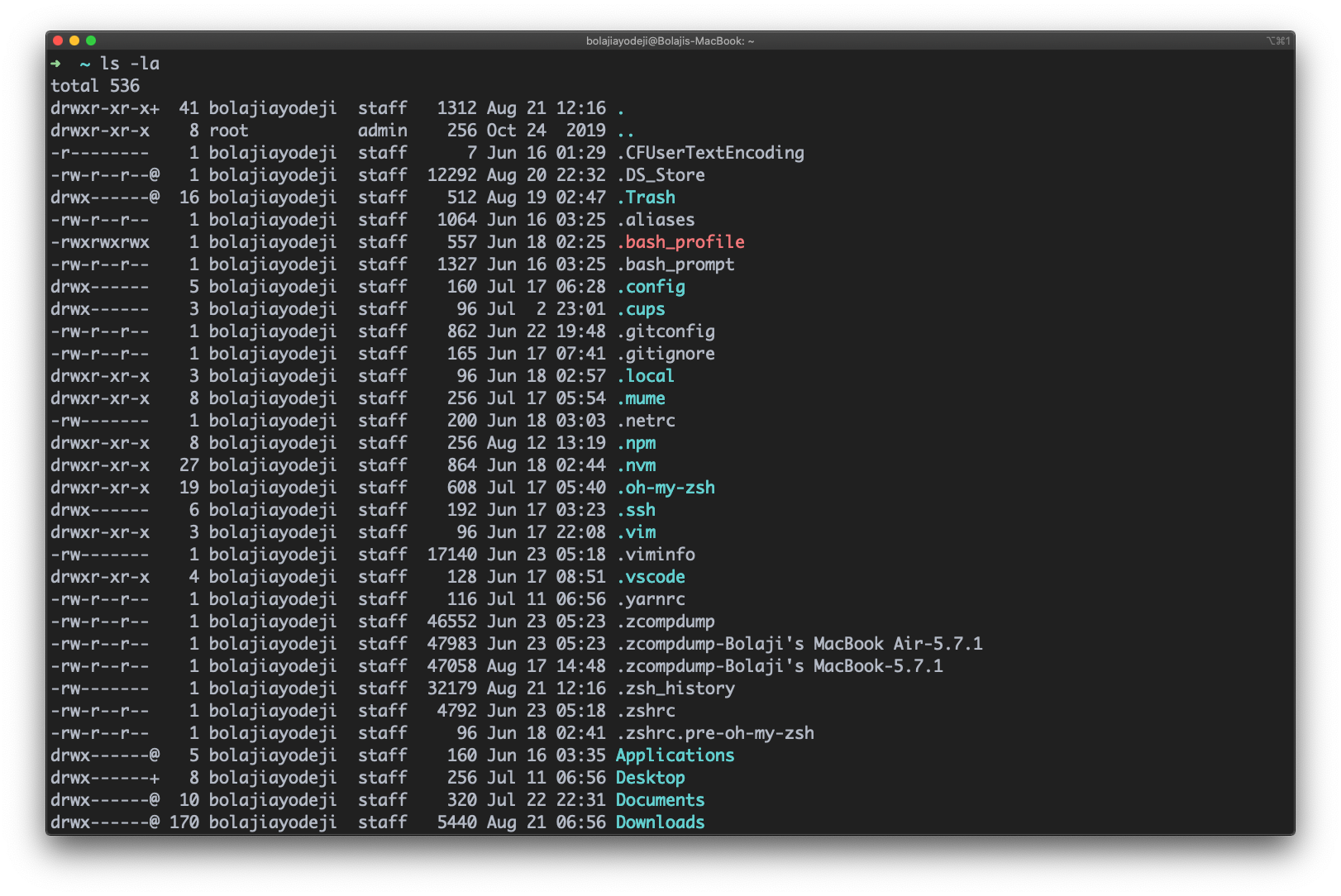
List files in long format including hidden files
Type the ls -l -a or ls -a -l or ls -la or ls -al command to list files or directories in a table format with extra information including hidden files or directories:
List files and sort by date and time
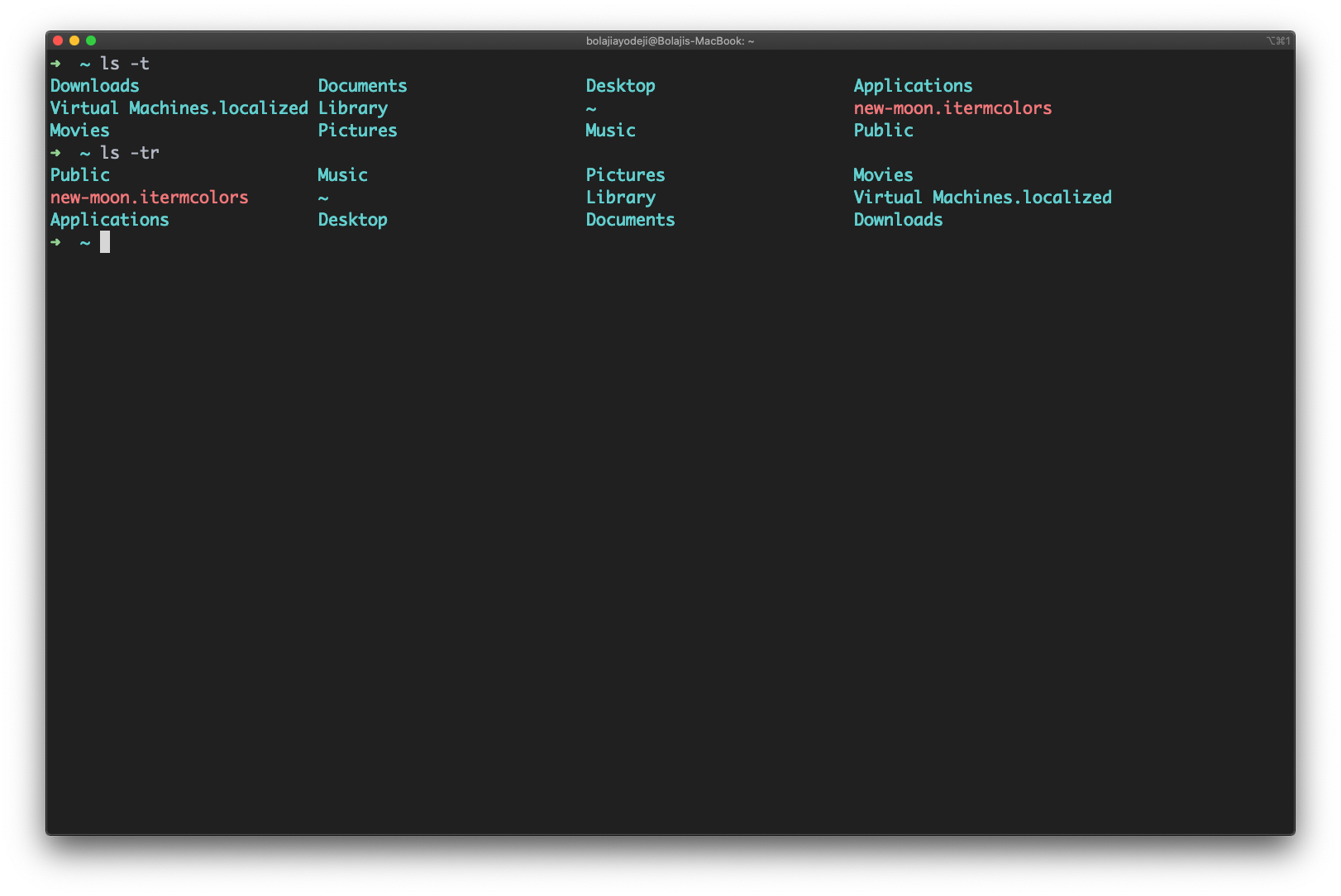
Type the ls -t command to list files or directories and sort by last modified date and time in descending order (biggest to smallest).
You can also add a -r flag to reverse the sorting order like so: ls -tr :
List files and sort by file size
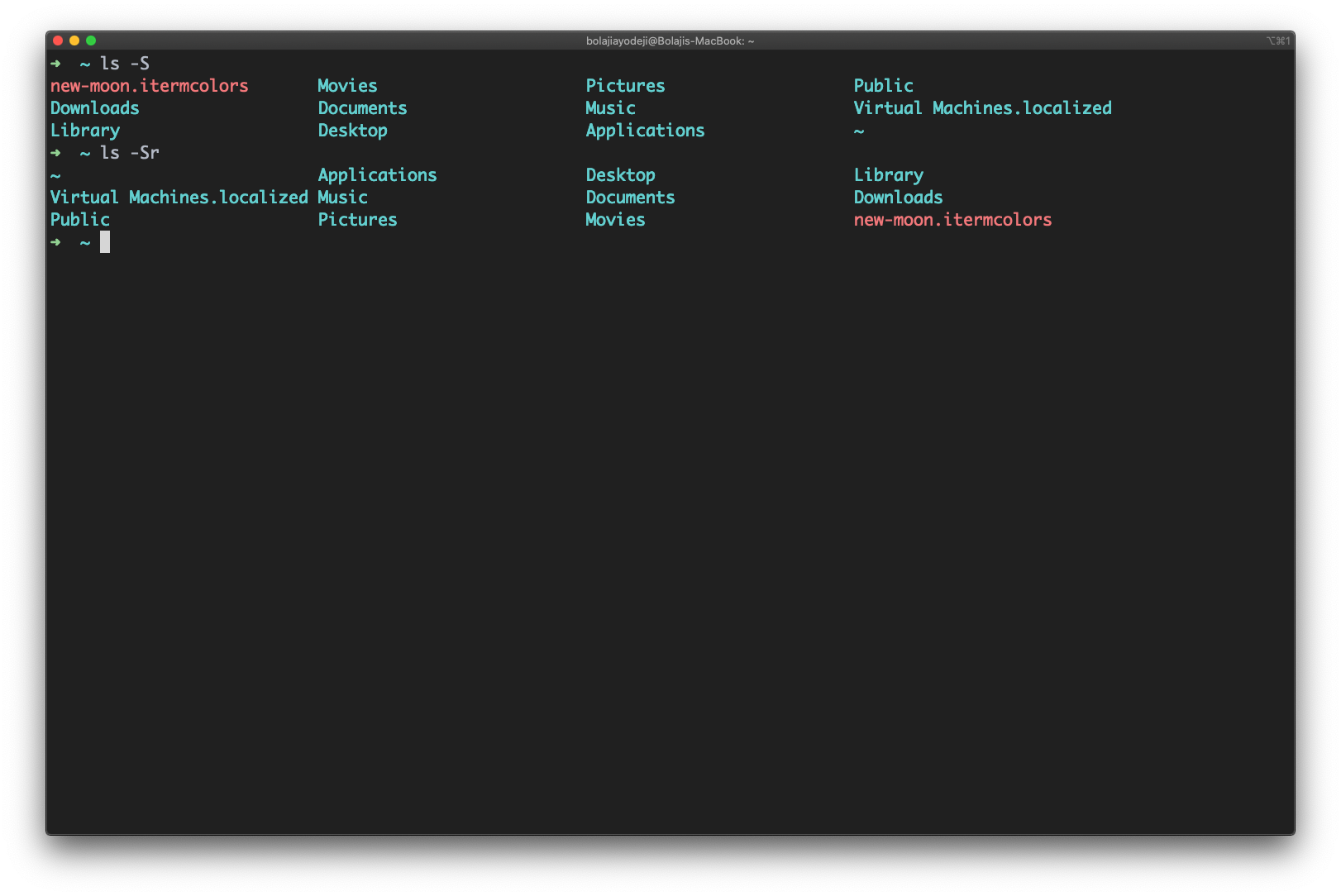
Type the ls -S (the S is uppercase) command to list files or directories and sort by date or time in descending order (biggest to smallest).
You can also add a -r flag to reverse the sorting order like so: ls -Sr :
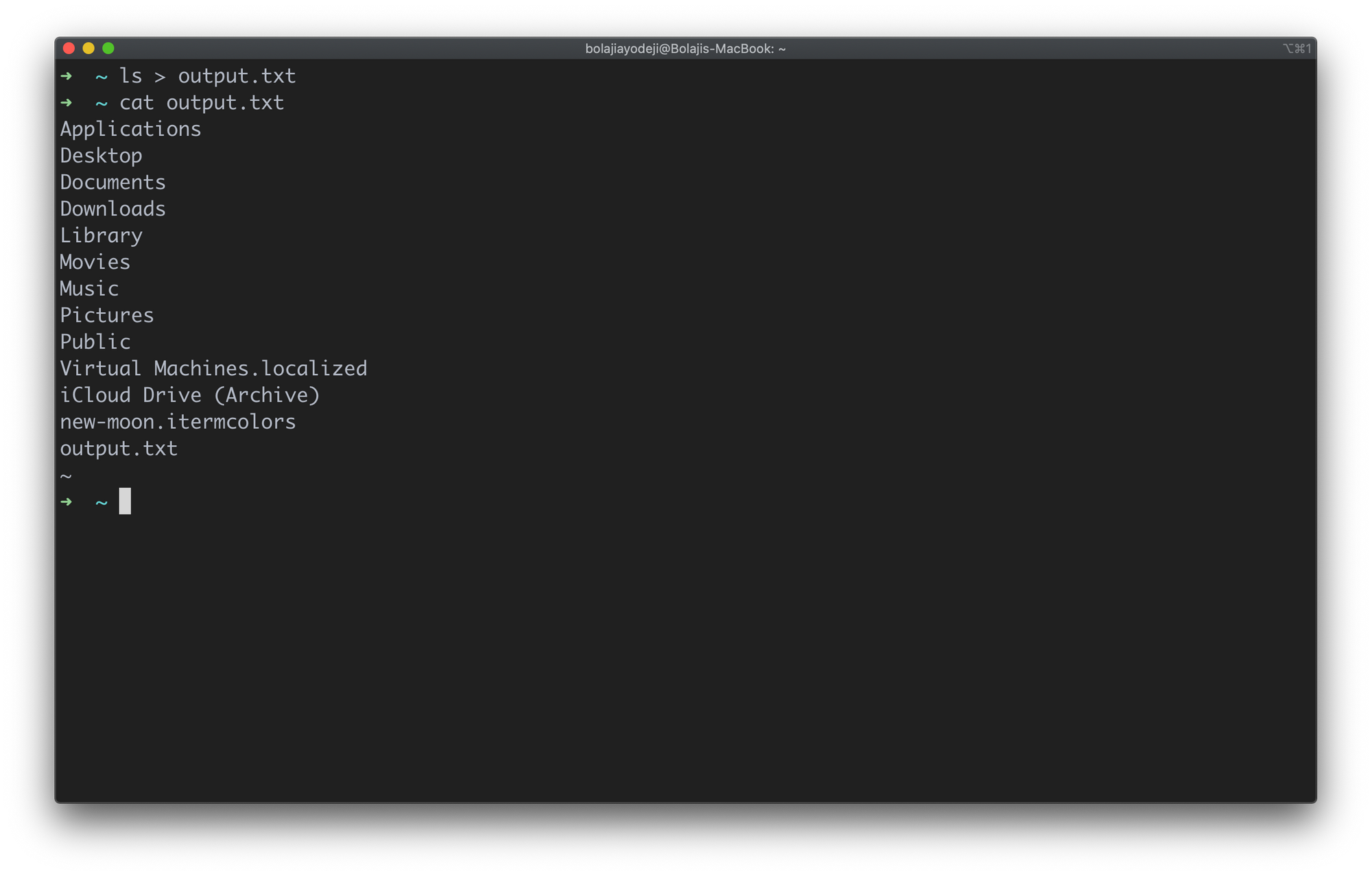
List files and output the result to a file
Type the ls > output.txt command to print the output of the preceding command into an output.txt file. You can use any of the flags discussed before like -la — the key point here is that the result will be outputted into a file and not logged to the command line.
Then you can use the file as you see fit, or log the contents of the file with cat output.txt :
Conclusion
There are tons of other commands and combinations you can explore to list out files and directories based on your needs. One thing to remember is the ability to combine multiple commands together at once.
Imagine you want to list a file in long format, including hidden files, and sort by file size. The command would be ls -alS , which is a combination of ls -l , ls -a , and ls -S .
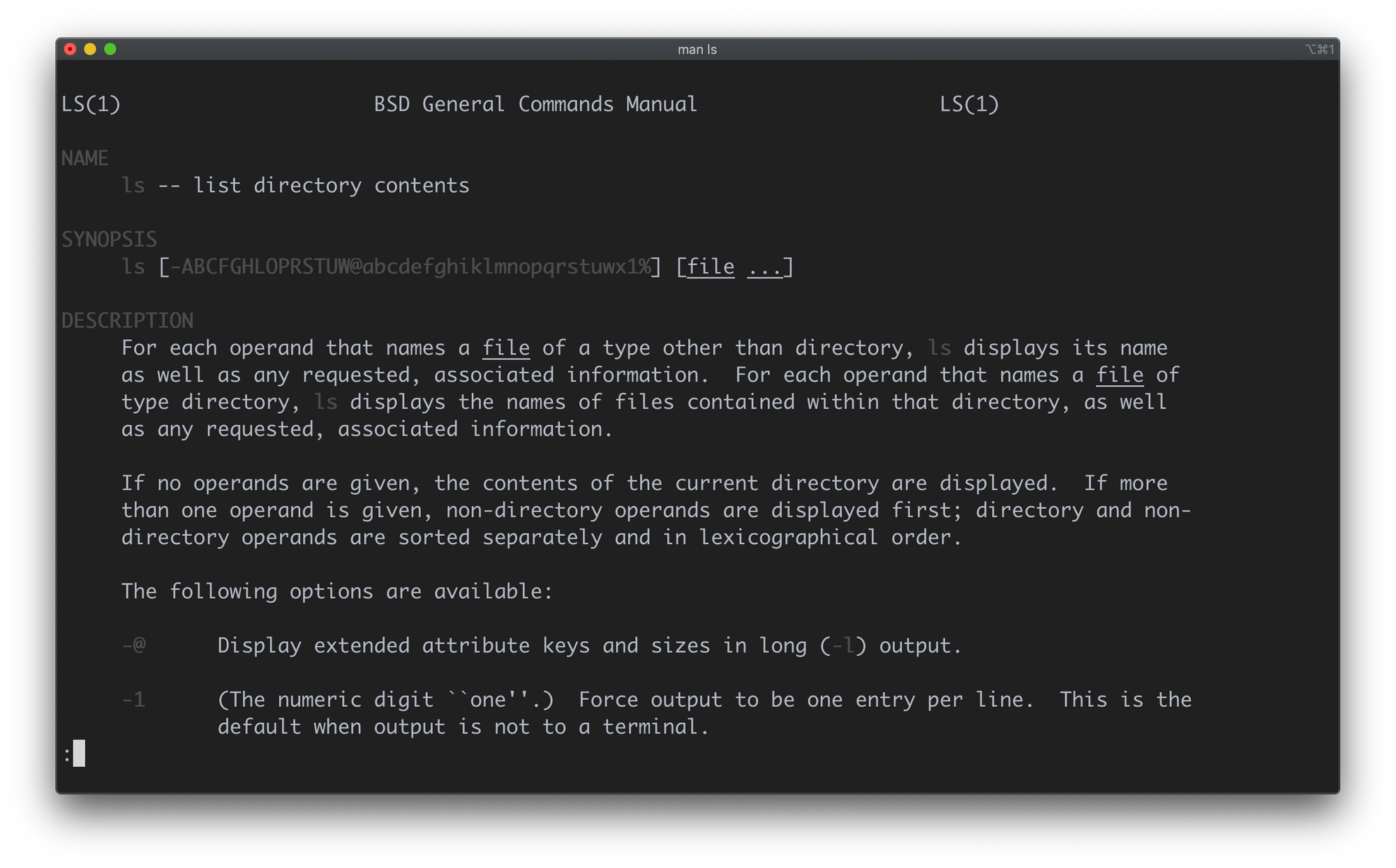
If you forget any command or are unsure about what to do, you can run ls —help or man ls which will display a manual with all possible options for the ls command:
Thanks for reading!
Software Engineer, Content Creator & Developer Advocate.
If you read this far, tweet to the author to show them you care. Tweet a thanks
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp’s open source curriculum has helped more than 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started
freeCodeCamp is a donor-supported tax-exempt 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization (United States Federal Tax Identification Number: 82-0779546)
Our mission: to help people learn to code for free. We accomplish this by creating thousands of videos, articles, and interactive coding lessons — all freely available to the public. We also have thousands of freeCodeCamp study groups around the world.
Donations to freeCodeCamp go toward our education initiatives and help pay for servers, services, and staff.
Источник