- Как посмотреть и очистить историю команд в Терминале на Mac
- Как посмотреть историю команд в Терминале на Mac
- Как очистить историю команд в Терминале на Mac
- How to view and clear the command history of the Terminal app
- Why to view and clear your command history
- How to view Terminal command history
- How to clear Terminal command history
- Wrapping up
- Question: Q: clearing command history from terminal
- Helpful answers
- Terminal: Viewing Your Command History in OS X
- OS X terminal history missing commands
- 5 Answers 5
Как посмотреть и очистить историю команд в Терминале на Mac
Возможность просмотра истории введенных команд в Терминале на Mac может быть чрезвычайно полезной. Вы, например, можете захотеть вспомнить команды, которыми меняли настройки операционной системы несколько недель или месяцев назад. И сделать это можно описанным нами ниже простым способом.
Как посмотреть историю команд в Терминале на Mac
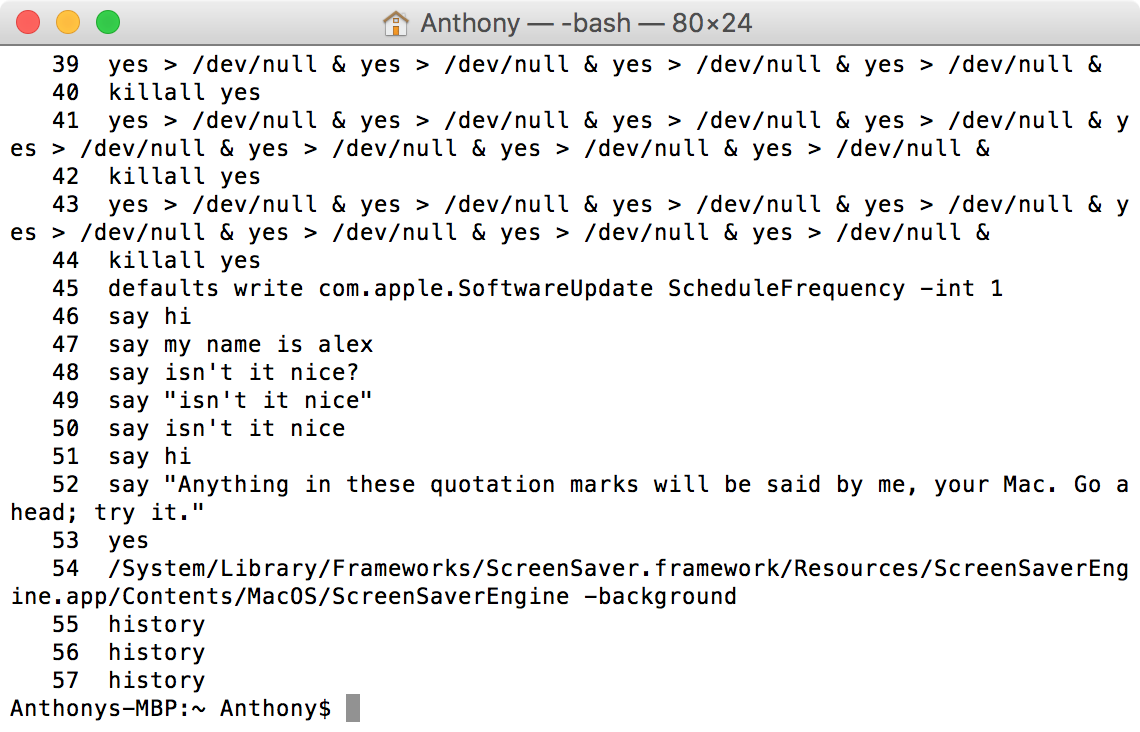
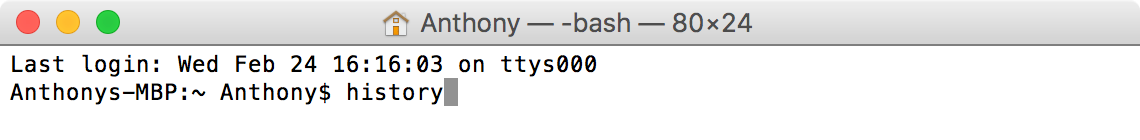
Шаг 1. Запустите Терминал и наберите команду, расположенную ниже
Шаг 2. Нажмите клавишу Return
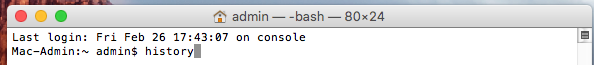
Как очистить историю команд в Терминале на Mac
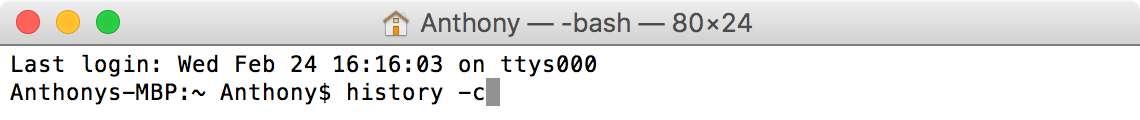
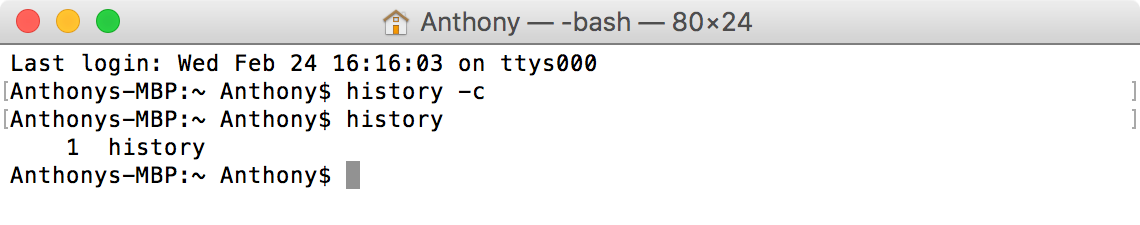
Шаг 1. Шаг 1. Запустите Терминал и наберите команду, расположенную ниже
Шаг 2. Нажмите клавишу Return 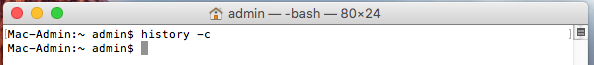
Источник
How to view and clear the command history of the Terminal app
If you’ve ever wanted to see a running history of all the Terminal commands you’ve used on your Mac, or that you suspect another user of your Mac has used, there is a simple command you can run.
In this tutorial, we’ll show you how you can view your Terminal command history, as well as clear your command history from being seen by unwanted eyes.
Why to view and clear your command history
Viewing your command history in macOS could be a useful feature if you want to see a long command you’ve used recently that you just can’t remember; this makes it easy to simply copy and paste the command and re-use it. Seeing your command history can also be useful if you have other users on your Mac and you want to see what kinds of things they’re doing with the Terminal app.
As for clearing your command line history, if you’re using Terminal on an institutional machine and need to hide commands you’re using from your administrator, or you want to increase your own privacy and keep your Terminal usage from being seen by other users of your computer, then clearing it will be an effective way of doing so.
How to view Terminal command history
The first thing we’ll show you is how to view your command line history in Terminal. This command will let you see all the commands entered since the most recent clear command was used.
To view your command history in the Terminal app, follow these steps:
1) Launch the Terminal app and enter the following command and then press the Return key on your keyboard.
2) Your entire command line history up to the last clear will be displayed.
At this point, you’re free to scroll up and down in the Terminal window to see what kinds of commands have been used. If at any point you see a command you want to re-use, you can simply highlight it, copy it, and paste it back into the Terminal window and press the Return key on your keyboard to run it.
How to clear Terminal command history
If you don’t want someone using the above steps to see what commands you’ve been using in your Terminal app, then you can cover your tracks by clearing your command line history. This is done with another simple command, so just follow these steps:
1) Launch the Terminal app and enter the following command, then press the Return key from your keyboard to initiate it.
2) Your command line history is cleared, and you can perform the “history” command again immediately afterwards to verify that your command line history no longer exists:
Wrapping up
Viewing and clearing your Terminal command line history is easy, and it’s a great way to keep track of your commands and to cover your tracks if you have to.
These may also interest you:
If you found this tutorial helpful, let us know in the comments below!
Источник
Question: Q: clearing command history from terminal
Is there a way to clear all the history of remembered commands in Terminal? I am referring to the «Run Command» box after «New Command» is selected showing the most recent command highlighted and a collection of recent commands in a «scroll down» underneath this. They wont delete permanently. Same ones reappear each time box is closed and «new command» is selected.
Is it any problem if I am unable to clear them? I believe it is normal for the computer to remember these recent commands. Thanks
Posted on Mar 14, 2008 7:44 AM
Yes, when an application have an Preference menu, you should use them to set the settings. If the Preference menu has not an option to set or remove an setting, in this case the history, you could use
This is also an official way to modify Preference files, when the Application or Process have not an Preference dialog, or the funktion is not implemented.
To delete the Preference file is a simply methode, but not the best, because you lost all settings.
Better you use an AppleScript to modify the setting.
Create an AppleScript and write the command in the last post into. Then close the Terminal and run the AppleScript. At the next start of the Terminal, the history drop down should be clear.
Posted on Mar 15, 2008 5:52 AM
Helpful answers
No Sorry, I have you not understood correctly. These was an instruction to clear the history direct in the shell.
The history from the drop down menu stand in the com.apple.Terminal.plist Preference file in
in your homefolder. You can delete the preference file, or you could create an AppleScript with the command because the terminal write at quit the historycache back to the preference file, when you run the command direct in the shell.
No. When you open an terminal window, you awake the standard shell. In your case the tcsh. This is not the wrong shell, it is familiarization, wich you favored. I don´t know, why you have the tcsh as standard.
Mar 14, 2008 1:19 PM
This is is good method, very well thought out. Yet I see no need for this. It does not consume disk space and is a good reference for future use. Why not leave it be. If you ever need a check-up, Apple can look back to see what may have led to the problem. Trust me, leave it the way it is and forget of it. Like I claimed, it uses no disk space.
Mar 15, 2008 6:13 AM
There’s more to the conversation
Loading page content
Page content loaded
When you use the bash, try This removed temporary the history for the actual Session.
For delete the history completely, you can remove the history and overwrite the .bash_history with
When you not clear the history, it is not a problem, except that is a little bit confusing.
Mar 14, 2008 10:47 AM
Thanks for reply. First, I am referring to the history of remembered commands as shown in the drop down that appears after «new command» is selected and includes the last command entered, which is highlighted. Is this what you understood I was referring to?
Second, by «bash» do you mean the window that appears when terminal is opened? The window I am seeing is titled «terminal-tcsh-80X24» Lower down it says «welcome to Darwin» plus some other text. In an article «Mac OS X: How to change the Terminal shell» it is written that tcsh as default is meant for pre 10.4 systems and bash as default for 10.4 (which I am running). Does this mean I have the wrong default shell?
Third, I never use Terminal. I don’t understand Unix and only got into this by accident (too long a story). I just want to make sure I haven’t disturbed anything that will upset the computer. Since all of this is unfamiliar I would be grateful for an answer that includes more detail and explanation. Thanks for your patience.
Mar 14, 2008 12:12 PM
No Sorry, I have you not understood correctly. These was an instruction to clear the history direct in the shell.
The history from the drop down menu stand in the com.apple.Terminal.plist Preference file in
in your homefolder. You can delete the preference file, or you could create an AppleScript with the command because the terminal write at quit the historycache back to the preference file, when you run the command direct in the shell.
No. When you open an terminal window, you awake the standard shell. In your case the tcsh. This is not the wrong shell, it is familiarization, wich you favored. I don´t know, why you have the tcsh as standard.
Источник
Terminal: Viewing Your Command History in OS X
Last week, I had a very nice reader email me to ask a question about how to look through the commands he’d previously typed into Terminal. So if, for example, he’d used a “defaults write” command to alter how OS X looks or acts, he could find exactly what he did in his history to know how to reverse the changes.
There are quite a few ways you could go about this; I mentioned one method a couple of years ago that’ll help you search through the history, which is useful if you at least know a keyword in the command you’re trying to find. However, you could also just view your history in either the Terminal window or as a text file. To do the former, simply type “history” in at the prompt, and you’ll get what you’re looking for.
If you’re familiar with using the “greater than” (“>”) symbol in Terminal, that’s an easy way to make “history” easier to read—it’ll take the command and create a file you designate with the output. So this example…
…means “run the ‘history’ command, and then create a new file on Melissa’s desktop called ‘history.txt’ with the results.” That little “greater than” symbol is handy for all sorts of stuff within Terminal, but be aware of its one big caveat: If there is already an existing file in your requested location with the same name, using the command above will replace it. If you want to add to existing text instead of replacing it, type “greater than” twice (“>>”).
Finally, there is one more method I’m going to suggest, and I think it’s the simplest of all. You could just open the file containing your history and view it as text! Unsurprisingly, though, that file is hidden by default, so to access it, open a new Terminal window, type this command in, and press Return:
That should open your list of previously entered commands within your default text editor, and you can search through it at your leisure.
(If the command above didn’t work, you may have navigated away from your user folder within Terminal, and if so, you can use the “cd
” command [without the quotes] before running “open .bash_history” again.)
And finally, it wouldn’t be a command-line tip if I didn’t offer the usual disclaimers—be very careful of what you type, always copy and paste commands if you aren’t confident in your skills, blah de blah blah. Terminal’s awesome, but boy, could you cause issues if you really tried. Please don’t try, OK?
Источник
OS X terminal history missing commands
I know that I entered a command the other day, but now I can’t find it using history or .bash_history. Any ideas why this happens? I suspect it has to do with using multiple tabs in my OS X terminal, and somehow the history doesn’t carry over between tabs, but I don’t know.
5 Answers 5
I had this issue with my terminal. It turns out it was saving to newly generated files in the
/.bash_sessions folder. This is part of a new method of managing bash sessions introduced with El Capitan outlined in the /etc/bashrc_Apple_Terminal file. This is confirmed by the outpit of echo $HISTFILE . To disable this behaviour, simply run touch
/.bash_sessions_disable . Then quit the Terminal app and restart it. It should now save the history properly, as can be confirmed again via echo $HISTFILE . I hope this helps!
As of OS X El Capitan 10.11, by default Bash is configured to save separate command histories for each terminal, so they can be restored separately for Resume.
Each individual history is also appended to the global history in
/.bash_history when the shell is exited. If you quit Terminal and then re-open it—with or without Resume enabled—you should find that commands from every terminal are in
/.bash_history. If you have Resume enabled, each restored terminal will only contain its restored history, but when you create a new terminal it will start with the latest global history.
Because all the command histories are appended to the global
/.bash_history file, you may wish to increase the number of commands stored by setting the HISTFILESIZE environment variable so the latest terminal histories don’t push the other terminal histories out of the file too soon. The default value is 500. I have mine set to 10,000. I also set HISTSIZE to 10,000 so I can navigate through the entire history (otherwise, only the last 500 will be read from the history file).
The script that arranges for separate command histories is in /etc/bashrc_Apple_Terminal in OS X El Capitan 10.11 and later. It contains extensive comments describing how the mechanism works, and how to customize or disable it.
Источник