- How to Run Windows Apps on M1 MacBook Air, MacBook Pro, and Mac mini
- What is CrossOver For Mac?
- How to Run Windows Apps on M1 Macs
- The 5 Best Ways to Run Windows on Your Mac
- Find out which option best fits you
- Boot Camp
- Virtualization
- ТОП-3 способа запуска программ Windows в MacOS
- Как пользоваться эмулятором Wine на macOS?
- Достоинства и недостатки Wine
- Виртуальные машины
- Какие бывают виртуальные машины — топ лучших
- Достоинства и недостатки виртуальных машин
- Что такое Boot Camp?
- Достоинства и недостатки Boot Camp
- Что выбрать: эмулятор Wine, виртуальные машины, Boot Camp?
- Заключение
- How to Run Windows Programs on Mac
- Emulation
- Virtualization
How to Run Windows Apps on M1 MacBook Air, MacBook Pro, and Mac mini
Apple’s M1 chip has revolutionized the Mac with outstanding performance and incredibly power-efficiency. But there’s a catch; it’s architecture is radically different from the older Intel microprocessors, and that stops you from dual-booting into Windows using Boot Camp. Also, popular Windows virtualization software such as Parallels are yet to adapt to the new chipset. Don’t give up hope, though. If you use a MacBook Air, a MacBook Pro, or a Mac Mini with an M1 chip inside, you can still run Windows apps on it using the CrossOver compatibility layer.
What is CrossOver For Mac?
CrossOver is an application that provides a Windows compatibility layer on the Mac. It allows you to download, install, and run Windows apps in a simulated Windows environment without having to install Windows itself. It’s also updated for macOS Big Sur and fully supports the Apple M1 chip. Here’s The Witcher 3: Wild Hunt running — almost — perfectly on an M1 Mac with CrossOver.
Not all Windows apps may run well on CrossOver, however. So, it’s best to head over to the CrossOver compatibility database and check out the compatibility rating — on a scale of 1-5 stars — for any specific Windows app that you want to run on your M1 Mac. You can also check that before installing an app in CrossOver itself.
That said, CrossOver isn’t free — it costs $14.95 for a single license or $20.95 for a license with 12 months of support. However, it does offer a fully functional 14-day trial, which is what we recommend that you use first.
How to Run Windows Apps on M1 Macs
Installing CrossOver is not complicated in the slightest. Just head over to the CodeWeavers website and download CrossOver. Then, install CrossOver just like you would any other program and you’re ready to go.
The following steps will show you how to use CrossOver to install and run a Windows-only program on an M1 Mac.
Step 1: Launch CrossOver.
Step 2: Select the Install a Windows Application button.
Step 3: Type the name of the Windows application that you want to install. Then, pick it from the search suggestions. As an example, let’s search for and pick the charting platform MetaTrader 4.
Step 4: You will see a compatibility rating for the selected program — as long as the app has a rating of at least three stars, you should be able to run the app without major issues. Ideally, however, a program should have 4-5 stars to run properly. If you want to proceed, select Continue.
Step 5: Select an installer source. Usually, CrossOver will automatically come up with a direct download link for an app and you won’t have to do anything. But in some cases, you must manually download the program’s installer using your web browser and select the file from your Mac’s download folder — use the Choose installer file or Choose installer folder to do that and select Continue.
Step 6: Select a “bottle.” But what is it? A “bottle” is basically the simulated Windows environment that you must use to run the selected program. In most instances, CrossOver will automatically select the correct “bottle,” so simply click Continue.
Step 7: Install the app. CrossOver will automatically download the required files — or use the files from the download installer — and begin to install the program. It will also install any dependencies that the application needs to run properly.
Step 8: You may have to deal with a few pop-up prompts along the way. If CrossOver fails to add something, it will ask you to Retry or Skip — if it fails repeatedly, consider skipping the file.
Step 9: After installing the program, select the Bottles icon from the top-left of the CrossOver window. Then, select the program “bottle” on the side-bar and double-click the program’s icon to run it.
If CrossOver managed to install the program properly, you should be able to use it without issues.
CrossOver makes it ridiculously easy to run numerous Windows apps on your M1 Mac. Not every app will work optimally (and some won’t run at all), but that’s as good as it gets for the time being. So, what are your thoughts about CrossOver? Sound off in the comments below.
The 5 Best Ways to Run Windows on Your Mac
Find out which option best fits you
While macOS is made to run using Mac hardware, it is not the only operating system that can run on a Mac computer.
Plenty of other operating systems, including Window and Linux, will work on a Mac device. That makes the Mac among the most versatile computers you can buy. Here’s what we’d use to install Windows on a Mac.
Boot Camp
Supports Windows 7, 8.1, and 10
Windows runs natively on Mac hardware for best performance
Requires a full Windows license for the initial install.
Cannot run Windows and Mac OS concurrently.
Perhaps the best-known option for running Windows on a Mac is Boot Camp. Included free with your Mac, Boot Camp allows you to install Windows and then choose between Mac and Windows on startup.
Because Boot Camp runs Windows directly on your Mac’s hardware (there is no virtualization or emulation to be performed) Windows can run at the best possible speed your Mac is able to deliver.
Installing Windows on your Mac is no more difficult than installing Windows on a PC. Apple even provides the Boot Camp Assistant to partition the startup drive to make room for Windows as well as to install all the drivers Windows needs for special Apple hardware.
Virtualization
Run both macOS and a guest OS side-by-side.
Not limited to Windows; a large number of guest operating systems are supported.
Performance tuning and customization needed to achieve the best performance.
May impact the performance of your Mac.
Virtualization allows several operating systems to run on computer hardware at the same time. Virtualization abstracts the hardware layer, making it look like each operating system has its own processor, RAM, graphics, and storage.
Virtualization on the Mac makes use of a software layer called a hypervisor to emulate all of the underlying hardware. As a result, the guest operating system running on the virtual machine does not run as fast as in Boot Camp. But unlike Boot Camp, both the Mac operating system and the guest operating system run at the same time.
There are three primary virtualization apps for Mac:
- Parallels: The first to bring virtualization to the Mac. Parallels supports a wide range of guest OS, including Windows, Linux, and Mac.
- VMWare Fusion: Fusion is the Mac virtualization app offered by VMWare — a leader in virtualization tech. Fusion supports the installation of many different operating systems, including Windows, Linux, and macOS.
- VirtualBox: Oracle supports an open source virtualization app known as VirtualBox. This free virtualization app runs on multiple computer systems, including Mac. Like the other virtualization apps, VirtualBox can be used to run many different operating systems, including Windows, Linux, and macOS.
Installing the virtualization apps is similar to any other Mac app. Guest OS may be more involved with some customization required to obtain the best performance. All three apps have lively forums and support services to help with tuning the performance.
ТОП-3 способа запуска программ Windows в MacOS
Если вам необходимо запустить на Макбуке программу Windows, то придется воспользоваться сторонним софтом. Самым популярным решением станет бесплатный эмулятор Wine. Он отличается высокой производительностью, благодаря которой программы не «тормозят». Минусами эмулятора Windows для mac OS является то, что он не дружит с некоторыми приложениями.
Как пользоваться эмулятором Wine на macOS?
- Чтобы эмулятор работал на ПК с системой macOS, нужно предварительно скачать и установить утилиту XQuartz. В последних версиях macOS открытый программный код вмонтирован в оболочку системы. Его можно найти по адресу: Applications/Utilities/Xquartz.app.
- После ее установки компьютер необходимо перезагрузить.
- Далее скачайте сам эмулятор . Wine скачать на mac можно с официального сайта.
- Дождитесь завершения установки. После чего софт можно найти в следующей директории: /Users/ваша_учетная_запись/.wine. Она будет скрыта, поэтому воспользуйтесь гайдом, как находить скрытые папки.
- Для запуска Windows нужно ввести команду «wine program.exe» либо запустить установочный файл скрытой папки в предыдущем пункте.
Достоинства и недостатки Wine
Плюсы эмуляторов для Windows:
- Не нужно лицензионное ПО.
- Данный способ значительно экономит ресурсы системы.
- Сложная настройка. Перед использованием любого софта, его предварительно нужно настроить. Особенно это сложно делать с играми.
- Совместимость. Некоторые «тяжелые» приложения, забирающие много ресурсов системы, могут некорректно работать или не работать вовсе.
Виртуальные машины
На выходе получается полноценная оперативная система, только располагается она на «виртуальном» железе. Получается, что внутри одной ОС создается другая, которая при запуске забирает часть ее оперативной памяти.
На данный момент существует несколько таких виртуальных машин. Они бывают платные и бесплатные. По большей части они ничем не различаются между собой. Разве что, в бесплатных функционал ограничен. Но в то же время, при полном образе можно легко запустить на mac программу для Windows.
- Установка дополнительной ОС со съемного носителя или образа загрузочного диска.
- Указание количества ресурсов, которые может использовать дополнительная ОС.
- Установка и пользование приложениями.
Какие бывают виртуальные машины — топ лучших
- Parallels Desktop – самая популярная платная программа. Благодаря ей создается гибрид систем. Любые приложения запускаются сразу, вне зависимости от того, к какой системе они принадлежат.
Достоинства и недостатки виртуальных машин
- Возможность работать с двумя системами одновременно.
- Легко получить доступ к файлам.
- Потеря производительности из-за одновременной работы двух систем.
- Некоторые приложение (чаще игры) не работают.
Что такое Boot Camp?
Это программа, позволяющая устанавливать «окна» на Макбук. Система займет отдельное место на жестком диске и будет работать независимо от «яблочной».
Для этого вам потребуется:
- 50 Гб свободного места во внутренней памяти.
- Загрузочный диск с Windows.
Достоинства и недостатки Boot Camp
- Такой метод не ресурсоемкий, потому что одновременно пользоваться можно только одной ОС.
- Все приложения и игры беспроблемно устанавливаются и работают.
- Чтобы переключаться между ОС, нужно каждый раз перезапускать компьютер.
- Не будет доступа к файлам разных систем.
Что выбрать: эмулятор Wine, виртуальные машины, Boot Camp?
Если вы не можете определиться, каким способом воспользоваться, то следующие рекомендации для вас:
- Boot Camp нужен, в первую очередь, для тех, кто будет пользоваться играми.
- Виртуальная машина нужна тогда, когда необходимо пользоваться одновременно двумя ОС.
- Эмулятор подходит для простых задач и нечастого применения.
Заключение
Нет таких людей, которые не имели бы дело с ОС Windows. Со временем некоторые пользователи «окон» переходят на «яблочную» систему. Но у них остаются на «окнах» программы, не имеющие аналогов на Mac, и без которых не получается обходиться.
Для такой проблемы есть несколько решений: запуск программ Windows в MacOS с помощью эмулятора Wine, виртуальных машин или Boot Camp. Каждое имеет свои особенности и недостатки, и только вы определите, что вам больше всего подойдет.
Ставь лайк, если нравится материал и подписывайся на наш Дзен канал!
How to Run Windows Programs on Mac
Windows programs which don’t have a dedicated version for Mac OS X cannot be ran on Mac directly, but they can be ran with the help of a special tool. There are two basic ways to run Windows programs on a Mac. One is emulation, and another is virtualization.
Emulation
Emulation refers to simulating the basic portions of the Windows environment necessary to run some Windows programs on a non-Windows system. The most well known emulator is WINE, which is a humorous acronym for “WINE Is Not an Emulator”. While it is possible to build WINE on Mac an official pre-built binary package is not available, and building it yourself is probably exceedingly difficult. That’s where third party WINE distributions come in.
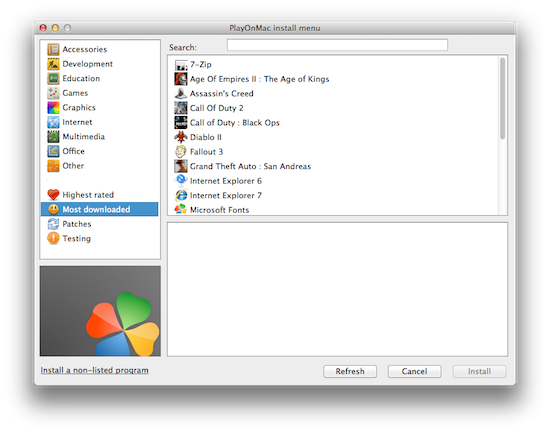
There is a full list of those available on this wiki page. Likely the best among them is PlayOnMac which comes as a standard Mac app and features an easy to use interface with which you can browse and install compatible Windows applications.
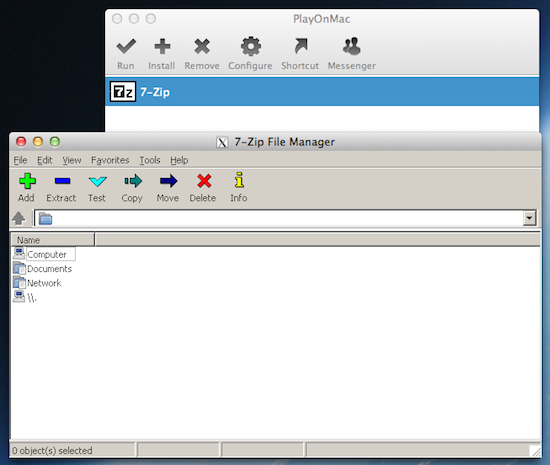
To install a Windows program using PlayOnMac just click on the Install button in the toolbar, navigate through the lists of available programs, select one, and click install. Then just follow prompts on the screen. If the program installs successfully it will be listed in the main PlayOnMac window where you can select it and click “Run” on the toolbar to launch it.
Another way to try running Windows programs with PlayOnMac is to simply download a Windows executable and try running it. PlayOnMac will be automatically associated with all Windows .exe files, and will try to help you install the program. This is a way to try out installing those Windows programs which aren’t on PlayOnMac’s install list. It just might work.
As an alternative solution there is a pay-for Crossover package which offers a potentially more polished experience. You can try it out and see if your program can run through it, and if you are satisfied you can choose to buy it.
The shortcoming of this method is a limited selection of available programs, and potential quirks in running some of them because they are not running in their native environment. The WINE process can also take quite a bit of CPU time.
The advantage, however, is that it is relatively fast to get going with it so it may be worth trying out to see if the program you want to run is supported before trying a more involved method.
Virtualization
Virtualization refers to running an entire operating system in a virtual machine. The virtual machine is a software simulation of a real machine. It is then possible to simulate a Windows PC on a Mac, and run Windows programs in it.
The downside to this approach is somewhat greater usage of memory and CPU resources because you are not only simulating a virtual computer, but also running two operating systems at the same time. The virtual computer also may not be able to fully utilize your real hardware capabilities, such as graphics acceleration. That said, if you have at least 4GB of memory and a recent dual core processor in your Mac you’ll probably be fine. You will also need to have a Windows install DVD.
The advantage of virtualization as a method of running Windows programs is that they have a full blown Windows environment to work with so the program should function just as it does on a real Windows PC without any loss of functionality. It is also a way to run virtually any Windows program on Mac since you are running a complete Windows system within your Mac system.
There are multiple pieces of software you can use to virtualize the Windows system and programs. VirtualBox is a Free and Open Source virtual machine manager, which is what we will be covering here. If you would like more features you can also opt to buy VMWare Fusion or Parallels Desktop. The general principles of functioning should apply to all of them.
Running Windows programs in VirtualBox
The first thing to do is download the right VirtualBox package for Mac. Go to the VirtualBox download page and click on the “x86/amd64” link next to the VirtualBox version for OS X hosts. Once you open the downloaded DMG archive launch the VirtualBox.mpkg installer to start the installation.
Once you install and launch VirtualBox you will see a VirtualBox Manager dialog that allows you to add a new virtual machine. To start the process click on the “New” button in the toolbar and follow the prompts on the screen.
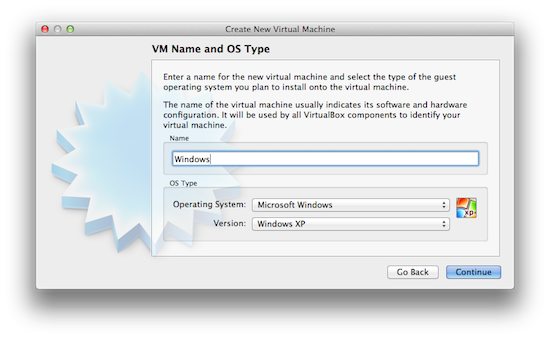
1. Select Windows version
You will first need to provide a name for your new virtual machine. It can be anything you want, but something clear like “Windows” should do. You’ll also leave “Microsoft Windows” selected as an Operating System, but choose the version which you wish to run. If you have a Windows XP CD, for example, then make sure “Windows XP” is selected. If you have Windows 7 select Windows 7.
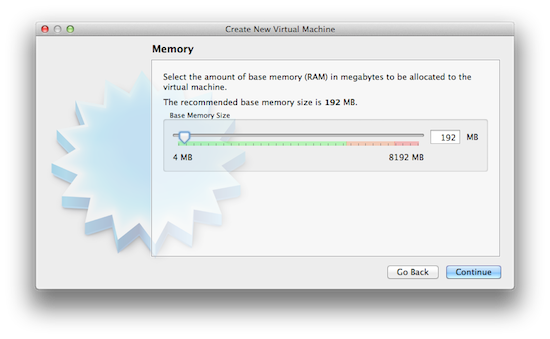
2. Allocate some memory to the virtual machine
The next step is to allocate some of your system memory to the virtual machine. The default and recommended amount for Windows XP is 192 MB, and for Windows 7 it is 512 MB. How much memory you will ultimately need depends on the Windows programs you want to run. If they are heavier and more memory hungry they will consume more memory.
A limiting factor will be the overall amount of memory you have on your machine. If you have 4GB then allocating 1GB is probably safe. If you’re unsure just stick to the defaults.
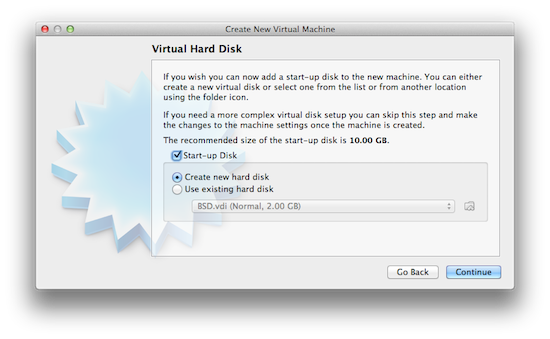
3. Create a virtual hard disk
Now we need to create a virtual hard disk to install Windows on. Just leave “Create new hard disk” selected and click continue. VirtualBox will recommended a start-up disk size depending on the Windows version you’ve selected. For Windows 7 it recommends 20GB.
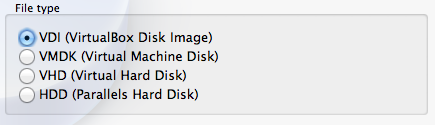
When you click continue it will offer a few options for the format of the virtual hard disk. If unsure simply leave it at the default selection (VDI).
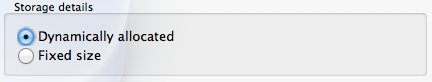
On the next screen you can select if you want the virtual hard disk size to be dynamically allocated or of fixed size. With dynamic allocation your virtual hard disk will only take as much space on your real hard disk as it needs, which is the safest option if you’re hard pressed for free disk space. If you have plenty of space to spare fixed size may provide a better option as it may make your virtual machine perform somewhat faster.
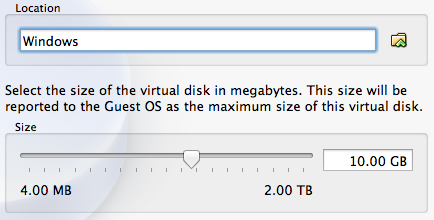
Finally, the next screen allows you to select the location of your virtual disk, which can be anywhere on your hard drive or on your external hard drive. This is where you can also select the virtual disk size. This matters most if you previously chose fixed size. If you previously selected dynamic allocation just leave it as is.
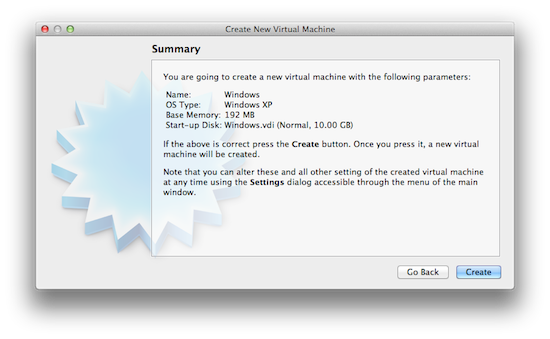
Once you click continue, review your virtual disk settings and click “Create”. Then review your overall virtual machine settings and click “Create” again to create the machine. The new virtual machine will be added to your VirtualBox manager where you can see all information about it, edit its settings, and start it up.
4. Install Windows
Simply click on the “Start” button in the toolbar to turn on your new virtual machine. This will display a new wizard that allows you to select where to boot the machine from. Your options are the internal DVD drive, which is selected by default, or an existing disk image. Since you probably don’t have a virtual Windows install disk you can keep the DVD drive selected as is.
Then you should insert a Windows install DVD to your DVD drive and click continue. The virtual machine will then try booting from the disk and initiate a Windows install process. You should be safe following the instructions on the screen as it will already have the previously created virtual disk drive detected, and will install Windows to it. Nothing you do here would delete any data on your actual hard drive.
5. Boot up and run your program
After Windows installation completes you can boot up the virtual machine and use it as you would a normal computer. The virtual machine should support an internet connection and the DVD drive so you can install any Windows program you wish to run in it.
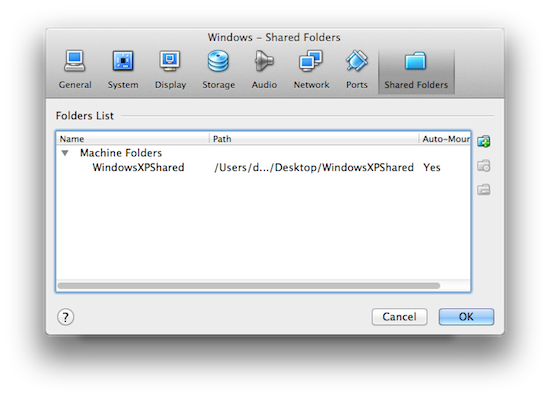
You can also set up a shared folder on your Mac, which will appear as a separate drive in your virtual Windows installation. To set it up go to the Devices menu while in the virtual machine, click Shared Folders, and then click the small add (+) icon to add a new shared folder. You can also set to make it permanent, making it persist when you boot the machine next time, or transient to make it temporary. Of course, this folder has to exist on your Mac, and otherwise you need to create it before making it a shared folder.
You can also access the Shared Devices set up by selecting the virtual machine in the Virtualbox manager, clicking on the “Settings” button in the toolbar, and then the “Shared Devices” tab.
After adding the shared folder reboot Windows in your VM to have it detected. Now you can drop files in this folder when you want to make them visible on a virtual disk drive within your virtual Windows machine.
It is also possible to run the virtual machine in full-screen mode selecting it from the View menu or pressing Command-F. You could put it in its own Space, and make it full-screen on that Space to make it easy to switch between your normal Mac system and your virtual Windows system.
Another great feature is the seamless mode which allows you to see your virtual Windows dialogs, menus and windows alongside your Mac user interface for a more natural workflow, albeit only within a single Space. You can enable seamless mode from the View menu or by pressing Command-S. When in seamless mode it is recommended to move your dock to the right edge of the screen so it doesn’t interfere with the bottom Windows panel and the Start menu, as shown on the screenshot below.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/BootCampPartition-5849de633df78c491eaf721b.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ParallelsWizard-576f016d5f9b585875b92396.jpg)