- Как открыть скрытую папку «Библиотеки» (Library) на Mac (macOS Sierra)
- Как открыть папку «Библиотеки» (Library) на macOS Sierra
- Подробный видеообзор macOS Sierra
- Доступ к папке Библиотеки (
- Способ №1
- Способ №2
- Способ №3
- Способ №4
- what does mac os /Library folder store?
- 1 Answer 1
- File System Programming Guide
- macOS Library Directory Details
- Как найти папку Library в Mac OS
- Что такое папка «Library»?
- Показать Library при помощи клавиши ALT
- Показать Library при помощи опции «Переход к папке»
- Заключение
- Как показать скрытые файлы в MacOS
- Как почистить клавиатуру ноутбука?
- IPad 5G: стоимость и обзор будущей новинки
Как открыть скрытую папку «Библиотеки» (Library) на Mac (macOS Sierra)
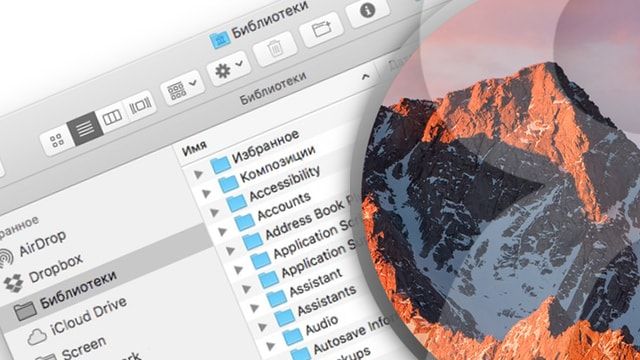
В macOS Sierra разработчики посчитали уместным не отображать папку «Библиотеки» в пользовательском каталоге. Так как в этой папке сосредоточено много важных системных данных (кэш, настройки программ и прочее), девелоперы решили обезопасить юзеров от случайного удаления этих файлов.
Однако есть простой способ, как быстро вернуть отображение «Библиотеки» в пользовательском каталоге. Для этого не понадобится совершать действий в Терминале, необходимо лишь следовать нашей инструкции:
Как открыть папку «Библиотеки» (Library) на macOS Sierra
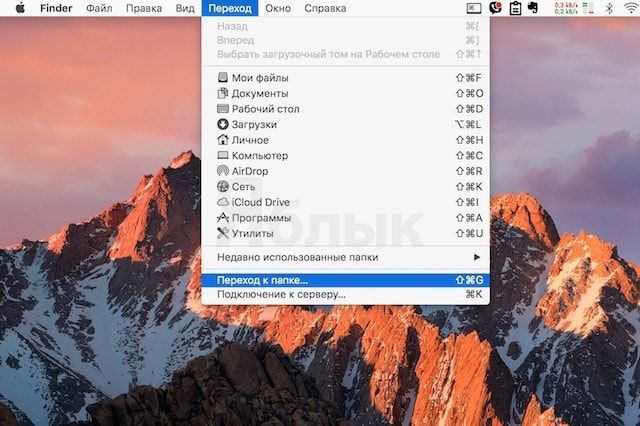
1. Для начала необходимо зайти в Finder и нажать на меню «Переход», а затем «Переход к папке». Альтернативный вариант – нажать сочетание клавиш ⌘Cmd + ⇧Shift + G (может быть и ⌘Cmd + ⇧Shift + H);
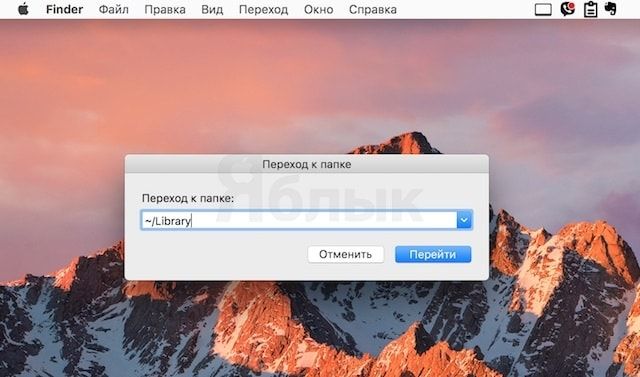
2. Появится строка, в которой следует ввести адрес «
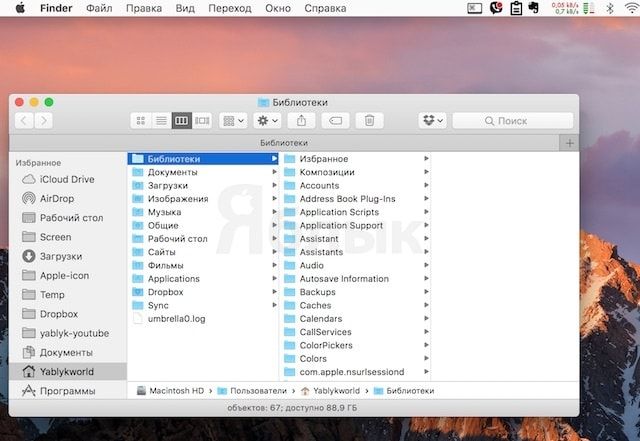
3. Сразу же после этого откроется искомый каталог «Библиотеки». В том случае, если работать с ним планируется нечасто, можно взять данный способ на заметку.
Но если предполагается обращаться к папке регулярно, можно перетянуть ее иконку в боковую панель. Таким образом, появится возможность быстрого и простого доступа к каталогу «Библиотеки».
Подробный видеообзор macOS Sierra
Источник
Доступ к папке Библиотеки (
/Library) в Finder
С версии Mac OS X — 10.7 папка “Library” (Библиотеки) по умолчанию в Finder спрятана от пользователя.
Способ №1
Эта возможность присутствует в OS X довольно давно. С помощью этого трюка можно быстро перейти в папку “Библиотеки”, при этом оставив её скрытой.
Нажмите на вкладку “Go” (Переход) в строке меню.
Зажмите клавишу Option ( Alt ). После этого в списке для перехода к папкам появится и папка “Библиотеки”:
Способ №2
Перейдите в домашнюю папку пользователя (для этого можно использовать сочетание клавиш Command+Shift+H ).
Нажмите на вкладку “View” (Вид) в строке меню и выберите пункт “Show View Options” (Показать параметры вида).
Отметьте пункт “Show Library Folder” (Показывать папку «Библиотеки»).
После этого папка “Библиотеки” будет видна в вашей домашней папке.
Способ №3
Нажмите на вкладку “Go” (Переход) в строке меню и выберите пункт “Go to Folder…” (Переход к Папке). Или используйте сочетание клавиш Cmd+Shift+G (Переход к Папке).
Введите адрес каталога:
Вы попадёте в каталог “Библиотеки”.
Способ №4
Этот способ использовался в OS X Lion и Mountain Lion, но так же работает в OS X Mavericks и Yosemite.
Запустите “Terminal” через “Spotlight” или “Launchpad” → “Utilities”
Введите следующую команду, чтобы показать спрятанную папку:
Папка “Библиотеки” станет видимой.
Возврат к стандартным настройкам:
Если эта статья помогла вам, пожалуйста, оставьте комментарий
Спасибо за прочтение!
Если этот пост помог вам, и вы хотели бы показать свою поддержку, подумайте о том, чтобы заправить будущие посты, купив мне чашку кофе!
Источник
what does mac os /Library folder store?
I am a new to mac osx. One thing confusing me is what does /Library or /System/Library folders store? As its name meaning, I thought is should be something like /lib or /usr/lib in Linux. However, it does not. Inside it, it looks more similar to application bundles. And all naming is very application-specific, like /Library/iChat . If they are application-specific, then why they are called Library ? Usually when named as Library , it is for codes or resources sharing purpose.
1 Answer 1
The library folders store settings, resources, and support files. There up to 6 «levels» of them:
- The user library,
/Library, stores per-user settings etc.
Sandboxed apps don’t have access to most of the user’s home folder. They’re mostly restricted to their own sandbox «container» (which is itself inside the user library), and as a result they get their own «private» libraries:
- Per-application sandbox libraries,
Источник
File System Programming Guide
macOS Library Directory Details
The Library directories are where the system and your code store all of their related data and resources. In macOS, this directory can contain many different subdirectories, most of which are created automatically by the system. In iOS, the app installer creates only a few subdirectories in
/Library (such as Caches and Preferences ) and your app is responsible for creating all others.
Table A-1 lists some of the common subdirectories you might find in a Library directory in macOS along with the types of files that belong there. You should always use these directories for their intended purposes. For information about the directories your app should be using the most, see The Library Directory Stores App-Specific Files .