- Как запустить Traceroute на MacBook, Mac: 2 метода
- Как запустить Traceroute на MacBook Pro, Mac, iMac
- Метод 1: через приложение-терминал
- Метод 2: запустите Traceroute на Mac с помощью приложения Network Utility
- The WWW Blog
- How to Use Traceroute
- How Do I Run A Traceroute?
- To Run a Traceroute in Windows
- To Run a Traceroute in Mac OS X
- To Run a Traceroute in Linux
- What Does the Traceroute Show You?
- How To: Traceroute in Mac OS X Terminal
- Как запустить и использовать Traceroute на macOS
Как запустить Traceroute на MacBook, Mac: 2 метода
Traceroute — это встроенный инструмент для диагностики проблем сетевого подключения и маршрутизации между Mac и сервером. При открытии веб-сайта приложение показывает, что сайт недоступен или какая-либо другая ошибка, и в конечном итоге вы не сможете посетить веб-сайт. Чтобы преодолеть это и найти причину этой ошибки, на картинке появляется трассировка трассировки. В отчете traceroute вы можете отслеживать, как пакеты перемещаются по пути, где произошла поломка и как ее исправить.
На MacBook и Mac есть два способа запустить traceroute: один — с помощью приложения «Терминал», а другой — приложения «Сетевая утилита», оба функции одинаковы. Вы можете попробовать любой из них, чтобы найти и просмотреть traceroute в macOS.
Как запустить Traceroute на MacBook Pro, Mac, iMac
Метод 1: через приложение-терминал
- Откройте приложение «Терминал» на Mac. Щелкните Finder. Выберите «Приложения» и выберите «Утилиты».
- Оттуда откройте Терминал.
- Введите следующую команду в Терминале.
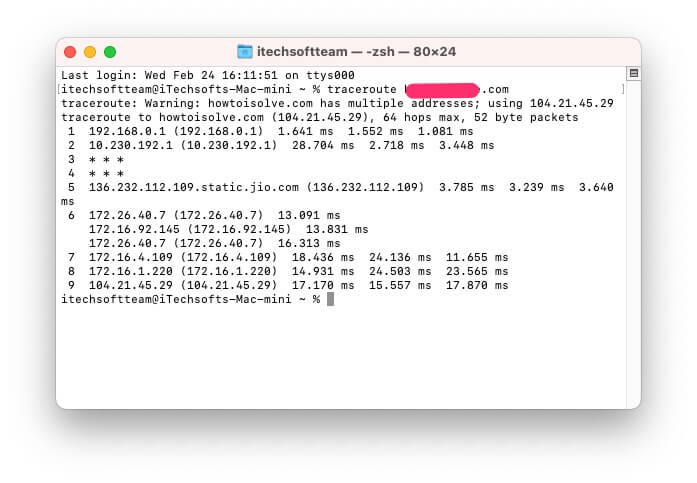
- Здесь имя хоста относится к имени сервера, который вы хотите протестировать. Это может быть ссылка на любой сайт. Например, если вы хотите узнать результаты трассировки сайта howtoisolve.com, команда будет выглядеть так:
- traceroute howtoisolve.com
- Нет необходимости вводить www или https: // в команде при отслеживании отчета traceroute сервера.
- Mac потребуется несколько минут, чтобы сгенерировать отчет трассировки между соединениями.
- Если отображается знак *, значит время ожидания запроса истекло, проверьте результаты.
- Вот и все.
Метод 2: запустите Traceroute на Mac с помощью приложения Network Utility
Примечание: Сетевая утилита устарела в macOS Big Sur, Так что этот способ бесполезен…
- Пользователи MacOS Catalina и более ранних версий Mac могут использовать Traceroute с помощью сетевой утилиты.
- Нажмите Command + пробел, чтобы открыть поиск Spotlight, а затем выполните поиск в приложении Network Utility. или Открыть из Finder, Открыть Finder на Mac, Из верхнего меню Mac Перейти> Перейти в папку…>
/ Система / Библиотека / CoreServices / Приложения> В папке приложений.
- Выберите вкладку Traceroute.
- Введите URL-адрес веб-сайта, например howtoisolve.com, и нажмите «Трассировка».
Надеюсь, это поможет вам узнать, что вы ищете. Дайте нам знать в комментариях, если у вас есть какие-либо сомнения или вам нужно изучить то же самое.
Источник
The WWW Blog
Traceroute is a tracking way with which you can know how web pages actually reach your computer, from the server. Your computer is not directly related to any web page, or any downloadable file, but gets connected through a pathway or chain where you send an information to your router, and from there to the next destination in the pathway.
Sometimes due to a problem in any link, the site loading doesn’t happen. Here is where traceroute helps you in finding the loopholes and problems in the loading of the website.
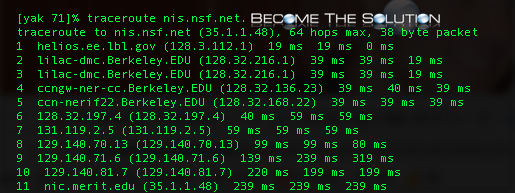
Here is how to run traceroute in Mac OS –
1. Through the terminal.app in utilities –
The terminal app in mac helps you find the roots of the whole file systems and the operating system. Most of the system processes can be found through the terminal application.
Open the Terminal.app from the list of Utilities in Applications, and enter the following –
traceroute www.thewwwblog.com (replace www.thewwwblog.com with the domain name you want to traceroute)
Hit enter/return and you would see the traceroute process happening.
2. Through Network Utility –
The network utility in mac is useful in many ways to monitor the network usage, and the availability of network etc. Through that you can ping a website, lookup the availability of a domain, the WHOIS data etc. You just need to select the traceroute option, and enter the web address there –
The tracerouting starts and the IPs hit are displayed as shown in the pic –
This is what traceroute helps in –
The results area in the lower part of the window now shows you the trace or track for the signal your computer sends to the address you specified.
When you run a trace your machine sends out a tiny packet of data (40 bytes). The next device along the line sends a notification to you that the data reached it. That all takes a little time, measured in milliseconds. 1 millisecond (ms) = 1/1000th of a second.
The traceroute shows the path of a query sent, first from the local modem to the service provider, and from there to the main hosting site, and so on.
Источник
How to Use Traceroute
Traceroute is an application that traces the path data takes from one computer to another.В Basically a traceroute is a map that shows what stops or locations that data must pass through in order to go from one computer to another.
To be an effective troubleshooting tool, the traceroute needs to be run from a computer experiencing the problem while the problem is occurring.
How Do I Run A Traceroute?
To Run a Traceroute in Windows
The command application (cmd.exe) is used to run a traceroute on Windows. Launching it is slightly different depending on your version of Windows:
- In Windows 7:
- click on the Start menu
- type “cmd” and press Enter to get a command prompt.
- In Windows 8:
- move your mouse to the bottom-left corner of the screen to bring up the Start icon.
- Right-click on Start and select Run.
- Then type “command” and press Enter to launch the application.
- Alternatively, you can type “command” into the Search field in the Charms menu after moving your mouse to the lower right corner of your desktop.
- In Windows 10, type “command” into the search menu and press Enter for a command prompt.
To run the traceroute, type:
into the command prompt, where “domainname.com” is the name of the server to which you are having difficulty connecting.
The traceroute may take only a few seconds or a few minutes. Typically, the closer you are to the server, geographically, the more quickly the traceroute will complete.
To Run a Traceroute in Mac OS X
If you have a Mac, you can use the built-in network tools to run a traceroute.
- Launch Spotlight (with вЊ + SPACE or by clicking on the magnifying glass in your menu) to search for and launch Network Utility.
- Select the Traceroute tab and enter the hostname or domain name.
- You also can perform a traceroute from the Terminal app. Simply enter: traceroute domainname.com
To Run a Traceroute in Linux
At the command line, type:
What Does the Traceroute Show You?
Let’s take a few sample traceroute outputs.
The output from that command shows a successful trace:
traceroute to msu.edu (35.8.10.134), 30 hops max, 40 byte packets
1 lw-dc2-hsrp-vlan132.rtr.liquidweb.com (67.43.8.129) 1.330 ms 1.420 ms 1.554 ms
2 lw-dc2-core4-po2.rtr.liquidweb.com (209.59.157.131) 1.092 ms 1.311 ms 1.451 ms
3 lw-dc1-core1-ge3-5.rtr.liquidweb.com (209.59.157.93) 1.596 ms 1.897 ms 2.209 ms
4 lw-dc1-border3-ge4.rtr.liquidweb.com (209.59.157.29) 1.657 ms 1.748 ms 1.894 ms
5 12.116.80.97 (12.116.80.97) 4.748 ms 5.382 ms 5.453 ms
6 cr81.dtrmi.ip.att.net (12.122.102.2) 12.893 ms 12.035 ms 11.043 ms
7 cr1.cgcil.ip.att.net (12.123.139.157) 11.509 ms 11.615 ms 11.769 ms
8 12.123.7.33 (12.123.7.33) 10.645 ms 10.711 ms 10.760 ms
9 12.90.96.6 (12.90.96.6) 9.473 ms 9.537 ms 9.605 ms
10 xe-0-0-0x14.msu6.mich.net (198.108.22.10) 15.047 ms 14.458 ms 14.487 ms
11 192.122.183.227 (192.122.183.227) 16.976 ms 20.066 ms 20.137 ms
12 cc-t1-ge1-23.net.msu.edu (35.9.101.209) 20.228 ms 20.432 ms 20.312 ms
13 www.msu.edu (35.8.10.134) 16.856 ms 17.071 ms 16.341 ms
It looks like gibberish, right? But it’s actually fairly easy to understand. After the traceroute command, the program tells you what it’s doing:
- It has looked up the domain msu.edu
- It found msu.edu on the IP address of 35.8.10.134
- It now will attempt to find its way there using no more than 30 “hops” (stops along the way, or connections to routers), and it will send a packet of 40 bytes.
The numbers at the far left are the number of the hop, followed by the name and/or IP address of the router that hop is going through. You can see that this trace started within the Liquid Web network, progressed through AT&T and found its way to msu.edu.
The set of three numbers on the right side of the lines indicate the amount of time, in milliseconds, it took for that hop to complete. Traceroute performs each hop three times.
In this example, there are no asterisks (which indicate a failure to respond within 5 seconds) and no inordinately long delays. If your traceroute to your VPS server looks like this, you’re in good shape in terms of network connectivity.
Now, let’s look at a simulated traceroute that ends without reaching its destination:
traceroute to liquidweb.com (209.59.139.21), 30 hops max, 40 byte packets
1 lw-dc2-hsrp-vlan132.rtr.liquidweb.com (67.43.8.129) 0.947 ms 1.028 ms 1.101 ms
2 lw-dc2-core4-po2.rtr.liquidweb.com (209.59.157.131) 1.275 ms 1.308 ms 1.385 ms
3 lw-dc1-core1-ge3-5.rtr.liquidweb.com (209.59.157.93) 1.849 ms 1.921 ms 1.980 ms
4 lw-dc1-dist1-ge1.rtr.liquidweb.com (209.59.157.2) 92.082 ms 92.155 ms 92.347 ms
5 * * *
6 * * *
7 * * *
8 * * *
[truncated]
In this example, our trace failed because we deliberately ran it from our internal network (just to demonstrate what a failed trace would look like).
You can see that, beginning on the fifth hop, we have nothing but packet loss. The traceroute continued for the full 30 hops, each reporting * * * as it went.
If your traceroute to the server ends with asterisks like this one, and never displays an IP address or server name after the asterisks, that means that the connection was not able to be completed. This could be for a variety of reasons including:
- A network outage
- High amounts of traffic causing network congestion
- A firewall dropping traffic from your IP address
However, if the traceroute picks back up following a series of asterisks and ultimately ends with a server name and IP address, it means that the connection was successful — regardless of how many hops exceeded the 5-second response time. This can be an indication of network issues along the routes used in those hops, but it does not indicate a network problem on either your end or the server’s.
Источник
How To: Traceroute in Mac OS X Terminal
Traceroute allows you to discover a network path from one host to another. Traceroute is extremely helpful examining network hops (or network devices traversed over) and information including IP Address, DNS servers, and average time taken over each hop. A popular use of traceroute is to identify network bottlenecks (poor speed performance) happening in network equipment you do not own (network equipment in the Internet). Use Terminal in Mac OS X to traceroute any network address on your local network or the Internet.
Note: While traceroute attempts to explore network path hosts typically outside your private network, traceroute results always vary depending on the network hops you attempt to resolve. For instance, you may not receive replies from every device in your traceroute. Unresponsive devices are represented as 3 asterisks ***. Traceroute will always try to resolve hosts, but it can’t always. Devices that it cannot resolve are usually blocked by a firewall.
1. Open Terminal (Applications -> Utilities -> Terminal)
2. Type the following command
3. Terminal will send a network packet to google.com. Watch as the network packet moves out of your local network, past your ISP, and into the wild. Eventually, the traceroute will complete and it should look like something similar below.
As you see, traceroute provides detailed information about a network destination. Traceroute has a variety of command options you can play with in Terminal. Take a look below.
Источник
Как запустить и использовать Traceroute на macOS
Как и многие другие служебные приложения для MacBook и iMac, traceroute встроена в ваш Mac и предназначена для диагностики проблем с подключением. Это скорее диагностический инструмент, чем обычное приложение. Traceroute может быть ценным инструментом для многих пользователей Mac, хотя он не является специфичным для Mac. Пользователи могут рассчитывать на использование Traceroute для анализа того, насколько плохое сетевое соединение и какой трафик трафик используют Mac для перехода на веб-сайт.
Это также образовательный инструмент для наблюдения за магией Интернета и за тем, как ваш компьютер использует определенные коды и команды для перехода на веб-сайт, который вы видите на экране.
Traceroute не предназначен для предоставления конкретных деталей, таких как сетевые интерфейсы. Это требует больше исследований. Единственная информация, которую Traceroute предоставляет, – это имя хоста или IP-адрес.
Как открыть Traceroute через сетевую утилиту
Вы можете сделать это одним из двух способов. Первый способ – открыть его через приложение Network Utility, которое поставляется с каждым компьютером Mac. Ярлык для сетевой утилиты:
/ System / Library / CoreServices / Применение
Вы можете либо выполнить действия на своем Mac, перечисленные в этом ярлыке, либо открыть Finder, щелкнуть «Перейти», нажать «Перейти в папку», ввести ярлык, нажать «Перейти», а затем нажать «Сетевая утилита». Отсюда будет несколько вкладок, на которые вы можете нажать. Нажмите на тот, который говорит Traceroute.
Когда вы будете здесь, введите адрес любого веб-сайта, который вам необходим для проверки сетевого подключения.
Как открыть Traceroute через терминал
Другой способ открыть Traceroute – через приложение Terminal на каждом Mac. Для этого нажмите Finder, затем «Приложения», затем «Утилиты» и, наконец, «Терминал». Терминал требует очень определенных команд, чтобы делать то, что вы хотите. Когда вы наконец доберетесь до этого приложения, введите команду:
имя хоста traceroute
Имя хоста – это место для любого сервера или веб-сайта, для которого вы хотите проверить соединение. Вы можете указать здесь любой веб-сайт или имя сервера.
Этот процесс может занять некоторое время, поэтому помните, что терпение – это добродетель. Также помните, что символ * означает «истекло время ожидания запроса». Просто продолжайте помнить, что терпение – это добродетель, когда вы видите это и продолжаете ждать.
В то время как все остальное о Mac, или любой Apple Продукт работает быстро и способен дать вам все, что вы хотите в мгновение ока, traceroute является одним из немногих медленных аспектов Apple, Это потому, что он опирается на обмен сообщениями ICMP, который, естественно, вызывает задержку. Он был разработан на «медленном пути», а не на типичном «быстром пути», который Apple продукты известны.
Note что в Traceroute отсутствует историческая информация, а это означает, что он покажет вам состояние подключения только одного дня, а не прошлых дней. Например, если Traceroute покажет, что веб-сайт не подключился успешно один день, но он установил предыдущий день, он не покажет вам, какой маршрут трафика был использован для успешного подключения накануне.
Источник
 / Система / Библиотека / CoreServices / Приложения> В папке приложений.
/ Система / Библиотека / CoreServices / Приложения> В папке приложений.